-
 Long-Standing Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation: A Comprehensive Review and Proposal of a Treatment Algorithm
Long-Standing Temporomandibular Joint Dislocation: A Comprehensive Review and Proposal of a Treatment Algorithm -
 Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)—An Evidence-Based Review of Indications, Efficacy, Harms, and Deprescribing
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)—An Evidence-Based Review of Indications, Efficacy, Harms, and Deprescribing -
 Artificial Intelligence and Advanced Digital Health for Hypertension: Evolving Tools for Precision Cardiovascular Care
Artificial Intelligence and Advanced Digital Health for Hypertension: Evolving Tools for Precision Cardiovascular Care -
 The Journey of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Cutaneous Melanoma: A Brief Narrative Review from Scalpel to Smart Tech
The Journey of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Cutaneous Melanoma: A Brief Narrative Review from Scalpel to Smart Tech -
 The Impact of Basal Inflammatory Status on Post-CABG Atrial and Ventricular Ectopy and Remodeling Pathways
The Impact of Basal Inflammatory Status on Post-CABG Atrial and Ventricular Ectopy and Remodeling Pathways
Journal Description
Medicina
Medicina
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal covering all problems related to medicine. It is the official journal of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences (LUHS) and published monthly online. The Lithuanian Medical Association, the Vilnius University, the Rīga Stradiņš University, the University of Latvia, and the University of Tartu are affiliated to Medicina, which serves as the official journal. Their members receive discount on article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Medicine, General and Internal) / CiteScore - Q1 (General Medicine)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 17.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
2.4 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.8 (2024)
Latest Articles
Association Between Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone and Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate in the Third Trimester of Pregnancy: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study in Euthyroid Women
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2046; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112046 (registering DOI) - 16 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: This study investigated the relationship between thyroid function and renal parameters during the third trimester of pregnancy in euthyroid women, a physiological interaction that remains poorly characterized. Materials and Methods: In this retrospective, single-center cross-sectional study, 820 euthyroid
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: This study investigated the relationship between thyroid function and renal parameters during the third trimester of pregnancy in euthyroid women, a physiological interaction that remains poorly characterized. Materials and Methods: In this retrospective, single-center cross-sectional study, 820 euthyroid pregnant women (≥28 weeks of gestation) were evaluated. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free triiodothyronine (fT3), free thyroxine (fT4), serum creatinine, and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) were analyzed using tertile-based comparisons, correlation tests, and linear regression analysis. Results: Higher TSH levels were associated with slightly higher serum creatinine (p = 0.011) and a weak negative correlation with eGFR (r = −0.079, p = 0.023). Conversely, fT3 levels were positively correlated with eGFR (r = 0.106, p = 0.002) and inversely correlated with creatinine (r = −0.074, p = 0.035), while fT4 showed weaker associations. Regression analysis confirmed that fT3 (β = 0.099, p = 0.005) and fT4 (β = 0.083, p = 0.019) were independent positive predictors of eGFR. Conclusions: The correlations observed were statistically significant but clinically modest. Regression analysis confirmed that FT3 and FT4 were independent positive predictors of GFR, suggesting that subtle variations in thyroid activity may reflect physiological rather than pathological renal adaptations in late pregnancy. Monitoring TSH and fT3 may enhance understanding of maternal endocrine and renal interplay, though the clinical utility of such associations remains limited and warrants confirmation in prospective studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Obstetrics and Maternal-Fetal Medicine)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Intravenous Lidocaine for Postoperative Pain and Recovery After Robotic Prostate Adenomectomy: A Retrospective Observational Cohort Study
by
Georgiana Maria Popa, Simona-Alina Abu-Awwad, Ahmed Abu-Awwad, Carmen-Ioana Marta, Erika Bimbo-Szuhai, Mihaela Gabriela Bontea, Adrian Gheorghe Osiceanu, Anca Mihaela Bina, Cristian Mihai Moisa Cezar, Ciprian Dumitru Puscas and Mihai O. Botea
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2045; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112045 (registering DOI) - 16 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Effective perioperative pain management remains a key goal of enhanced recovery protocols, especially in minimally invasive urologic surgery, where optimizing comfort while limiting opioid exposure is essential. Intravenous lidocaine has gained attention for its multimodal analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties,
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Effective perioperative pain management remains a key goal of enhanced recovery protocols, especially in minimally invasive urologic surgery, where optimizing comfort while limiting opioid exposure is essential. Intravenous lidocaine has gained attention for its multimodal analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties, yet evidence in robotic prostatectomy remains limited. This study evaluated whether intraoperative lidocaine infusion was associated with lower early postoperative pain scores and reduced opioid use in patients undergoing robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy. Materials and Methods: A retrospective, single-center analysis was conducted at Pelican Clinical Hospital, Oradea, Romania, including 112 patients operated on between January 2020 and December 2023. All procedures were performed by the same surgical and anesthetic teams using standardized ERAS-based protocols. Patients were divided into two groups: the Lidocaine Group (LG, n = 51), who received a bolus of 1.5 mg/kg lidocaine followed by an infusion of 1.5 mg/kg/h during surgery, and the Control Group (CG, n = 61), who received standard anesthesia without lidocaine. Postoperative pain was measured using the visual analog scale (VAS) at 0, 4, 12, and 24 h, and opioid use was converted into morphine milligram equivalents (MME). Secondary outcomes included time to ambulation, gastrointestinal recovery, oral intake, hospital stay, and complications. Results: Pain intensity was significantly lower in the lidocaine group at 4 h postoperatively (VAS 3.5 ± 1.1 vs. 4.3 ± 1.3; p = 0.01), with similar scores later. Total opioid use was reduced by about 18% in the lidocaine group (25.7 ± 9.4 vs. 31.2 ± 10.5 MME; p = 0.03). Recovery parameters and complication rates were comparable between groups, and no lidocaine-related adverse events were recorded. Conclusions: Intraoperative intravenous lidocaine was associated with lower early postoperative pain scores and reduced opioid requirements after robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy without affecting recovery or safety. Its favorable profile and low cost support its inclusion as a practical adjunct in multimodal analgesia within ERAS pathways.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Anesthesiology, Resuscitation, and Pain Management)
►▼
Show Figures
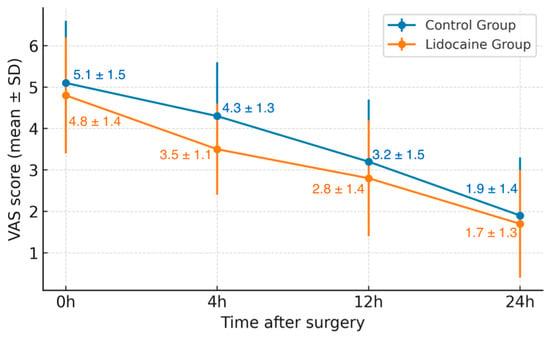
