SmartRead: A Multimodal eReading Platform Integrating Computing and Gamification to Enhance Student Engagement and Knowledge Retention
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background and Literature Review
Impact on Student Engagement and Assimilation
- How do multimodal computing tools affect student engagement in personal reading?
- What impact do digital reading tools have on knowledge assimilation?
- Which features of digital reading platforms are most preferred by students?
- What challenges do students face when using digital reading tools?
- How can the design and technical features of a digital reading platform be optimized to improve usability, engagement, and comprehension
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Research Design
3.2. Research Approach
3.3. Data Collection Method
3.4. Sample Selection
3.5. Analytical Framework
4. Results
4.1. Impact of Computing on Engagement
4.2. Top eReading Features
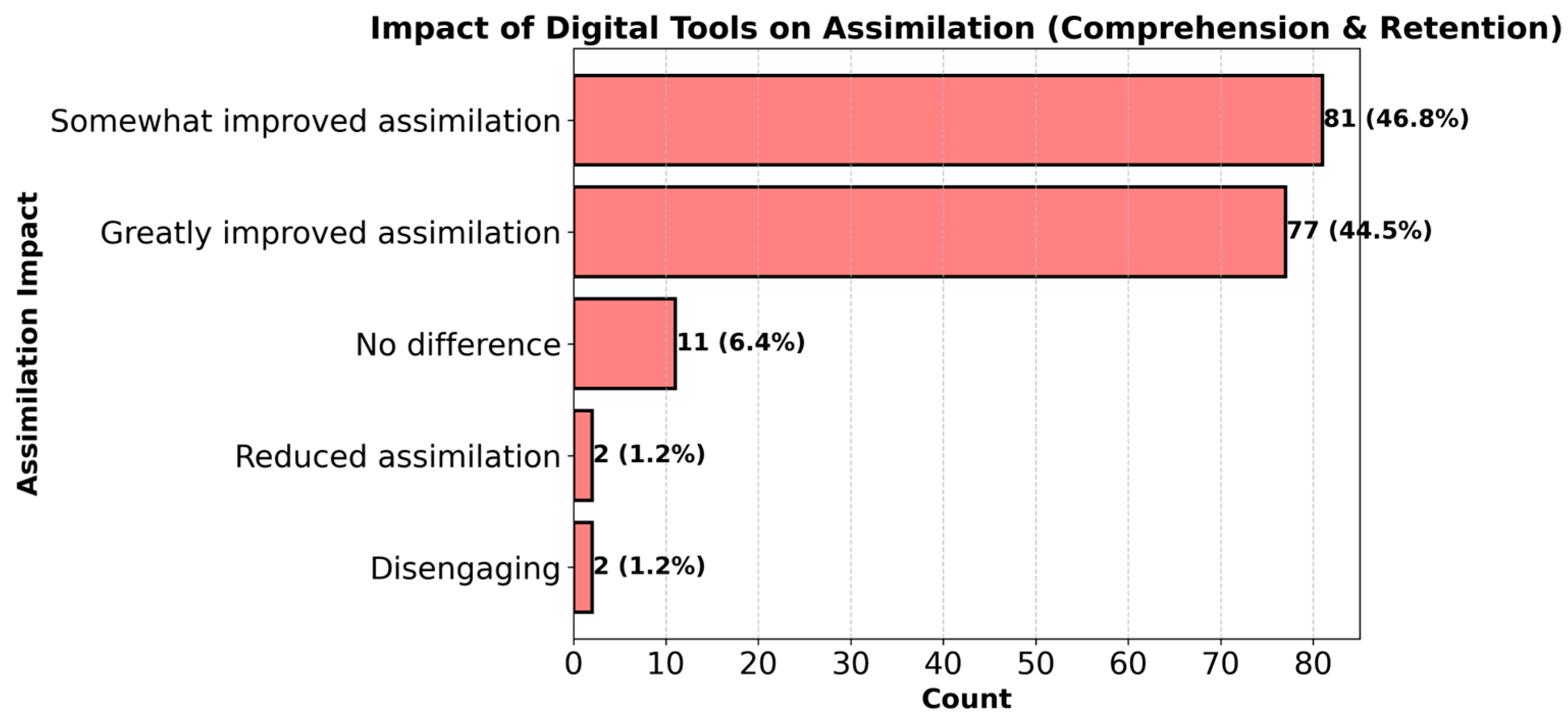
4.3. Impact of eReading Tools on Assimilation
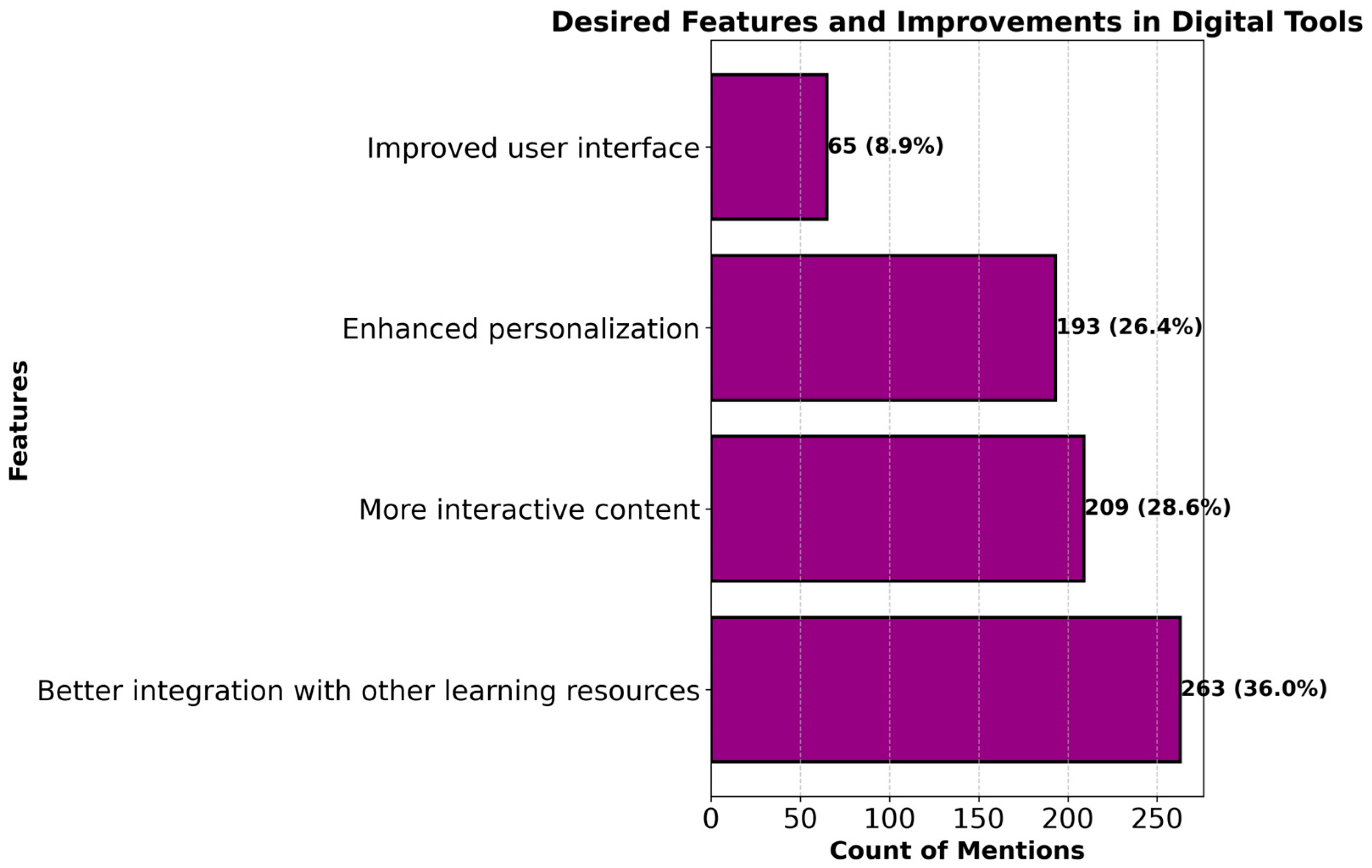
4.4. Desired Technical Features
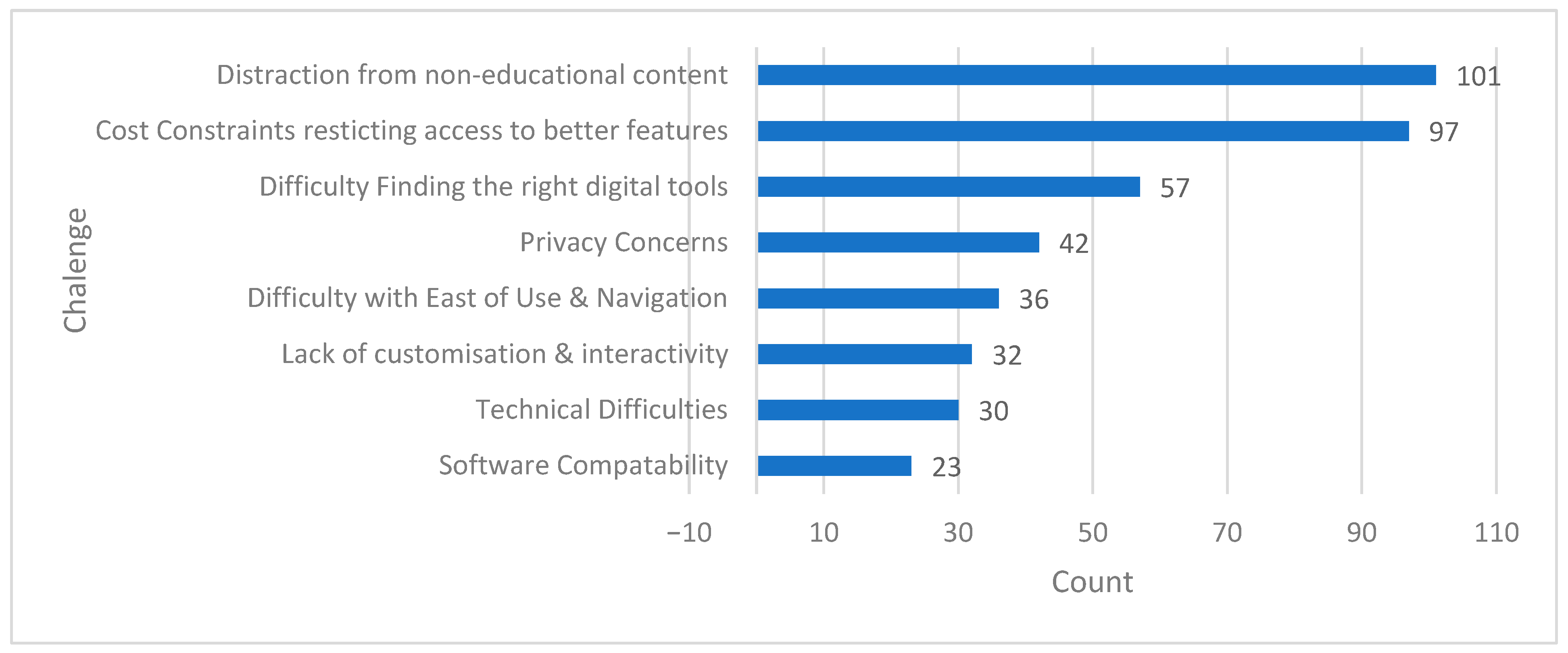
4.5. Challenges
- Computing tools substantially increase student engagement and assimilation;
- Tools like AI-powered assistants are most effective for improving comprehension and retention;
- Compared with traditional methods, digital tools are overwhelmingly preferred, with limited concerns about distractions or lack of personalization;
- Students value personalized experiences, interactivity, and better tool integration for a more user-friendly environment;
- Despite their benefits, digital tools pose challenges, including difficulty in finding the right tools (13.6%), privacy concerns (10.0%), and ease-of-use/navigation issues (8.6%).
