- Review
Trends in Marine Mammal Literature in Human Care: A Need for More Welfare-, Environmental- and Management-Related Research
- Sabrina Brando,
- Sara Torres Ortiz and
- Geoff Hosey
- + 1 author
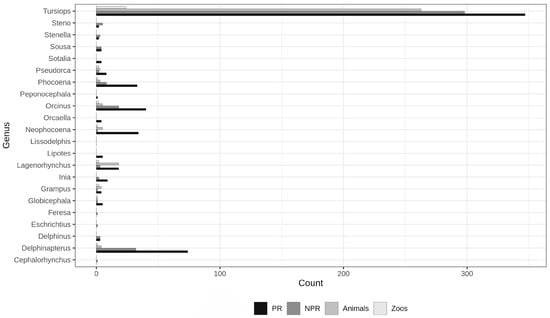
Marine mammals have been successfully maintained under human care; however, the media, public, and professionals within the field frequently voice welfare concerns. This study systematically surveyed peer-reviewed (PR) literature from 1948 to 2024 (n = 1308) and included an opportunistic sample of non-peer-reviewed (NPR) literature from the past 40 years (n = 756) to evaluate research efforts associated with species housed in zoos and aquariums. The current study updates and extends previous efforts to assess research categories. The findings indicate that the volume of research published mirrors the species abundance in human care. Across taxa, PR papers concentrate on science that enhances the understanding of biological functions (Acoustics, Biology, Breeding, Behaviour, Health) but is not necessarily tailored to improve management or optimal care. In contrast, a substantial portion of the NPR literature focuses on daily handling and management, highlighting Environment and Management and Enrichment-related activities. While welfare-related research has increased in both PR and NPR literature, this review underscores the need for additional welfare-related empirical studies to further enhance animal care and wellbeing. We encourage those involved in the practical care of such taxa to empirically evaluate these interventions and disseminate their findings in the PR literature.
18 December 2025