- Hypothesis
The Hidden Anatomy of Low Back Pain: Uncovering the Impact of Mamillo-Accessory Ligament Ossification
- Jordan Allan Piper,
- Koko Faen and
- Alessandro Castorina
- + 4 authors
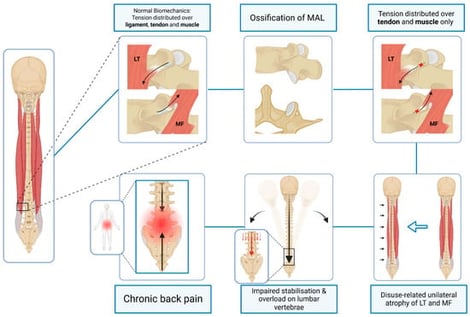
Low back pain (LBP) remains a leading cause of disability worldwide, imposing substantial socioeconomic burdens. Among its many causes, facetogenic pain accounts for a significant proportion of cases and is generally attributed to irritation of the richly innervated facet joint capsule, mediated by the medial branches of the dorsal rami. This narrative, hypothesis-driven review synthesises the current anatomical, biomechanical, neurophysiological, and clinical literature and advances a conceptual framework proposing a novel anatomical mechanism that may contribute to LBP. We hypothesise that ossification of the mamillo-accessory ligament (MAL) may be a plausible but under-recognised anatomical variant that may influence lumbar biomechanics and neural interfaces. The MAL connects the mammillary and accessory processes of lumbar vertebrae, serving as a stabilising anchor for deep paraspinal muscles and forming a conduit for the medial branch of the dorsal ramus (MBDR). Ossification of the MAL, resulting in a mamillo-accessory foramen, may theoretically impair spinal biomechanics via three principal mechanistic domains: (1) disruption of muscle attachment and segmental stabilisation, (2) potential compression of the MBDR causing denervation and muscle atrophy, and (3) chronic nerve entrapment leading to asymmetrical postural adaptations and persistent pain. Collectively, these pathways may contribute to spinal instability, facet degeneration, and variable response to standard interventional treatments such as radiofrequency ablation. Recognition of MAL ossification may have potential implications for clinical assessment, targeted imaging strategies, and treatment stratification in patients with chronic, non-specific LBP.
27 February 2026