Abstract
Background/Objectives: Colorectal carcinoma (CRC) is among the most commonly diagnosed cancers in both men and women. Although CRC mortality is generally decreasing, new therapeutic options are needed for unresponsive subgroups of CRC patients. Methods: A series of known and new tyrphostin derivatives was tested for their efficacy against three CRC cell lines with varying KRAS, p53, and/or BRAF statuses. Growth inhibition, apoptosis induction, and inhibition of EGFR and VEGFR-2 were investigated. Results: Tyrphostin A9, the known RG13022-related tyrphostin 1a and its dichlorido(p-cymene)ruthenium(II) complex 1b, and the new SF5-substituted compounds 2a and 2b showed selective antiproliferative activity against KRAS-mutant HCT-116 CRC cells expressing wildtype p53, while p53-knockout HCT-116 and KRAS-wildtype BRAF/p53-mutant HT-29 CRC cells were distinctly less sensitive. In HCT-116 cells, only tyrphostin A9 increased mRNA expression of caspases 3 and 8, as well as the kinases MEK1 and MEK2, whereas 2a reduced caspase 8 mRNA levels. Tyrphostin A9 increased caspase 3 activity and induced apoptosis in HCT-116 p53-wildtype cells while simultaneously inhibiting the receptor tyrosine kinases EGFR and VEGFR-2 at low nanomolar concentrations. Conclusions: Tyrphostin A9 could be a promising therapeutic option for the treatment of KRAS-mutant CRC that expresses wildtype p53.
Keywords:
anticancer agents; colorectal carcinoma; tyrphostin A9; p53; kinase inhibitors; EGFR; VEGFR 1. Introduction
Colorectal carcinoma (CRC) is one of the most common and most lethal cancer diseases all over the world [1]. In particular, CRC is expected to become a major health problem in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) by 2030. Relatively high CRC incidences were observed in MENA countries of the Persian Gulf (Kuwait, Qatar, Bahrain), as well as in Jordan and Lebanon [2]. Sub-populations of CRC patients classified based on the presence and mutation of various tumor suppressors and oncogenes (e.g., p53, KRAS, and BRAF) can differ distinctly in their response to currently approved treatments of CRC [3,4]. Dysregulation of RAS/MAPKKK (RAF)/MAPKK (MEK)/MAPK (ERK) and PI3K/AKT signaling in CRC was associated with increased proliferation, metastasis formation, and angiogenesis, leading to malignancy. Mutations of RAS and BRAF were found responsible for resistance in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) and poor prognosis in patients undergoing EGFR inhibitor therapy (cetuximab) [5,6,7,8]. Activating mutations in RAS (such as KRAS) and BRAF maintain oncogenic signaling downstream from EGFR, while EGFR can reactivate MAPK signaling in BRAFV600E CRCs resistant to therapy with the clinically approved BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib [9,10]. Moreover, it was shown that the transcription factor p53 has an influence on the outcome of EGFR inhibitor therapy by regulating EGFR promoter. Increased p53 expression led to resistance to EGFR-targeting therapies in mCRC [11].
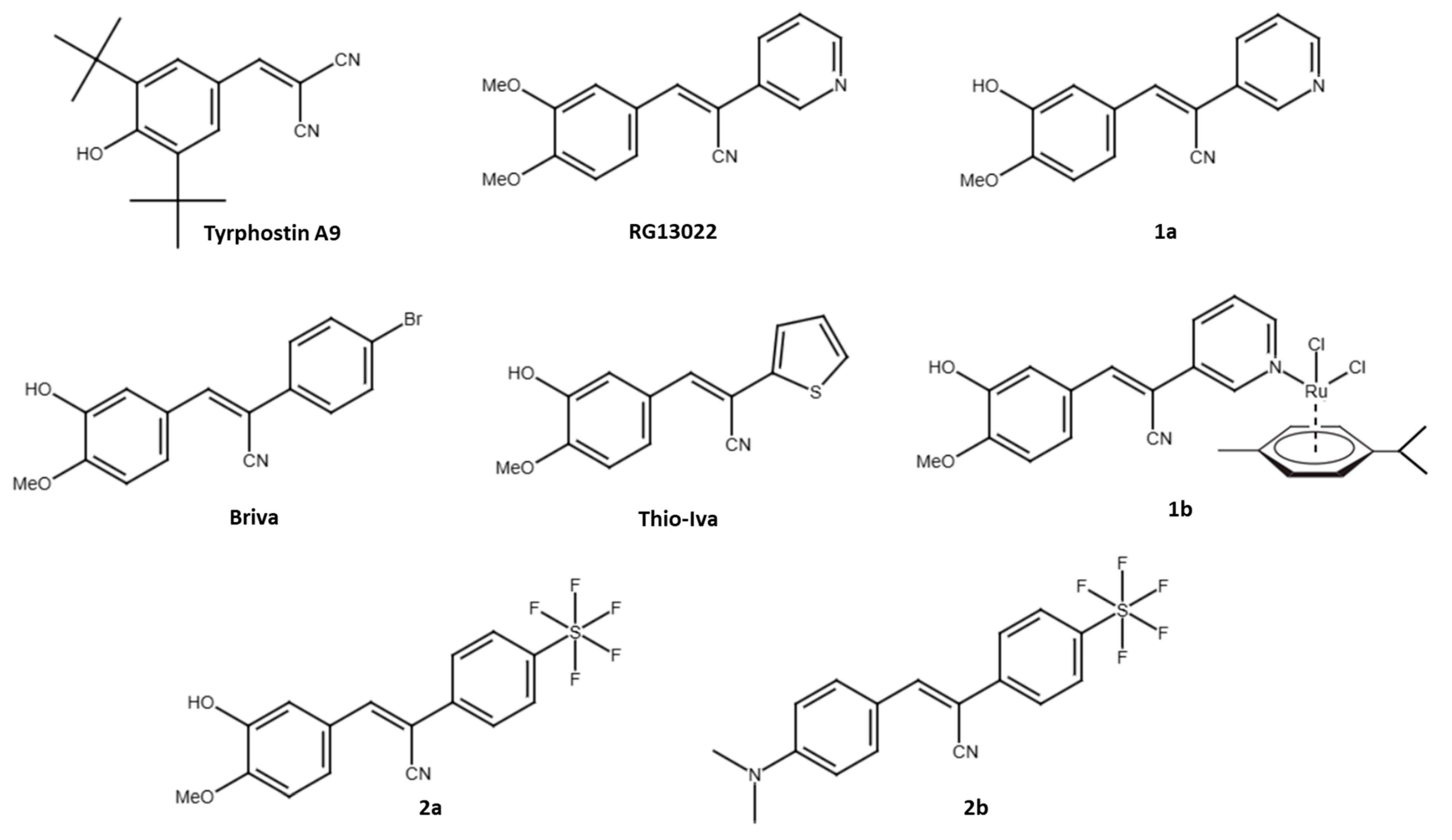
In addition to EGFR, other receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) associated with CRC malignancy include VEGFR, PDGFR, IGF-1R, FGFR, and c-Met, and many selective and multi-kinase inhibitors have been developed to treat CRC and other cancers. Approved RTK inhibitors for the therapy of CRC are cetuximab (an anti-EGFR antibody) and regorafenib (a multi-kinase inhibitor targeting PDGFR and VEGFR) [12]. The first compounds with tyrosine phosphorylation inhibitory activities were called tyrphostins and included erbstatin and benzylidenemalononitrile (BMN) compounds [13,14]. A