Reliability and Inter-Device Agreement Between a Portable Handheld Ultrasound Scanner and a Conventional Ultrasound System for Assessing the Thickness of the Rectus Femoris and Vastus Intermedius
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Training for Standardization of Ultrasound Measurements
2.3. Study Procedures
2.4. Ultrasound Assessment and Muscle Thickness Measurement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Intra-Rater Reliability
3.2. Inter-Rater Reliability
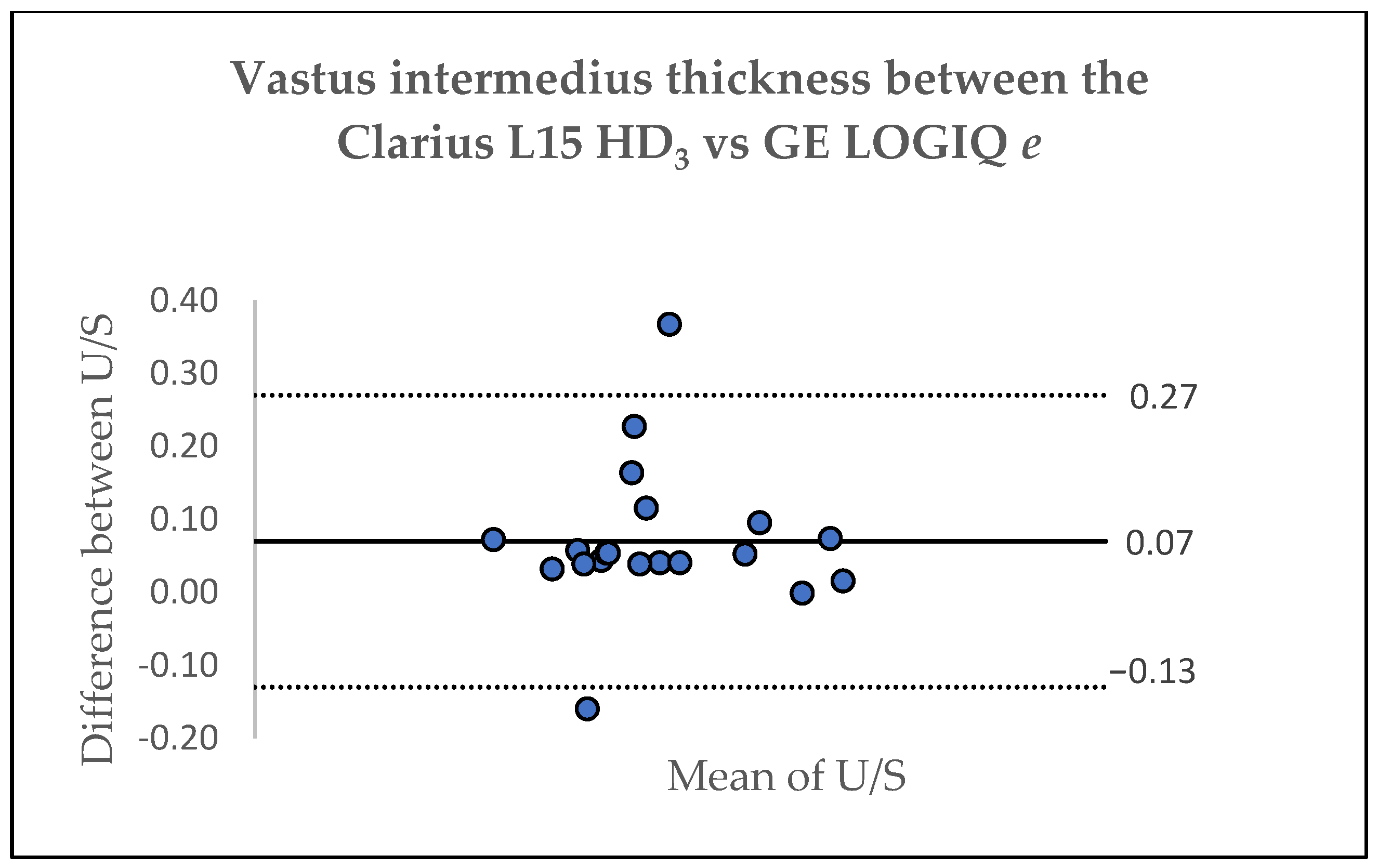
3.3. Inter-Device Agreement
3.4. Precision
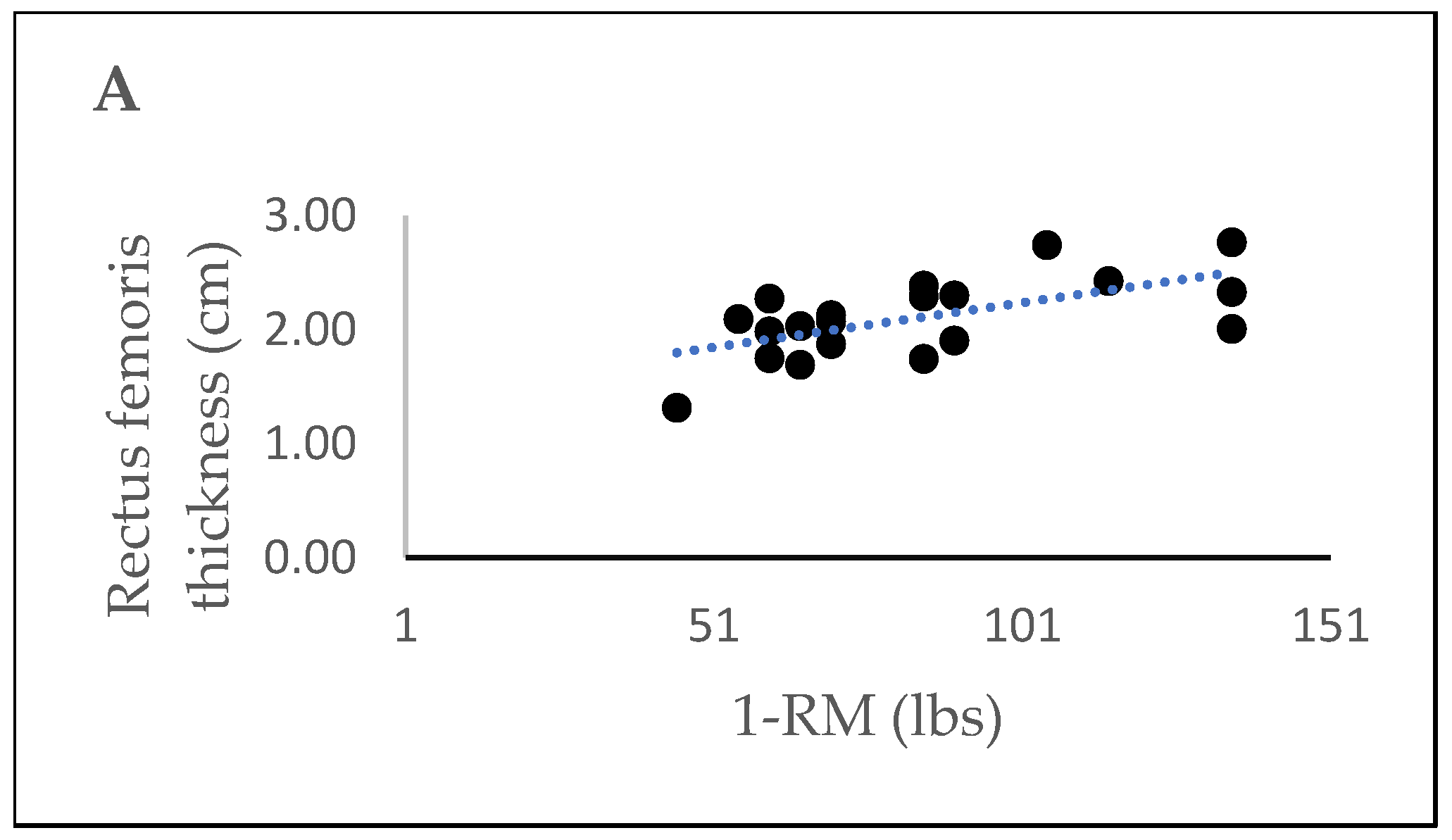
3.5. Correlations Between Muscle Thickness and 1-RM for Leg Extension
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CT | Computed tomography |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| DXA | Dual X-Ray absorptiometry |
| U/S | Ultrasound |
| RF | Rectus femoris |
| VI | Vastus intermedius |
| PARQ+ | Physical activity readiness questionnaire for everyone |
| IPAQ-SF | International Physical Activity Questionnaire-Short Form |
| 1-RM | 1-repetition-maximum |
| ICC | Intraclass correlation coefficient |
| TE | Typical error |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SEM | Standard error of measurement |
| MDC | Minimal detectable change |
| LSC | Least significant change |
| ISCD | International Society for Clinical Densitometry |
| RMSSD | Root-mean-square standard deviation |
| RMS%CV | Root-mean-square coefficient of variation |
References
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Sayer, A.A. Sarcopenia. Lancet 2019, 393, 2636–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hao, Q.; Ge, M.; Dong, B. Association of sarcopenia and fractures in community-dwelling older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 29, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Tao, W.; Dou, Q.; Yang, Y. Sarcopenia as a predictor of hospitalization among older people: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2018, 18, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabett Cipolli, G.; Sanches Yassuda, M.; Aprahamian, I. Sarcopenia Is Associated with Cognitive Impairment in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2019, 23, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, X.; Liu, J.; Long, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Lu, S. An analysis and systematic review of sarcopenia increasing osteopenia risk. