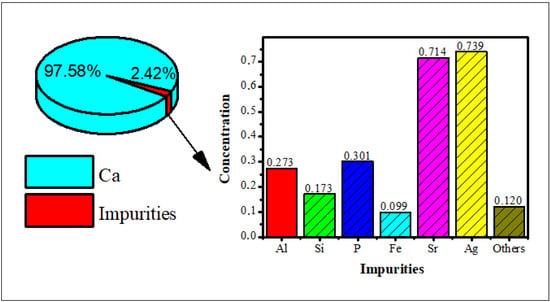
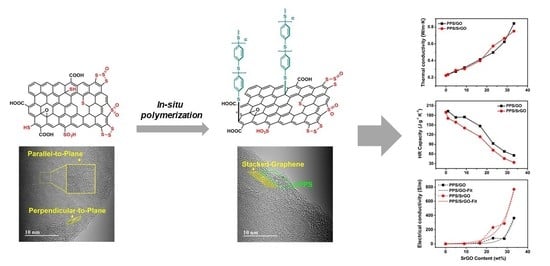
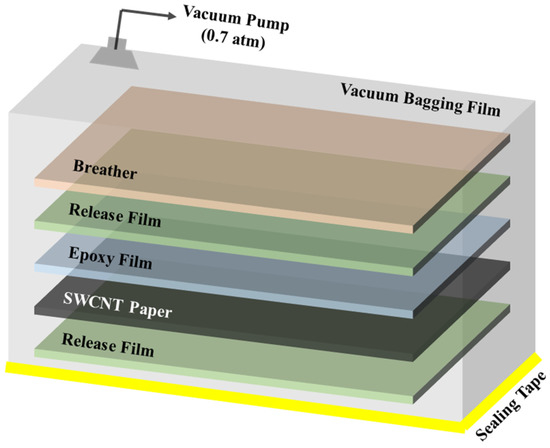
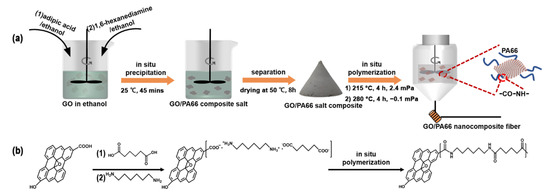
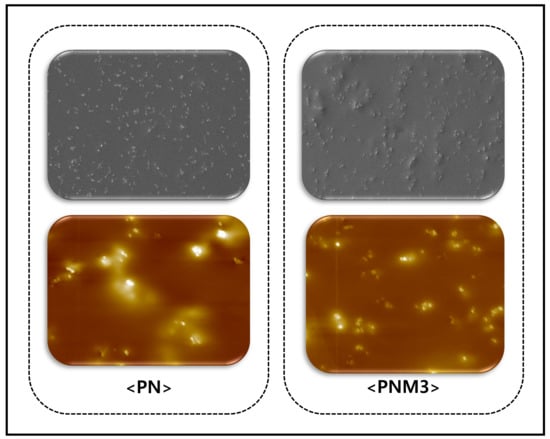
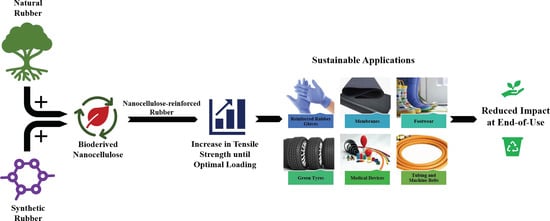
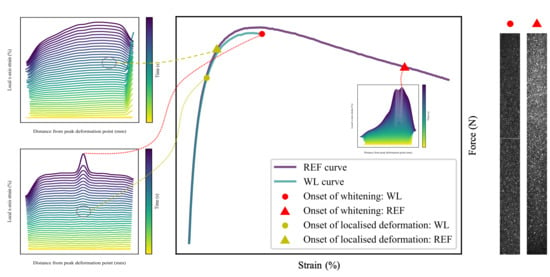
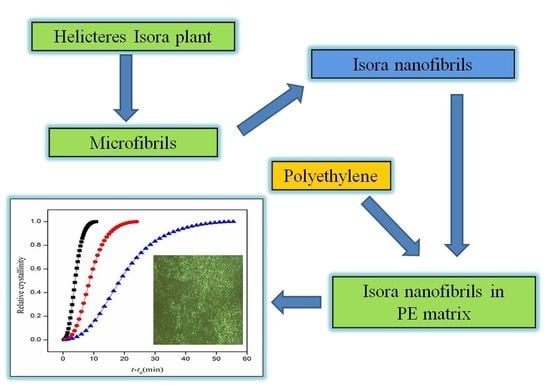
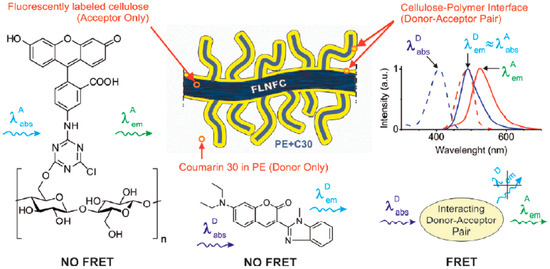
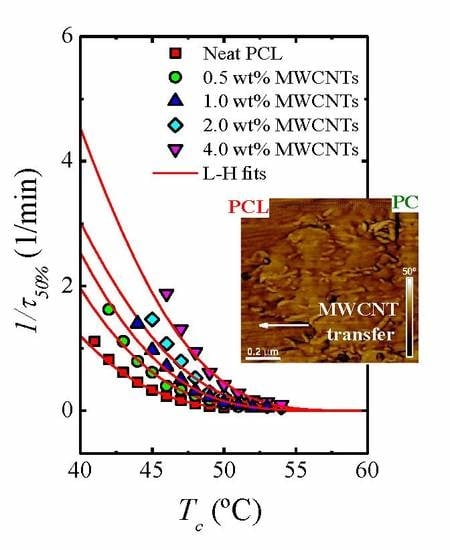
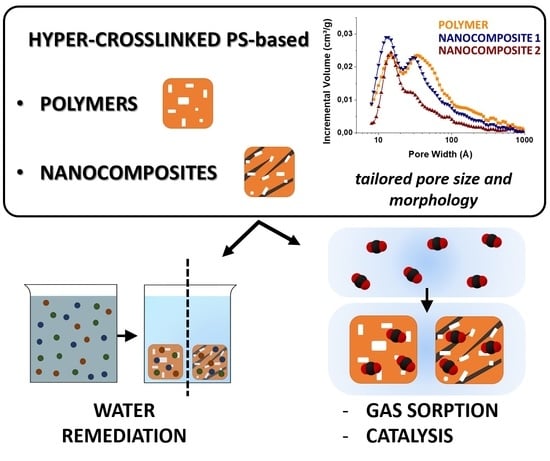
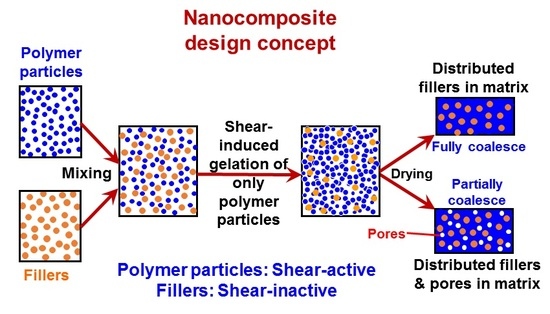
Polymer Nanocomposite
A topical collection in Polymers (ISSN 2073-4360). This collection belongs to the section "Polymer Composites and Nanocomposites".
Submission Status: Closed | Viewed by 24502Editor
Interests: polymer processing; mechanical behaviour of polymer-based systems; rheological behaviour of polymer-based systems; green composites; biocomposites; nanocomposites; biodegradable polymers; polymer blends; degradation and recycling of polymer-based systems
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
This Topic Collection focuses on recent advances in polymer nanocomposites. Polymer nanocomposites are new polymeric systems which show very interesting properties and behaviours that are drastically different from those of microcomposites and, of course, from those of the polymer matrix, nevertheless the very low amounts of nanofiller used in these composites. Moreover, these systems can be considered to be very useful for many industrial applications. However, these polymer systems give rise to new challenges in polymer science and polymer technology because of the nanometric dimensions of the inert fillers which can give rise to many problems due to the dispersion and distribution of the filler nanoparticles. Indeed, despite their interesting properties, there are only a few established industrial applications. Morphology, rheology, processing and degradation behaviours are not yet completely understood. Consequently, this Special Issue aims to reflect the current efforts and progress made in this field.
This Topic Collection covers all the fields related to polymer nano composites, but special attention will be given to the following aspects:
- Nanocomposites
- Nanobiocomposites
- Characterization
- Morphology
- Processing
- Rheology
- Degradation
- Recycling
Prof. Dr. Francesco Paolo La Mantia
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Polymers is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Related Special Issues
- Polymer Nanocomposites in Polymers (27 articles - displayed below)
- Polymer Nanocomposites II in Polymers (13 articles - displayed below)