prominent example is tyrphostin A9 (3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzylidenemalononitrile, also known as tyrphostin 9, tyrphostin AG17, SF-6847, malonoben), which was described early on as a suppressor of EGF and inhibitor of EGFR phosphorylation in pancreatic cancer cells (Figure 1) [15]. However, tyrphostin A9 is better known for its PDGFR inhibitory activities and mitochondria-disrupting properties (as a protonophor) [16,17]. Further interesting targets of tyrphostin A9 were identified, e.g., the cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase PYK2 and the lipoxygenase 5-LO [18,19]. Replacement of one of the nitrile groups of BMNs by a 3-pyridyl group led to promising anticancer active EGFR inhibitors such as RG13022 (Figure 1) [20]. We found that the analogous isovanillyl derivative 1a (replacement of the RG13022 meta-methoxy group by a hydroxy group) and its dichlorido(p-cymene)ruthenium(II) complex 1b possess higher anticancer activity than RG13022 (Figure 1) [21]. Both tyrphostin A9 and compounds 1a and 1b have a phenolic hydroxy group, which seems to be important for anticancer activity. Substitution of the 3-pyridyl ring by 2-thienyl (Thio-Iva) or 4-bromophenyl moieties (Briva) led to selective activities against BRAF-mutant CRCs such as BRAFV600E HT-29 cells (Figure 1) [22].
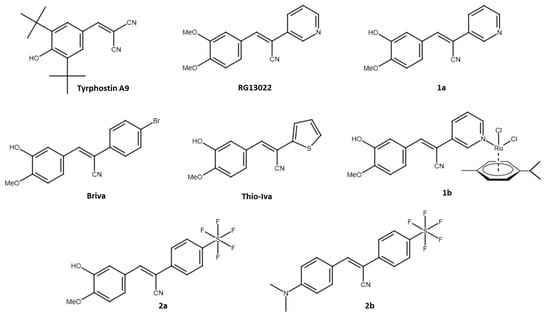
Figure 1.
Structures of tyrphostins used in this study and in our previous work.
The current knowledge of the activity of tyrphostin A9 against CRCs is limited. In this study, we investigated the effects of tyrphostin A9 and two known isovanillyl derivatives of RG13022, compounds 1a and 1b, on CRC cells (HCT-116 and HT-29 cell lines) with varying p53, KRAS, and BRAF statuses (wildtype, mutant, and/or knockout). In addition, two new SF5-substituted compounds 2a and 2b were prepared and studied for their anti-CRC activities (Figure 1). The SF5-group is also known as “super trifluoromethyl group” and has already led to considerable improvements in various drug candidates [23,24].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemistry and Test Compounds
Tyrphostin A9 was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Darmstadt, Germany). The RG13022 derivative 1a and its Ru(II) complex 1b were prepared and analyzed previously [21]. The syntheses and analyses of the new SF5-substituted compounds 2a and 2b can be found in the Supplementary Material. Starting compounds were purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany), Alfa Aesar (Karlsruhe, Germany), and TCI (Zwijndrecht, Belgium). The analyzers used for the analysis of the new compounds (i.e., NMR, IR, and MS machines) were described before [25].
2.2. Biological Assays
2.2.1. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
The human cancer cell lines HT-29 (ACC 299, p53R273H, BRAFV600E) CRC, HCT-116 p53-wildtype/wt CRC (ACC 581, BRAF-wildtype, activating KRASG13D mutation), and human normal mammary MCF10A (CRL-10317), renal monkey Vero, and canine renal MDCK cells from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) were used. The HCT-116 p53-knockout/KO CRC cells were a gift from Bert Vogelstein, Johns Hopkins University (Baltimore, MD, USA). The HT-29 and HCT-116 CRC cells were kept in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). The MCF10A, Vero (CCL-81), and MDCK (CCL-34) cells were grown in DMEM/F12, 5% horse serum, epidermal growth factor (EGF; 20 ng/mL), insulin (10 μg/mL), cholera toxin (100 ng/mL), and hydrocortisone (0.5 mg/mL). Vero and MDCK cells were grown in Eagle’s Minimum Essential Medium with 10% FBS. Cells were cultured at 37 °C, 5% CO2, and 95% humidity.