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Interstitial Lung Disease Secondary to Sjogren’s Syndrome and Antisynthetase Syndrome: Converging Disease Trajectories
by
Giuseppe Muscato, Giulia Morina, Evelina Fagone, Mary Fruciano, Elisa Gili, Serafina Martella, Stefano Palmucci, Domenico Sambataro, Carlo Vancheri and Gianluca Sambataro
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2044; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112044 (registering DOI) - 15 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Interstitial lung disease is one of the main causes of mortality in Sjögren’s Syndrome (SjS) and Anti-Synthetase Syndrome (ASyS). The objective of the study is to compare clinical, serological and radiological features of these conditions, as well as their
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Interstitial lung disease is one of the main causes of mortality in Sjögren’s Syndrome (SjS) and Anti-Synthetase Syndrome (ASyS). The objective of the study is to compare clinical, serological and radiological features of these conditions, as well as their prognosis. Materials and Methods: we retrospectively enrolled 34 SjS-ILD and 33 ASyS-ILD patients. The two cohorts were jointly followed by rheumatologists and pulmonologists for at least two years. Results: From a clinical point of view, ASyS-ILD patients showed a greater prevalence of myositis (18.2% vs. 2.3%, p = 0.04), whereas more SjS patients had sicca syndrome (85.3% vs. 9.1%, p < 0.001). No other clinical differences were noted. From a serological point of view, ASyS-ILD patients had a greater proportion of antinuclear antibody positivity with a cytoplasmic pattern (24.9% vs. 2.9%, p = 0.005) and positivity for Anti-Synthetase Antibodies (ASA), which were not found in the SjS cohort. SjS-ILD patients were mainly positive for anti-Ro52kD (61.8% vs. 27.3%, p = 0.002). No significant differences were noted in radiological pattern of ILD, functional values, disease progression and prognosis. Conclusions: SjS-ILD and ASyS patients show several common features. It could be hypothesized that some patients classified as SjS-ILD could have undetectable or unknown ASA, and the upcoming ASyS classification criteria may be useful in highlighting these patients for deeper research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pulmonology)
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Optimization of Postoperative Antimicrobial Therapy in Surgical Patients Using a Clinical Decision Support System: Use Patterns and Clinical Outcomes
by
Miguel Ángel Amor García, Irene Orozco Cifuentes, Raquel Moreno Díaz, José Antonio Martínez Consuegra and Carmen de Cáceres Velasco
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2043; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112043 (registering DOI) - 15 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Antimicrobial stewardship plays a key role in the surgical setting by reducing the incidence of healthcare-associated infections and limiting the emergence of antimicrobial resistance. Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSSs), when integrated into routine practice, are valuable tools for optimizing
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Antimicrobial stewardship plays a key role in the surgical setting by reducing the incidence of healthcare-associated infections and limiting the emergence of antimicrobial resistance. Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSSs), when integrated into routine practice, are valuable tools for optimizing antimicrobial prescribing. However, evidence regarding their impact on surgical patients, particularly across different specialties, remains limited. Materials and Methods: We conducted a quasi-experimental time series study in surgical patients at a primary-level hospital, evaluating the effect of a CDSS on postoperative antimicrobial therapy. The pre-intervention period included patients admitted from April 2017 to September 2020, and the post-intervention period included those admitted from October 2020 to March 2024. Antimicrobial consumption and expenditures were measured as defined daily doses (DDDs) per 1000 patient-days and euros (€) per 1000 patient-days, respectively. Subgroup analyses were performed by the surgical service. Clinical outcomes included mortality and length of stay (LOS). Results: Following CDSS implementation, overall antimicrobial consumption decreased by 4.4%. Significant reductions were observed in aminoglycosides (−52.0%), macrolides, lincosamides and streptogramins (−40.6%), and fluoroquinolones (−32.3%). Reductions were heterogeneous across surgical services, with significant reductions in Traumatology (−21.3%) and Urology (−14.3%). Expenditures decreased from 3185.4 to 2733.9€/1000 patient-days (−14.2%; p = 0.17). Mortality remained stable, whereas significant reductions in LOS were observed in Urology (5 to 4 days, p = 0.03) and traumatology (16 to 8.5 days, p < 0.01). During the post-intervention period, 476 stewardship recommendations were issued for 330 patients, with an acceptance rate of 76.1%. The most frequent interventions were discontinuation of antimicrobials (25.8%), transition to oral therapy (21.0%), and de-escalation (18.7%). Conclusions: Implementation of a CDSS in the surgical setting was associated with reduced antimicrobial consumption, a downward trend in expenditures, and high acceptance of stewardship recommendations. Mortality remained unchanged, while reductions in LOS in selected services support the safety and potential efficiency of this approach.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Evaluation, Management, and Outcomes in Perioperative Medicine)
Open AccessArticle
Integrating Renal and Metabolic Parameters into a Derived Risk Score for Hyperuricemia in Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study in Northwest Romania
by
Lorena Paduraru, Dana Carmen Zaha, Timea Claudia Ghitea, Radu Fodor, Cosmin Mihai Vesa and Mihaela Simona Popoviciu
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2042; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112042 (registering DOI) - 15 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Hyperuricemia is frequent in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes (T2D) and may reflect intertwined renal and metabolic dysfunction. Simple tools to identify those at highest risk are lacking. Materials and Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 253 adults with uncontrolled
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Hyperuricemia is frequent in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes (T2D) and may reflect intertwined renal and metabolic dysfunction. Simple tools to identify those at highest risk are lacking. Materials and Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 253 adults with uncontrolled T2D (HbA1c ≥ 7%) hospitalized at a tertiary center (2022–2023). Patients were stratified by hyperuricemia status (serum uric acid >7.0 mg/dL in men and >6.0 mg/dL in women). Demographic, clinical, biochemical, and pharmacological data were compared. Independent predictors were explored with multivariable modeling. A two-parameter Renal–Metabolic Risk Score (serum urea and triglyceride-to-LDL cholesterol ratio [TG/LDL]) was derived and evaluated by ROC analysis. Results: Compared with non-hyperuricemic patients (n = 20), those with hyperuricemia (n = 233) had higher serum urea (32.15 ± 21.21 vs. 19.76 ± 10.02 mg/dL; p < 0.001) and numerically higher TG/LDL (2.94 ± 6.73 vs. 1.95 ± 1.28; p = 0.062). Serum uric acid was lower in the hyperuricemia group due to categorical definition thresholds and treatment effects (5.69 ± 1.87 vs. 6.77 ± 2.12 mg/dL; p = 0.038). The derived Renal–Metabolic Risk Score showed an AUC = 0.67 and differed significantly between groups (p ≈ 1.2 × 10−5). Conclusions: The derived RMRS, based on simple and inexpensive laboratory parameters, offers a preliminary tool for assessing hyperuricemia risk in uncontrolled T2D. From a clinical and assistive practice perspective, this score may help nephrology nurses and multidisciplinary teams identify high-risk patients who require closer monitoring of renal and metabolic complications. It could further guide early dietary counseling, pharmacological optimization, and frailty assessment in chronic kidney disease care. Future studies are needed to validate the score in larger and more diverse populations before its integration into routine practice.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Endocrinology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Multimodal Rehabilitation in Spinal Cord Lesion: Comparative Outcomes of Vojta Therapy and Lokomat Training
