-
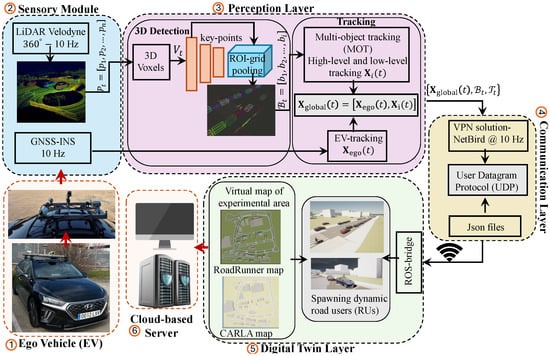
 Digital Twinning Mechanism and Building Information Modeling for a Smart Parking Management System
Digital Twinning Mechanism and Building Information Modeling for a Smart Parking Management System -
 LLM-Driven Offloading Decisions for Edge Object Detection in Smart City Deployments
LLM-Driven Offloading Decisions for Edge Object Detection in Smart City Deployments -
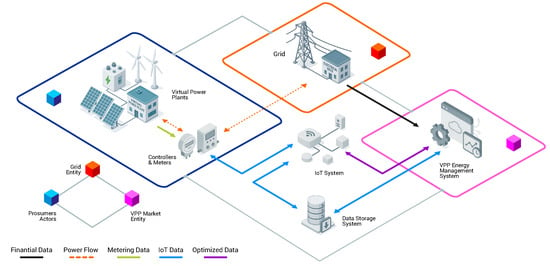
 Evaluating Acoustic vs. AI-Based Satellite Leak Detection in Aging US Water Infrastructure: A Cost and Energy Savings Analysis
Evaluating Acoustic vs. AI-Based Satellite Leak Detection in Aging US Water Infrastructure: A Cost and Energy Savings Analysis
Journal Description
Smart Cities
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), Inspec, AGRIS, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Urban Studies) / CiteScore - Q1 (Urban Studies)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 26.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Latest Articles
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Deadline: 10 December 2025
Deadline: 31 December 2025
Deadline: 20 January 2026
Deadline: 20 February 2026
Conferences
Special Issues
Deadline: 31 December 2025
Deadline: 31 December 2025
Deadline: 28 February 2026
Deadline: 28 February 2026