2.2.2. MTT Assay
The cytotoxic effects of the test compounds were determined using the colorimetric MTT assay [26]. Cells (1 × 104 cells/well) were incubated in 96-well plates for 24 h followed by treatment with 8 different concentrations (0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10, 30 and 100 μM) of the test compounds, erlotinib (a standard EGFR inhibitor), and sorafenib (a multi-kinase inhibitor commonly applied as standard VEGFR-2 inhibitor) for 72 h. After incubation of the cells with 0.5 µg/µL yellow MTT salt 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide for 3–4 h, isopropanol/DMSO (1:1) was added to dissolve the purple formazan precipitate, and the absorbance (570 nm) was measured using a 96-well plate reader (Biotek Synergy HT Multi-Mode Microplate Reader, VT, USA).
2.2.3. qRT-PCR Assay
Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to determine the quantity of mRNA for caspase 3, caspase 4, caspase 8, caspase 9, PI3K, MEK1, and MEK2. After cultivation of HCT-116 p53-wt cells (6 × 105) in 60-mm dishes overnight, they were treated with IC50 concentrations of tyrphostin A9, 1b, and 2a for 72 h. RNA was extracted (Direct-Zol RNA MicroPrep, Zymo Research, Irvine, CA, USA), and cDNA was prepared using PrimeScript RT Master Mix (TaKaRa, Shiga, Japan). The target genes and the house-keeping gene β-actin were amplified using TB Green Premix Ex Taq II (TaKaRa) on a Line Gene 9680 BioGR instrument. The cDNA template (100 ng) was mixed with the forward and reverse primers (150 nM, OriGene, Rockville, MD, USA, Table S1), 10 µL master mix, and nuclease-free water. The applied thermal conditions were: hold stage at 95 °C for 3 min, 40 cycles of PCR stage at 95 °C for 15 s, 58 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 30 s, with a final extension at 72 °C for 10 min. The RT-PCR reaction was run three times in triplicate for each primer pair.
2.2.4. Caspase Activity
The Caspase 3/4/8/9 Assay Kits (Abbkine, Atlanta, GA, USA) were used to evaluate the activity of caspase 3, 4, 8, and 9 in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. p-Nitroaniline (pNA) production was determined with the Synergy HTX Multimode Reader (BioTek, Shoreline, WA, USA) at 405 nm. The experiment was conducted twice, in triplicate.
2.2.5. TUNEL Assay
Apoptosis induction was studied by the TUNEL (terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labelling) assay using the TACS® 2 TdT-Fluor In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kit (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA). The assay was performed in triplicate according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.2.6. Clonogenic Assay
After cultivation of HCT-116 p53-wt cells (2 × 105) in 6-well tissue culture plates for 24 h, the cells were treated with eight concentrations (0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10, 30 and 100 μM) of tyrphostin A9 for 3 h. 1000 cells (control and tyrphostin A9-treated cells) per well of a 6-well plate were seeded and cultured for 12 days, followed by cell fixing in 6% glutaraldehyde. The cells were stained with crystal violet, and colonies of 50 cells or more were counted.
2.2.7. EGFR and VEGFR-2 Inhibition Assay
The EGFR tyrosine kinase and VEGFR-2 tyrosine kinase kits (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) were used to determine the EGFR inhibition by tyrphostin A9 and erlotinib, and the VEGFR-2 inhibition by tyrphostin A9 and sorafenib. A Biotek Synergy HT Multi-Mode Microplate Reader (VT, USA) was used to measure the luminescence. The percentage of autophosphorylation inhibition by the test compounds was calculated using the following formula: 100—[control/treated-control] using the curves of percentage inhibition of 8 concentrations (0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10, 30, and 100 μM) of each compound. EC50 values were calculated using the EC50 Calculator (AAT Bioquest, Sunnyvale, CA, USA). The experiment was repeated twice in triplicate.
2.2.8. Statistical Analysis
The Student’s t-test was used to determine the differences between two means. Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad prism [GraphPad, free trial option, Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA (version 8.0.2)], and a value of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All experiments were repeated three times.
3. Results
3.1. Antiproliferative Activity
Tyrphostin A9, the RG13022 derivatives 1a and 1b, and the new SF5-substituted analogs 2a and 2b were used in this study (Figure 1). Initially, the test compounds were evaluated for their antiproliferative activity against CRC cells (KRASG13D HCT-116, HCT-116 p53KO, and p53R273H/BRAFV600E HT-29 cells) [27]. For comparison purposes, non-malignant MCF10A mammary, Vero kidney, and MDCK kidney cells were also tested. These three normal cell lines express functional wild-type p53 proteins similar to HCT-116 wild-type cells and thus appear to be suitable non-malignant cell models for this study [28,29,30]. The clinically approved protein kinase inhibitors erlotinib and sorafenib and our previously described tyrphostin Briva served as positive controls (Table 1) [22].

Table 1.
Antiproliferative activity (IC50 in µM 1 after 72 h) of tyrphostin A9 and compounds 1a, 1b, 2a, and 2b against HCT-116 (p53-wt, KRASG13D, BRAF-wt), HCT-116 p53KO, and HT-29 (p53R273H, KRAS-wt, BRAFV600E) CRC cells, and against non-malignant MCF10A mammary, Vero kidney, and MDCK kidney cells. Briva, erlotinib, and sorafenib were used as control compounds.