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, S.; Gao, T.; Zhong, F.; Cai, J.; Sun, Y.; Ma, A. Association between Sarcopenia and Metabolic Syndrome in Middle-Aged and Older Non-Obese Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wan, C.S.; Ktoris, K.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Maier, A.B. Sarcopenia Is Associated with Mortality in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gerontology 2022, 68, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijholt, W.; Scafoglieri, A.; Jager-Wittenaar, H.; Hobbelen, J.S.M.; van der Schans, C.P. The reliability and validity of ultrasound to quantify muscles in older adults: A systematic review. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaes, T.; Thomis, M.; Onkelinx, S.; Coudyzer, W.; Cornelissen, V.; Vanhees, L. Reliability and validity of the ultrasound technique to measure the rectus femoris muscle diameter in older CAD-patients. BMC Med. Imaging 2012, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijholt, W.; Jager-Wittenaar, H.; Raj, I.S.; van der Schans, C.P.; Hobbelen, H. Reliability and validity of ultrasound to estimate muscles: A comparison between different transducers and parameters. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 35, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neira Alvarez, M.; Vazquez Ronda, M.A.; Soler Rangel, L.; Thuissard-Vasallo, I.J.; Andreu-Vazquez, C.; Martinez Martin, P.; Rabago Lorite, I.; Serralta San Martin, G. Muscle Assessment by Ultrasonography: Agreement with Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) and Relationship with Physical Performance. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2021, 25, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vongchaiudomchoke, W.; Cho, A.R.; Mahmoud, I.; Carli, F. Ultrasound for skeletal muscle assessment in surgical oncology: A scoping review. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2025, 51, 109676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nies, I.; Ackermans, L.; Poeze, M.; Blokhuis, T.J.; Ten Bosch, J.A. The Diagnostic Value of Ultrasound of the Rectus Femoris for the diagnosis of Sarcopenia in adults: A systematic review. Injury 2022, 53, S23–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, A.L.C.; Carvalho, R.F.; Mogami, R.; Meirelles, C.M.; Gomes, P.S.C. Effect of resistance training on quadriceps femoris muscle thickness obtained by ultrasound: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2024, 39, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellhorn, A.C.; Stumph, J.M.; Zikry, H.E.; Creelman, C.A.; Welbel, R. Ultrasound