- Case Report
Congenital External Auditory Canal Atresia in Two Dogs: Clinical Presentation, Diagnosis, and Surgical Management
- Mandalena Markou,
- Thomas Koutis and
- Vassiliki Tsioli
- + 3 authors
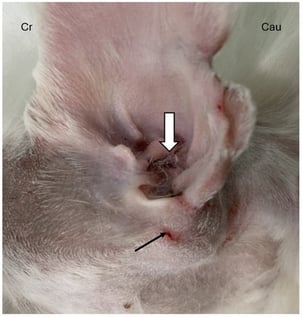
Congenital external auditory canal atresia (EACA) is a rare developmental anomaly in dogs with limited information to guide management. This report describes the clinical presentation, diagnostic work-up, surgical technique, and long-term outcome in two young dogs with unilateral congenital EACA. An 8-month-old Caucasian Shepherd and a 9-month-old Maltese presented with left-sided otalgia and absence of the external canal opening. Computed tomography identified segmental atresia of the vertical canal with intraluminal soft-tissue attenuating material and mild otitis externa and media in both dogs. Cytology and culture of canal contents were unremarkable, supporting a congenital, non-infectious origin. Both dogs underwent a canal-preserving vertical canal-to-external acoustic meatus anastomosis using a pull-through approach. Minor postoperative complications (partial wound dehiscence, mild canal stenosis) were successfully managed. At the 5-year and 1.5-year follow-up, respectively, both dogs remained free of clinical signs, with preserved hearing, supporting this procedure as a functional, cosmetically acceptable option in carefully selected dogs.
10 February 2026



![Average annual expenses of French pet owners in 2016 [28].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/pets/pets-03-00009/article_deploy/html/images/pets-03-00009-g001-550.jpg)