Tyrphostin A9 and compound 1a showed the highest activity against the KRAS-mutant HCT-116 p53-wt cells, while HCT-116 p53KO and BRAFV600E/p53R273H HT-29 cells were less sensitive to tyrphostin A9 and 1a. Both compounds were twice as active as Briva against the HCT-116 p53-wt cells. Compound 2a was more active against the HCT-116 p53-wt cells than 1b and 2b. Tyrphostin A9 was more active against HCT-116 p53KO than 1a, 1b, 2a, and 2b. Among the tested tyrphostins, 1a was the most cancer-selective compound, apparent from its low activity against the non-malignant cells with selectivity index (SI) values of 4.9 (MCF10A), 9.9 (Vero), and 5.7 (MDCK). Tyrphostin A9 also showed distinctly reduced toxicities to Vero (SI = 6.8) and MDCK kidney cells (SI = 5.3) in comparison to its activity against the wildtype HCT-116 CRC cells. Erlotinib and sorafenib were more active against p53-wt HCT-116 and BRAFV600E/p53R273H HT-29 cells (IC50 below 10 µM). While erlotinib and sorafenib were active against HCT-116 p53-wt and HT-29 cells, tyrphostin A9 and compounds 1a and 2a were distinctly less active against HT-29 cells and showed considerable activity only against HCT-116 cells. Thus, the following mechanistic studies were performed in the HCT-116 p53-wildtype cells, which turned out to be most sensitive to the test compounds.
3.2. Expression of Caspase and Kinase mRNAs
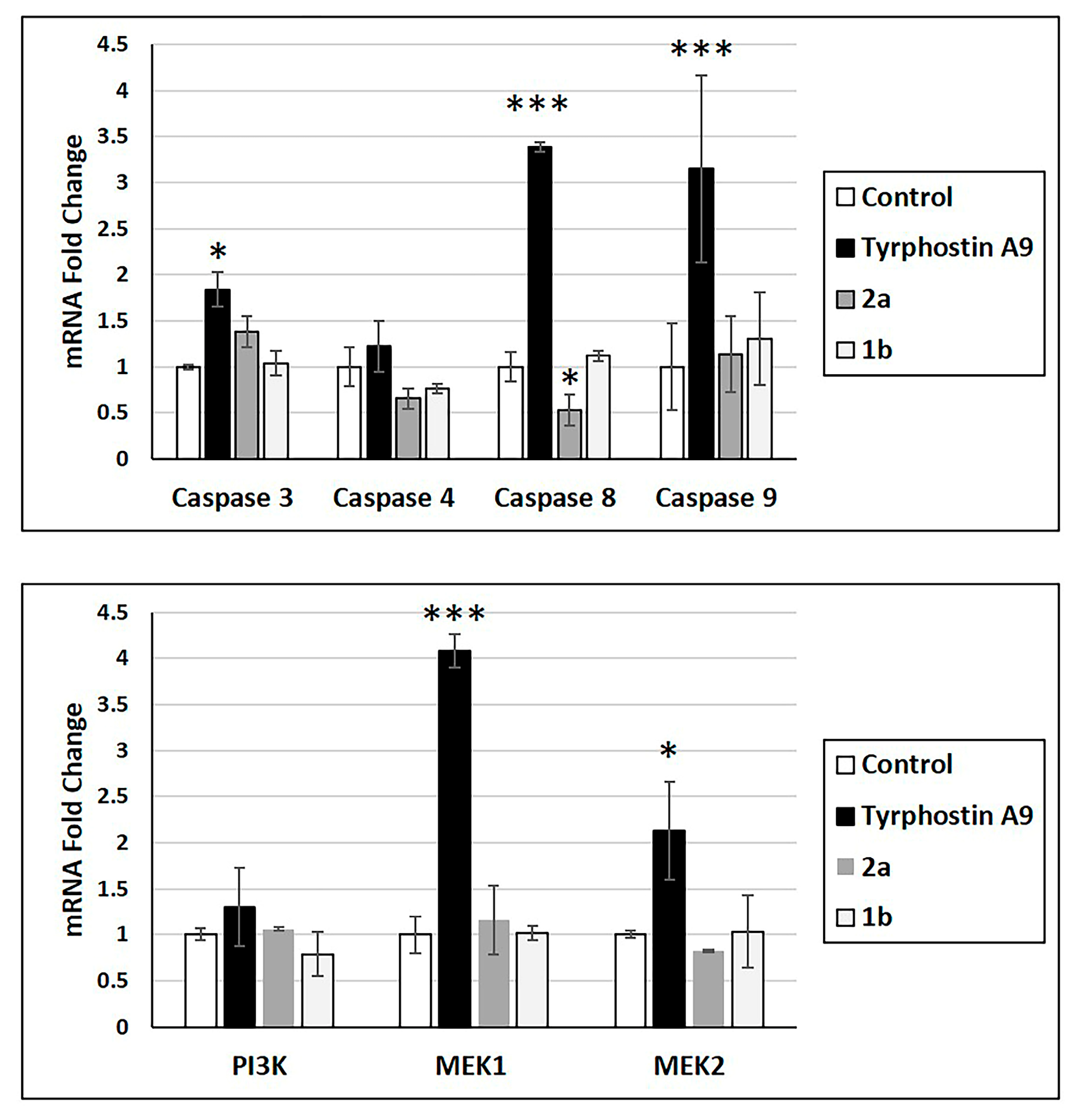
Anticancer drugs can alter the mRNA expression of essential proteins. Thus, the effects of tyrphostin A9, 1b, and 2a on mRNA expression of caspase 3, 4, 8, and 9, as well as protein kinases PI3K, MEK1, and MEK2 were studied (Figure 2). Only tyrphostin A9 led to increased mRNA expression of caspase 3, caspase 8, and caspase 9, as well as of MEK1 and MEK2. Tyrphostin A9 exhibited a slight insignificant upregulation of caspase 4 and PI3K mRNA. Notably, 1b showed only a slight increase in caspase 9 mRNA and downregulation of caspase 4 and PI3K, while 2a downregulated caspase 4 and caspase 8 more strongly (caspase 8 even significantly). The upregulation of caspase 3, caspase 8, and caspase 9 might be a hint at an efficient apoptosis induction by tyrphostin A9 in HCT-116 p53-wt cells.