measures of muscle thickness may be superior to strength testing in adults with knee osteoarthritis: A cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 19, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyere, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostron, Z.P.; Green, R.A.; Kingsley, M.; Zacharias, A. Associations Between Measures of Physical Activity and Muscle Size and Strength: A Systematic Review. Arch. Rehabil. Res. Clin. Transl. 2021, 3, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchowny, K.A.; Peters, K.E.; Cummings, S.R.; Orwoll, E.S.; Hoffman, A.R.; Ensrud, K.E.; Cauley, J.A.; Evans, W.J.; Cawthon, P.M.; Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) Study Research Group. Association of change in muscle mass assessed by D3-creatine dilution with changes in grip strength and walking speed. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromaras, K.; Zaras, N.; Stasinaki, A.N.; Mpampoulis, T.; Terzis, G. Lean Body Mass, Muscle Architecture and Powerlifting Performance during Preseason and in Competition. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2024, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredin, S.S.; Gledhill, N.; Jamnik, V.K.; Warburton, D.E. PAR-Q+ and ePARmed-X+: New risk stratification and physical activity clearance strategy for physicians and patients alike. Can. Fam. Physician 2013, 59, 273–277. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjostrom, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.C.; Gerstner, G.R.; Voskuil, C.C.; Harden, J.E.; Dunnick, D.; Badillo, K.M.; Pagan, J.I.; Harmon, K.K.; Girts, R.M.; Beausejour, J.P.; et al. The Influence of Sonographer Experience on Skeletal Muscle Image Acquisition and Analysis. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2021, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, K.; Mampilly, J.; Laghi, F.A.; Goyal, A.; Collins, E.G.; McBurney, C.; Jubran, A.; Tobin, M.J. Validity and reliability of rectus femoris ultrasound measurements: Comparison of curved-array and linear-array transducers. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2014, 51, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, S.P.; Tarpenning, K.M.; Marino, F.E. Independent and combined effects of liquid carbohydrate/essential amino acid ingestion on hormonal and muscular adaptations following resistance training in untrained men. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 97, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baim, S.; Binkley, N.; Bilezikian, J.P.; Kendler, D.L.; Hans, D.B.; Lewiecki, E.M.; Silverman, S. Official Positions of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry and executive summary of the 2007 ISCD Position Development Conference. J. Clin. Densitom. 2008, 11, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buehring, B.; Krueger, D.; Libber, J.; Heiderscheit, B.; Sanfilippo, J.; Johnson, B.; Haller, I.; Binkley, N. Dual-energy X-Ray absorptiometry measured regional body composition least significant change: Effect of region of interest and gender in athletes. J. Clin. Densitom. 2014, 17, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, P.; Pascoal, A.G.; Sancho, F.; Bo, K. Test-retest and intrarater reliability of 2-dimensional ultrasound measurements of distance between rectus abdominis in women. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2012, 42, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfuraih, A.M.; Alqarni, M.A.; Alhuthaili, H.S.; Mubaraki, M.Y.; Alotaibi, N.N.; Almusalim, F.M. Reproducibility and feasibility of a handheld ultrasound device compared to a standard ultrasound machine in muscle thickness measurements. Australas. J. Ultrasound Med. 2023, 26, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritsche, P.; Schmid, R.; Franchi, M.V.; Faude, O. Agreement and reliability of lower limb muscle architecture measurements using a portable ultrasound device. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 981862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benatti de Oliveira, G.; Vilar Fernandes, L.; Summer Chen, X.; Drumond Andrade, F.C.; Scarlazzari Costa, L.; Junqueira Vasques, A.C.; Pires Corona, L. Intra- and inter-rater reliability of muscle and fat thickness measurements obtained using portable ultrasonography in older adults. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2024, 60, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turton, P.; Hay, R.; Welters, I. Assessment of peripheral muscle thickness and architecture in healthy volunteers using hand-held ultrasound devices; a comparison study with standard ultrasound. BMC Med. Imaging 2019, 19, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewiecki, E.M.; Binkley, N.; Morgan, S.L.; Shuhart, C.R.; Camargos, B.M.; Carey, J.J.; Gordon, C.M.; Jankowski, L.G.; Lee, J.K.; Leslie, W.D.; et al. Best Practices for Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Measurement and Reporting: International Society for Clinical Densitometry Guidance. J. Clin. Densitom. 