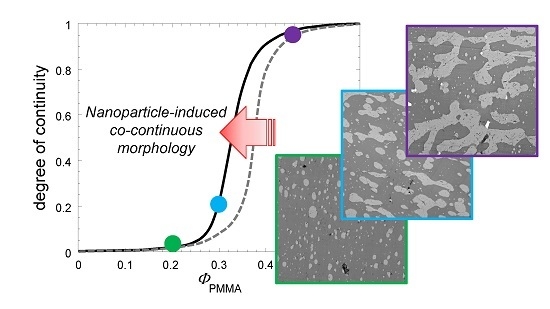
Interfacially-Located Nanoparticles Anticipate the Onset of Co-Continuity in Immiscible Polymer Blends
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Polymer Blends
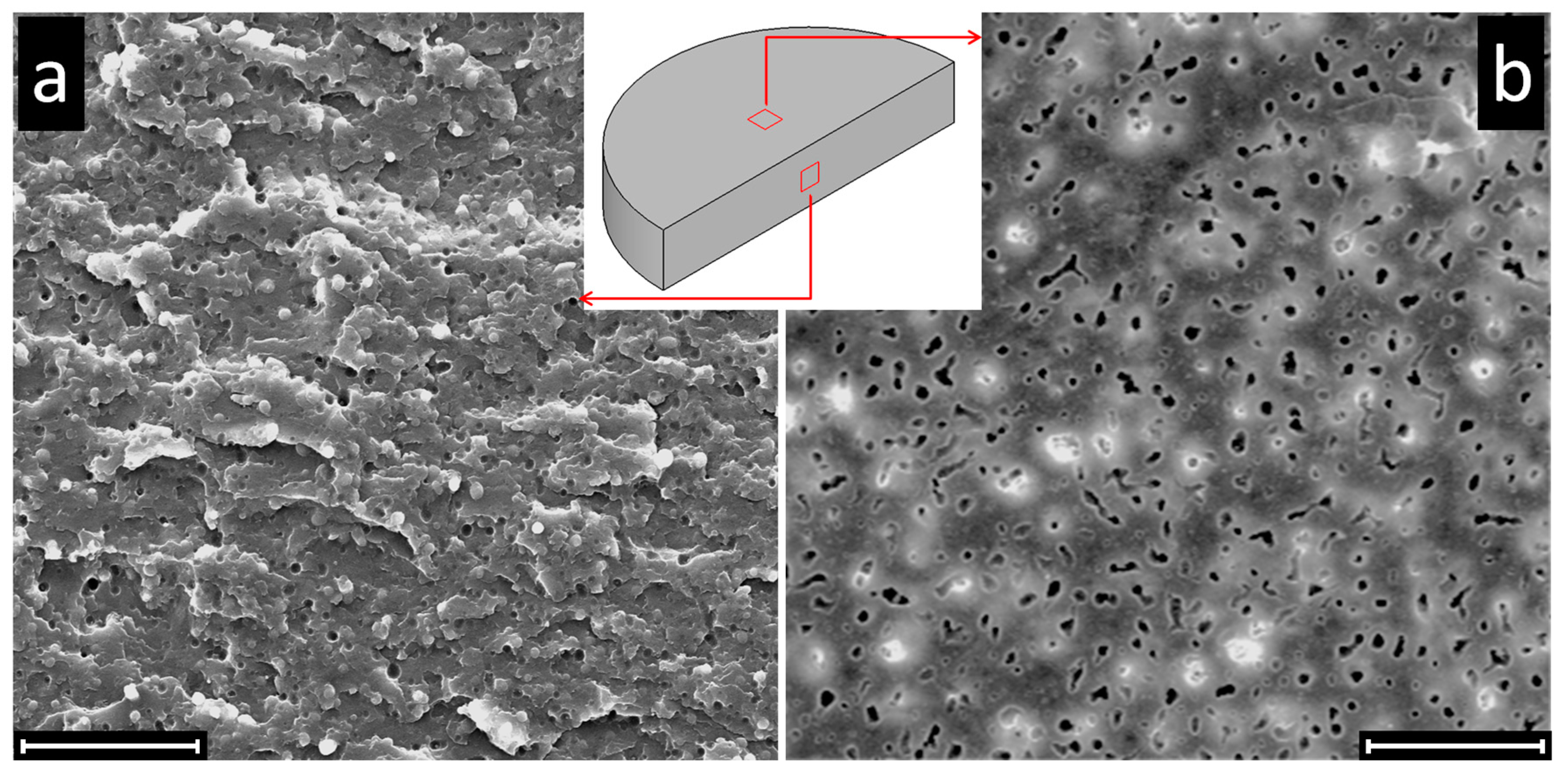
2.3. Characterization
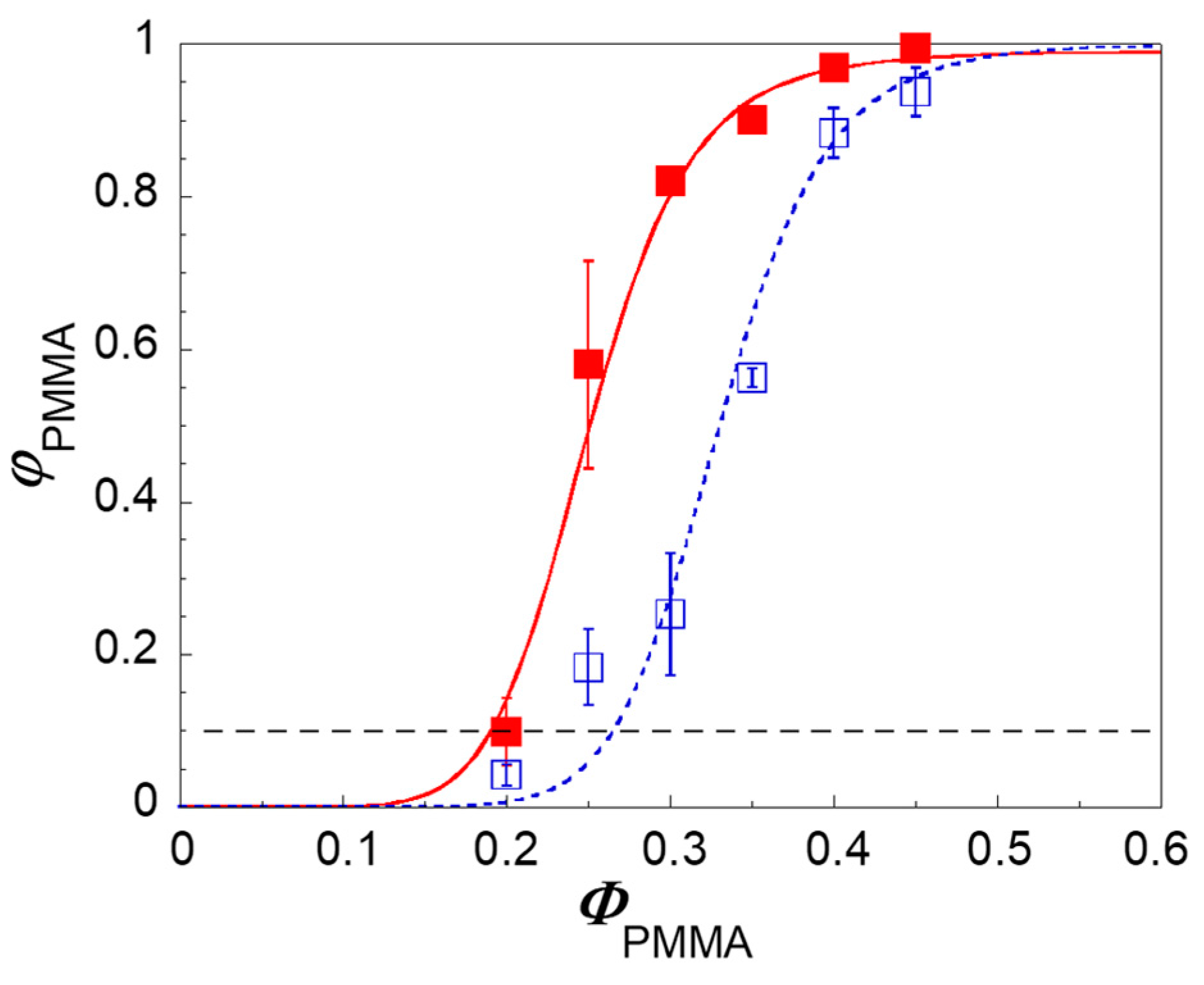
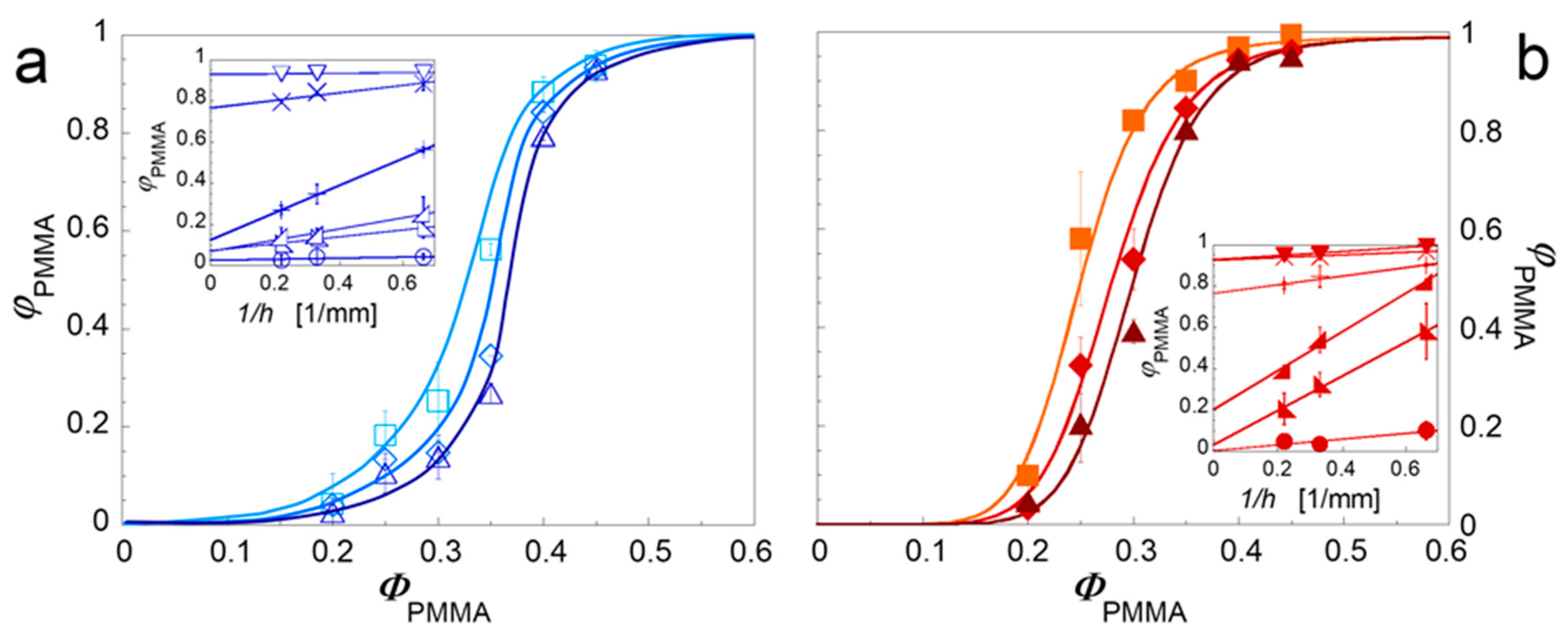
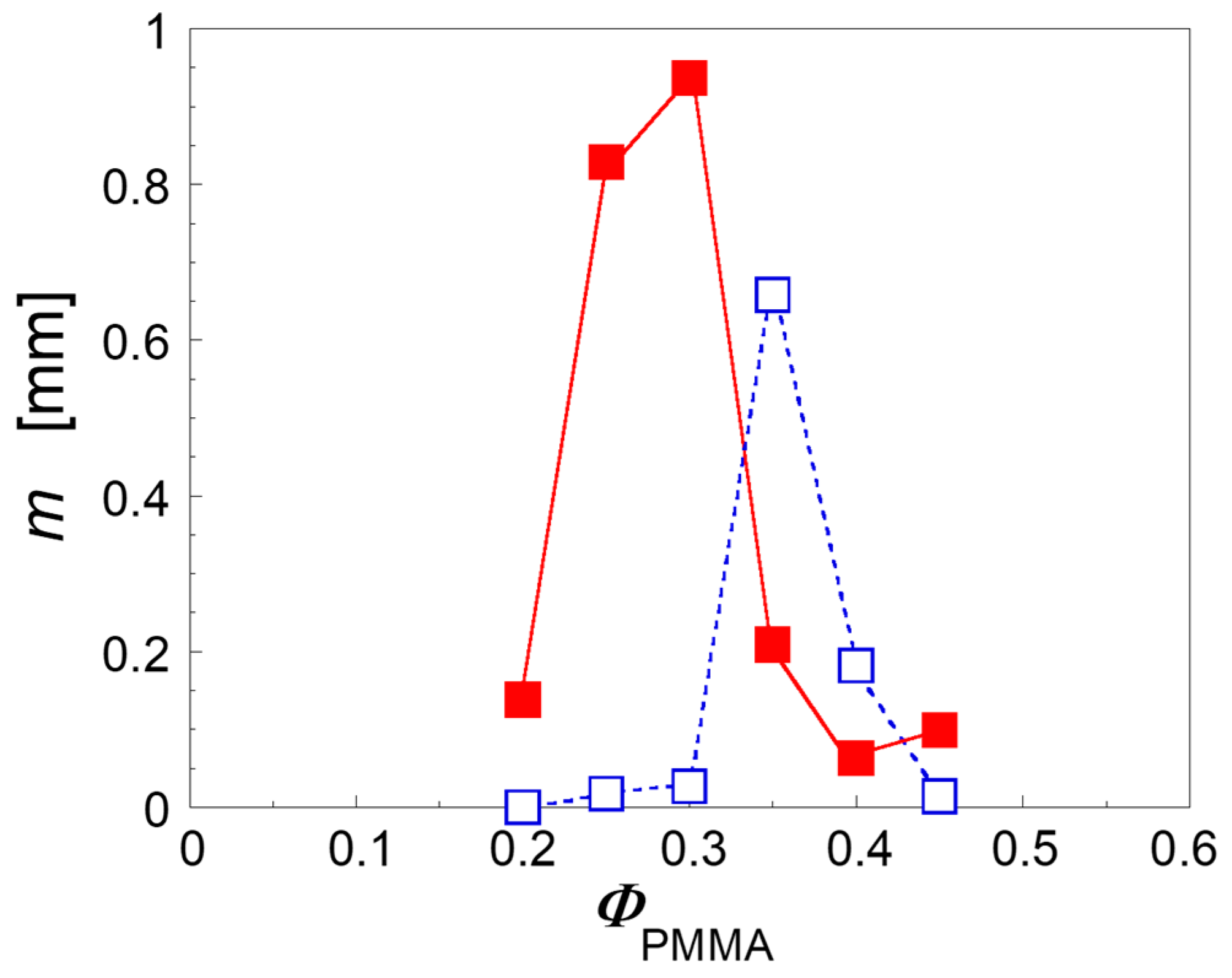
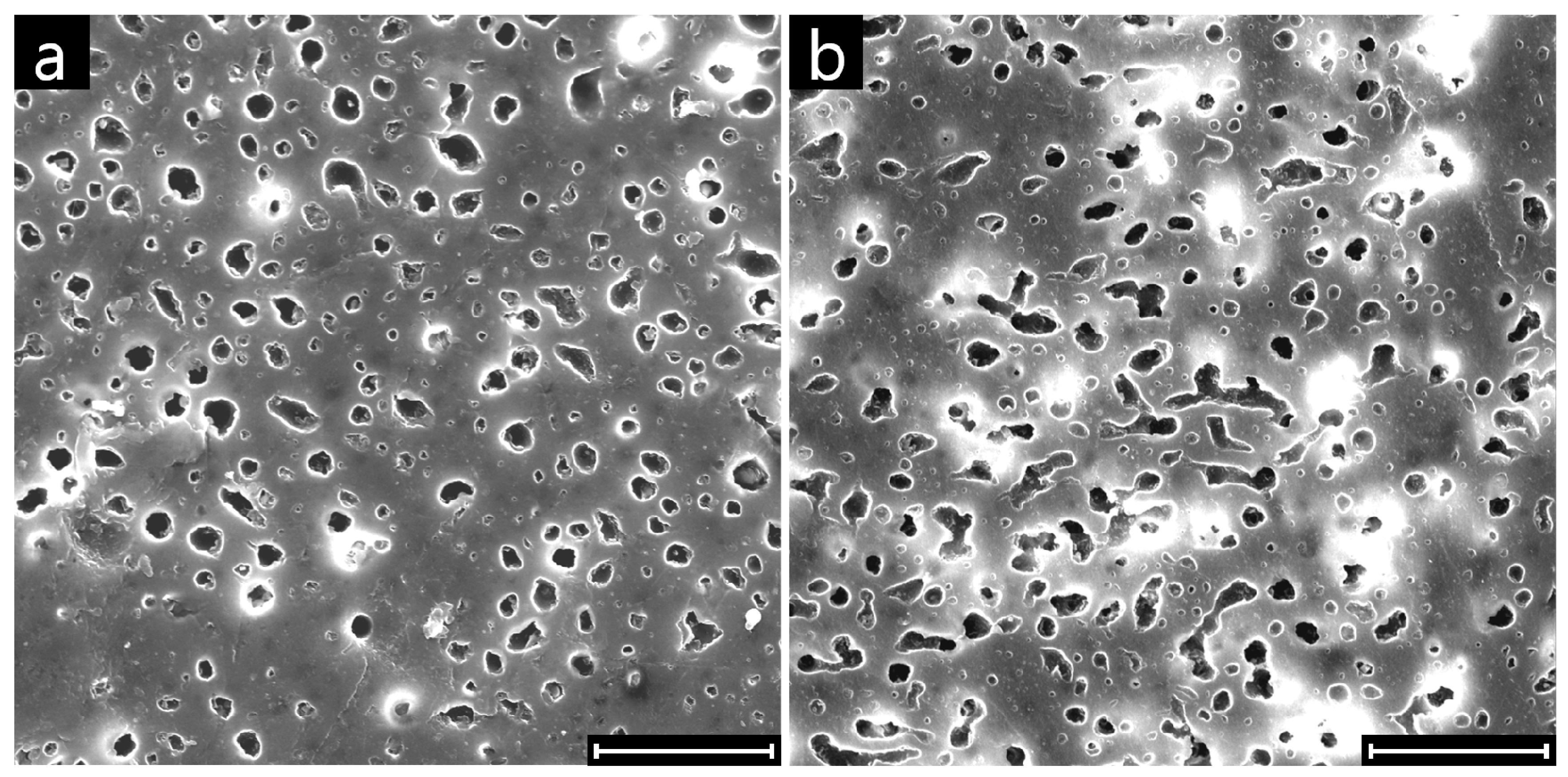
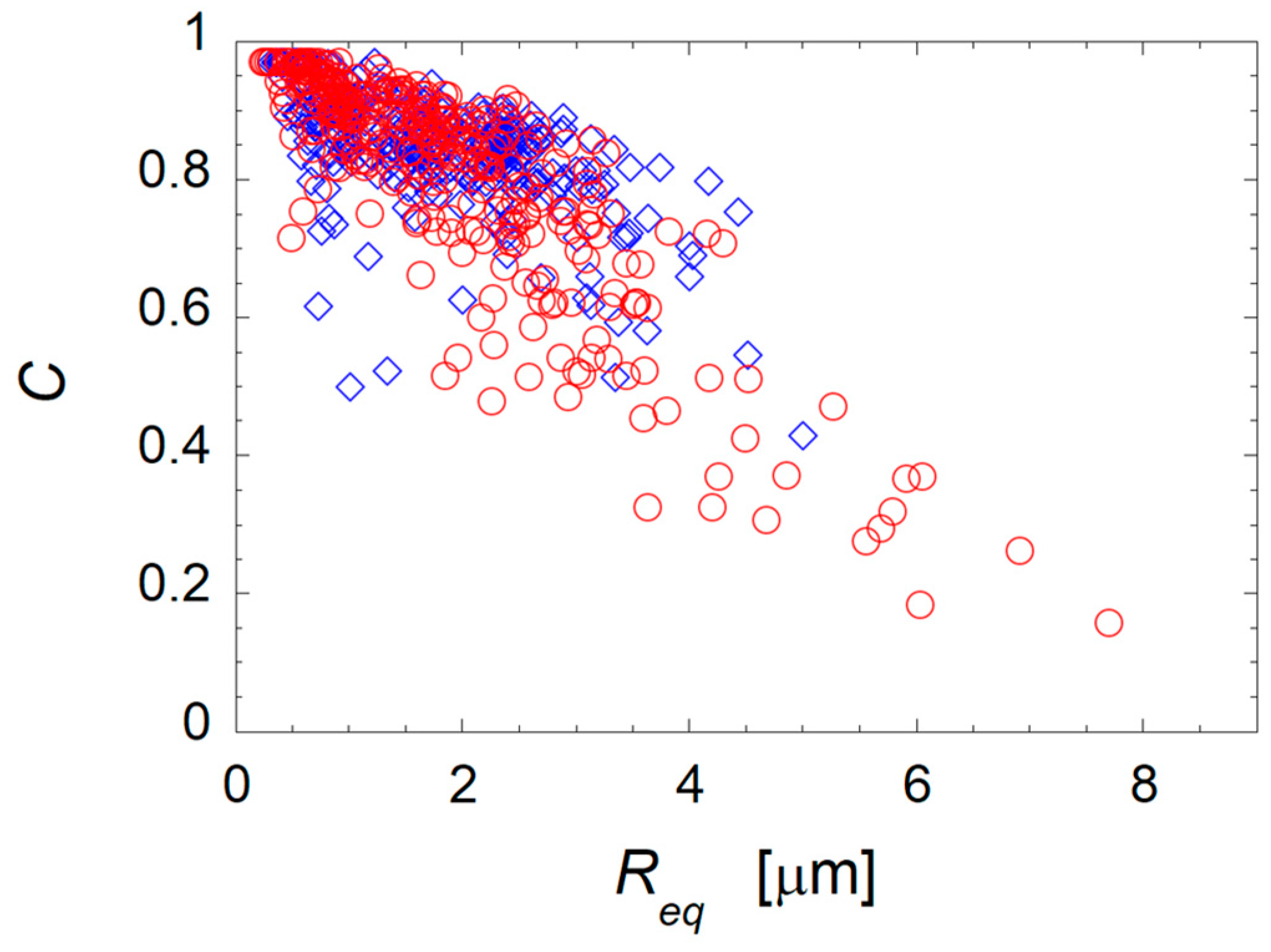
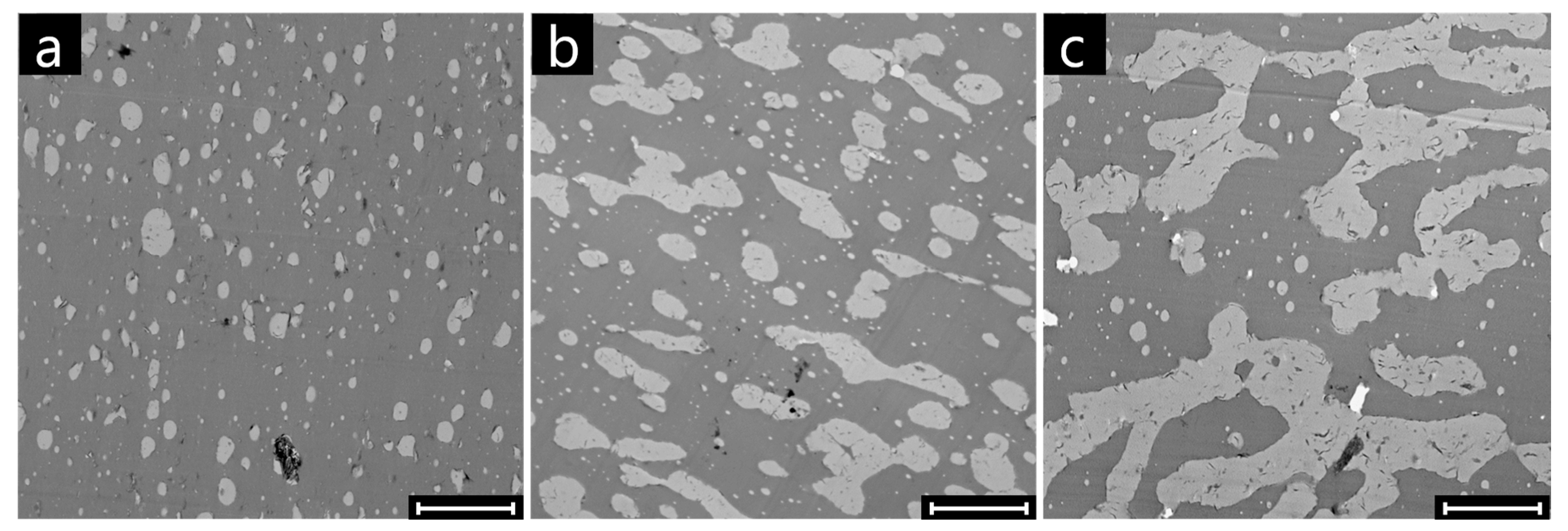
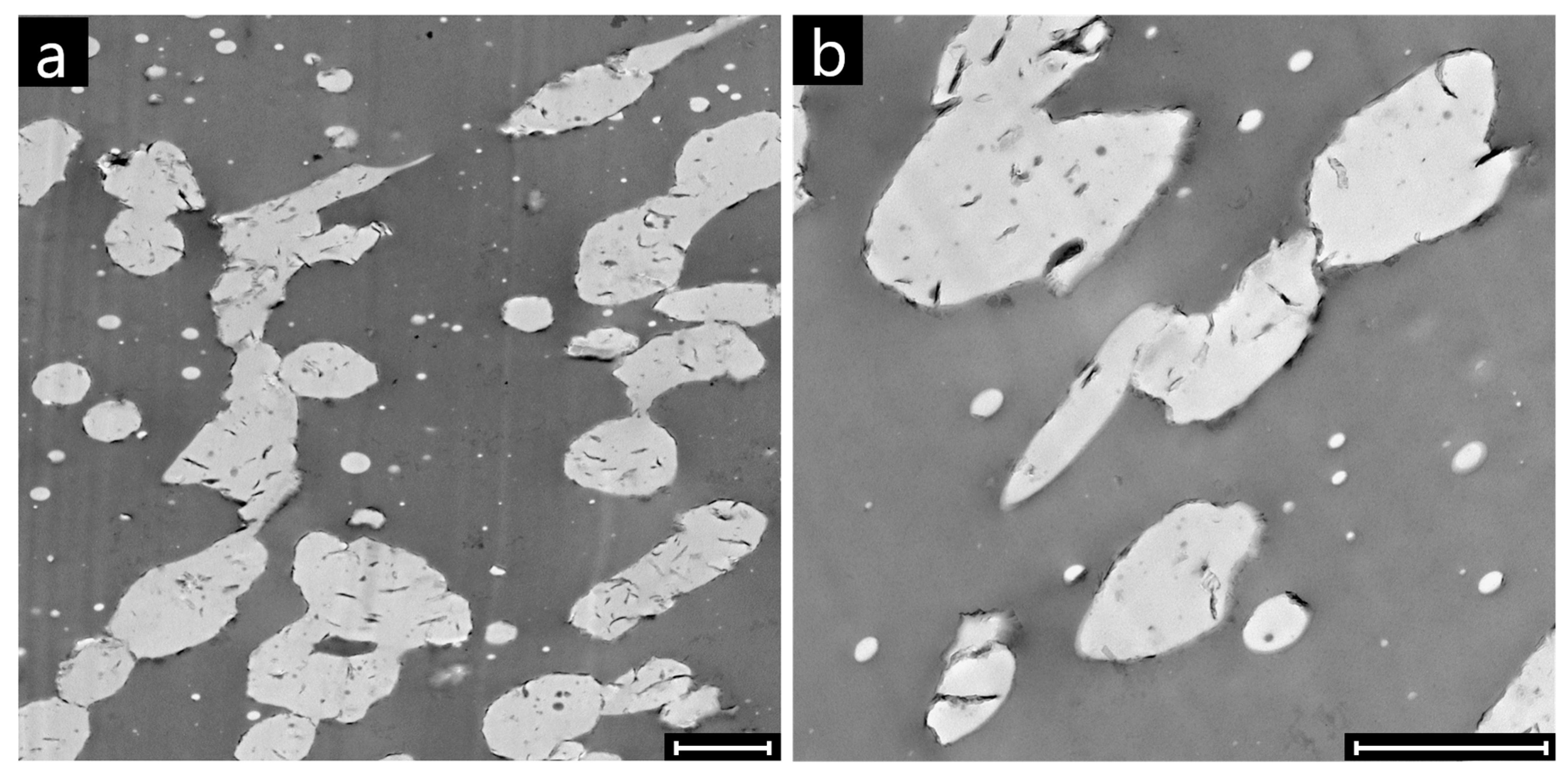
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Nanoparticles on the Co-Continuity of Immiscible Polymer Blends
3.2. Mechanisms of Nanoparticle-Induced Alteration of the Co-Continuity Interval
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Macosko, C.W. Morphology development and control in immiscible polymer blends. Macromol. Symp. 2000, 149, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luna, M.S.; Filippone, G. Effects of nanoparticles on the morphology of immiscible polymer blends—Challenges and opportunities. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 79, 198–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mural, P.K.S.; Banerjee, A.; Rana, M.S.; Shukla, A.; Padmanabhan, B.; Bhadra, S.; Madras, G.; Bose, S. Polyolefin based antibacterial membranes derived from PE/PEO blends compatibilized with amine terminated graphene oxide and maleated PE. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 17635–17648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luna, M.S.; Galizia, M.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Rosa, R.; Lojkowski, W.; Leonelli, C.; Acierno, D.; Filippone, G. Dispersing hydrophilic nanoparticles in hydrophobic polymers: HDPE/ZnO nanocomposites by a novel template-based approach. Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koning, C.; Van Duin, M.; Pagnoulle, C.; Jerome, R. Strategies for compatibilization of polymer blends. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1998, 23, 707–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veenstra, H.; van Lent, B.J.; van Dam, J.; de Boer, A.P. Co-continuous morphologies in polymer blends with SEBS block copolymers. Polymer 1999, 40, 6661–6672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbels, F.; Blacher, S.; Vanlathem, E.; Jérôme, R.; Deltour, R.; Brouers, F.; Teyssie, P. Design of electrical composites: Determining the role of the morphology on the electrical properties of carbon black filled polymer blends. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 1559–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmann, S.; Gronski, W.; Friedrich, C. Influence of selective filling on rheological properties and phase inversion of two-phase polymer blends. Polymer 2002, 43, 4467–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S. Effect of nano-particles-induced phase inversion on largely improved impact toughness of PVC/α-methylstyrene-acrylonitrile copolymer (α-MSAN)/CPE-matrix composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 86, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, W.; Zhao, X.; Tian, T.; Chen, T. Self-formation of elastomer network assisted by nano-silicon dioxide particles: A simple and efficient route toward polymer nanocomposites with simultaneous improved toughness and stiffness. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippone, G.; Dintcheva, N.T.; La Mantia, F.P.; Acierno, D. Using organoclay to promote morphology refinement and co-continuity in high-density polyethylene/polyamide 6 blends—Effect of filler content and polymer matrix composition. Polymer 2010, 51, 3956–3965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, A.; Coiai, S.; Carroccio, S.C.; Dintcheva, N.T.; Gambarotti, C.; Filippone, G. Heat-Resistant Fully Bio-Based Nanocomposite Blends Based on Poly (lactic acid). Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2014, 299, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippone, G.; Acierno, D. Clustering of coated droplets in clay-filled polymer blends. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2012, 297, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippone, G.; Causa, A.; de Luna, M.S.; Sanguigno, L.; Acierno, D. Assembly of plate-like nanoparticles in immiscible polymer blends—Effect of the presence of a preferred liquid-liquid interface. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 3183–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, J.A.; Koester, K.; Paasch, B.J.; Macosko, C.W. Effect of sample size on solvent extraction for detecting cocontinuity in polymer blends. Polymer 2004, 45, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S. Phase structure and adhesion in polymer blends: A criterion for rubber toughening. Polymer 1985, 26, 1855–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pötschke, P.; Paul, D.R. Formation of co-continuous structures in melt-mixed immiscible polymer blends. J. Macromol. Sci. C Polym. Rev. 2003, 43, 