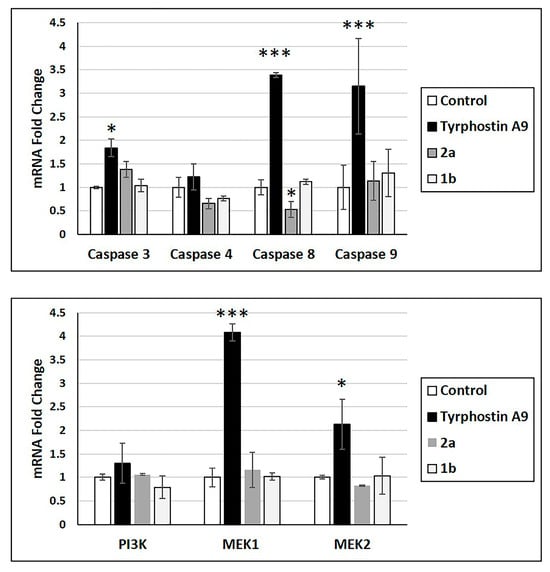
Figure 2.
mRNA expression of indicated caspases and protein kinases (RT-PCR) in HCT-116 (p53-wt) cells treated with tyrphostin A9, 1b, and 2a at IC50 doses after 72 h. Values are the means of three independent experiments (± SD). * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001.
3.3. Apoptosis Induction—Caspase Activity and DNA Fragmentation
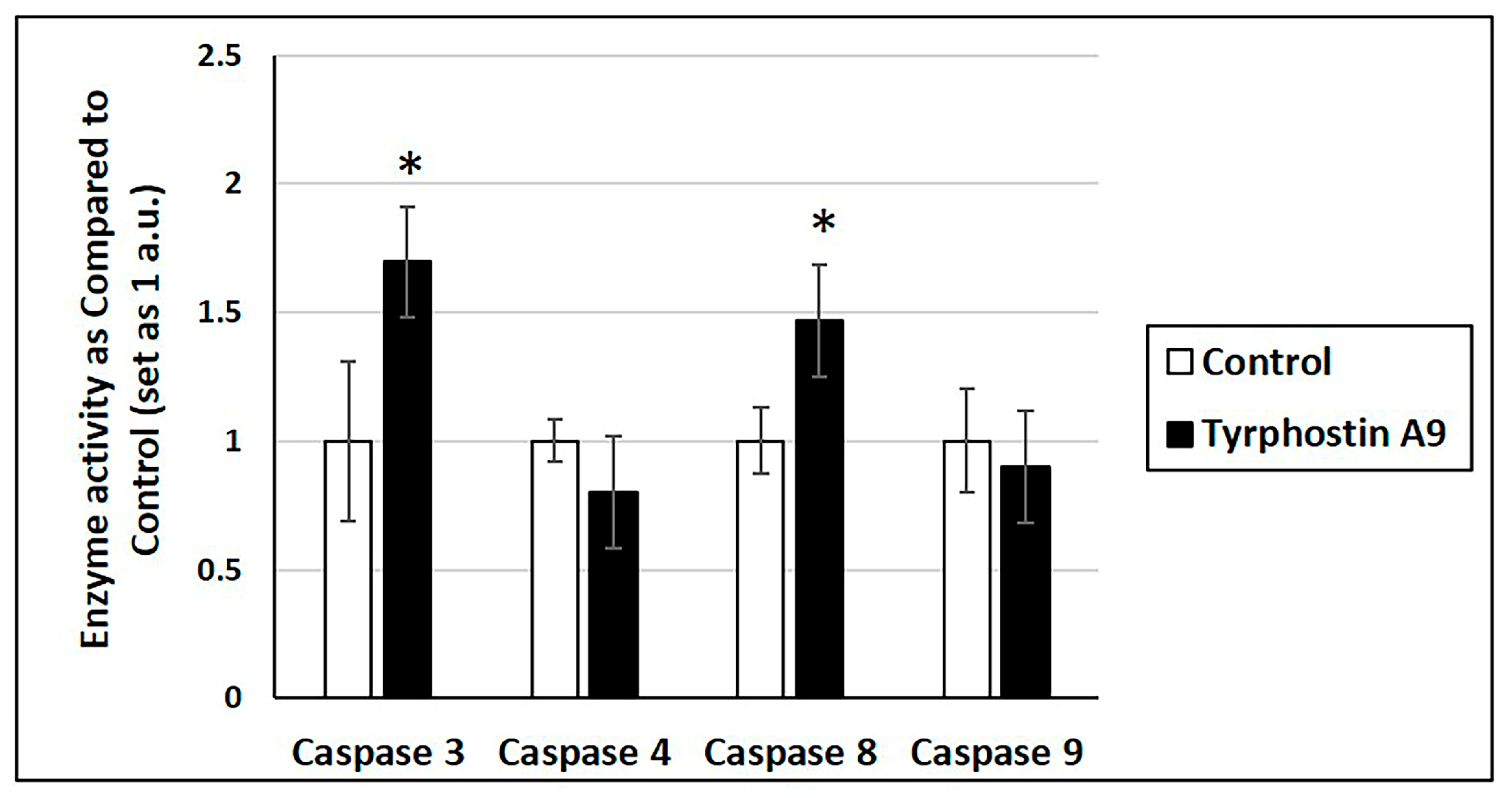
Increased mRNA expression may not always translate into increased cellular activity. Thus, tyrphostin A9 was further investigated for its influence on caspase enzyme activity (Figure 3). Notably, tyrphostin A9 increased the activities of caspase 3 and caspase 8, which is in line with the upregulated mRNA expression of these enzymes by this compound. But despite the strongly increased caspase 9 mRNA production, tyrphostin A9 did not enhance caspase 9 activity. No increase in caspase 4 activity was observed either, which could be expected based on the absent mRNA induction by tyrphostin A9.
