The Tensile Behaviour of Highly Filled High-Density Polyethylene Quaternary Composites: Weld-Line Effects, DIC Curiosities and Shifted Deformation Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The elongation and orientation of the amorphous regions between the lamellae;
- The onset of nucleated inter- and intralamellar slips;
- The collective inter- and intralamellar slips;
- The onset of fibrillation; and
- The onset of chain disentanglement.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Formulation and Processing Methods
2.3. Characterisation
2.3.1. Tensile Testing
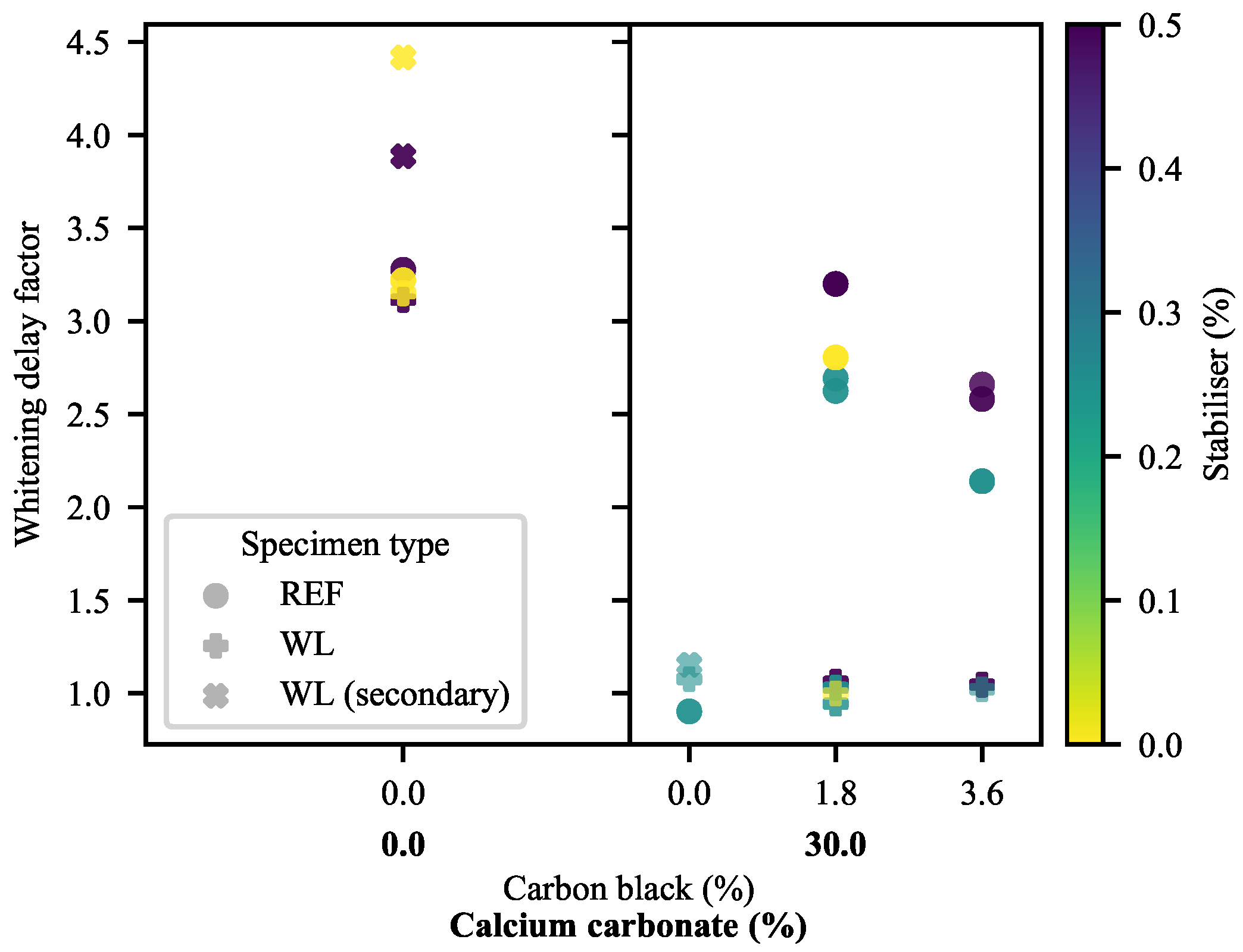
 represents a WL specimen of a 0-CB/30-CC/0.5-SP material.
represents a WL specimen of a 0-CB/30-CC/0.5-SP material.2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.4. Fitting
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Conventional Tensile Testing
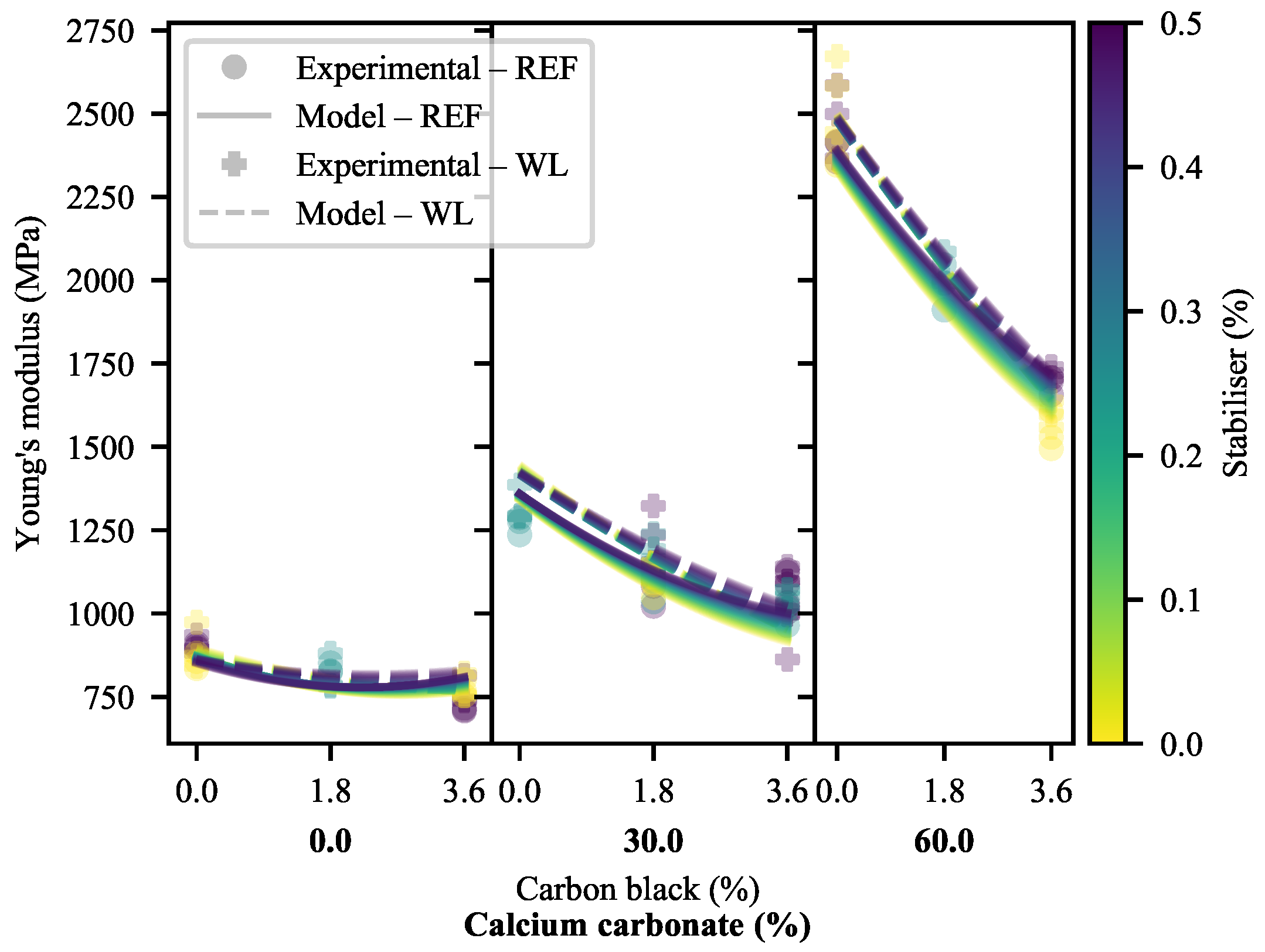
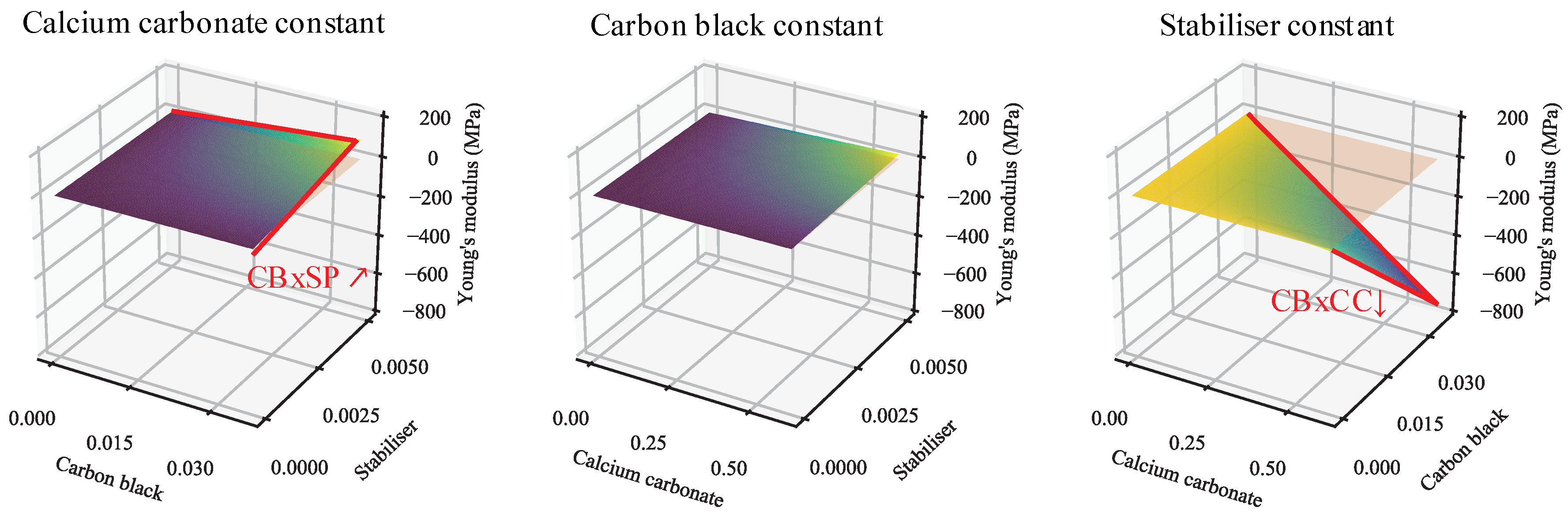
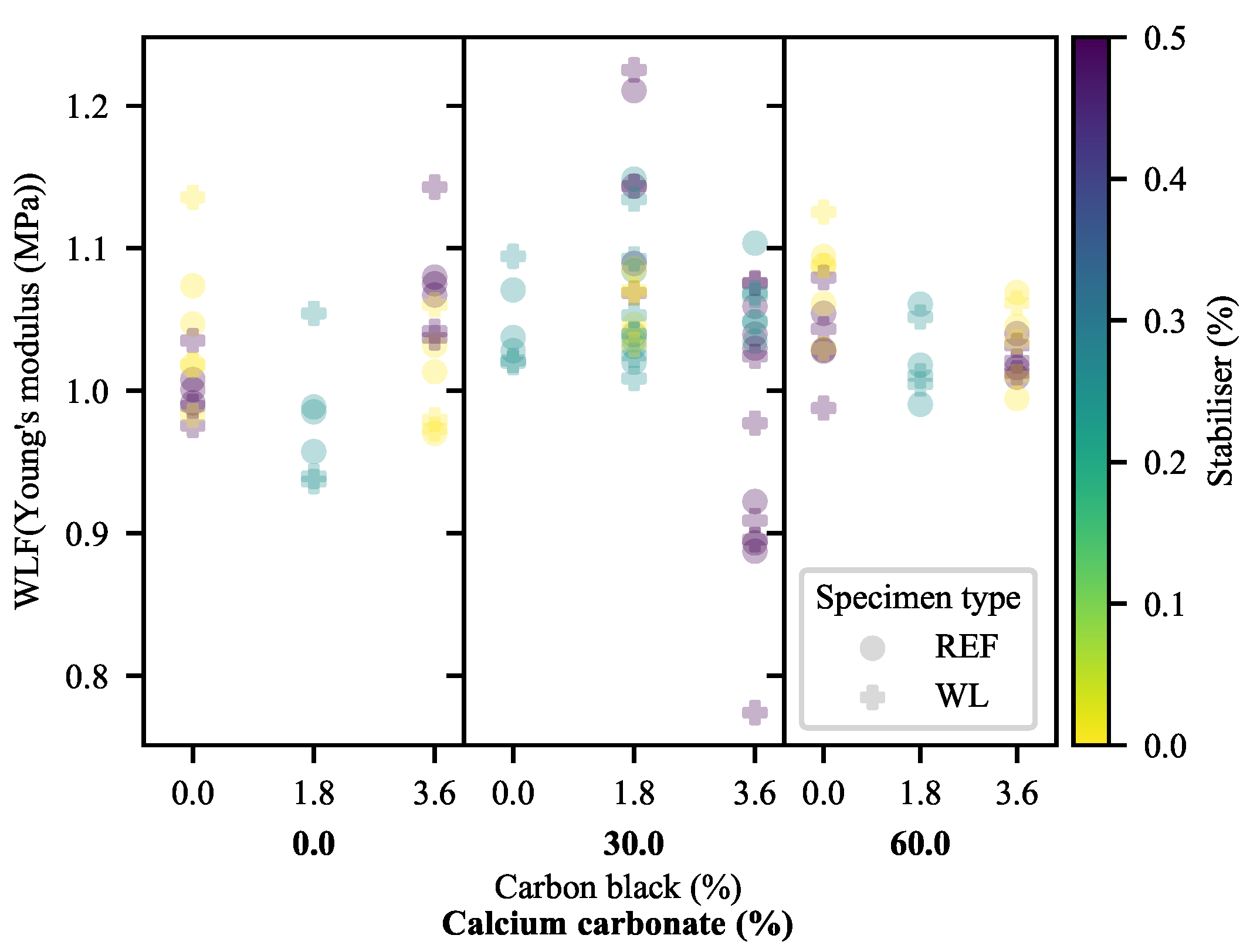
3.1.1. Young’s Modulus
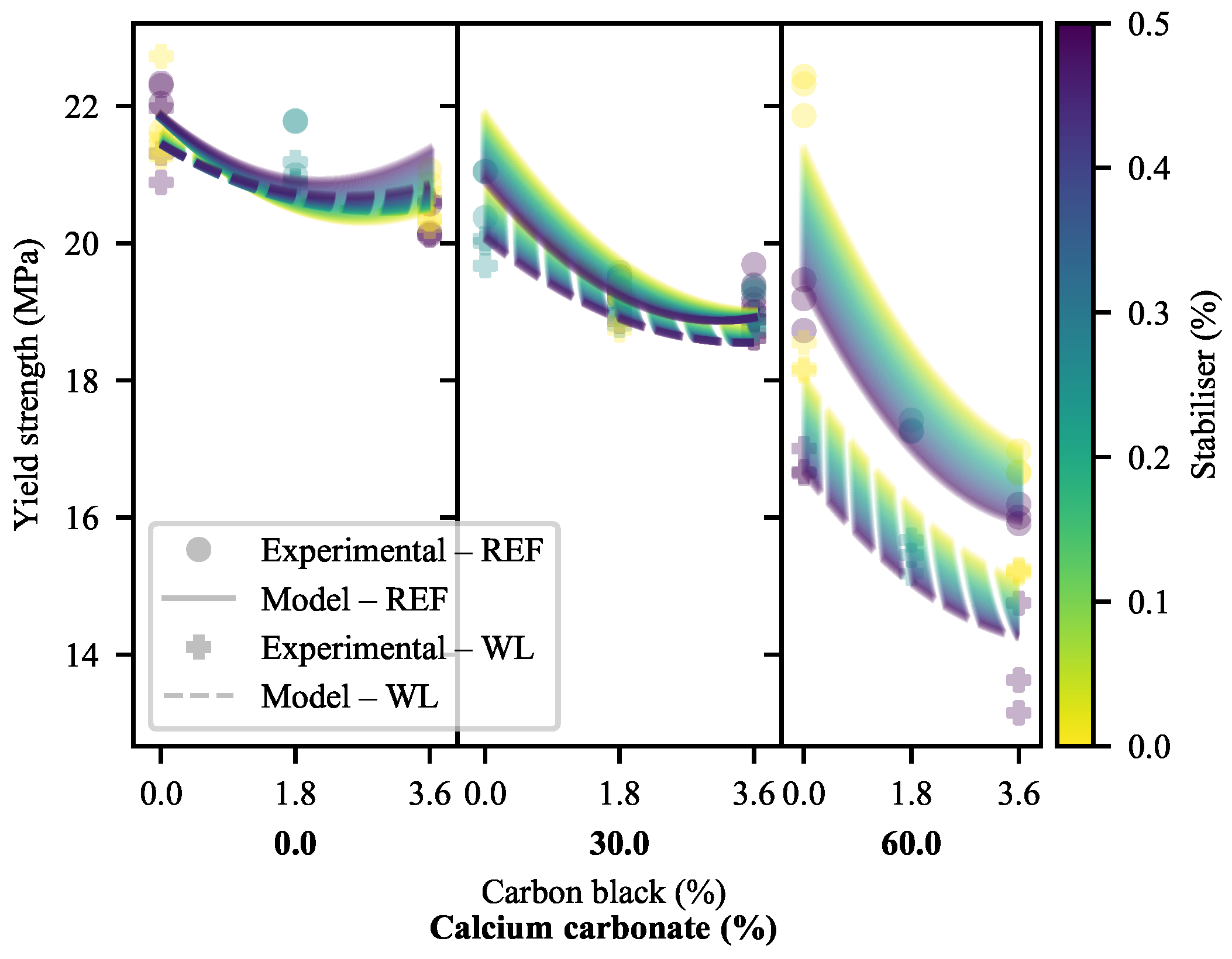
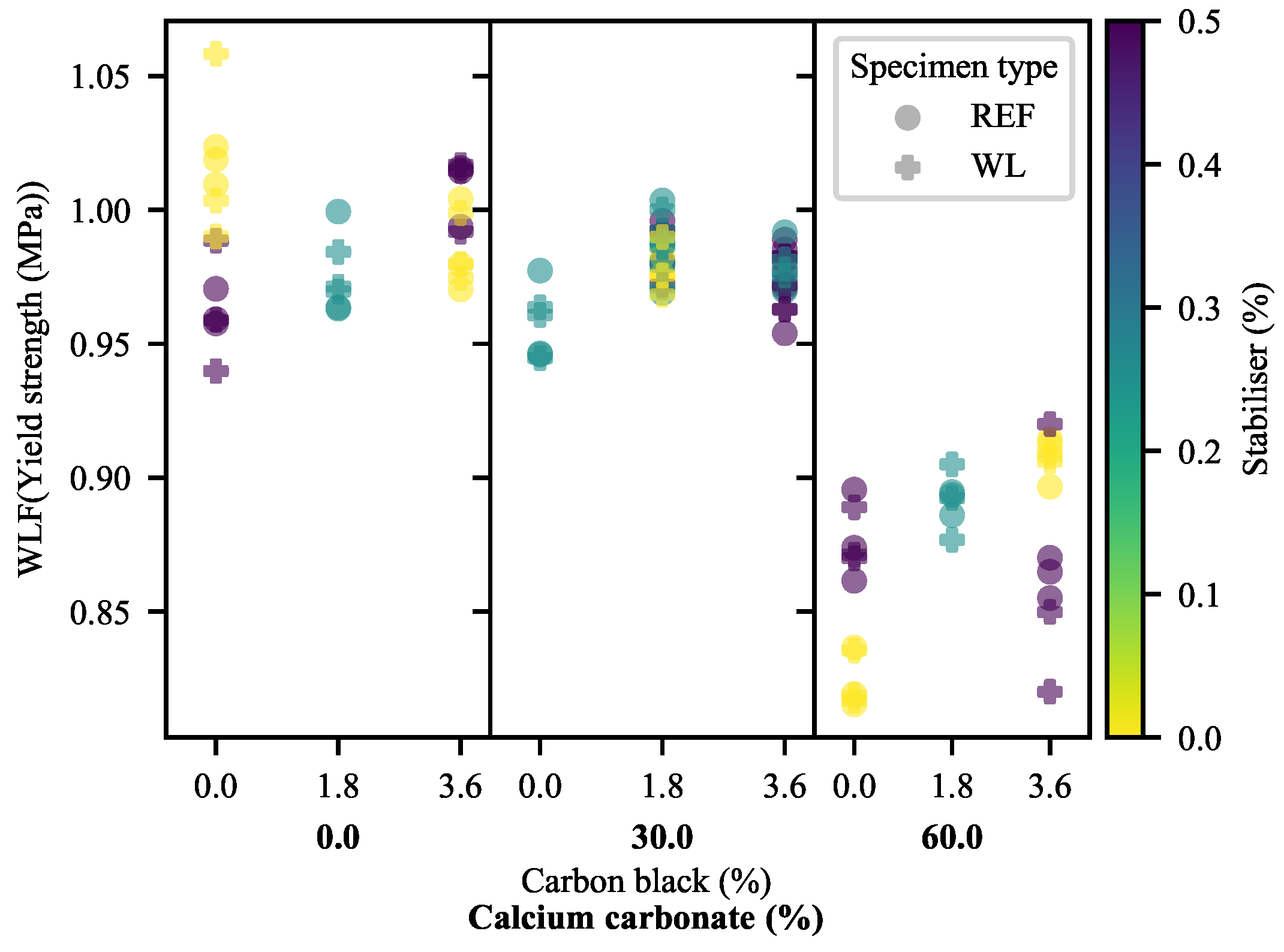
3.1.2. Yield Strength
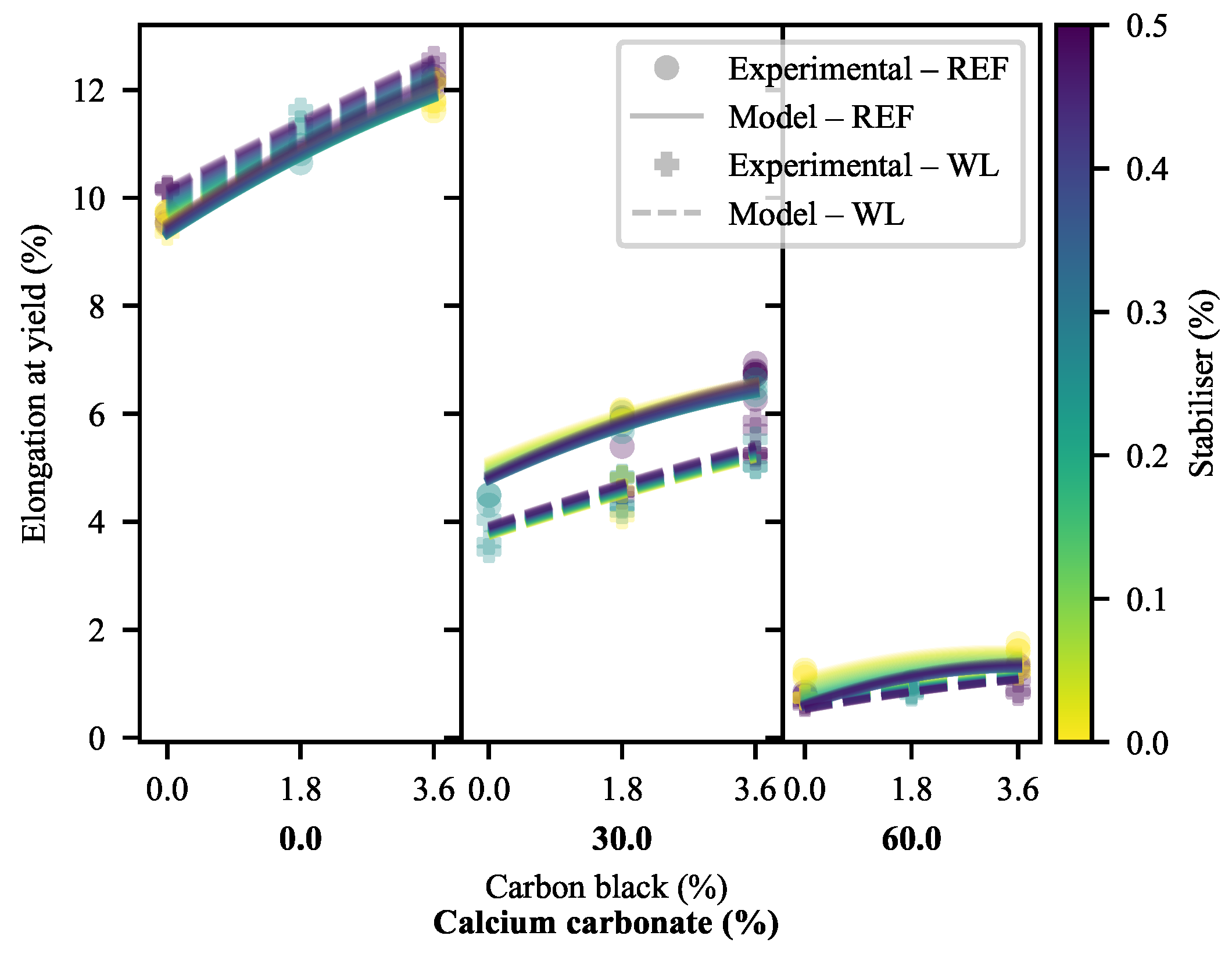
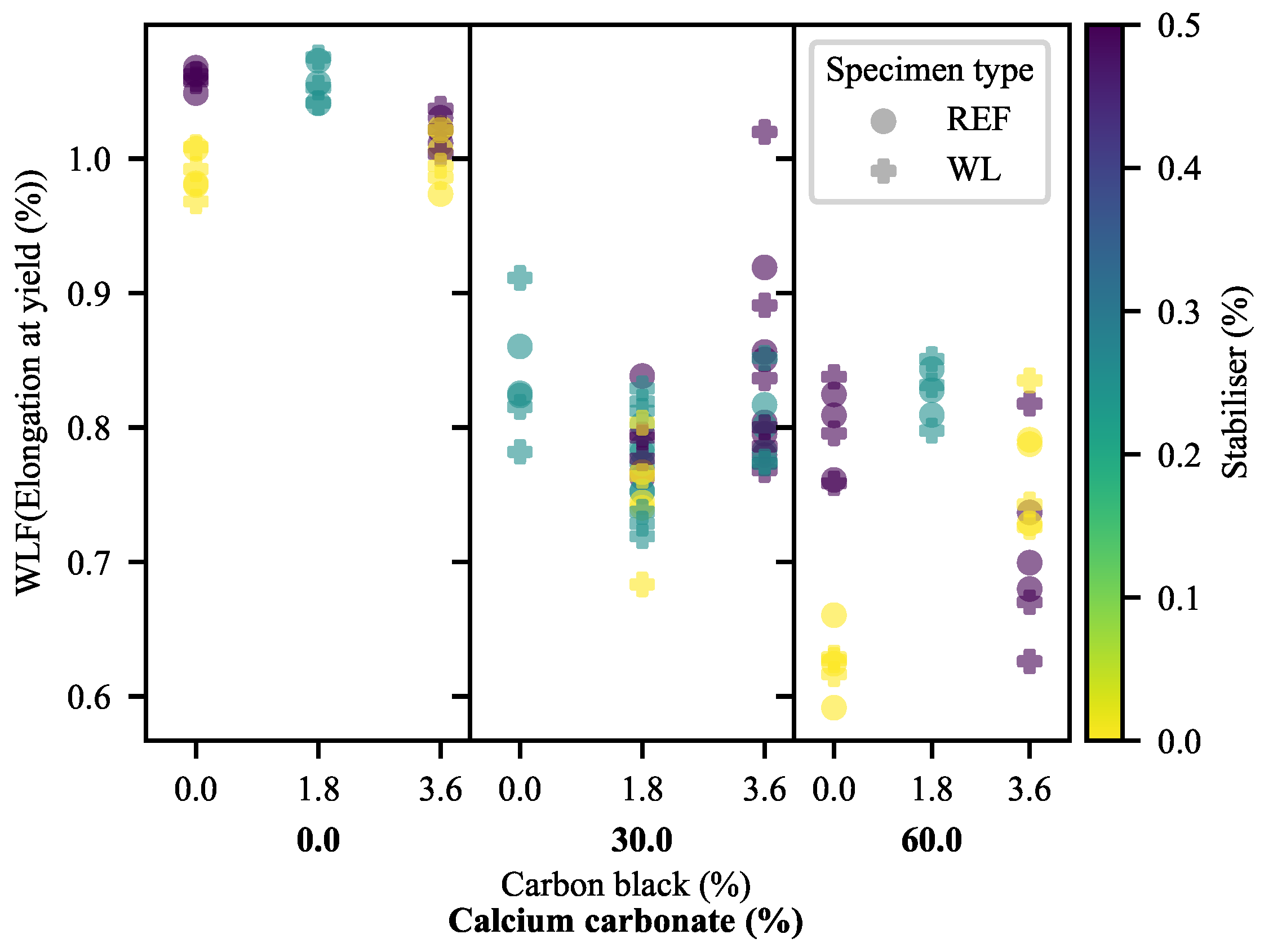
3.1.3. Elongation at Yield
3.1.4. Elongation at Break
3.1.5. Summary: Conventional Tensile Testing
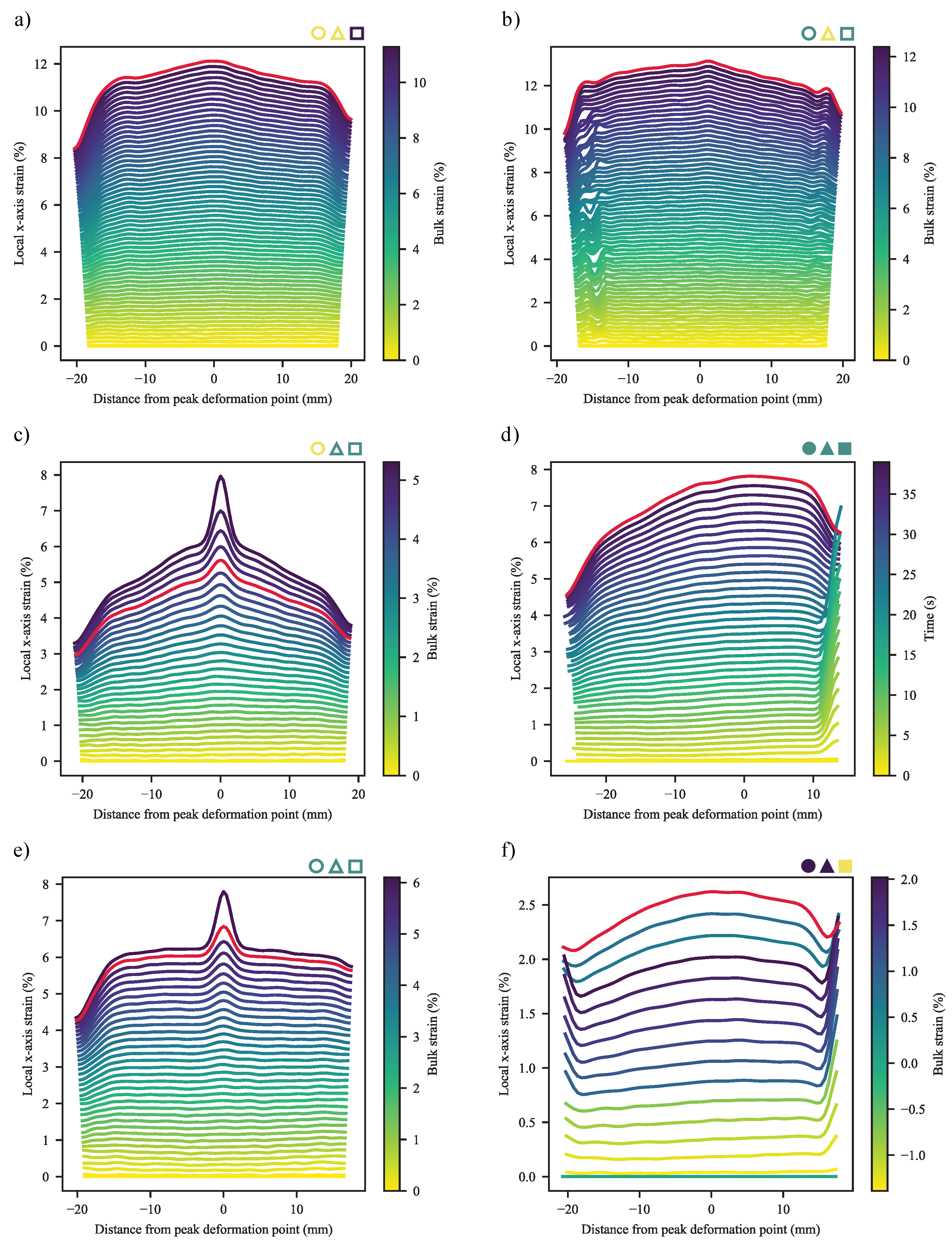
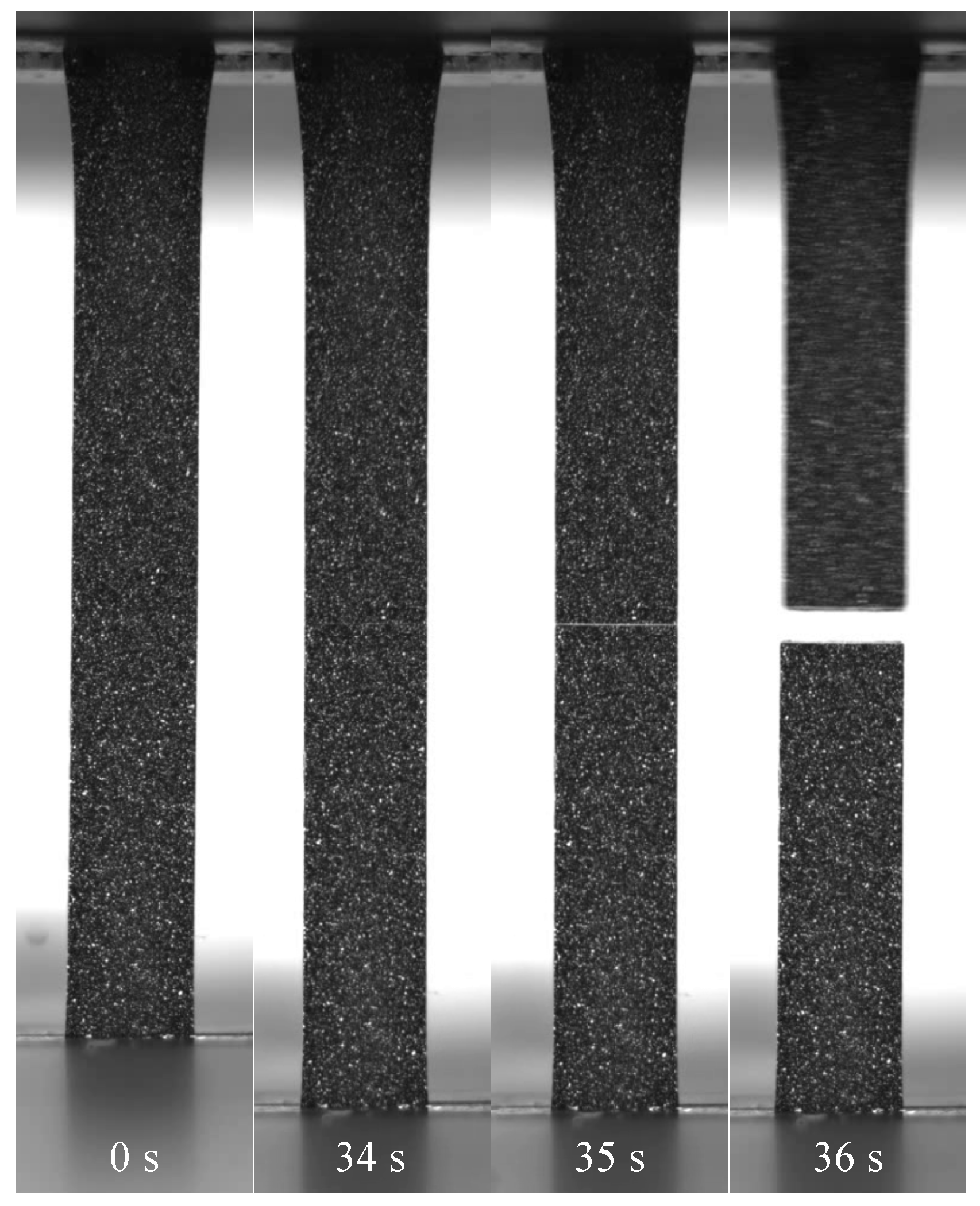
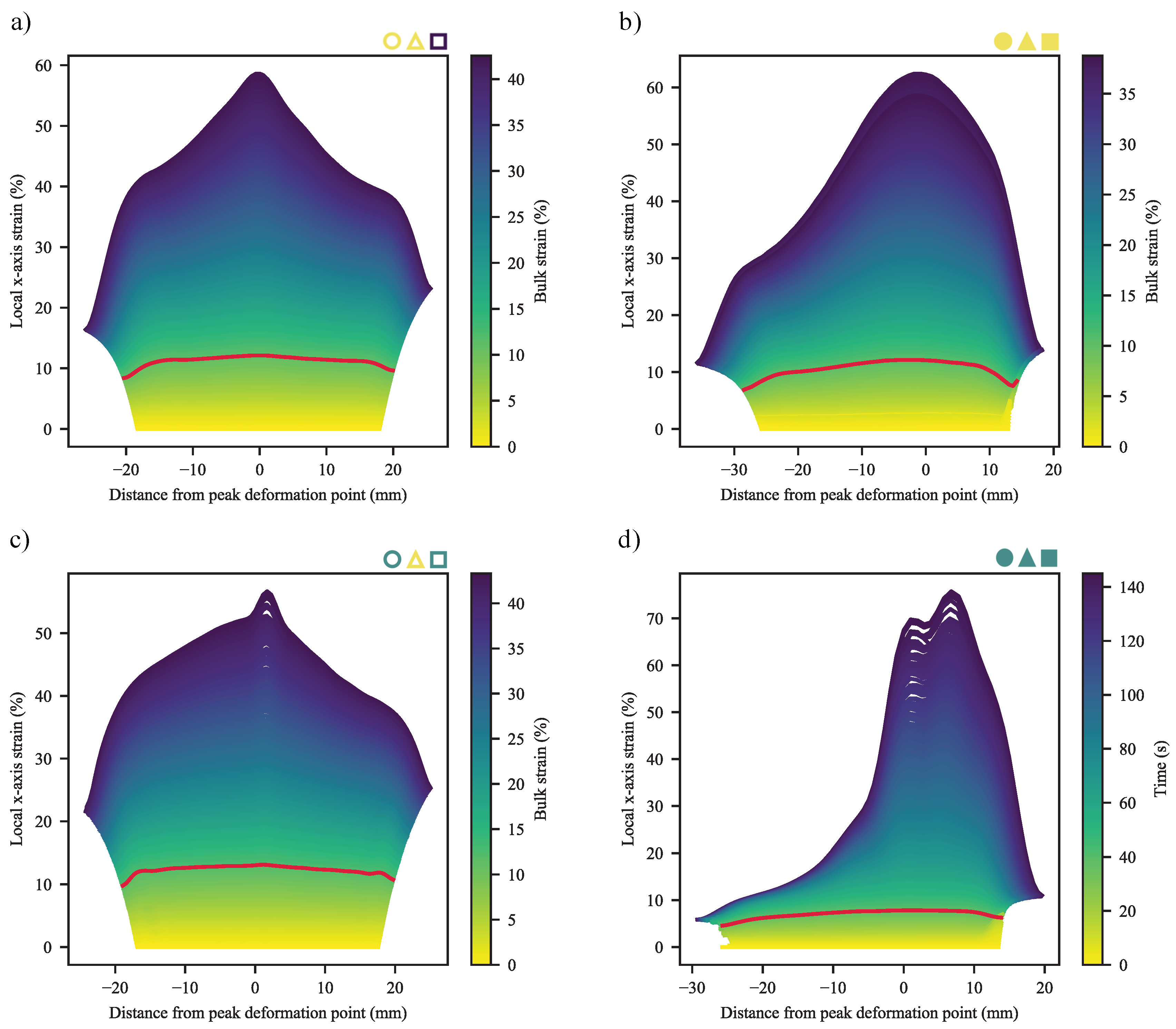
3.2. Digital Image Correlation
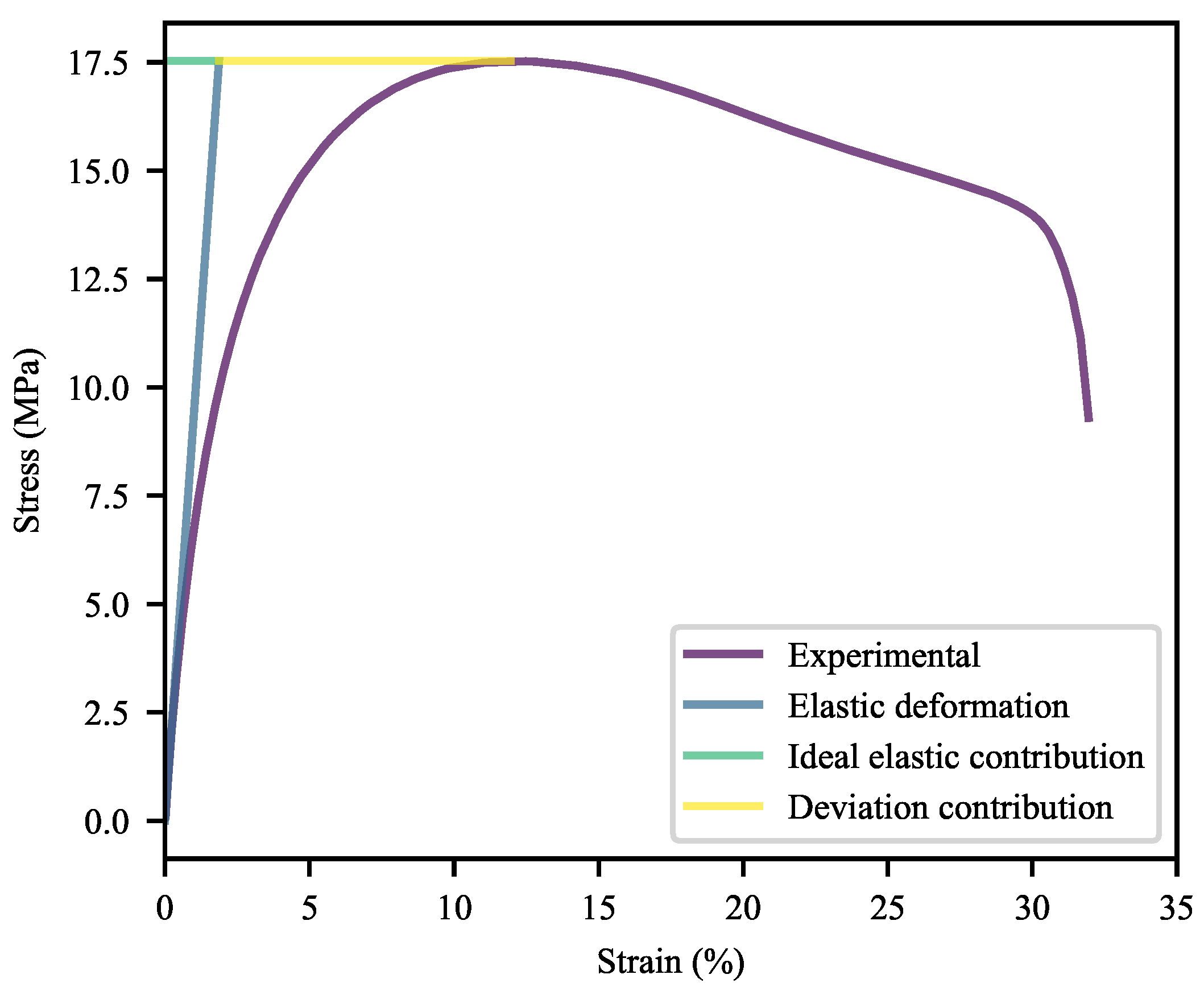
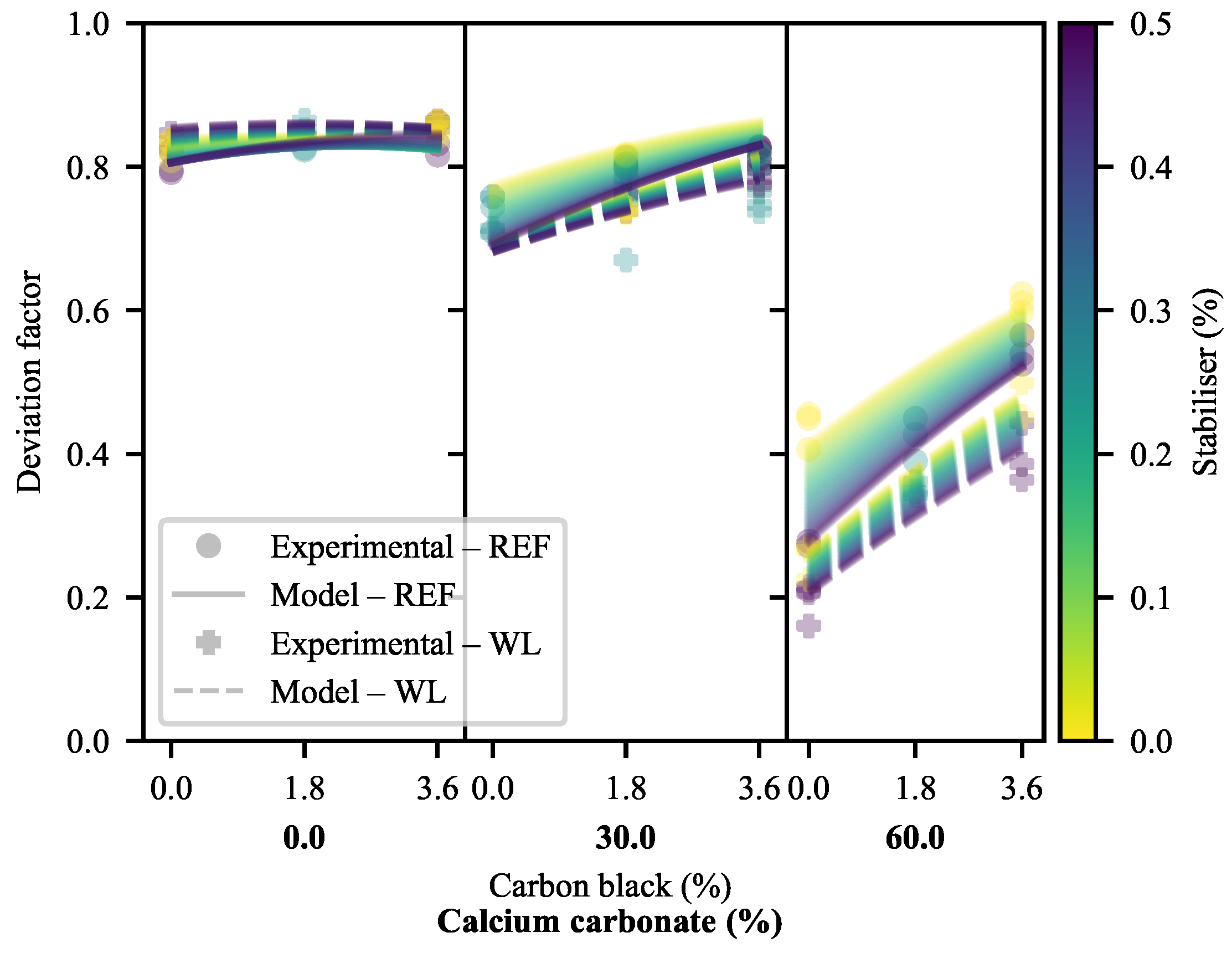
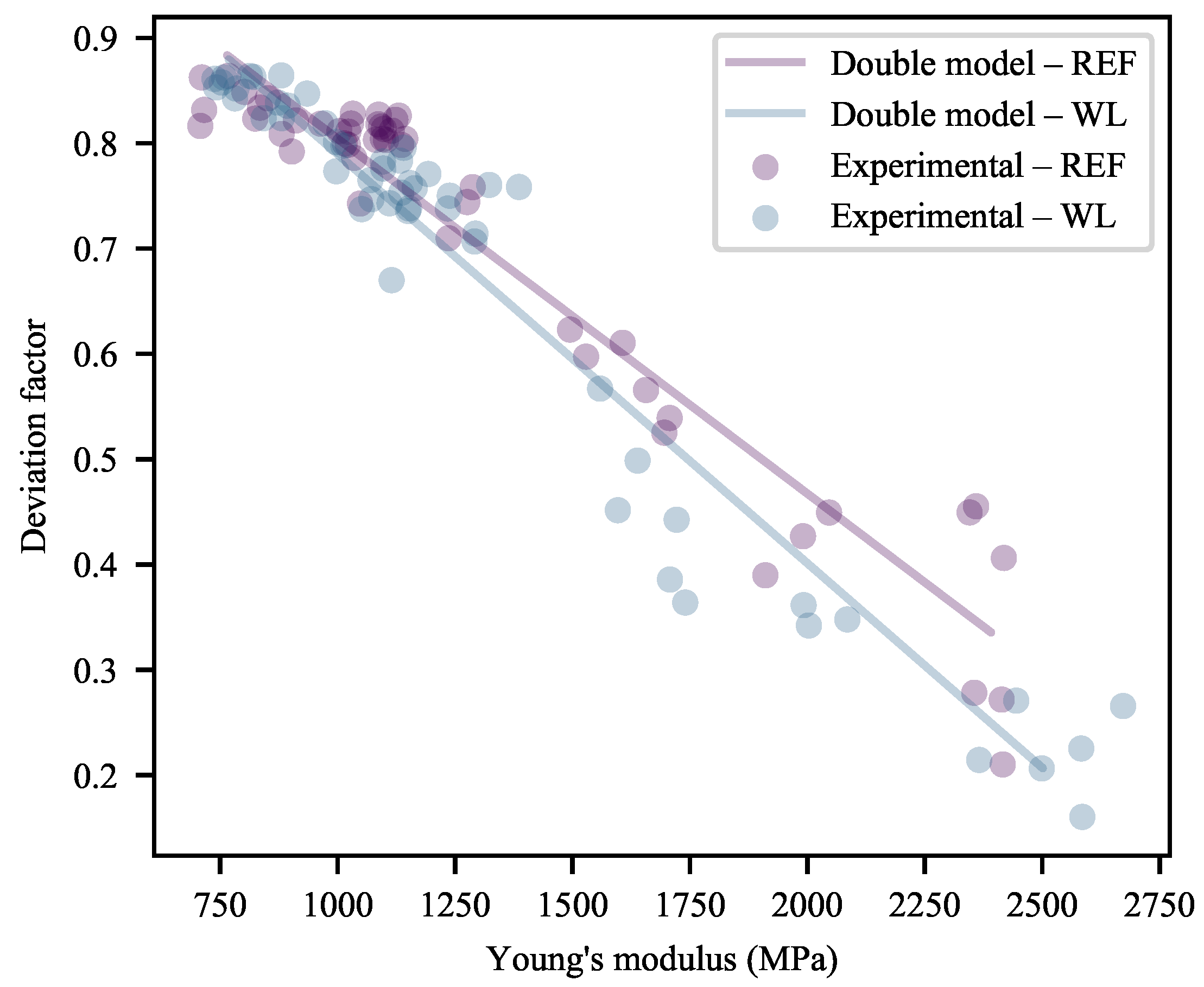
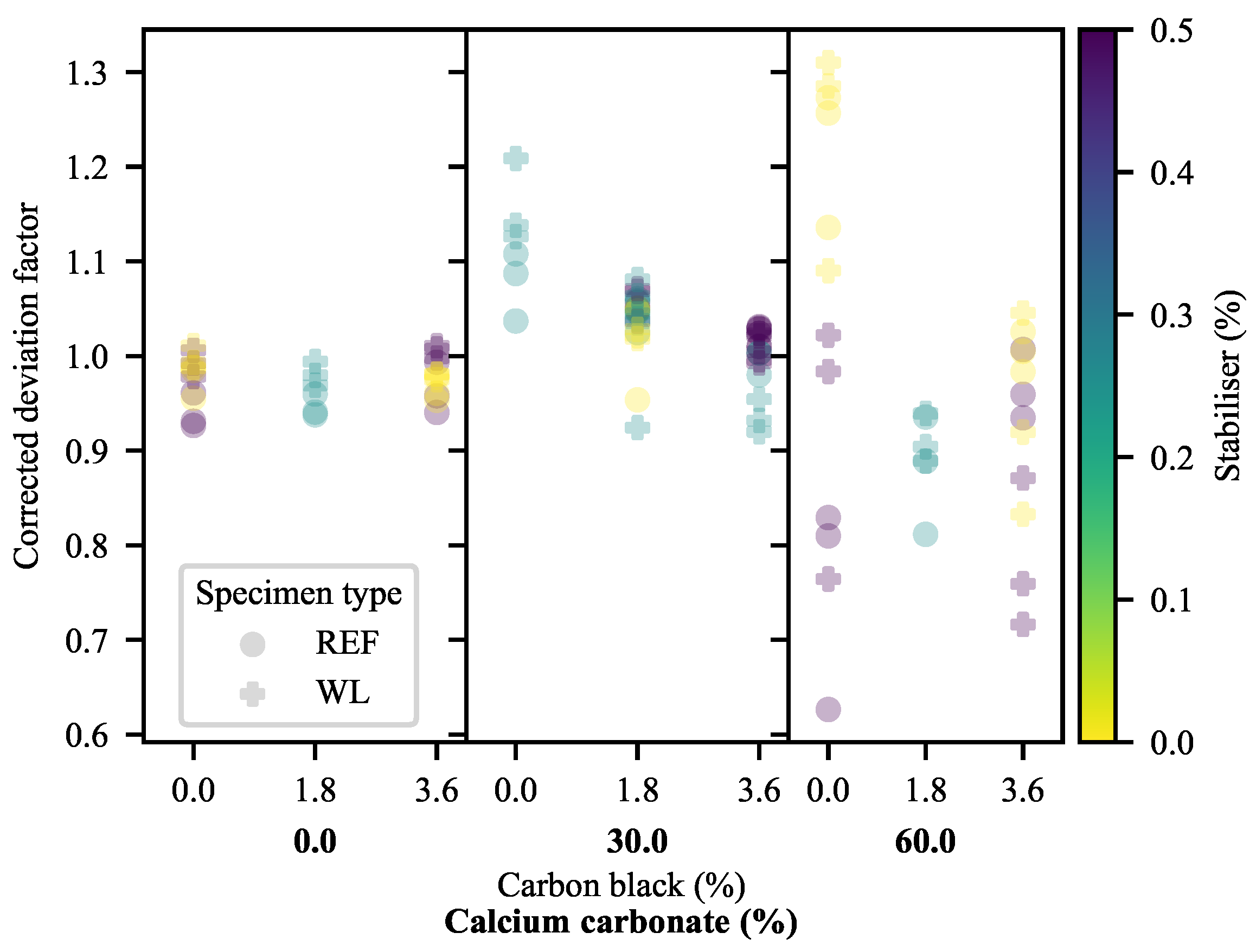
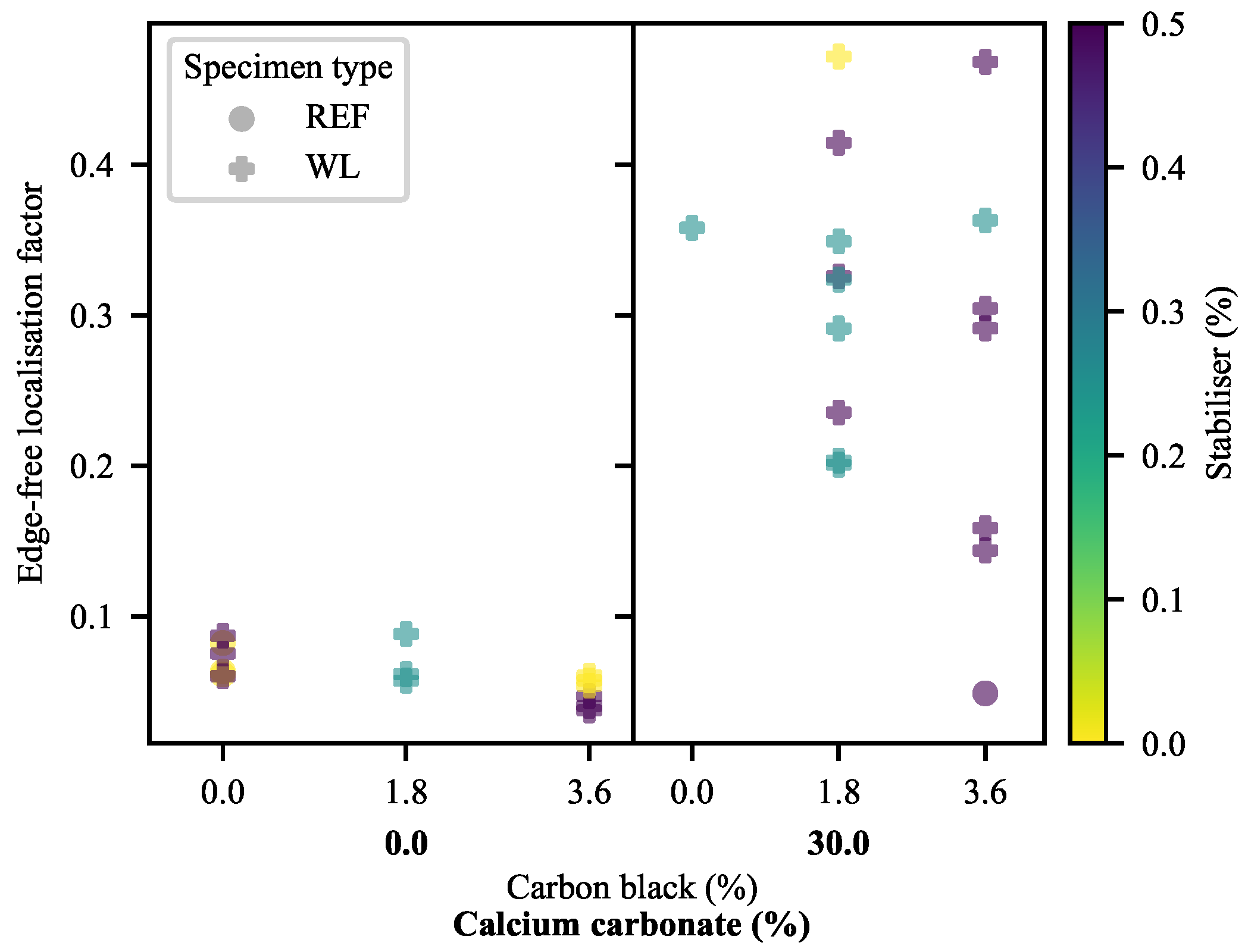
3.2.1. Deformation at Yield
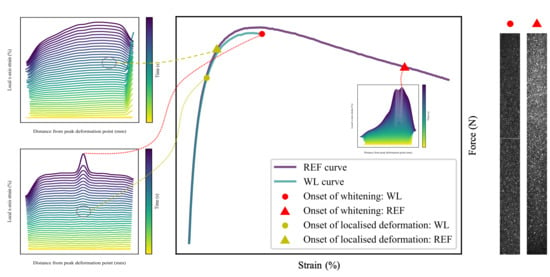
3.2.2. Deformation at Last Viable Instance
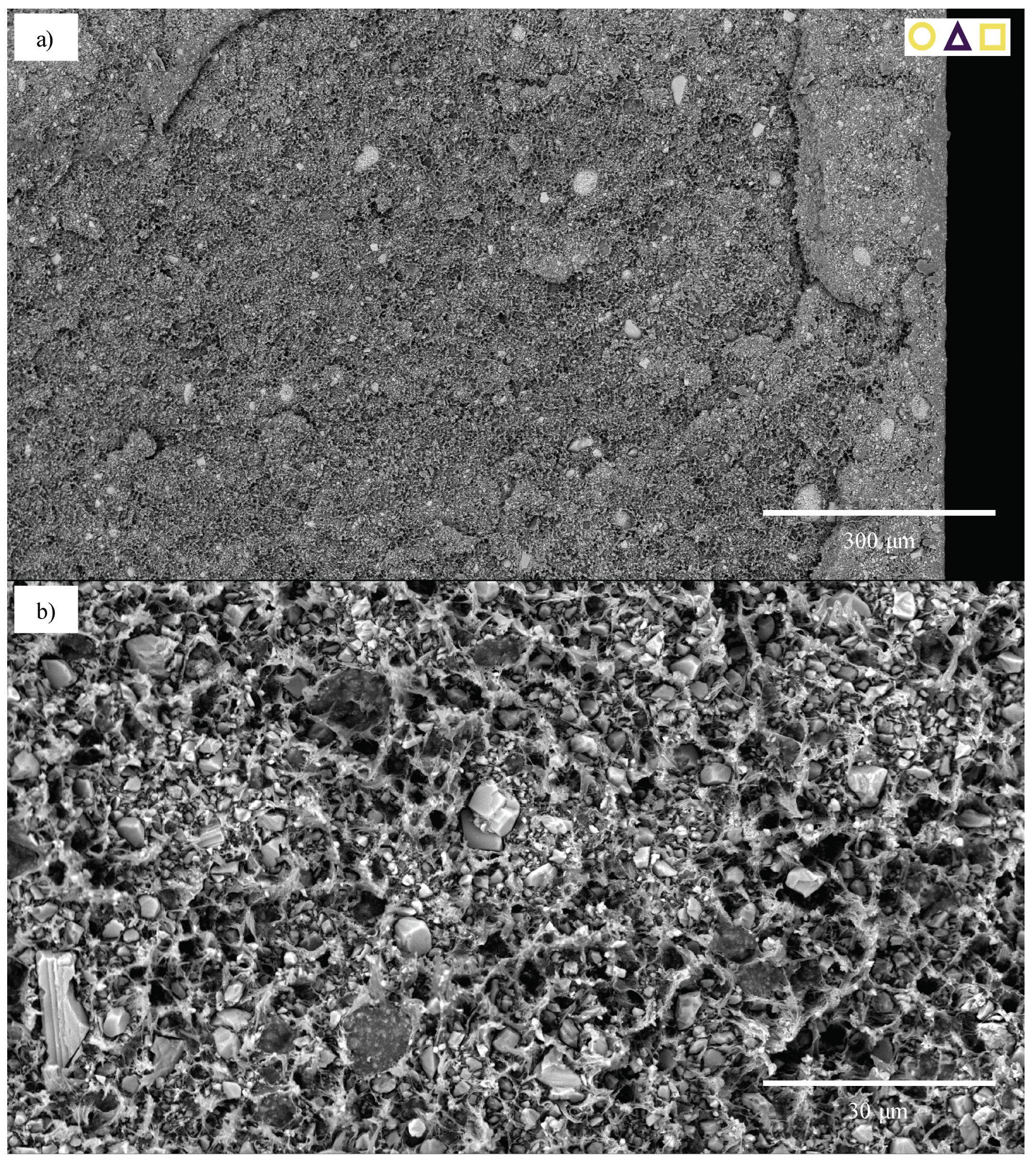
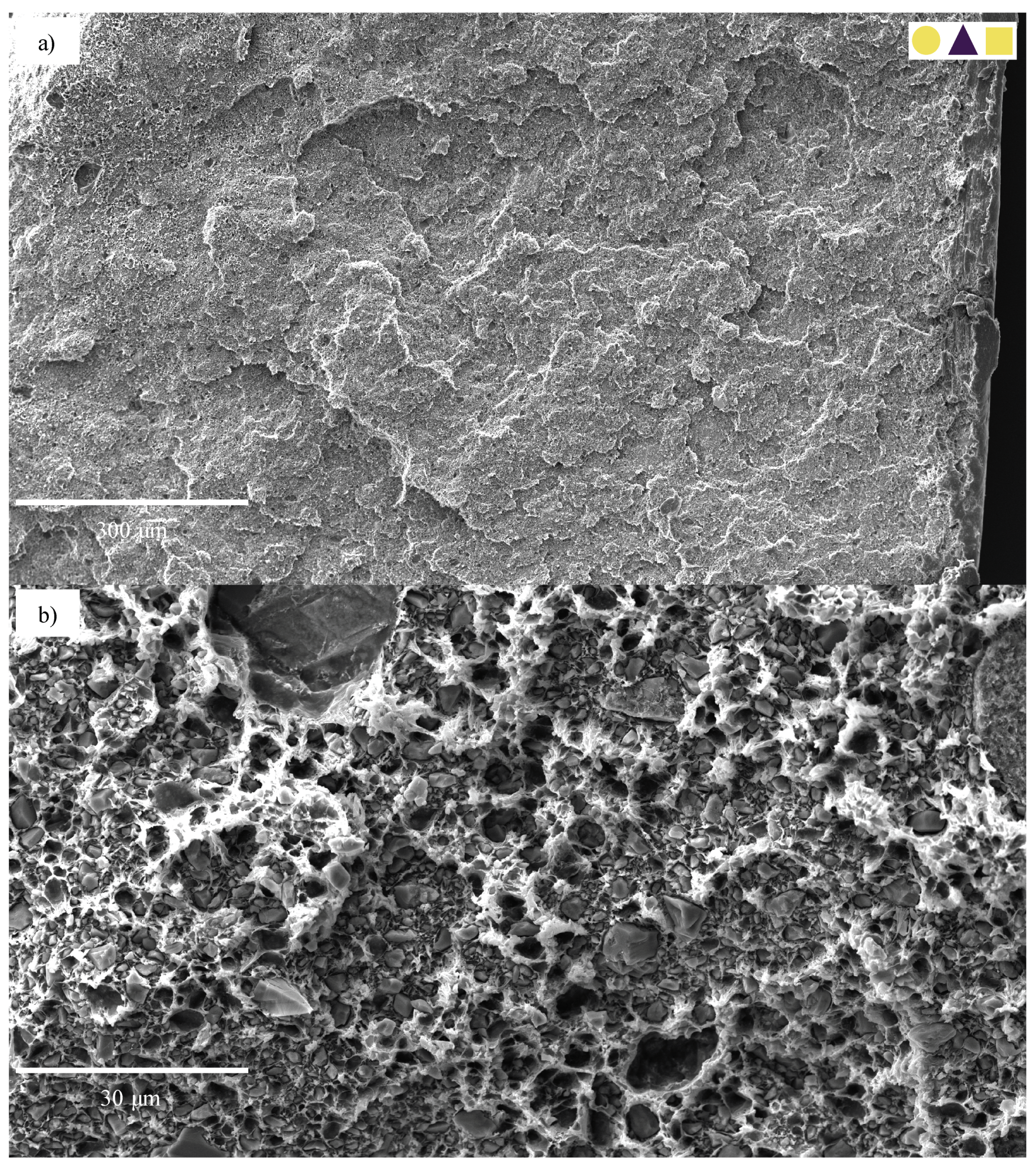