by
Anamaria Gherle, Carmen Delia Nistor-Cseppento, Liviu Lazar, Ștefania Deac, Mirela Elena Bodea, Florin Mihai Marcu, Sebastian Tirla and Mariana Lidia Cevei
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2041; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112041 (registering DOI) - 15 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Spinal cord lesion is a severe disorder of the central nervous system, leading to partial or complete interruption of nerve impulse transmission between the brain and the periphery and causing severe neurological and functional deficits. Conventional rehabilitation offers limited
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Spinal cord lesion is a severe disorder of the central nervous system, leading to partial or complete interruption of nerve impulse transmission between the brain and the periphery and causing severe neurological and functional deficits. Conventional rehabilitation offers limited outcomes, while robotic gait training (Lokomat®) and Vojta Therapy have shown benefits individually. Evidence on their combined effect remains scarce. To evaluate the combined effect of Vojta Therapy and Lokomat-assisted gait training on motor recovery, functional independence, and quality of life in SCL patients. Materials and Methods: A retrospective clinical study was conducted on 205 patients with traumatic and non-traumatic SCL. Patients were allocated to four groups: (F)—conventional rehabilitation; (V)—conventional + Vojta; (L)—conventional + Lokomat; (VL)—conventional + Vojta + Lokomat. Assessments included the ASIA Impairment Scale (AIS), ASIA motor/sensory scores, spasticity (Modified Ashworth Scale, MAS), functional independence (Functional Independence Measure, FIM), and health-related quality of life (EQ-5D), performed at admission and discharge. Statistical analyses comprised paired t-tests, Wilcoxon signed-rank tests, chi-square tests, Kruskal–Wallis with Dunn’s post hoc corrections, and linear regression. Results: The most frequent lesion levels were C7 (21%) and L1 (20%). All groups showed improvement in FIM scores, with the greatest gains in the VL group (from 79.25 to 84.79, p < 0.05). Post hoc analysis confirmed significantly higher FIM outcomes in VL compared with L. Regression analysis identified the ASIA motor score as the strongest predictor of functional independence (β = 0.76, p < 0.001), with VL group membership adding +10.3 points (p = 0.004). EQ-5D indicated persistent deficits in mobility and self-care, especially in VL patients, consistent with higher lesion severity. Conclusions: Combining Vojta Therapy with Lokomat training provides additional functional benefits compared with Lokomat or Vojta alone. Multimodal individualized rehabilitation appears promising for patients with spinal cord lesions. Prospective randomized controlled trials with long-term follow-up are warranted.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Clinical Applications of Modern Technologies in Neurosurgery and Spine Surgery)
►▼
Show Figures
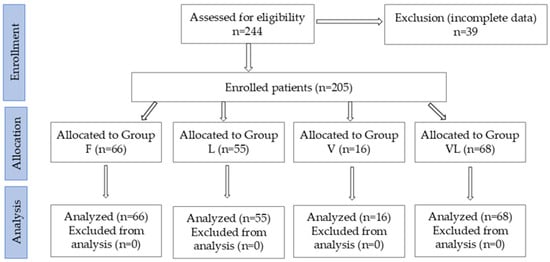
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Familial Versus Non-Familial Vitiligo: Clinical Features, Anatomical Distribution, and Autoimmune Comorbidity from a Southern Taiwan Hospital
by
Ning-Sheng Lai, Hsiu-Hua Chang, Hui-Chin Lo, Ming-Chi Lu and Malcolm Koo
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2040; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112040 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Familial clustering and autoimmune multimorbidity are frequently observed in vitiligo. However, the clinical implications of a positive family history across generations remain unclear. In this study, a positive family history was defined as having at least one affected parent
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Familial clustering and autoimmune multimorbidity are frequently observed in vitiligo. However, the clinical implications of a positive family history across generations remain unclear. In this study, a positive family history was defined as having at least one affected parent or grandparent. Materials and Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the electronic medical records of 972 adults with vitiligo who attended the rheumatology division in a regional teaching hospital in southern Taiwan between 2006 and 2022. Demographic characteristics, family history, clinical features, and autoimmune comorbidities were extracted from electronic medical records. Associations between family history and clinical parameters were assessed using logistic regression analyses adjusted for age and sex. Results: A total of 157 patients (16.2%) reported a family history, more often through parents than grandparents; maternal history was more common than paternal. Compared with those without a family history, affected families showed significantly younger age at diagnosis and a higher prevalence of lower-limb involvement. In adjusted models, family history was associated with greater odds of lower-limb involvement (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 1.78, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.22–2.58) and lower odds of eyebrow/eyelash depigmentation (aOR 0.39, 95% CI 0.16–0.92). Hashimoto thyroiditis was more frequent among familial cases (aOR 7.56, 95% CI 1.23–46.65). In sex-stratified analyses, associations were stronger in females, notably for lower-limb involvement (aOR 1.87), axillary depigmentation (aOR 2.33), and Hashimoto thyroiditis (aOR 11.27). Conclusions: Familial vitiligo shows earlier onset, distinct anatomical patterns, and increased thyroid autoimmunity, supporting systematic family-history assessment and targeted thyroid screening.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Autoimmune Diseases: Advances and Challenges)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Machine Learning Methods for the Prediction of Intraoperative Hypotension with Biosignal Waveforms
by
Jae-Geum Shim, Wonhyuck Yoon, Sang Jun Lee, Se-Hyun Chang, So-Ra Jung and Jun Young Chung
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2039; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112039 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Intraoperative hypotension (IOH) is of great importance in preventing diseases such as postoperative myocardial infarction, acute kidney injury, and mortality. This study aimed to develop and validate machine learning and deep learning models that predict IOH using both biosignals