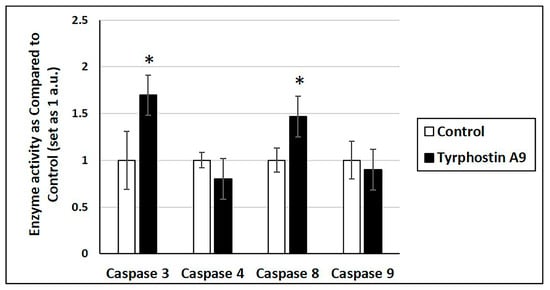
Figure 3.
Caspase activity in HCT-116 (p53-wt) cells treated with tyrphostin A9 at IC50 dose for 72 h by colorimetric assays. Values are the means of two independent experiments (±SD). * p < 0.05.
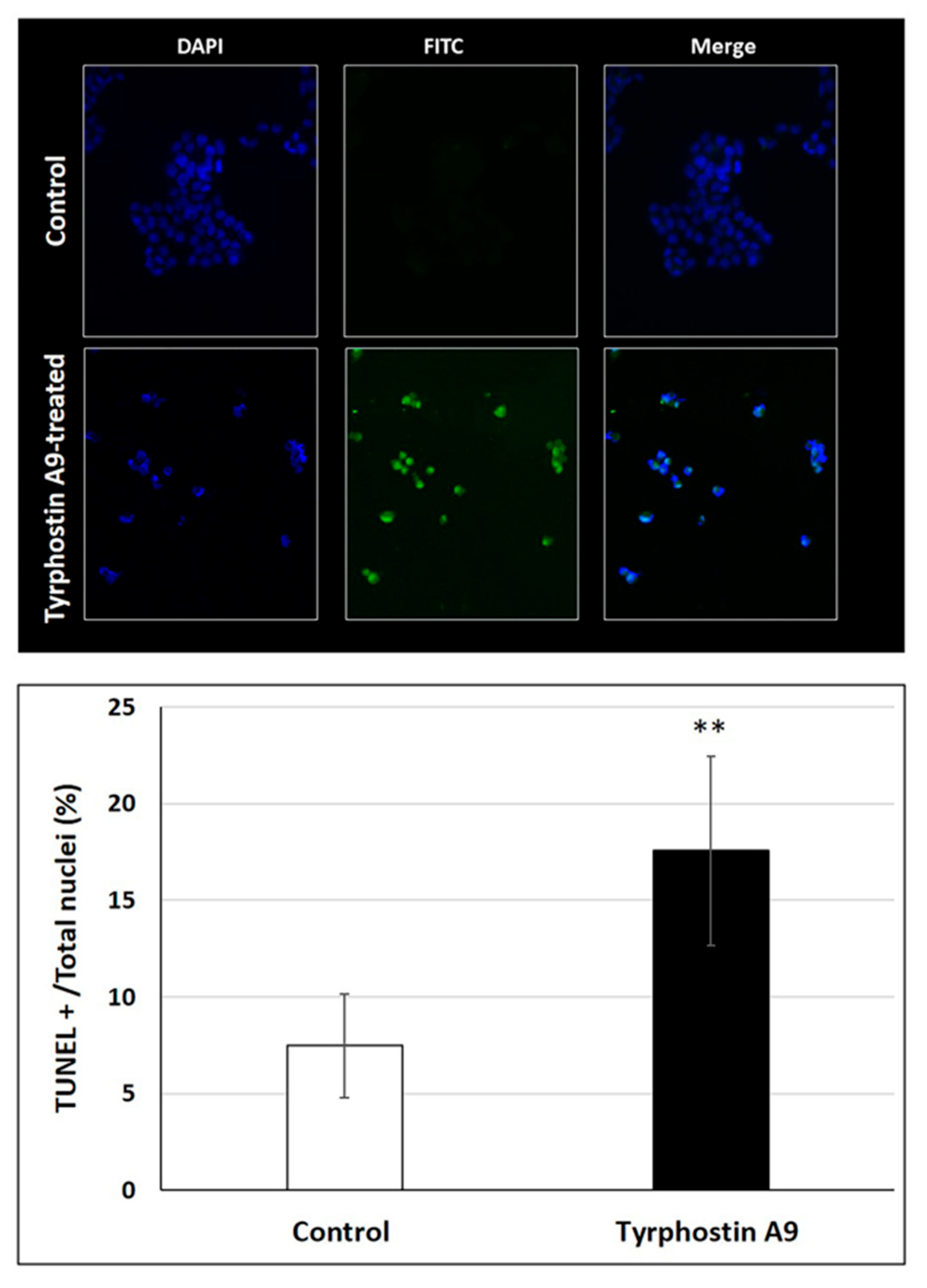
DNA fragmentation as a consequence of apoptosis induction by tyrphostin A9 was also investigated by the TUNEL assay (Figure 4). As expected, tyrphostin A9 led to a much higher degree of DNA fragmentation in HCT-116 cells when compared with untreated cells. The strong DNA fragmentation induced by tyrphostin A9 is an indicator of the pro-apoptotic properties of this compound and is in line with its observed activation of caspase 3 in these CRC cells.