4.6. P-Test Analysis
4.6.1. Assimilation by Reading Frequency
4.6.2. Engagement by Reading Frequency
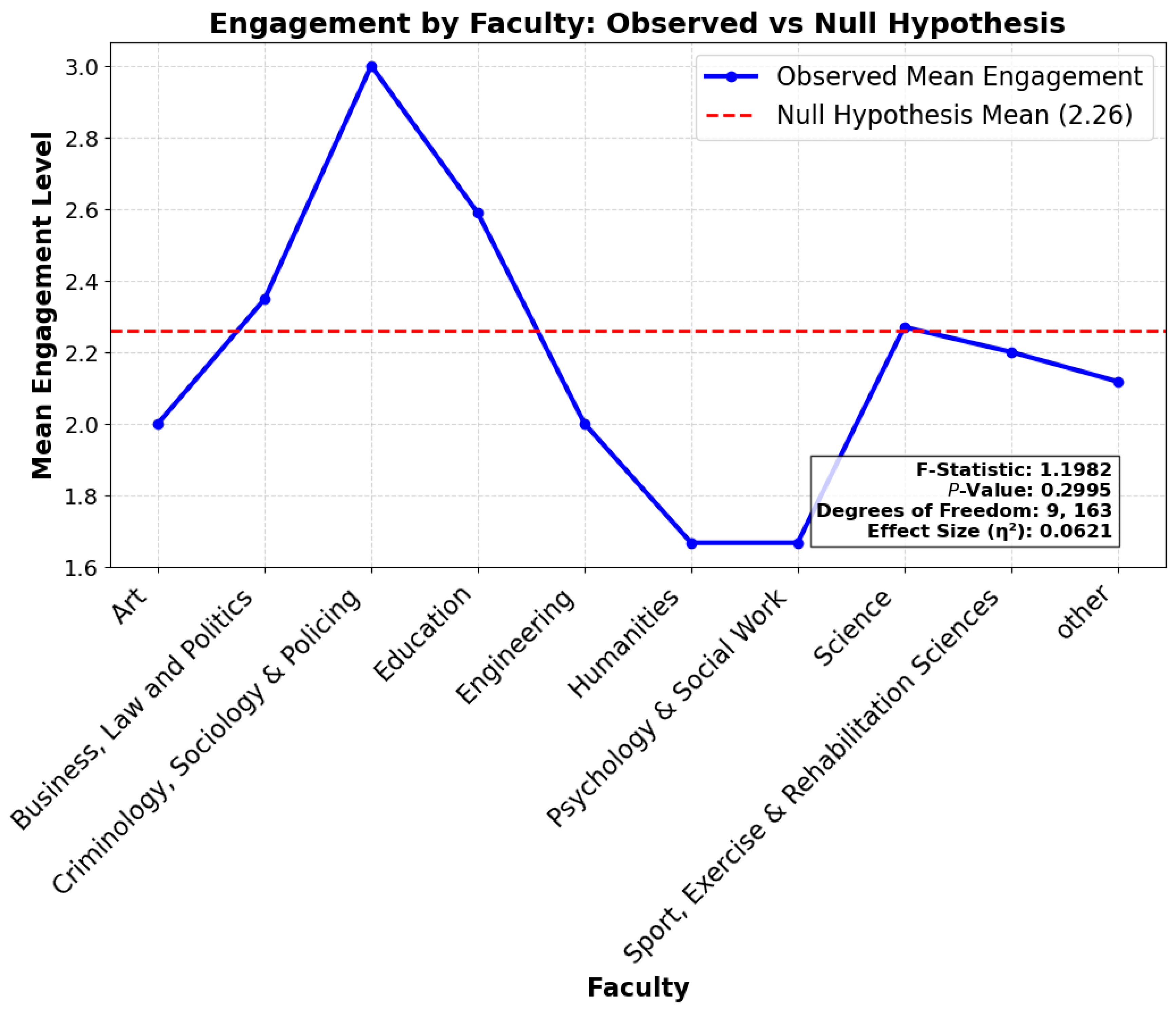
4.6.3. Engagement by Faculty
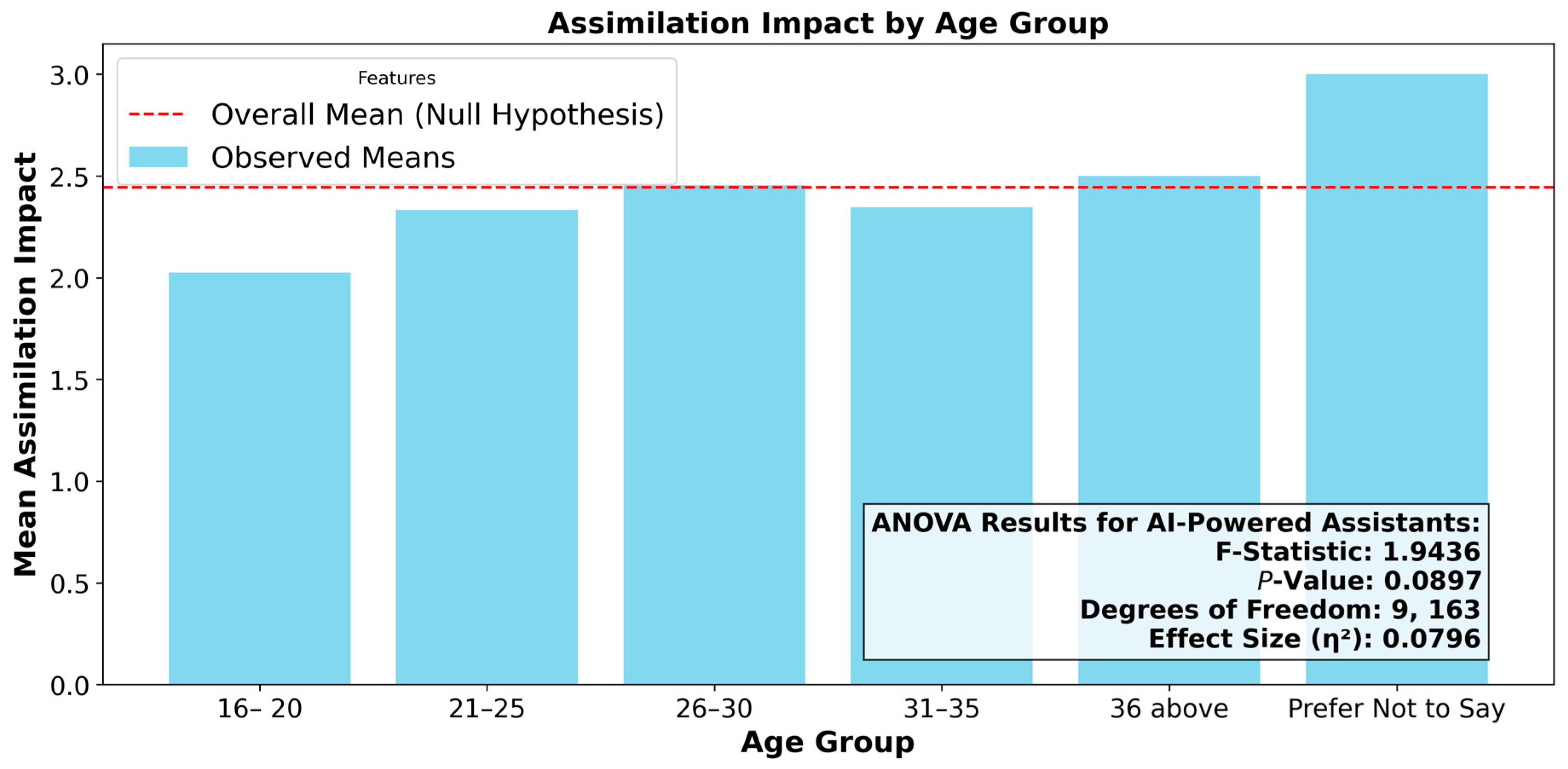
4.6.4. Test: Assimilation by Age Group
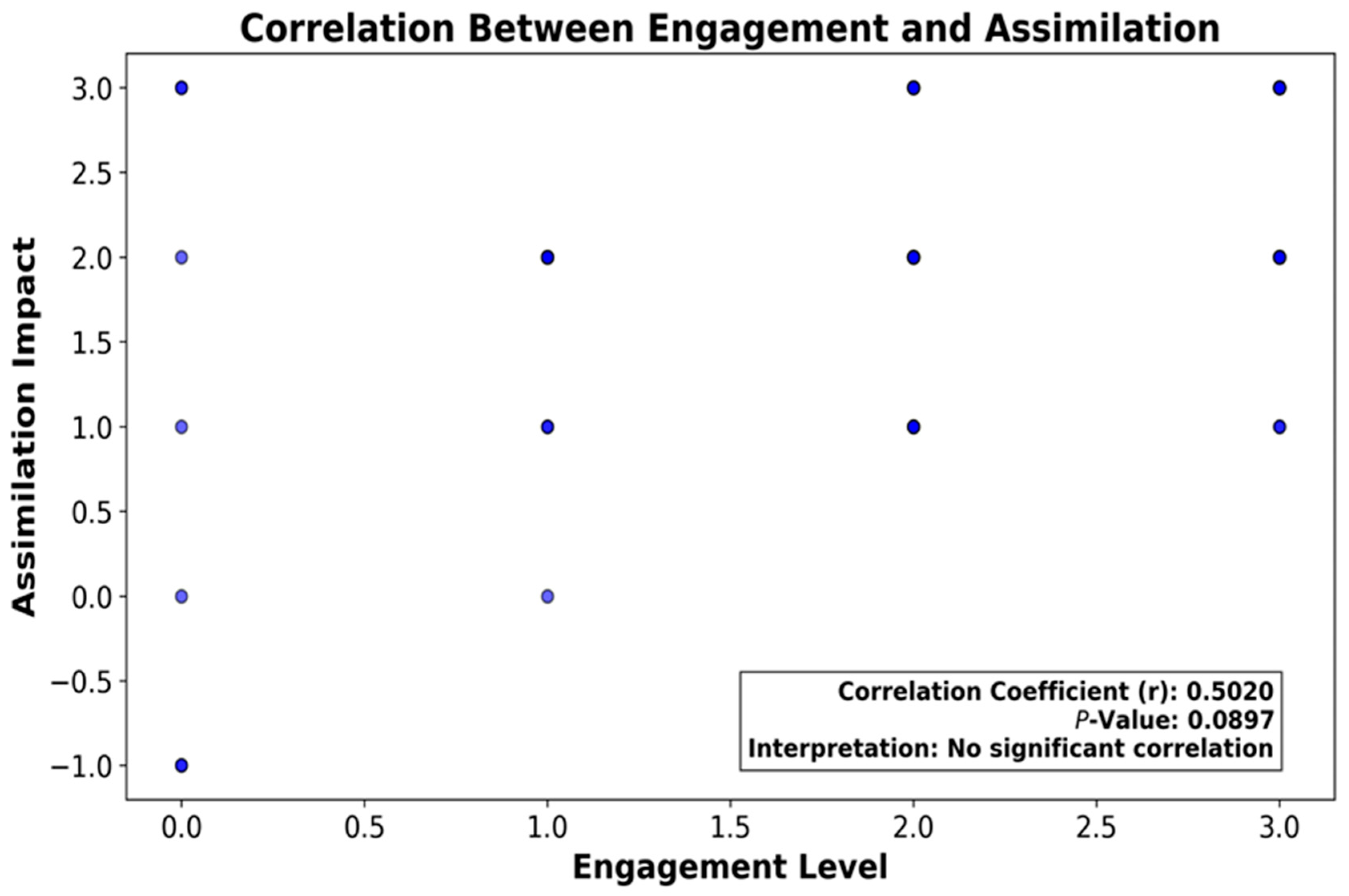
4.6.5. Correlation Between Engagement and Assimilation
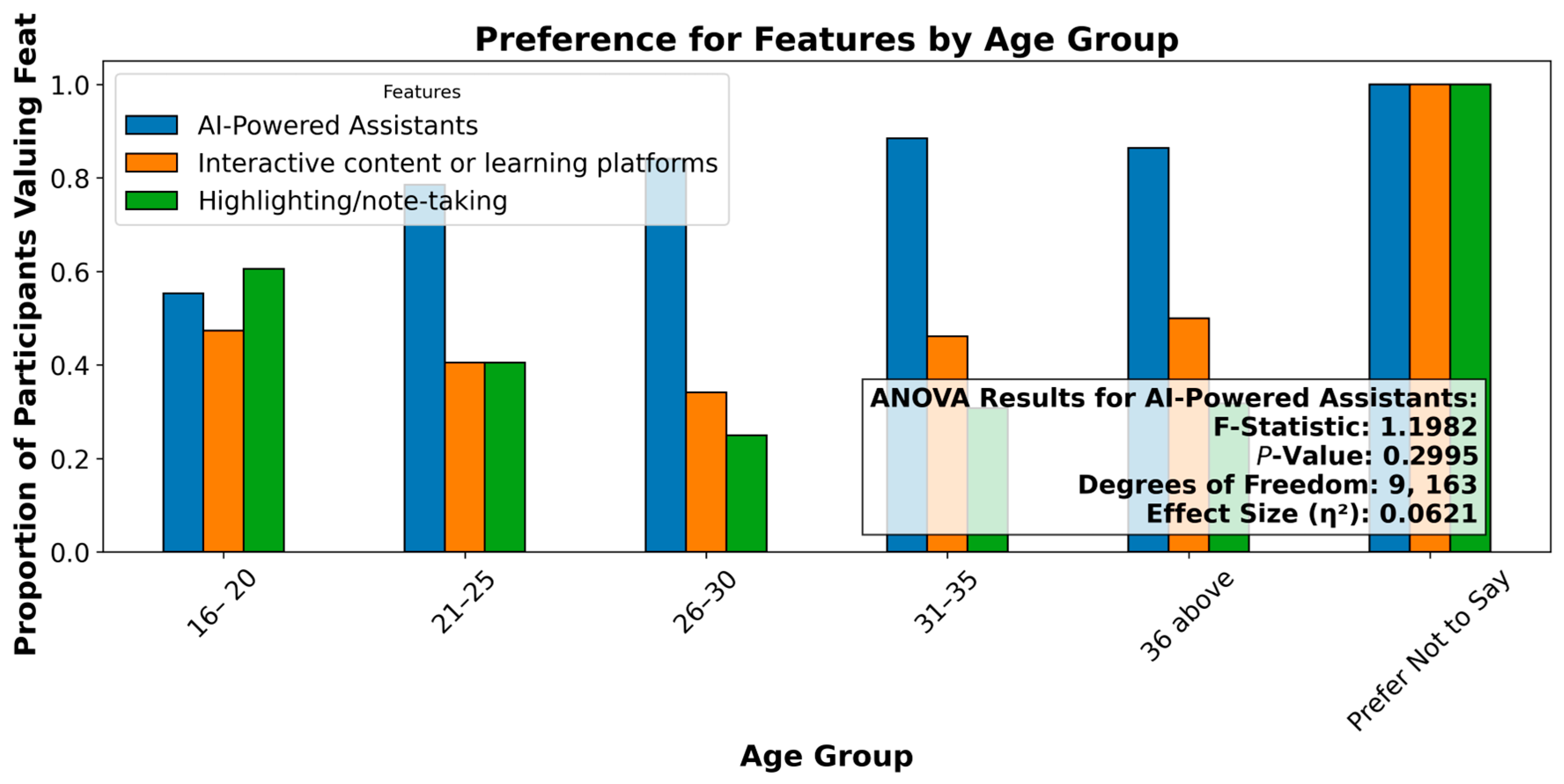
4.6.6. Preferences for AI-Powered Assistants by Age Group
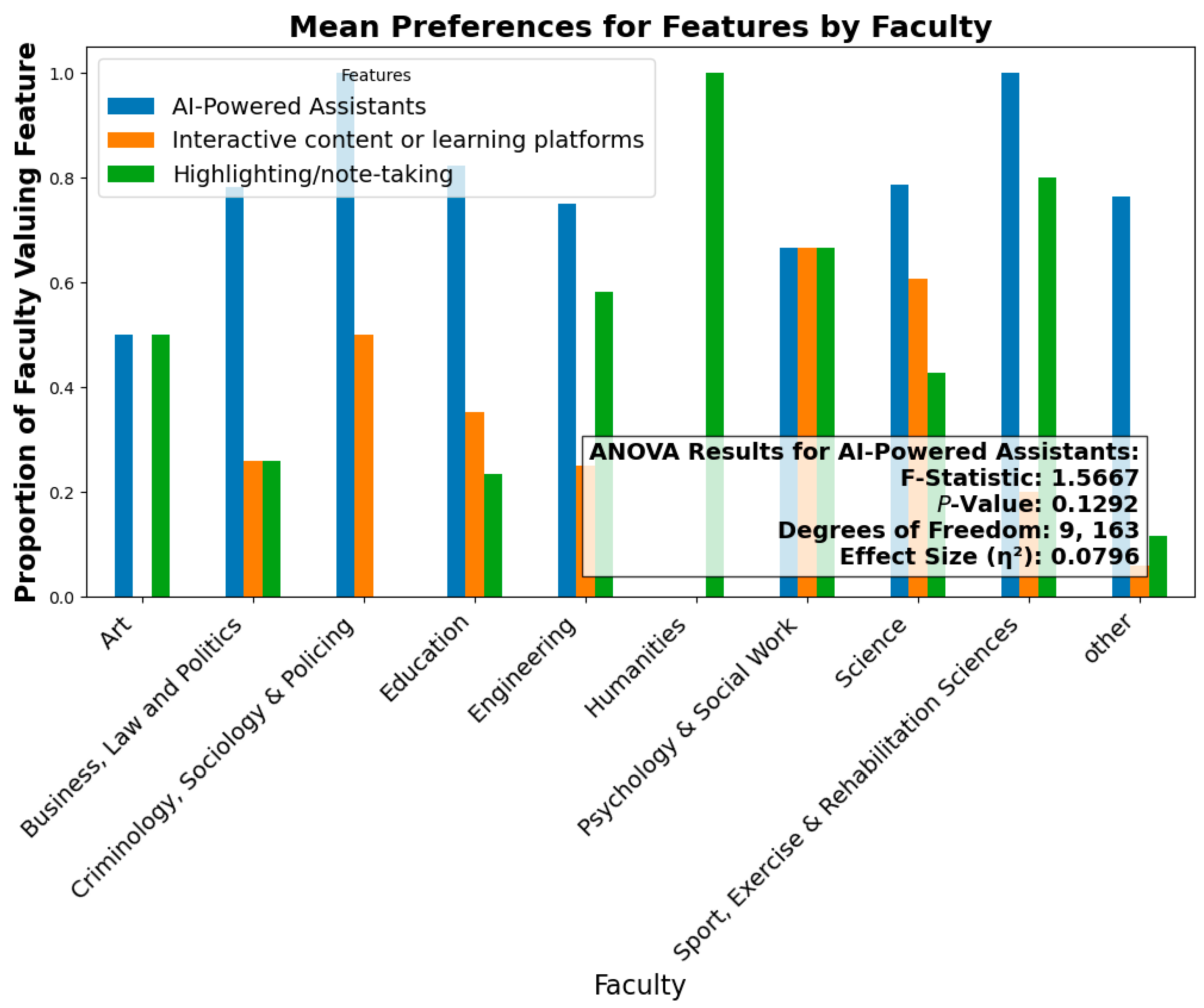
4.6.7. Preferences for AI-Powered Assistants by Faculty
4.6.8. Overall P-Test Result and the Original Hypothesis
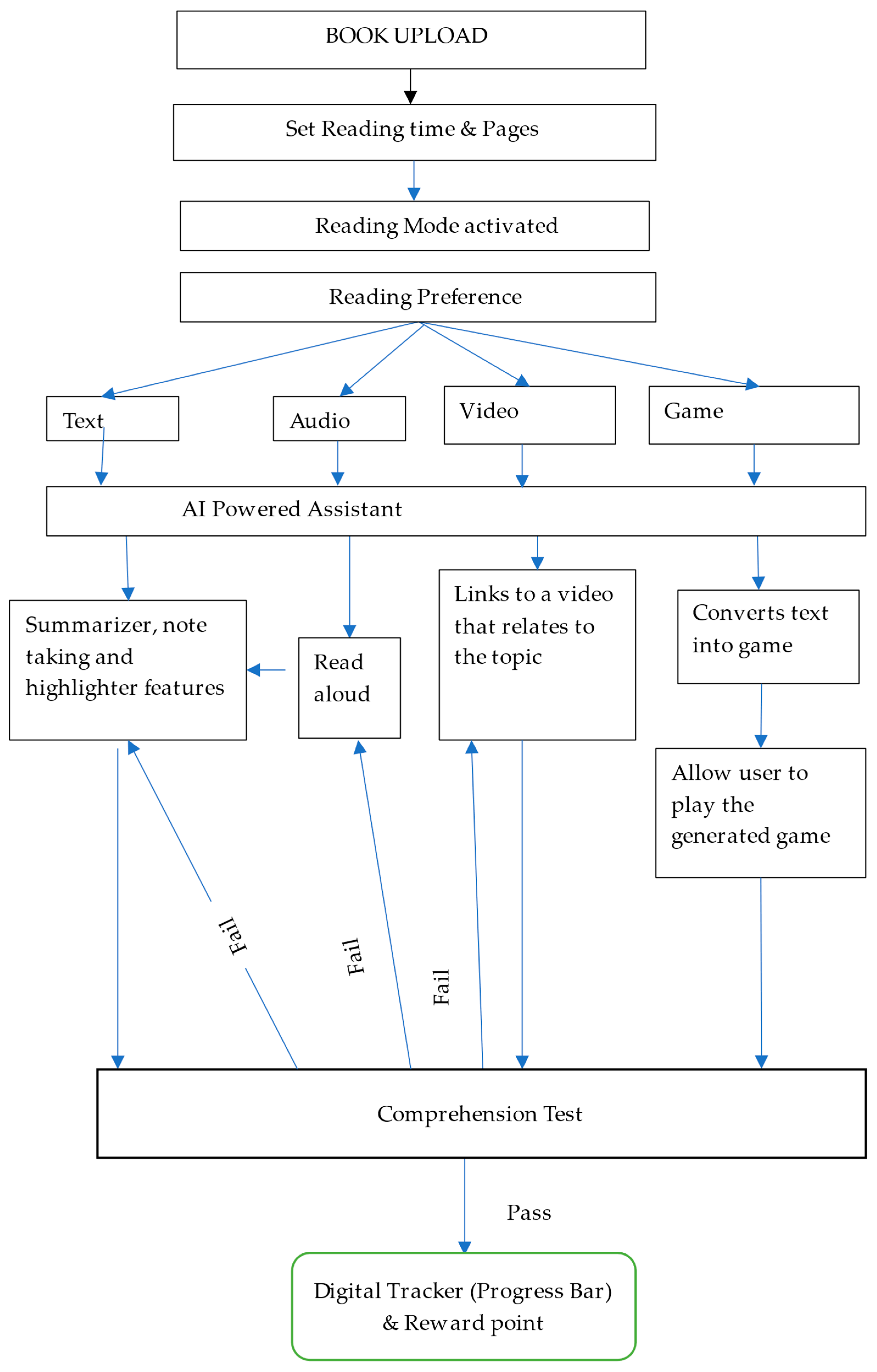
5. Strategic Framework for SmartRead Development
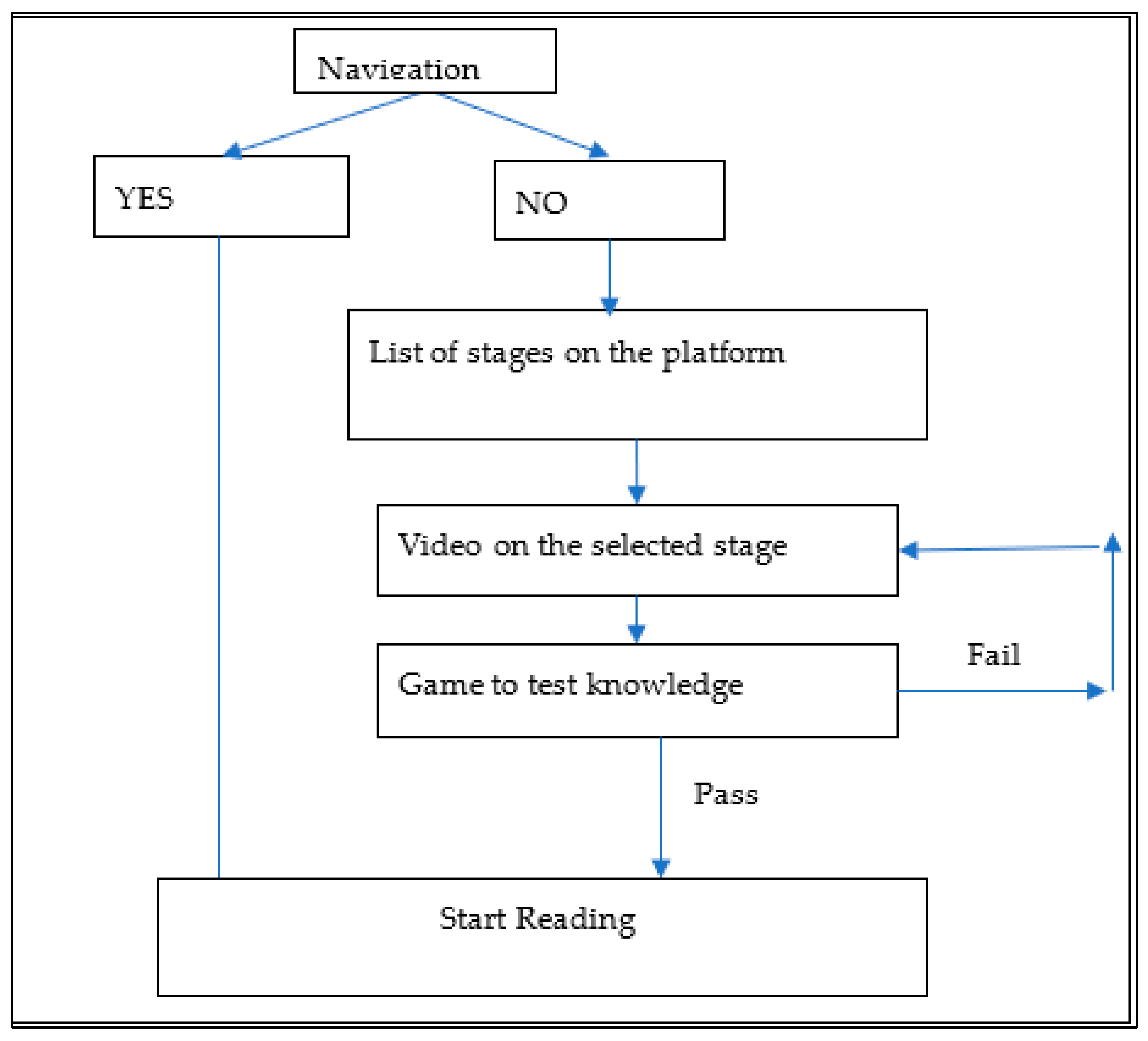
5.1. Strategic Navigation Design to Enhance Engagement
5.2. Benefits of SmartRead
5.2.1. Benefits for the Student
5.2.2. Benefits for Institutions
5.2.3. Benefits for Educators
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
8. Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
References
- Almasri, F. Exploring the Impact of Artificial Intelligence in Teaching and Learning of Science: A Systematic Review of Empirical Research. Res. Sci. Educ. 2024, 54, 977–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, Y. Embracing the future of Artificial Intelligence in the classroom: The relevance of AI literacy, prompt engineering, and critical thinking in modern education. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2024, 21, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.Y.; Lee, Y.H. Computer-supported knowledge building to enhance reading motivation and comprehension. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2023, 54, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besele, M. Challenges of Online Learning to University Students; Education Resources Information Center: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gaddis, M.L. Faculty and student technology use to enhance student learning. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 2020, 21, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dontre, A.J. The influence of technology on academic distraction: A review. Hum. Behav. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 3, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W. Personalized learning paths: Impact on student engagement and learning outcomes. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2022, 19, 207–221. [Google Scholar]
- Meridha, J.M. The causes of poor digital literacy in educational practice, and possible solutions among the stakeholders: A systematic literature review. SN Soc. Sci. 2024, 4, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Z.Y.; Liem, G.A.D.; Chan, M.; Datu, J.A.D. Student engagement and its association with academic achievement and subjective well-being: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Educ. Psychol. 2024, 116, 48–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, S.; Bertel, L.B.; Lyngdorf, N.E.R.; Markman, A.O.; Andersen, T.; Ryberg, T. Emerging Digital Practices Supporting Student-Centered Learning Environments in Higher Education: A Review of Literature and Lessons Learned from the COVID-19 Pandemic. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2024, 29, 1673–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audrin, C.; Audrin, B. Key factors in digital literacy in learning and education: A systematic literature review using text mining. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2022, 27, 7395–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajúzová, M.; Hrmo, R. Digital Tools in Education The Impact of Digital Tools in Education on Students’ Creativity. R&E Source 2024, 11, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yu, Z. Extending Technology Acceptance Model to higher-education students’ use of digital academic reading tools on computers. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2023, 20, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, O.J.; Palaoag, T. AI-driven mobile application: Unraveling students’ motivational feature preferences for reading comprehension. J. Res. Innov. Teach. Learn. 2024, 17, 226–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, B.C.Y.; Liu, L.W.L.; Hou, C.C. Investigating the effects of interactive e-book towards academic achievement. Asian J. Univ. Educ. 2020, 16, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.; Rumbold, K. Reading for Pleasure: A Research Overview; National Literacy Trust: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bacak, J.; Wagner, J.; Martin, F.; Byker, E.; Wang, W.; Alhgrim-Delzell, L. Examining technologies used in K-12 school districts: A proposed framework for classifying educational technologies. J. Educ. Technol. Syst. 2023, 51, 282–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Stephens, J.M.; Lee, K. Assessing Student Engagement in Collaborative Learning: Development and Validation of New Measure in China. Asia-Pac. Educ. Res. 2024, 33, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Măduţa, G. Digital Tools Adoption in Pedagogy Approaches in Language Learning for Economics Students. Rom. Econ. Bus. Rev. 2023, 18, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Nkomo, L.M.; Daniel, B.K.; Butson, R.J. Synthesis of student engagement with digital technologies: A systematic review of the literature. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2021, 18, 34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, A. Does the digital divide matter? Factors and conditions that promote ICT literacy. Telemat. Inform. 2021, 58, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selwyn, N. Education in a Digital World: Global Perspectives on Technology and Education; Routledge: Abington-on-Thames, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Department of Education. Professional Development for Teachers in the Digital Age. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2023, 45, 123–134. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Juárez, M.Á.; González-Ortega, D.; Aguiar-Pérez, J.M. Digital Distractions from the Point of View of Higher Education Students. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Spector, J.M.; Yang, J. The impact of interactive e-books on secondary school students’ reading comprehension. Comput. Educ. 2022, 150, 103842. [Google Scholar]
- Jaramillo-Mediavilla, L.; Basantes-Andrade, A.; Cabezas-González, M.; Casillas-Martín, S. Impact of gamification on motivation and academic performance: A systematic review. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahli, S.; Spriet, T. Gamification Based Collaborative Learning: The Impact of Rewards on Student Motivation. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Interactive Collaborative Learning, Paris, France, 27 August–1 September 2023; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Shafiee Rad, H. Reinforcing L2 reading comprehension through artificial intelligence intervention: Refining engagement to foster self-regulated learning. Smart Learn. Environ. 2025, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.A.; Brown, A.; Moro, C. Virtual and augmented reality text environments support self-directed multimodal reading. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2025, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaberri, M.; Gil, M.; Sylla, C. GamAll: Playing Beyond Boundaries—Gamification and Multimodal Literacy. In Proceedings of the 5th EAI International Conference on Design, Learning, and Innovation, Virtual Event, 10–11 December 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, M.; Perez-Cabarcas, M.M.; Kallakuri, U.; Waytowich, N.R.; Lin, X.; Mohsenin, T. Multi-RAG: A Multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Generation System for Adaptive Video Understanding. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.23990. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Leitch, A. LLMs as Academic Reading Companions: Extending HCI Through Synthetic Personae. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.19506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P. Effects of highlights and annotations on EFL learners’ Reading comprehension: An application of computer-assisted interactive reading model. Comput. Assist. Lang. Learn. 2024, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-M.; Li, M.-C.; Chen, T.-C. A web-based collaborative reading annotation system with gamification mechanisms to improve reading performance. Comput. Educ. 2020, 144, 103697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turčáni, M.; Balogh, Z.; Kohútek, M. Evaluating computer science students reading comprehension of educational multimedia-enhanced text using scalable eye-tracking methodology. Smart Learn. Environ. 2024, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, M.T. Effectiveness of AI-Based Personalised Reading Platforms in Enhancing Reading Comprehension. J. Learn. Dev. 2024, 11, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keelor, J.L.; Creaghead, N.; Silbert, N.; Horowitz-Kraus, T. Text-to-speech technology: Enhancing reading comprehension for students with reading difficulty. Assist. Technol. Outcomes Benefits 2020, 14, 19–35. [Google Scholar]