87–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.A.; Macosko, C.W. Comparison of methods for the detection of cocontinuity in poly(ethylene oxide)/polystyrene blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2004, 44, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Li, B.; Jiang, J. Carbon black self-networking induced co-continuity of immiscible polymer blends. Polymer 2010, 51, 2077–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippone, G.; Romeo, G.; Acierno, D. Role of Interface Rheology in Altering the Onset of Co-Continuity in Nanoparticle-Filled Polymer Blends. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2011, 296, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, N.; Li, H. Enhancement of electrical conductivity by changing phase morphology for composites consisting of polylactide and poly (ε-caprolactone) filled with acid-oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. ACS App. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 4858–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Kong, M.; Zhu, H.; Chen, G.; Yang, Q. Morphology and rheology of poly (l-lactide)/polystyrene blends filled with silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, C.; Bai, H.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Deep insight into the key role of carbon black self-networking in the formation of co-continuous-like morphology in polylactide/poly (ether) urethane blends. Polymer 2016, 82, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J. Intermolecular and Surface Forces, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Thareja, P.; Moritz, K.; Velankar, S.S. Interfacially active particles in droplet/matrix blends of model immiscible homopolymers: Particles can increase or decrease drop size. Rheol. Acta 2010, 49, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemse, R.C.; De Boer, A.P.; Van Dam, J.; Gotsis, A.D. Co-continuous morphologies in polymer blends: A new model. Polymer 1998, 39, 5879–5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luna, M.S.d.; Causa, A.; Filippone, G. Interfacially-Located Nanoparticles Anticipate the Onset of Co-Continuity in Immiscible Polymer Blends. Polymers 2017, 9, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9090393
Luna MSd, Causa A, Filippone G. Interfacially-Located Nanoparticles Anticipate the Onset of Co-Continuity in Immiscible Polymer Blends. Polymers. 2017; 9(9):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9090393
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuna, Martina Salzano de, Andrea Causa, and Giovanni Filippone. 2017. "Interfacially-Located Nanoparticles Anticipate the Onset of Co-Continuity in Immiscible Polymer Blends" Polymers 9, no. 9: 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9090393
APA StyleLuna, M. S. d., Causa, A., & Filippone, G. (2017). Interfacially-Located Nanoparticles Anticipate the Onset of Co-Continuity in Immiscible Polymer Blends. Polymers, 9(9), 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9090393