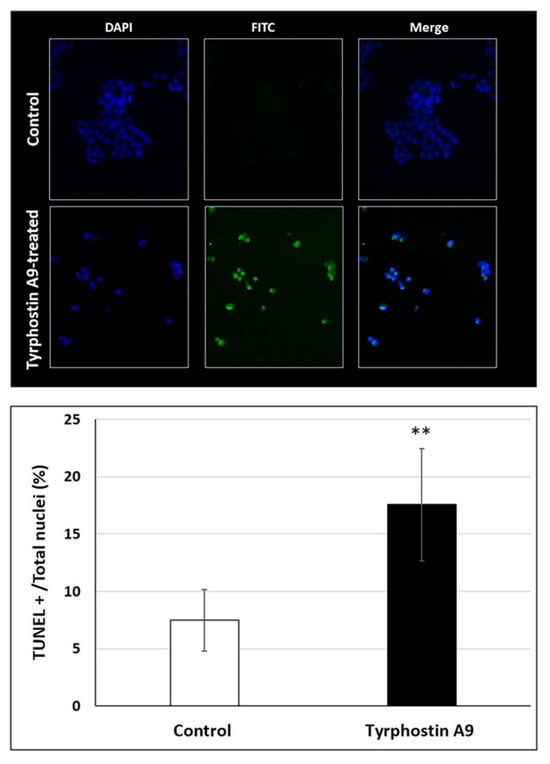
Figure 4.
DNA fragmentation in HCT-116 (p53-wt) cells treated with IC50 doses of tyrphostin A9 for 72 h according to the TUNEL assay. Values are the means of three independent experiments (±SD). ** p < 0.01.
3.4. Colony Formation
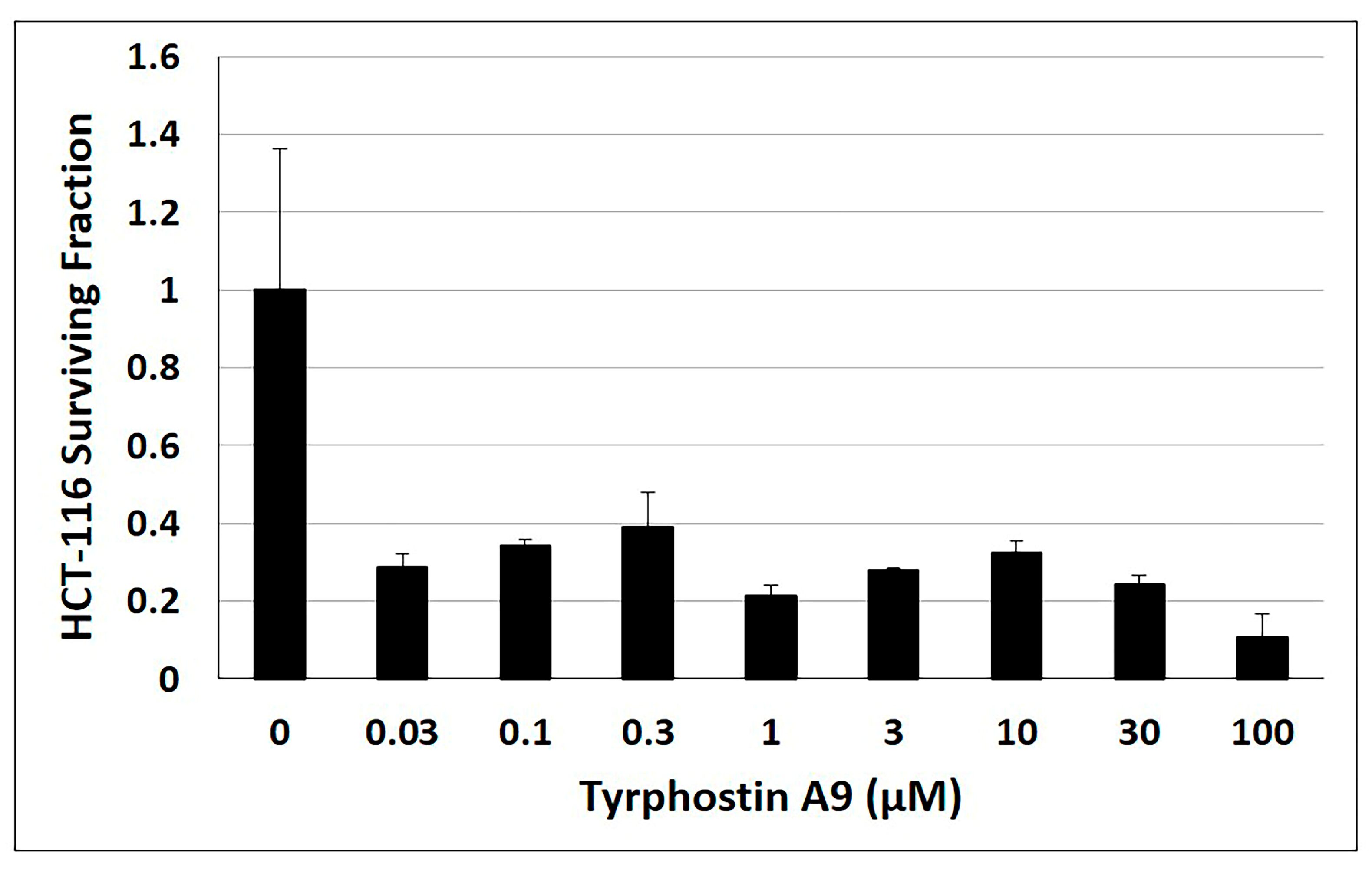
An important property of potent anticancer agents is the ability to suppress tumor cell growth for a longer time period. Hence, the anti-clonogenic properties of tyrphostin A9 in HCT-116 p53-wt cells were also investigated over 12 days (Figure 5). Tyrphostin A9 effectively inhibited HCT-116 cell colony formation at low doses (as low as 0.03 µM), indicating the long-term action of this kinase inhibitor in CRC cells.