2016, 19, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hind, K.; Slater, G.; Oldroyd, B.; Lees, M.; Thurlow, S.; Barlow, M.; Shepherd, J. Interpretation of Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry-Derived Body Composition Change in Athletes: A Review and Recommendations for Best Practice. J. Clin. Densitom. 2018, 21, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemski, A.J.; Hind, K.; Keating, S.E.; Broad, E.M.; Marsh, D.J.; Slater, G.J. Same-Day Vs Consecutive-Day Precision Error of Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry for Interpreting Body Composition Change in Resistance-Trained Athletes. J. Clin. Densitom. 2019, 22, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, K.E.; Paris, M.T.; Samuel, M.; Mourtzakis, M. Reliability of ultrasound measurements of muscle thickness and echointensity in older adults with type 2 diabetes. WFUMB Ultrasound Open 2024, 2, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraki, S.; Fukumoto, K.; Fukuda, O. Prediction of the muscle strength by the muscle thickness and hardness using ultrasound muscle hardness meter. Springerplus 2013, 2, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Harada, R.; Yoshikawa, R.; Ueda, Y.; Takamiya, D.; Sakai, Y. Reliability and Validity of Quadriceps Muscle Thickness Measurements in Ultrasonography: A Comparison with Muscle Mass and Strength. Prog. Rehabil. Med. 2023, 8, 20230008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, Y.; Ikezoe, T.; Yamada, Y.; Tsukagoshi, R.; Nakamura, M.; Mori, N.; Kimura, M.; Ichihashi, N. Skeletal muscle quality assessed from echo intensity is associated with muscle strength of middle-aged and elderly persons. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillip, J.G.; Minet, L.R.; Smedemark, S.A.; Ryg, J.; Andersen-Ranberg, K.; Brockhattingen, K.K. Comparative analysis of hand-held and stationary ultrasound for detection of sarcopenia in acutely hospitalised older adults—A validity and reliability study. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2024, 15, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kraats, A.M.; Peeters, N.H.C.; Janssen, E.R.C.; Lambers Heerspink, F.O. Handheld Ultrasound Does not Replace Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears. Arthrosc. Sports Med. Rehabil. 2023, 5, e381–e387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagobian, S.D.; Wallace, S.R.; Fowler, J.R. A comparison of handheld versus cart-based ultrasound in the evaluation and diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Hand Microsurg. 