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Intraoperative hypotension (IOH) is of great importance in preventing diseases such as postoperative myocardial infarction, acute kidney injury, and mortality. This study aimed to develop and validate machine learning and deep learning models that predict IOH using both biosignals and personalized clinical information for each patient. Materials and Methods: In this retrospective observational study, we used the VitalDB open dataset, which included intraoperative biosignals and clinical information from 6388 patients who underwent non-cardiac surgery between June 2016 and August 2017 at Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, South Korea. The predictive performances of models trained with four waveforms (arterial blood pressure, electrocardiography, photoplethysmography, and capnography) and clinical information were evaluated and compared at time points at 5 min before the hypotensive event. To predict hypotensive events during surgery, we developed two predictive models: machine learning and deep learning. In total, 2611 patients were enrolled in this retrospective study. Machine and deep learning algorithms were developed and validated using raw waveforms and clinical information as inputs. Results: Gradient boosting machine showed predicted IOH with an AUROC and accuracy of 0.94 (0.93–0.95) and 0.88 (0.86–0.89). A hybrid CNN-RNN model also showed similar performance with an AUROC and accuracy of 0.94 (0.93–0.95) and 0.88 (0.87–0.89). Conclusions: This study developed and validated machine and deep learning models to predict IOH using waveform data and covariate values. In the future, we anticipate that the results of our study will contribute to predicting IOH in real time in the operating room and reducing the occurrence of IOH.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Clinical Approaches in Perioperative Pain Management)
Open AccessArticle
Integrative Evaluation of Atrial Function and Electromechanical Coupling as Predictors of Postoperative Atrial Fibrillation
by
Mladjan Golubovic, Velimir Peric, Marija Stosic, Milan Lazarevic, Dalibor Stojanovic, Dragana Unic-Stojanovic, Vesna Dinic and Dejan Markovic
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2038; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112038 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Postoperative atrial fibrillation (POAF) remains one of the most frequent complications after cardiac surgery, increasing the risk of morbidity, prolonged hospitalization, and adverse long-term outcomes. Although several clinical and echocardiographic factors have been associated with POAF, the integrated contribution
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Postoperative atrial fibrillation (POAF) remains one of the most frequent complications after cardiac surgery, increasing the risk of morbidity, prolonged hospitalization, and adverse long-term outcomes. Although several clinical and echocardiographic factors have been associated with POAF, the integrated contribution of atrial conduction delay, biatrial mechanics, and atrioventricular coupling to arrhythmogenesis remains unclear. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study included 131 adult patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting and/or aortic valve replacement. Preoperative echocardiography within one week before surgery provided detailed assessment of atrial phasic function, valvular motion, and total atrial conduction time (TACT). Univariate analysis was followed by multivariable modeling using penalized logistic regression (Elastic Net) to identify the most robust predictors of POAF. Discriminative performance and calibration were evaluated via receiver operating characteristic (ROC) and calibration analysis. An exploratory Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) model with SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) analysis was used to confirm the stability and directionality of nonlinear feature interactions. Results: POAF occurred in 47 (36%) patients. The Elastic Net model identified prolonged TACT, reduced right atrial active emptying fraction (RAAEF), increased indexed minimal left atrial volume (MIN LA/BSA), and lower tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) as the most informative predictors. The model demonstrated excellent internal discrimination (AUC = 0.95; 95% CI 0.91–0.99) and satisfactory calibration (Hosmer–Lemeshow p = 0.41). Exploratory XGBoost analysis yielded concordant feature hierarchies, confirming the physiological consistency of the results. Conclusions: POAF arises from an identifiable electromechanical substrate characterized by atrial conduction delay, biatrial mechanical impairment, and reduced atrioventricular coupling. A parsimonious, regularized statistical model accurately delineated this profile, while complementary machine-learning analysis supported its internal validity. These findings underscore the potential of echocardiographic electromechanical parameters for refined preoperative risk stratification, pending prospective multicenter validation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Intensive Care/ Anesthesiology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Epidemiological and Clinical Profiling of Heart Failure—A Retrospective and Comparative Analysis of Cases Before, During, and After the COVID-19 Pandemic in a Romanian Emergency County Clinical Hospital
by
Maria Cristina Tătar, Martin Manole, Iuliu Gabriel Cocuz and Alexandru-Constantin Ioniță
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2037; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112037 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Heart failure (HF) represents a clinical syndrome characterized by symptoms and signs such as fatigue, dyspnea, edema of the lower limb, or pulmonary rales. It usually occurs in elderly individuals due to decreased cardiac pumping function and/or increased diastolic
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Heart failure (HF) represents a clinical syndrome characterized by symptoms and signs such as fatigue, dyspnea, edema of the lower limb, or pulmonary rales. It usually occurs in elderly individuals due to decreased cardiac pumping function and/or increased diastolic ventricular filling pressures. The COVID-19 pandemic deeply altered many daily life habits, and one of the most affected groups of people were those with chronic diseases because of their need for regular medical follow-up. Furthermore, SARS-CoV-2 infection itself has been shown to exacerbate cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). Materials and Methods: This retrospective, observational, and comparative study aimed to characterize and compare patients with chronic heart failure hospitalized in the Cardiology Department of Medical Clinic II, Mureș County Emergency Clinical Hospital, in Târgu Mureș, Romania, between January and December 2019 (pre-pandemic), January and December 2021 (pandemic), and January and December 2023 (post-pandemic). Results: A total of 406 patients were analyzed: 202 patients hospitalized in 2019, 101 patients hospitalized in 2021, and 103 patients hospitalized in 2023. Women with HF were significantly older (median age 72 years) than men (median age 65 years; p < 0.001). During the pandemic, the median length of hospitalization increased (8 days vs. 7 days in the other periods). The pandemic period was also associated with a decrease in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), as reflected by a higher incidence of patients with HF with reduced ejection fraction (42% during the pandemic; p < 0.01). Conclusions: During and after the pandemic, men exhibited significantly higher rates of right and left bundle branch blocks, as well as chronic obliterating artery disease of the lower limb. Left ventricular function declined during the pandemic in both men and women. Throughout the years, we observed distinct patterns between male and female patients regarding associated diseases or behaviours, suggesting lifestyle and psychological changes due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Insights into Heart Failure)
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of a Hybrid CNN Model for Automatic Detection of Malignant and Benign Lesions
by
Karima Bahmane, Sambit Bhattacharya and Alkhalil Brahim Chaouki
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2036; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112036 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Stratifying thyroid nodules according to malignancy risk is a crucial step in early diagnosis and patient care. Recently, deep learning techniques have emerged as powerful tools for medical diagnostics, particularly with convolutional neural networks (CNNs) applied to medical image classification.
