- Article
Factors Associated with Para-Aortic Lymph Node Metastasis in High-Risk Endometrial Cancer
- Fatma Ceren Güner,
- Elif Iltar and
- Müge Ateş Tıkız
- + 4 authors
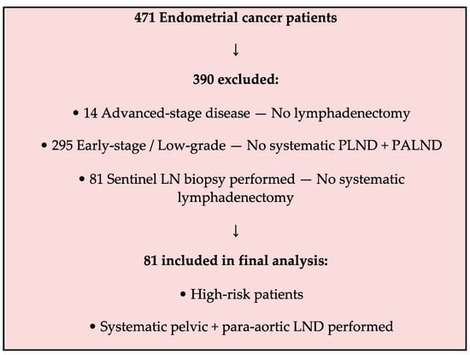
Background and Objectives: Para-aortic lymph node involvement is a key prognostic factor in high-risk endometrial cancer. This study aimed to identify factors associated with para-aortic lymph node metastasis and to assess their predictive value for surgical decision-making. Materials and Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 81 patients with high-risk endometrial cancer who underwent systematic pelvic and para-aortic lymphadenectomy between January 2015 and December 2024. Factors evaluated included histologic subtype, lymphovascular space invasion (LVSI), cervical stromal involvement, depth of myometrial invasion, and tumor diameter. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed to identify independent predictors of para-aortic metastasis. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was used to determine the optimal tumor size threshold. Results: Para-aortic lymph node metastasis was identified in 21.0% of patients, and isolated para-aortic metastasis was observed in 2.5%. In univariate analysis, pelvic lymph node positivity, LVSI, cervical stromal invasion, deep myometrial invasion, and tumor size ≥ 3.55 cm were significantly associated with para-aortic spread. Multivariate analysis revealed that pelvic lymph node positivity was the only independent predictor (OR 39.0; 95% CI 5.06–301.46; p < 0.001). Conclusions: Pelvic lymph node status serves as a strong and independent predictor of para-aortic metastasis in high-risk endometrial cancer. A tumor diameter greater than 3.5 cm may also indicate an increased risk of para-aortic spread. These findings suggest that selective and individualized para-aortic assessment strategies may be considered to improve staging accuracy and optimize surgical planning in this patient population.
10 December 2025