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tolinski, M. Additives for Polyolefins: Getting the Most out of Polypropylene, Polyethylene and TPO; William Andrew: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wypych, G. Handbook of Fillers, 4th ed.; ChemTec Publishing: Scarborough, ON, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, J. Additives for Plastics Handbook; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Papathanasiou, A.; Kühnert, I. Flow-induced alignment in injection molding of fiber-reinforced polymer composites. In Flow-Induced Alignment in Composite Materials, 2nd ed.; Papathanasiou, T.D., Benard, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Chapter 5. [Google Scholar]
- Akay, M.; Barkley, D. Flow-aberrations and weld lines in glass-fibre reinforced thermosplastic injection mouldings. Plast. Rubber Compos. Process. Appl. 1993, 20, 137–149. [Google Scholar]
- Brahimi, B.; Ait-Kadi, A.; Ajji, A. Weld lines and mechanical properties of injection molded polyethylene/polystyrene/copolymer blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1994, 34, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellahi, S.; Meddad, A.; Fisa, B.; Favis, B.D. Weldlines in injection-molded parts: A review. Adv. Polym. Technol. J. Polym. Process. Inst. 1995, 14, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisa, B.; Rahmani, M. Weldline strength in injection molded glass fiber-reinforced polypropylene. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1991, 31, 1330–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekhilef, N.; Ait-Kadi, A.; Ajji, A. Weld lines in injection-moulded immiscible blends: Model predictions and experimental results. Polymer 1995, 36, 2033–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühnert, I.; Spörer, Y.; Zimmermann, M. Weld lines in injection molded parts: Strength, morphology and improvement. In Proceedings of the ANTEC 2016, Indianapolis, IN, USA, 23–25 May 2016; pp. 1255–1259. [Google Scholar]