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Stratifying thyroid nodules according to malignancy risk is a crucial step in early diagnosis and patient care. Recently, deep learning techniques have emerged as powerful tools for medical diagnostics, particularly with convolutional neural networks (CNNs) applied to medical image classification. This study aimed to develop a new hybrid CNN model for classifying thyroid nodules using the TN5000 ultrasound image dataset. Materials and Methods: The TN5000 dataset includes 5000 ultrasound images, with 3572 malignant and 1428 benign nodules. To address the issue of class imbalance, the researchers applied an R-based anomaly data augmentation method and a GAN-based technique (G-RAN) to generate synthetic benign images, resulting in a balanced dataset for training. The model architecture was built on a pre-trained EfficientNet-B3 backbone, further enhanced with squeeze-and-excitation (SE) blocks and residual refinement modules to improve feature extraction. The task was to classify malignant nodules (labeled 1) and benign nodules (labeled 0). Results: The proposed hybrid CNN achieved strong performance, with an accuracy of 89.73%, sensitivity of 90.01%, precision of 88.23%, and an F1-score of 88.85%. The total training time was 42 min. Conclusions: The findings demonstrate that the proposed hybrid CNN model is a promising tool for thyroid nodule classification on ultrasound images. Its high diagnostic accuracy suggests that it could serve as a reliable decision-support system for clinicians, improving consistency in diagnosis and reducing human error. Future work will focus on clinical validation, explainability of the model’s decision-making process, and strategies for integration into routine hospital workflows.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Artificial Intelligence: A Possible 'Game Changer' in the Fight Against Cancer)
Open AccessArticle
Avocado–Soybean Unsaponifiables Enhance Tendon Healing via Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Mechanisms in a Rat Achilles Injury Model
by
Mustafa Dinç, Ömer Cevdet Soydemir, Hünkar Çağdaş Bayrak, Recep Karasu, Bilal Aykaç and Mehmet Emre Topcu
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2035; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112035 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background and Objectives: Tendon healing is a multifactorial process influenced by inflammation and oxidative stress. Avocado–soybean unsaponifiables (ASU), recognized for their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties in osteoarthritis, have not yet been evaluated in tendon repair. This study aimed to investigate the effects of
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Tendon healing is a multifactorial process influenced by inflammation and oxidative stress. Avocado–soybean unsaponifiables (ASU), recognized for their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties in osteoarthritis, have not yet been evaluated in tendon repair. This study aimed to investigate the effects of systemic ASU administration on histological, biomechanical, and biochemical parameters of tendon healing in a rat Achilles tendon injury model. Materials and Methods: Twenty male Wistar rats underwent bilateral Achilles tendon transection and repair. The ASU group received intraperitoneal ASU (300 mg/kg/day) for four weeks; controls received saline. Right tendons were analyzed histologically using a semiquantitative scoring system adapted from Curtis–DeLee, Bonar, and Modified Soslowsky criteria. Left tendons were tested biomechanically for maximum force, displacement, stress, stiffness, and energy parameters. Serum interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), total antioxidant status (TAS), total oxidant status (TOS), and oxidative stress index (OSI) were measured by ELISA. Results: ASU markedly improved histological healing with better collagen alignment, reduced inflammation, and normalized tenocyte morphology (p < 0.001). Biomechanical strength increased, with higher maximum force (p = 0.002), displacement (p = 0.004), stress (p = 0.001), and total energy to failure (p = 0.001). Serum IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α levels were lower (p < 0.001), while TAS increased and TOS/OSI decreased (p < 0.001). Conclusions: Systemic ASU administration enhances tendon healing by improving tissue organization, increasing mechanical strength, and modulating systemic inflammation and oxidative stress. These findings suggest that ASU may serve as a safe, clinically relevant adjunct therapy to promote tendon regeneration.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessPerspective
The Pullback Pressure Gradient: Transforming Invasive Coronary Physiology from Lesion Assessment to Disease Pattern Characterization—A Perspective
by
Artur Dziewierz, Barbara Zdzierak, Stanisław Bartuś and Wojciech Zasada
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2034; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112034 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
This perspective comprehensively analyzes the invasive pullback pressure gradient (PPG), a novel physiological index that characterizes the longitudinal distribution of coronary artery disease and guides revascularization strategy modified in 14% of patients in the PPG Global Registry based on PPG assessment. We trace
[...] Read more.
