- Article
In Vitro Effects of Hydrated Lime and an Acidic Liquid Conditioner on Mastitis-Associated Bacteria in Straw and Recycled Manure Solids
- Saskia Marie Pawlik,
- Nicole Wente and
- Volker Krömker
- + 3 authors
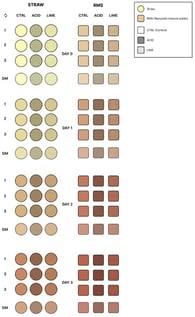
This study aimed to evaluate recycled manure solids (RMSs) as an alternative to straw as dairy bedding under controlled in vitro conditions using two different conditioners. Pre-cut straw and RMSs were treated once with either 10 wt.% hydrated lime, 200 mL/m2 of an acidic liquid conditioner or left untreated, and incubated for three days at room temperature. Daily, samples were inoculated with manure and Klebsiella (K.) pneumoniae. Outcomes were aesculin-positive Streptococcus spp. and coliform counts, pH, and dry matter (DM) content. Hydrated lime reduced all target bacteria by >99% in both materials. The acidic conditioner decreased K. pneumoniae and streptococcal counts by 98.62%/96.6% (straw) and 98.63%/99.58% (RMSs), respectively. It reduced Escherichia (E.) coli counts by ~67% in both materials without statistical significance (p = 0.064). RMSs showed higher bacterial loads and lower DM content than straw but could be substantially improved by lime treatment. As the conditioner were applied following different manufacturer-recommended dosing principles, these findings reflect effectiveness under practical use rather than intrinsic superiority of one conditioner. RMSs might represent an alternative bedding material when managed with appropriate hygienic measures, although straw showed more favorable microbiological and physicochemical aspects. Both materials contained substantial bacterial loads prior to treatment.
5 February 2026