- Baradi, M.B.; Cruz, C.; Riedel, T.; Régnier, G. Frontal weld lines in injection-molded short fiber-reinforced PBT: Extensive microstructure characterization for mechanical performance evaluation. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 4547–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradi, M.B.; Cruz, C.; Riedel, T.; Régnier, G. Mechanical and microstructural characterization of flowing weld lines in injection-molded short fiber-reinforced PBT. Polym. Test. 2019, 74, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.T.A.; Zhai, M.; Schneider, G.; Kalmar, R.; Fendler, M.; Locquet, A.; Citrin, D.; Declercq, N. Scanning acoustic microscopy investigation of weld lines in injection-molded parts manufactured from industrial thermoplastic polymer. Micron 2020, 138, 102925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malguarnera, S.C. Weld lines in polymer processing. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 1982, 18, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tocchetto, R.S.; Barros, L.A.; Rabello, M.S.; D’Almeida, J.R.M. Degradation Study of Polypropylene Based Composites Containing Weld Lines; Technical Report; SAE Technical Paper: Chicago, IL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hiss, R.; Hobeika, S.; Lynn, C.; Strobl, G. A general scheme derived from video-controlled stretching tests and WAXS for describing tensile deformations of polyethylenes. J. Macromol. Sci. 1999, 38, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiss, R.; Hobeika, S.; Lynn, C.; Strobl, G. Network stretching, slip processes, and fragmentation of crystallites during uniaxial drawing of polyethylene and related copolymers. A comparative study. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 4390–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobeika, S.; Men, Y.; Strobl, G. Temperature and strain rate independence of critical strains in polyethylene and poly (ethylene-co-vinyl acetate). Macromolecules 2000, 33, 1827–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Men, Y.; Strobl, G. Understanding of the tensile deformation in HDPE/LDPE blends based on their crystal structure and phase morphology. Polymer 2003, 44, 1927–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, Y.; Rieger, J.; Strobl, G. Role of the entangled amorphous network in tensile deformation of semicrystalline polymers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 095502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.; Strobl, G. Network stretching during tensile drawing of polyethylene: A study using X-ray scattering and microscopy. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.J.; Bowden, P.B.; Ritchie, J.M.; Rider, J.G. Deformation mechanisms in oriented high-density polyethylene. J. Mater. Sci. 1973, 8, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, P.B.; Young, R.J. Deformation mechanisms in crystalline polymers. J. Mater. Sci. 1974, 9, 2034–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, D.G.; Cherry, B.W. The role of recovery forces in the deformation of linear polyethylene. J. Mater. Sci. 1978, 13, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohse, D.J.; Gaylord, R.J. The amorphous contribution to the modulus of a semi-crystalline polymer. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1978, 18, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farge, L.; Boisse, J.; Dillet, J.; André, S.; Albouy, P.A.; Meneau, F. Wide-angle X-ray scattering study of the lamellar/fibrillar transition for a semi-crystalline polymer deformed in tension in relation with the evolution of volume strain. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2015, 53, 1470–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, L. Mechanical characterization of composite materials by optical techniques: A review. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2018, 104, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerabek, M.; Major, Z.; Lang, R.W. Strain determination of polymeric materials using digital image correlation. Polym. Test. 2010, 29, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crammond, G.; Boyd, S.W.; Dulieu-Barton, J.M. Speckle pattern quality assessment for digital image correlation. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2013, 51, 1368–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulain, X.; Kohlman, L.W.; Binienda, W.; Roberts, G.D.; Goldberg, R.K.; Benzerga, A.A. Determination of the intrinsic behavior of polymers using digital image correlation combined with video-monitored testing. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2013, 50, 1869–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godara, A.; Raabe, D.; Bergmann, I.; Putz, R.; Müller, U. Influence of additives on the global mechanical behavior and the microscopic strain localization in wood reinforced polypropylene composites during tensile deformation investigated using digital image correlation. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, E.M.; Boyce, M.C.; Parks, D.M.; Weinberg, M. Three-dimensional large-strain tensile deformation of neat and calcium carbonate-filled high-density polyethylene. Polymer 2005, 46, 2257–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.; Hopperstad, O.S.; Clausen, A.H. Volumetric strain measurement of polymeric materials subjected to uniaxial tension. Strain 2019, 55, e12314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudár, A.; Móczó, J.; Vörös, G.; Pukánszky, B. The mechanism and kinetics of void formation and growth in particulate filled PE composites. Express Polym. Lett. 2007, 1, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Bai, S.L.; G’Sell, C.; Hiver, J.M. Mechanical properties and volume dilatation of HDPE/CaCo3 blends with and without impact modifier. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2006, 46, 1512–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M.; Edwards, D.; Shah, A. Fractography in Failure Analysis of Polymers; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tanniru, M.; Misra, R. Reduced susceptibility to stress whitening during tensile deformation of calcium carbonate-reinforced high density polyethylene composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 424, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Móczó, J.; Pukánszky, B. Fillers and Reinforcing Agents for Polyethylene. In Handbook of Industrial Polyethylene and Technology; Spalding, M.A., Chatterjee, A.M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1033–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Suwanprateeb, J.; Tiemprateeb, S.; Kangwantrakool, S.; Hemachandra, K. The