This perspective comprehensively analyzes the invasive pullback pressure gradient (PPG), a novel physiological index that characterizes the longitudinal distribution of coronary artery disease and guides revascularization strategy modified in 14% of patients in the PPG Global Registry based on PPG assessment. We trace the historical development from subjective pullback curve analysis to a standardized, quantitative metric and describe the procedural aspects of both motorized and manual PPG acquisition. We synthesize evidence supporting PPG’s clinical utility in predicting post-percutaneous coronary intervention outcomes, guiding revascularization decisions, and improving patient-centered outcomes. A central focus is PPG’s mechanistic role in explaining the physiological basis of discordance between fractional flow reserve (FFR) and instantaneous wave-free ratio (iFR), linking focal disease to FFR-positive/iFR-negative patterns and diffuse disease to FFR-negative/iFR-positive patterns. We conclude that PPG represents a fundamental advancement in coronary physiology, shifting clinical focus from individual stenoses to overall disease patterns. This paradigm shift provides deeper understanding of coronary artery disease pathophysiology and offers a powerful predictive tool to guide personalized revascularization strategies. Prospective randomized trials will be essential to solidify its role as a cornerstone of modern interventional cardiology practice.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cardiology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prevalence and Characteristics of Sexual Dysfunction in Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
by
Betul Aktepe, Oktay Halit Aktepe, Pinar Ezgi Dama, Tugce Ulasli, Ilkay Tugba Unek, Aziz Karaoglu, Mehmet Hamid Boztas and Suayib Yalcin
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2033; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112033 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Sexual dysfunction (SD) is common in cancer but remains poorly characterized among patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). This study aimed to determine the prevalence and predictors of SD in ICI-treated patients using validated instruments. Materials and Methods:
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Sexual dysfunction (SD) is common in cancer but remains poorly characterized among patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). This study aimed to determine the prevalence and predictors of SD in ICI-treated patients using validated instruments. Materials and Methods: In this cross-sectional study, adults with histologically confirmed malignancies who received ≥ 3 cycles of ICIs and reported sexual activity were included. Sexual function was evaluated with the Arizona Sexual Experience Scale (ASEX) and the Golombok–Rust Inventory of Sexual Satisfaction (GRISS). Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses identified demographic and clinical predictors of SD. Results: Among 208 patients (median age 59 years; 35.1% female), SD prevalence was 66.3% by ASEX and 59.1% by GRISS. ASEX revealed impairment across five domains—sexual drive, psychological and physiological arousal, orgasm, and satisfaction—while GRISS indicated dysfunction mainly in impotence/orgasmic disorder, avoidance, and satisfaction subscales. In multivariate analysis, age ≥ 60 years (OR: 3.14, 95% CI 1.51–6.53, p = 0.002), female sex (OR: 3.19, 95% CI 1.31–7.74, p = 0.010), Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status ≥ 1 (OR: 2.82, 95% CI 1.39–5.71, p = 0.004), ≥2 metastatic sites (OR: 3.08, 95% CI 1.53–6.19, p = 0.002), and later treatment lines (OR: 2.43, 95% CI 1.20–4.94, p = 0.013) independently predicted ASEX-defined SD. GRISS-based analysis revealed comparable outcomes, identifying ECOG ≥1 and higher metastatic burden as the most prominent predictors of SD, consistent with ASEX findings. Conclusions: SD affected nearly two-thirds of patients receiving ICIs. Female sex, later treatment lines, poor ECOG performance status, and higher metastatic burden were key determinants, emphasizing the importance of routine sexual health evaluation in cancer care.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Oncology)
Open AccessArticle
Clinicopathological Profiles and Survival Outcomes of Patients with Gastric Cancer According to the Borrmann Endoscopic Classification: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study
by
Andrés Camilo Pachón-Mendoza, Oscar Daniel Pacheco-Can, Felipe Angulo-Várguez, Dayana Williams-Jacquez, Marlene Chaurand-Lara, Ana Ligia Gutiérrez-Solis, Azalia Avila-Nava, Mariana Irigoyen-Anguiano, Rodolfo Chim-Aké, Katy Sánchez-Pozos and Roberto Lugo
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2032; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112032 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objective: Gastric cancer (GC) is a serious public health problem in southeastern Mexico. Some cases go undiagnosed or are diagnosed at advanced stages of the tumors. Borrmann classification is the method used by endoscopists to classify gastric lesions and identify
[...] Read more.
Background and Objective: Gastric cancer (GC) is a serious public health problem in southeastern Mexico. Some cases go undiagnosed or are diagnosed at advanced stages of the tumors. Borrmann classification is the method used by endoscopists to classify gastric lesions and identify tumor stage. This study aimed to characterize GC patients treated at a specialized hospital in the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico, according to the Borrmann endoscopic classification, with a focus on clinicopathological characteristics and survival differences. Materials and Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted among patients aged 18 years or older who underwent an endoscopic procedure at the hospital to confirm a diagnosis of GC between January 2019 and December 2024. Clinical data were collected, including medical history, blood type, non-communicable diseases, tumor type, tumor location (primary or metastatic), and details of medical and/or surgical treatment. Survival curves were generated for all patients and stratified by the Borrmann classification. Results: A total of 209 cases of GC were included, with 115 men with a mean age of 59.3 years and 94 women with a mean age of 52.2 years. Acid peptic disease (70.3%), followed by wasting syndrome (66.9%), was the most common medical condition in patients with GC. Blood type O with a positive Rh factor was the most frequent (66.5%). According to the Borrmann classification, localized tumors (p = 0.001) were observed at lower Borrmann levels, whereas Helicobacter pylori (p = 0.040) was more frequent at higher levels. The overall survival time was 18 months for all patients; specifically, 18 months at higher Borrmann levels and 20 months at lower levels. Conclusions: GC is a highly prevalent malignancy in southeastern Mexico. The Borrmann classification remains a valuable and practical tool for evaluating GC. The association between Borrmann endoscopic classification and the clinicopathological and survival characteristics may contribute to accurate diagnosis assessment and improved prognostic stratification in future GC cases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Gastroenterology & Hepatology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Effects of Abdominal Bracing and Valsalva Maneuver on Cerebral and Peripheral Hemodynamics in Healthy Adults: A Randomized Crossover Study
by
Ji-Hyeon Yu, Ju-Yeon Jung, Yeong-Bae Lee, Jeong-Min Shim, Young-Don Son, Jiwon Yang and Chang-Ki Kang