2024, 16, 100159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantella, L.E.; Colledanchise, K.; Bullen, M.; Hetu, M.F.; Day, A.G.; McLellan, C.S.; Johri, A.M. Handheld versus conventional vascular ultrasound for assessing carotid artery plaque. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 278, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rispo, A.; Calabrese, G.; Testa, A.; Imperatore, N.; Patturelli, M.; Allocca, M.; Guarino, A.D.; Cantisani, N.M.; Toro, B.; Castiglione, F. Hocus Pocus: The Role of Hand-held Ultrasonography in Predicting Disease Extension and Endoscopic Activity in Ulcerative Colitis. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2023, 17, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, D.N.; Bach, A.J.E.; O’Brien, J.L.; Sainani, K.L. Calculating sample size for reliability studies. PMR 2022, 14, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
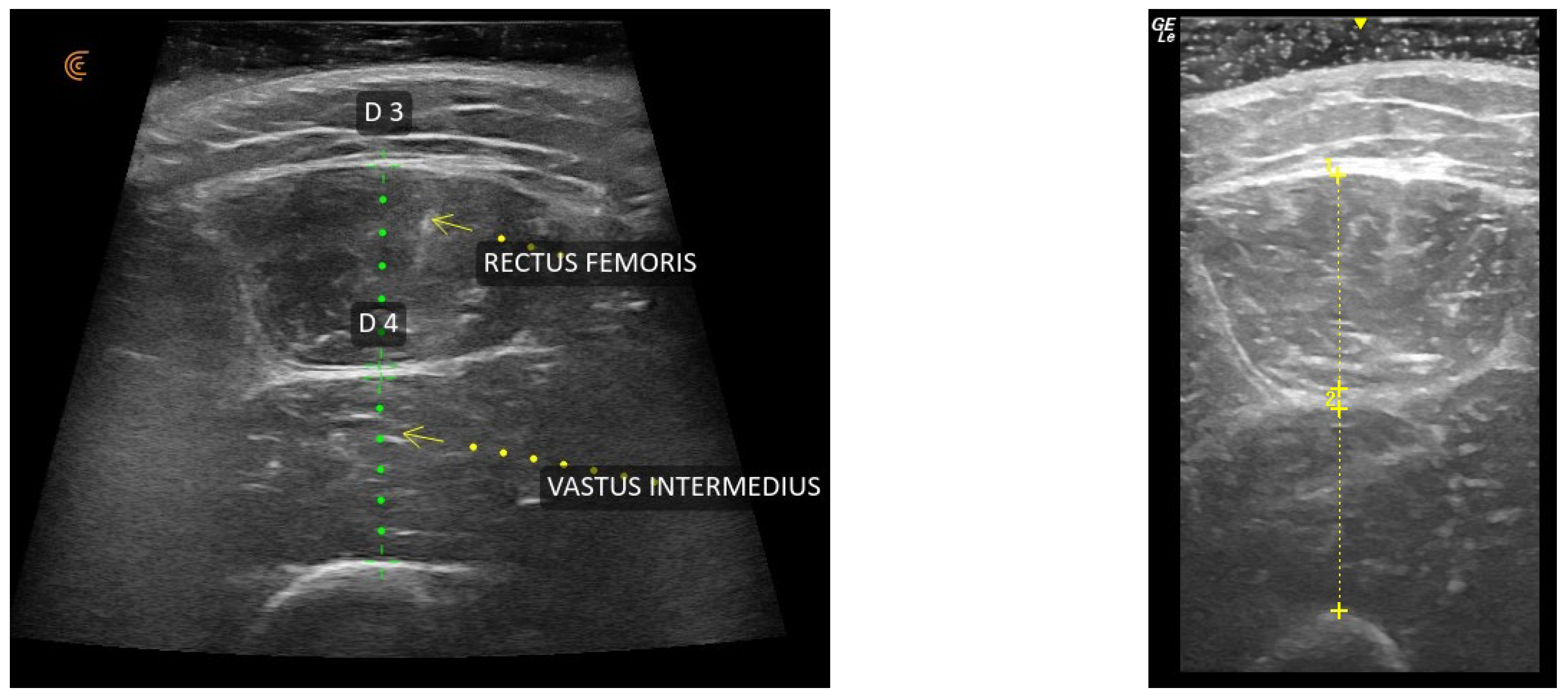


| Characteristic | N = 20 |
|---|---|
| Age, years (mean, SD) | 21.9 (2.7) |
| Sex (females), n (%) | 16 (80%) |
| Race, n (%) | |
| White | 12 (60%) |
| Black | 4 (20%) |
| Hispanic | 2 (10%) |
| Asian | 1 (10%) |
| Body mass index (kg/m2), mean (SD) | 23.7 (4.2) |
| Days of vigorous PA per week (mean, SD) | 2.8 (1.9) |
| Minutes of vigorous PA per week (mean, SD) | 187 (167.3) |
| Days of moderate PA per week (mean, SD) | 2.6 (1.8) |
| Minutes of moderate PA per week (mean, SD) | 48 (31.0) |
| Days of walking per week (mean, SD) | 5.9 (1.4) |
| Minutes of walking per week (mean, SD) | 71.8 (77.9) |
| Minutes of sitting per week (mean, SD) | 361.8 (142.9) |
| Thickness (cm) | Visit 1 (Mean, SD) | Visit 2 (Mean, SD) | Δ (%) | ICC (95%CI) | TE (cm) | RMSSD (cm) | LSCRMSD (cm) | RMS%CV | LSC%CV | SEM (%) | MDC (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF Clarius L15 HD3 | 2.11 (0.35) | 2.13 (0.32) | −1.54 (6.59) | 0.96 (0.90–0.98) | 0.09 | 0.093 | 0.258 | 4.51 | 12.49 | 2.66 | 0.07 |
| RF GE LOGIQ e | 2.14 (0.38) | 2.21 (0.33) | −3.91 (9.41) | 0.94 (0.84–0.98) | 0.12 | 0.122 | 0.339 | 6.23 | 17.26 | 4.02 | 0.11 |
| VI Clarius L15 HD3 | 1.86 (0.49) | 1.86 (0.41) | 1.08 (9.44) | 0.97 (0.92–0.99) | 0.12 | 0.112 | 0.311 | 6.16 | 17.05 | 2.83 | 0.08 |
| VI GE LOGIQ e | 1.90 (0.45) | 1.96 (0.45) | −4.16 (9.56) | 0.97 (0.91–0.99) | 0.11 | 0.116 | 0.321 | 6.61 | 18.31 | 2.65 | 0.07 |