role of filler volume fraction in the strain-rate dependence of calcium carbonate-reinforced polyethylene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 70, 1717–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartczak, Z.; Argon, A.S.; Cohen, R.E.; Weinberg, M. Toughness mechanism in semi-crystalline polymer blends: II. High-density polyethylene toughened with calcium carbonate filler particles. Polymer 1999, 40, 2347–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deblieck, R.A.C.; Van Beek, D.J.M.; Remerie, K.; Ward, I.M. Failure mechanisms in polyolefines: The role of crazing, shear yielding and the entanglement network. Polymer 2011, 52, 2979–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viljoen, W.D.; Labuschagne, F.J.W.J. The thermal stability of highly filled high-density polyethylene quaternary composites: Interactive effects and improved measures. Polym. Test. 2020, 85, 106424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, J.M.; Allen, N.S.; Edge, M.; Liauw, C.M.; Valange, B. Interactions between carbon black and stabilisers in LDPE thermal oxidation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2001, 72, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, I.; Krupa, I.; Janigová, I. Hybrid electro-conductive composites with improved toughness, filled by carbon black. Carbon 2005, 43, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OMYA Hydrocarb® 95 T-OG. Product Information Sheet; Omya GmbH: Cologne, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Carbon Black Pigments for Polymers: Americas. In Product Information Sheet; Orion Engineered Carbons: Houston, TX, USA, 2013.
- Li, S.; Zhao, J.; Lu, P.; Xie, Y. Maximum packing densities of basic 3D objects. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, D.W.; Snee, R.D. Test statistics for mixture models. Technometrics 1974, 16, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 527-2:2012. Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties—Part 2: Test Conditions for Moulding and Extrusion Plastics; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 527-1:2019. Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties—Part 1: General Principles; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- McCuen, R.H.; Leahy, R.B.; Johnson, P.A. Problems with logarithmic transformations in regression. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1990, 116, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvålseth, T.O. Note on the R2 measure of goodness of fit for nonlinear models. Bull. Psychon. Soc. 1983, 21, 79–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiess, A.N.; Neumeyer, N. An evaluation of R2 as an inadequate measure for nonlinear models in pharmacological and biochemical research: A Monte Carlo approach. BMC Pharmacol. 2010, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galeski, A. Strength and toughness of crystalline polymer systems. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2003, 28, 1643–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedde, U.W.; Hedenqvist, M.S. Fundamental Polymer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey, C.R.; Paul, D.R.; Barlow, J.W. Mechanical properties of HDPE-PS-SEBS blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1981, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjong, S.C.; Bao, S.P. Fracture toughness of high density polyethylene/SEBS-g-MA/montmorillonite nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjäder, T.; Seppälä, J.; Jääskeläinen, P. Effect of material characteristics of polyolefins on weld line morphology and its correlation to mechanical properties. J. Mater. Sci. 1998, 33, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldt, R.; Gohs, U.; Wagenknecht, U.; Stamm, M. Process-induced morphology and mechanical properties of high-density polyethylene. Polymer 2018, 136, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technical Information: DOWTM HDPE 25055E High Density Polyethylene Resin. In Product Information Sheet; The Dow Chemical Company: Midland, MI, USA, 2012.