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2031; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112031 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Blood flow is critical for tissue oxygenation, and alterations in cerebrovascular and peripheral circulation have important health implications. This study aimed to examine the impact of distinct mechanisms for increasing intra-cavity pressure through the abdominal bracing (AB) and Valsalva
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Blood flow is critical for tissue oxygenation, and alterations in cerebrovascular and peripheral circulation have important health implications. This study aimed to examine the impact of distinct mechanisms for increasing intra-cavity pressure through the abdominal bracing (AB) and Valsalva maneuver (VM) on central and peripheral hemodynamics. Materials and Methods: A randomized crossover design was used, and thirty healthy young adults (age 21.9 ± 1.5 years; BMI 20.9 ± 1.8 kg/m2) performed AB and VM in a randomized order. All participants provided written informed consent, and the study protocol was approved by the Clinical Research Information Service (KCT0009742; registered on 30 August 2024). Hemodynamic responses were measured before and after each intervention, including heart rate, blood pressure, pulse wave velocity, carotid artery diameter, pulsatility index, resistive index, peripheral oxygen saturation, and cerebral oxygenation. Repeated-measures analysis of variance and paired t-tests were conducted on the datasets. Results: Both the VM and AB significantly increased heart rate (p < 0.001) and systolic blood pressure (VM: p = 0.015; AB: p < 0.001). Cerebral oxygen saturation decreased significantly (VM: p < 0.05; AB: p < 0.05), whereas oxyhemoglobin increased during both interventions, suggesting higher cerebral oxygen demand. The VM specifically increased the carotid pulsatility index (pre = 1.76 ± 0.28; post2 = 1.87 ± 0.33; p = 0.008), reflecting elevated central vascular resistance. In contrast, AB decreased peripheral oxygen saturation (pre = 98.43 ± 0.71; post1 = 97.49 ± 1.76; p < 0.001) and increased peripheral (heart–finger) pulse wave velocity (Lt: p = 0.026; Rt: p = 0.010), indicating greater stimulation of peripheral circulation. Conclusions: Distinct mechanisms that elevate intra-cavity pressure differentially influence central and peripheral hemodynamics. These findings suggest that intra-cavity pressure can selectively modulate hemodynamic responses, with potential applications in both clinical and exercise settings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Physical Therapy: A New Perspective)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Formulation of α-Linolenic Acid-Based Microemulsions for Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Physicochemical Tests and HET-CAM Assays for Anti-Angiogenic Activities
by
Sang Gu Kang, Mahendra Singh, Gibaek Lee, Kyung Eun Lee and Ramachandran Vinayagam
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2030; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112030 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is an age-associated retinal disorder characterized by blood–retinal barrier (BRB) breakdown and pathological angiogenesis, leading to vascular leakage. The intravitreal administration of anti-VEGF agents remains the most effective treatment for neovascular AMD. However, repetitive intravitreal injections
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is an age-associated retinal disorder characterized by blood–retinal barrier (BRB) breakdown and pathological angiogenesis, leading to vascular leakage. The intravitreal administration of anti-VEGF agents remains the most effective treatment for neovascular AMD. However, repetitive intravitreal injections have risks, causing side effects such as cataracts, bleeding, retina damage, and, in severe cases, post-injection endophthalmitis. Hence, the development of innovative drug delivery systems is essential to minimize the risks and discomfort associated with intravitreal injections. Materials and Methods: We developed a microemulsion (ME)-based topical drug delivery system incorporating α-linolenic acid (ALA). In brief, pseudo-ternary phase diagrams were constructed by the water titration method using different combinations of surfactants and cosurfactants (Smix-Cremophor RH 40: Span 80: Transcutol P in ratios of 1:1.05, 1:1:1, 1:1:1.5) containing ALA as the oil phase. Three blank microemulsions (ME1, ME2, and ME3) were prepared and characterized based on the optimized pseudo-ternary phase equilibrium with a Smix ratio of 1:1:1. Results: ME3, with an average particle size of 38.59 nm, was selected as the optimized formulation for developing drug-loaded ME containing Fenofibrate, Axitinib, and Sirolimus. The drug-loaded ME showed particle size (46.94–56.39 nm) and in vitro release displayed sustained and longer time drug release for 240 h. The irritation and antiangiogenic activities were evaluated using the hen’s egg chorioallantoic membrane (HET-CAM) assay employing the optimized ME loaded with each drug. Among the three drug-loaded ME, the Sirolimus ME showed a reduction in blood vessel sprouting in the HET-CAM assay, indicating strong antiangiogenic activity. Treatment with the optimized blank ME and Sirolimus ME significantly (p < 0.05) reduced COX-2 protein expression in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells, suggesting their potential anti-inflammatory effects. Conclusions: Overall, we suggest that the α-linolenic acid-based Sirolimus microemulsion may serve as a promising topical therapeutic approach for managing AMD and offering a potential alternative to invasive intravitreal injections.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Ophthalmology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Emergency Management of Perforated Gastro-Duodenal Ulcers: Surgical Strategies, Outcomes, and Prognostic Determinants in a Tertiary Eastern European Center
by
Oprescu Macovei Anca Monica, Dana Paula Venter, Stefan Mihai, Constantin Oprescu, Andrei Gabriel, Dumitriu Bogdan, Valcea Sebastian, Gheorghiu Alexandra-Oana and Ilie Stan Madalina
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2029; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112029 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Perforated gastro-duodenal ulcers (PGDUs) are life-threatening surgical emergencies with high morbidity and mortality. This study aimed to evaluate surgical strategies, outcomes, and prognostic factors in patients treated for PGDUs in a tertiary Eastern European center. Materials and Methods:
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Perforated gastro-duodenal ulcers (PGDUs) are life-threatening surgical emergencies with high morbidity and mortality. This study aimed to evaluate surgical strategies, outcomes, and prognostic factors in patients treated for PGDUs in a tertiary Eastern European center. Materials and Methods: We conducted a retrospective cross-sectional analysis of 156 patients admitted with PGDUs between 2020 and 2024. Data on demographics, risk factors, ulcer location, type of surgical approach, operative details, hospital stay, and mortality were collected. Statistical analysis included chi-square, Mann–Whitney U, and multivariate logistic regression. Results: The mean age was 57.6 ± 15.9 years (range 18–91), with men accounting for 64.7% of cases. Alcohol use was significantly associated with male sex (p = 0.012), while NSAID use was equally distributed. Open surgery was the mainstay of treatment (85.9%), with laparoscopy performed in 12.8% and conversion in 1.9%. Median hospital stay was shorter after laparoscopic repair (7.5 vs. 9 days, p = 0.039. On multivariate analysis, both age and comorbidity burden were independent predictors of mortality (p < 0.01). Conclusions: PGDU management in Eastern Europe remains dominated by open surgery. Laparoscopy, though underutilized, is associated with shorter recovery. Age is the strongest determinant of mortality, highlighting the need for early risk stratification, wider adoption of minimally invasive techniques, and preventive measures targeting modifiable risk factors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Gastroenterology & Hepatology)