- Asif, M.; Sheeraz, M.; Sacco, S.J. Evaluating the Impact of Technological Tools on the Academic Performance of English Language Learners at Tertiary Level: A Pilot Investigation. Pegem J. Educ. Instr. 2022, 12, 272–282. [Google Scholar]
- Miles, H.; Ari, F. Implementing Personalized Reading Plans with an E-Book Library to Support First-Grade Students’ Reading Engagement and Comprehension. TechTrends 2022, 66, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pelumi, I.; Gordon, N. SmartRead: A Multimodal eReading Platform Integrating Computing and Gamification to Enhance Student Engagement and Knowledge Retention. Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2025, 9, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9100101
Pelumi I, Gordon N. SmartRead: A Multimodal eReading Platform Integrating Computing and Gamification to Enhance Student Engagement and Knowledge Retention. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction. 2025; 9(10):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9100101
Chicago/Turabian StylePelumi, Ifeoluwa, and Neil Gordon. 2025. "SmartRead: A Multimodal eReading Platform Integrating Computing and Gamification to Enhance Student Engagement and Knowledge Retention" Multimodal Technologies and Interaction 9, no. 10: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9100101
APA StylePelumi, I., & Gordon, N. (2025). SmartRead: A Multimodal eReading Platform Integrating Computing and Gamification to Enhance Student Engagement and Knowledge Retention. Multimodal Technologies and Interaction, 9(10), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9100101