- Viana, J. Development of the skin layer in injection moulding: Phenomenological model. Polymer 2004, 45, 993–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, K.M.B.; Van Dijk, D.J.; Husselman, M.H. Effect of processing conditions on shrinkage in injection molding. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1998, 38, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Pöhlmann, P.; Kühnert, I. Morphology and mechanical properties of micro injection molded polyoxymethylene tensile rods. Polym. Test. 2019, 80, 106078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, J.J.; King, R.E., III. Degradation and stabilization of polyethylene. In Handbook of Industrial Polyethylene and Technology; Chatterjee, A., Spalding, M.A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; Chapter 25; pp. 754–768. [Google Scholar]
- Rideal, G.R.; Padget, J.C. The thermal-mechanical degradation of high density polyethylene. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Symp. 1976, 57, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschweng, B.; Tátraaljai, D.; Földes, E.; Pukánszky, B. Natural antioxidants as stabilizers for polymers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 145, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahnoune, F.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.M.; Crespy, A. Effect of elastomer interfacial agents on tensile and impact properties of CaCo3 filled HDPE. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, A.; Piechatzek, A.; Schmitt, G.; Siegmund, G. Single-sided nuclear magnetic resonance for condition monitoring of cross-linked polyethylene exposed to aggressive media. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 887, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersoy, O.G.; Nugay, N. Combined effect of the nature of the filler and the compatibilizer on the weld line properties of filled blends. Compos. Part A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisa, B.; Dufour, J.; Vu-Khanh, T. Weldline integrity of reinforced plastics: Effect of filler shape. Polym. Compos. 1987, 8, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Ziegmann, G. Mechanical properties of the weld line defect in micro injection molding for various nano filled polypropylene composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utracki, L.A. Commercial Polymer Blends; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bin Rusayyis, M.A.; Schiraldi, D.A.; Maia, J. Property/morphology relationships in SEBS-compatibilized HDPE/poly(phenylene ether) blends. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 6513–6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielewski, D.F.; Bauer, D.R.; Schmitz, P.J.; Van Oene, H. Weld line morphology of injection molded polypropylene. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1998, 38, 2020–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, M.; Tada, N. Micro-, meso-to macroscopic modeling of deformation behavior of semi-crystalline polymer. Int. J. Plast. 2013, 49, 164–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, D.W.; Barlow, J.W.; Paul, D.R. Mechanical properties of blends containing HDPE and PP. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1982, 27, 2351–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.Z.; Yang, Q.Q. Mechanical properties of carbon black-filled high-density polyethylene antistatic composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2009, 28, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Bateman, S.A.; Wu, D. Mechanical and conductive properties of carbon black-filled high-density polyethylene, low-density polyethylene, and linear low-density polyethylene. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2010, 23, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, Q. Effects of carbon black content on microwave absorbing and mechanical properties of linear low density polyethylene/ethylene-octene copolymer/calcium carbonate composites. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2011, 50, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ognedal, A.S.; Clausen, A.H.; Berstad, T.; Seelig, T.; Hopperstad, O.S. Void nucleation and growth in mineral-filled PVC–An experimental and numerical study. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2014, 51, 1494–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleißner, M. Makroskopische und molekulare Orientierung in Hochpolymeren. Kolloid-Z. Z. Polym. 1973, 251, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katti, S.S.; Schultz, M. The microstructure of injection-molded semicrystalline polymers: A review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1982, 22, 1001–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokrini, A.; Huneault, M.A.; Shi, Z.; Xie, Z.; Holdcroft, S. Non-fluorinated proton-exchange membranes based on melt extruded SEBS/HDPE blends. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dontula, N.; Ramesh, N.S.; Campbell, G.A.; Small, J.D.; Fricke, A.L. An experimental study of polymer-filler redistribution in injection molded parts. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 1994, 13, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegler, R.; Mennig, G. Phase separation effects in processing of glass-bead-and glass-fiber-filled thermoplastics by injection molding. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1985, 25, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrauwen, B.A.G.; Breemen, L.C.A.; Spoelstra, A.B.; Govaert, L.E.; Peters, G.W.M.; Meijer, H.E.H. Structure, deformation, and failure of flow-oriented semicrystalline polymers. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 8618–8633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
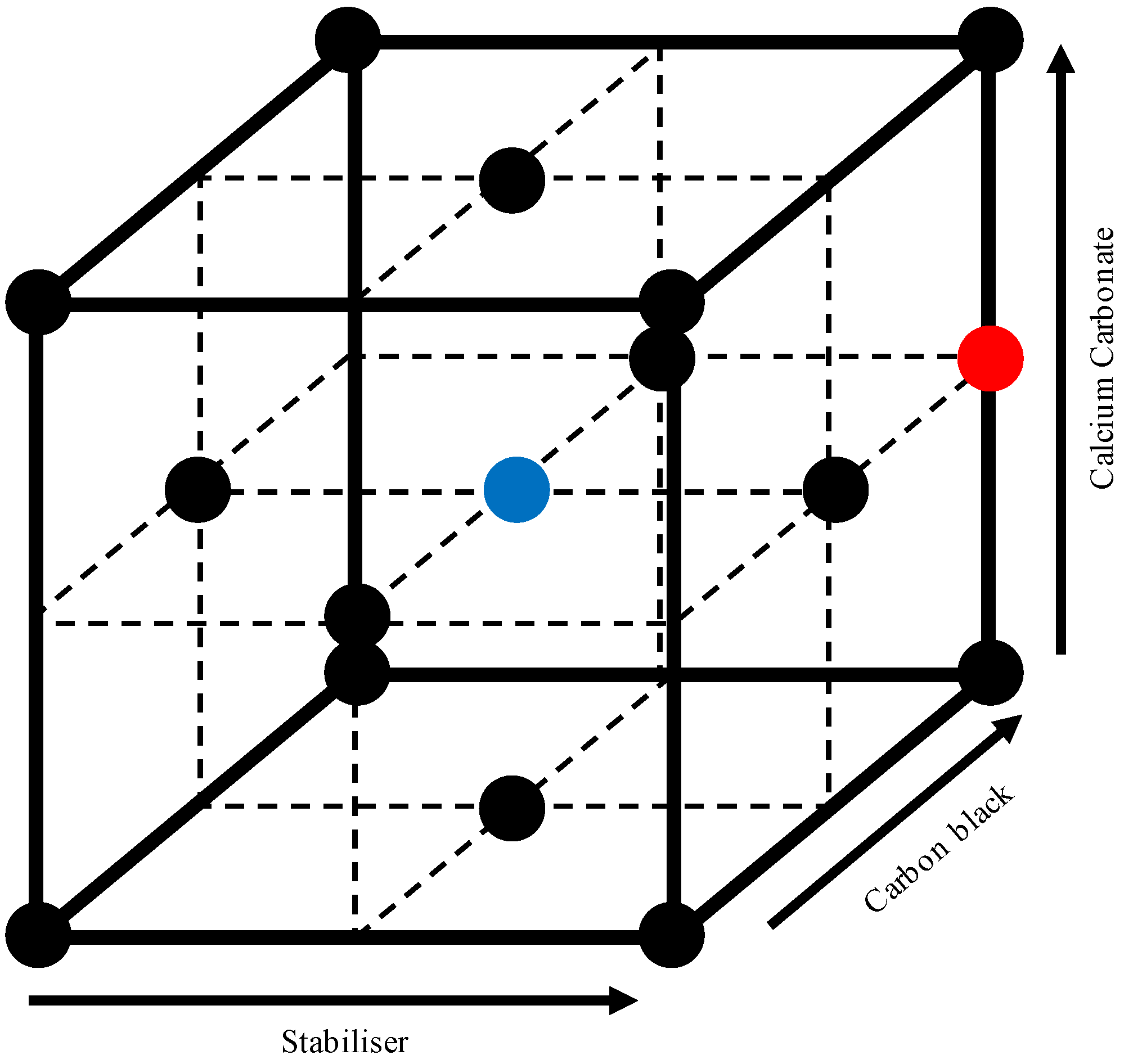







| Component (%) | CC Feed | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formulation | HDPE | CC | CB | C944 | I168 | 1 | 2 |
| 01 | 65.90 | 30 | 3.60 | 0.30 | 0.20 | • | |
| 02 | 65.90 | 30 | 3.60 | 0.30 | 0.20 | • | |
| 03 | 99.50 | 0 | 0 | 0.30 | 0.20 | ||
| 04 | 100.00 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 05 | 97.95 | 0 | 1.80 | 0.15 | 0.10 | ||
| 06 | 95.90 | 0 | 3.60 | 0.30 | 0.20 | ||
| 07 | 96.40 | 0 | 3.60 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 08 | 69.75 | 30 | 0 | 0.15 | 0.10 | • | |
| 09 | 67.70 | 30 | 1.80 | 0.30 | 0.20 | • | |
| 10 | 67.95 | 30 | 1.80 | 0.15 | 0.10 | • | |
| 11 | 67.95 | 30 | 1.80 | 0.15 | 0.10 | • | |
| 12 | 68.20 | 30 | 1.80 | 0 | 0 | • | |
| 13 | 66.15 | 30 | 3.60 | 0.15 | 0.10 | • | |
| 14 | 39.50 | 60 | 0.00 | 0.30 | 0.20 | • | • |
| 15 | 40.00 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 0 | • | • |
| 16 | 37.95 | 60 | 1.80 | 0.15 | 0.10 | • | • |
| 17 | 35.90 | 60 | 3.60 | 0.30 | 0.20 | • | • |
| 18 | 36.40 | 60 | 3.60 | 0.00 | 0.00 | • | • |
| CB | CC | SP | CBxCC | CBxSP | CCxSP | WL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YM | ↗ | ↑ | • | ↓ | ↗ | • | ↗ |
| ↘ | ↘ | • | ↓ | ↗ | ↘ | ||
| ↗ | ↓ | • | ↓ | • | ↘ | ||
| DF | • | ↓ | • | ↑ | •/ | ↘ | |
| • | ↓ | ↑ | ↗ | ↘/ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Viljoen, D.; Fischer, M.; Kühnert, I.; Labuschagné, J. The Tensile Behaviour of Highly Filled High-Density Polyethylene Quaternary Composites: Weld-Line Effects, DIC Curiosities and Shifted Deformation Mechanisms. Polymers 2021, 13, 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040527
Viljoen D, Fischer M, Kühnert I, Labuschagné J. The Tensile Behaviour of Highly Filled High-Density Polyethylene Quaternary Composites: Weld-Line Effects, DIC Curiosities and Shifted Deformation Mechanisms. Polymers. 2021; 13(4):527. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040527
Chicago/Turabian StyleViljoen, David, Matthieu Fischer, Ines Kühnert, and Johan Labuschagné. 2021. "The Tensile Behaviour of Highly Filled High-Density Polyethylene Quaternary Composites: Weld-Line Effects, DIC Curiosities and Shifted Deformation Mechanisms" Polymers 13, no. 4: 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040527
APA StyleViljoen, D., Fischer, M., Kühnert, I., & Labuschagné, J. (2021). The Tensile Behaviour of Highly Filled High-Density Polyethylene Quaternary Composites: Weld-Line Effects, DIC Curiosities and Shifted Deformation Mechanisms. Polymers, 13(4), 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040527