| Thickness (cm) | Assessor 1 (Mean, SD) | Assessor 2 (Mean, SD) | Δ (%) | p | ICC (95%CI) | TE (cm) | SEM (%) | MDC (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clarius L15 HD3 | ||||||||
| RF | 2.11 (0.35) | 2.08 (0.39) | 1.43 (6.00) | 0.38 | 0.97 (0.93–0.99) | 0.09 | 2.20 | 0.06 |
| VI | 1.86 (0.49) | 1.88 (0.46) | −1.33 (8.62) | 0.68 | 0.97 (0.93–0.99) | 0.11 | 2.72 | 0.08 |
| GE LOGIQ e | ||||||||
| RF | 2.14 (0.38) | 2.08 (0.39) | 2.86 (7.02) | 0.043 | 0.97 (0.91–0.99) | 0.09 | 2.17 | 0.06 |
| VI | 1.90 (0.45) | 1.90 (0.46) | −0.30 (10.27) | 0.99 | 0.97 (0.93–0.99) | 0.11 | 2.66 | 0.07 |
| Thickness (cm) | Clarius L15 HD3 (Mean, SD) | GE LOGIQ e (Mean, SD) | Δ (%) | ICC (95%CI) | TE (cm) | SEM (%) | MDC (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 2.11 (0.35) | 2.14 (0.38) | −1.47 (6.20) | 0.98 (0.94–0.99) | 0.08 | 1.58 | 0.04 |
| VI | 1.86 (0.49) | 1.90 (0.45) | −2.03 (7.20) | 0.98 (0.95–0.99) | 0.09 | 1.75 | 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Emerson, C.; Kim, H.K.; Irving, B.A.; Papadopoulos, E. Reliability and Inter-Device Agreement Between a Portable Handheld Ultrasound Scanner and a Conventional Ultrasound System for Assessing the Thickness of the Rectus Femoris and Vastus Intermedius. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2025, 10, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030299
Emerson C, Kim HK, Irving BA, Papadopoulos E. Reliability and Inter-Device Agreement Between a Portable Handheld Ultrasound Scanner and a Conventional Ultrasound System for Assessing the Thickness of the Rectus Femoris and Vastus Intermedius. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2025; 10(3):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030299
Chicago/Turabian StyleEmerson, Carlante, Hyun K. Kim, Brian A. Irving, and Efthymios Papadopoulos. 2025. "Reliability and Inter-Device Agreement Between a Portable Handheld Ultrasound Scanner and a Conventional Ultrasound System for Assessing the Thickness of the Rectus Femoris and Vastus Intermedius" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 10, no. 3: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030299
APA StyleEmerson, C., Kim, H. K., Irving, B. A., & Papadopoulos, E. (2025). Reliability and Inter-Device Agreement Between a Portable Handheld Ultrasound Scanner and a Conventional Ultrasound System for Assessing the Thickness of the Rectus Femoris and Vastus Intermedius. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 10(3), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk10030299