Open AccessArticle
The Microbiological Spectrum and Antibiotic Resistance in Acute Acalculous and Calculous Cholecystitis: A Seven-Year Study in a Tertiary Center
by
Cosmin Vasile Obleaga, Ovidiu Mircea Zlatian, Oana Mariana Cristea, Alexandra Rosu-Pires, Alexandru Marin Pascu, Mirela-Marinela Florescu, Claudiu Marinel Ionele, Ion Rogoveanu, Alexandru Valentin Popescu, Vlad Catanoiu and Sergiu Marian Cazacu
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2028; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112028 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Acute acalculous cholecystitis (AAC) is rare, mostly in older males, with cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, critical illness, or systemic infection. Antibiotherapy before or after cholecystectomy is important for preventing septic shock and postoperative infections. Increasing antibiotic resistance was recently noted
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: Acute acalculous cholecystitis (AAC) is rare, mostly in older males, with cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, critical illness, or systemic infection. Antibiotherapy before or after cholecystectomy is important for preventing septic shock and postoperative infections. Increasing antibiotic resistance was recently noted and can complicate antibiotherapy. Materials and Methods: A retrospective study of all patients who underwent cholecystectomy between 2018 and 2024 in the Clinical Emergency Hospital of Craiova was performed. The etiology of AAC, complications, hospitalization duration, mortality, positive bile cultures, and in vitro antibiotic resistance were analyzed. Results: A total of 802 calculous and 54 AAC were recorded. Patients with AAC were predominantly males (OR = 1.767, p = 0.043) with diabetes (OR = 2.049, p = 0.014) and were older (66.6 ± 13.2 vs. 61.4 ± 15.6, p = 0.014). Mortality was significantly higher in AAC (18.5 vs. 3.6%, OR = 6.058, p < 0.001), with longer hospitalization (mean 9.7 vs. 8.4 days) and more perforation. Positive bile cultures were recorded in 60.5–66.2% of cases, with a similar etiology in both forms of acute cholecystitis (mostly Gram-negative species, Enterococcus, and Staphylococcus); 10 ESBL Escherichia coli and Klebsiella strains, 11 Staphylococcus aureus MRSA, and 1 Enterococcus VRE strain were recorded. Antibiotic susceptibility in vitro was similar in both AAC and calculous cholecystitis. Significant resistance to cephalosporins and quinolones was recorded; the lowest resistance was noted for amikacin, carbapenems, chloramphenicol, colistin (Gram-negative bacteria), and vancomycin. Conclusions: AAC was encountered in older males with diabetes, with a higher rate of complications and in-hospital mortality. Bile cultures were positive in 60.5–66.2%, predominantly with Gram-negative, Enterococcus, and Staphylococcus species. Significant in vitro resistance to cephalosporins and quinolones was found.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Trends in Infectious Disease Prevention and Control)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Hemoglobin Levels During Definite Chemoradiotherapy of Patients with Locally Advanced Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma on Survival
by
Sandy Hazko, Amed Ahmed, Robert Michael Hermann, Mathias Alexander Sonnhoff, Athanasia Warnecke, Frank Bruns, Robert Blach, Hans Christiansen and Jan-Niklas Becker
Medicina 2025, 61(11), 2027; https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61112027 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background and Objectives: This study aims to investigate the impact of hemoglobin (Hb) level changes during radiochemotherapy (RCT) on the survival of patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Materials and Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: This study aims to investigate the impact of hemoglobin (Hb) level changes during radiochemotherapy (RCT) on the survival of patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Materials and Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 97 patients with HNSCC, treated with definitive RCT between January 2016 and October 2021. Hb levels were monitored weekly during RCT. Kaplan–Meier and Cox regression analysis were performed. Results: There was a significant association between Hb levels at the end of RCT and overall survival (p < 0.01). Initial Hb levels and Hb level changes were not significantly associated with survival. In multivariate analysis, a lower body mass index (BMI) and Hb levels at week six were identified as significant prognostic factors. Conclusions: At the end of RCT, rather than baseline levels or changes during treatment, Hb levels are a significant prognostic factor for overall survival in patients with HNSCC.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Medicina Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Clinics and Practice, Cosmetics, JCM, Medicina, Dermato, LabMed, Psychology International
Advances in Psychodermatology
Topic Editors: Jacek C. Szepietowski, Andrzej JaworekDeadline: 30 November 2025
Topic in
Cardiogenetics, Hearts, JCDD, JCM, Medicina
Biomarkers in Cardiovascular Disease—Chances and Risks, 2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Alexander E. Berezin, Michael LichtenauerDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
JFMK, Medicina, Therapeutics, Healthcare, JCM, Rheumato
New Trends in Physiotherapy Care: Improvements in Functionality, Pain Management, and Quality of Life
Topic Editors: Carlos Bernal-Utrera, Ernesto Anarte-Lazo, Juan José González GerezDeadline: 3 March 2026
Topic in
Diagnostics, Geriatrics, JCDD, Medicina, JPM, Medicines
New Research on Atrial Fibrillation
Topic Editors: Michele Magnocavallo, Domenico G. Della Rocca, Stefano Bianchi, Pietro Rossi, Antonio BisignaniDeadline: 31 March 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Medicina
Adenomyosis and Endometriosis-Related Infertility
Guest Editors: Simone Ferrero, Giuseppe GulloDeadline: 20 November 2025
Special Issue in
Medicina
Dermato-Engineering and AI Assessment in Dermatology Practice
Guest Editors: Emmanouil Karampinis, Paweł PietkiewiczDeadline: 20 November 2025
Special Issue in
Medicina
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Advances in Diagnosis, Treatment and Prognosis in Clinical Medicine
Guest Editors: Marko Barešić, Joško MitrovićDeadline: 20 November 2025
Special Issue in
Medicina
Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Management of Diseases During Pregnancy: Third Edition
Guest Editors: Marius L. Craina, Elena BernadDeadline: 20 November 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Medicina
Advances in Cornea, Cataract, and Refractive Surgery
Collection Editor: Ivo Guber
Topical Collection in
Medicina
Interventional Oncology
Collection Editors: François Cornelis, Matthias Barral, Adrian Kastler, Dimitrios Filippiadis
Topical Collection in
Medicina
Interdisciplinary Medicine – The Key For Personalized Medicine
Collection Editor: Camelia Diaconu
Topical Collection in
Medicina
Frontiers in Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Collection Editors: Jimmy T. Efird, Tithi Biswas