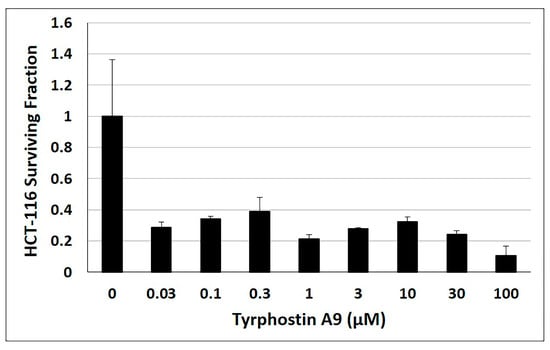
Figure 5.
Clonogenic assay with HCT-116 (p53-wt) cells treated with tyrphostin A9 for 12 days at the indicated concentrations. Values are the means of three independent experiments (±SD).
3.5. Inhibition of EGFR and VEGFR-2
As described above, tyrphostin A9 was identified as an inhibitor of protein kinases such as PDGFR and PYK2. Moreover, an early study with tyrphostin A9 reported its inhibitory effect on EGFR phosphorylation [15]. Thus, we investigated the inhibition of the RTKs EGFR and VEGFR-2 by tyrphostin A9 and compared the outcome with the activity of the known inhibitors erlotinib and sorafenib (Table 2). Indeed, tyrphostin A9 displayed EGFR and VEGFR-2 inhibition with EC50 values of 48.5 nM and 28.2 nM, respectively. Thus, tyrphostin A9 was almost twice as active against VEGFR-2 as against EGFR. Although tyrphostin A9 did not reach the activities of erlotinib and sorafenib, the dual inhibition of EGFR and VEGFR-2 adds well to the current knowledge of anticancer properties of this tyrphostin compound.

Table 2.
EGFR and VEGFR-2 kinase enzyme inhibition activities of tyrphostin A9 and positive controls (erlotinib, sorafenib) presented as EC50 (nM). Results are means ± SD from two independent experiments performed in triplicate.
4. Discussion
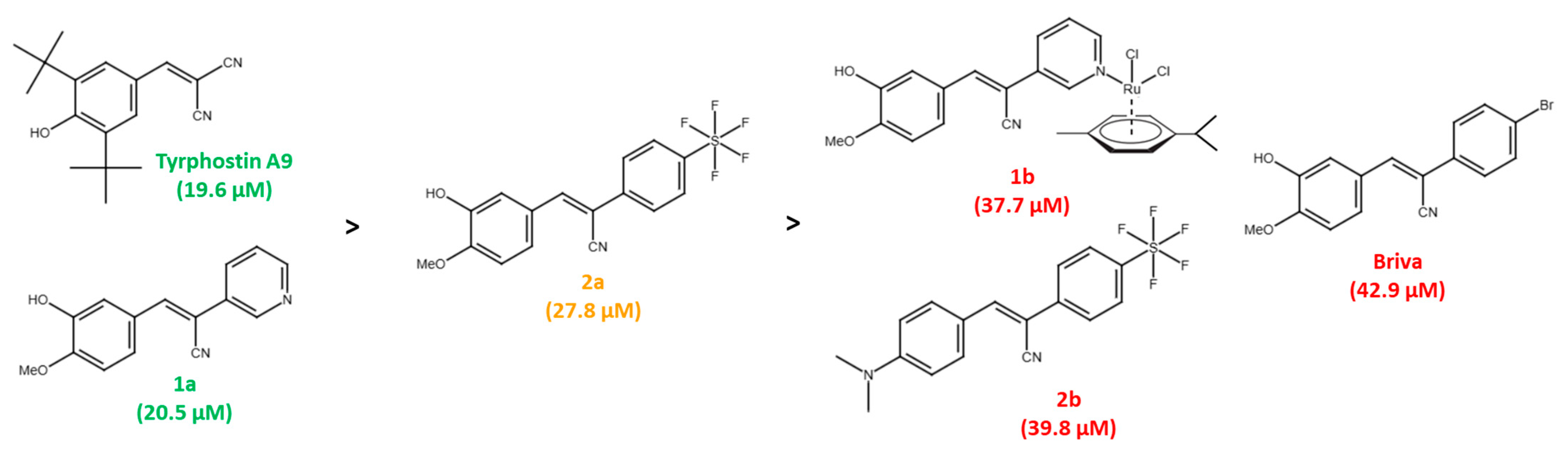
Among a small series of tyrphostin derivatives, tyrphostin A9 turned out to be the most promising derivative in KRAS-mutant CRC cells. The selectivity of tyrphostin A9 and compounds 1a and 2a for HCT-116 cells is remarkable when compared with the HT-29 selectivity of our previously published tyrphostin derivative Briva [22]. In particular, the structures of Briva, 1a and 2a are closely related. However, in contrast to Briva, both 1a and 2a were only weakly active against HT-29 cells but more active than Briva against the p53-wt HCT-116 cells. Thus, replacement of the 4-bromophenyl moiety of Briva by the 3-pyridyl ring of 1a, and of Briva’s 4-bromo substituent by a 4-SF5 group in 2a, can already lead to pronounced activity shifts. In addition, modification of the pyridine ring of 1a by ruthenation (=complex 1b) and replacement of the isovanillyl moiety of 2a by the N,N-dimethylaminophenyl ring in 2b led to reduced antiproliferative activity against p53-wt HCT-116 cells (Figure 6). The molecular reasons for these activity discrepancies remain to be studied. Although further modifications of 1a and 2a to yield compounds 1b (Ru complex) and 2b (N,N’-dimethylamino derivative) did not lead to enhanced activities against CRC cells, chemical fine-tuning of 1a and 2a still seems to be possible to achieve stronger anti-CRC effects, especially in KRAS-mutant cells.
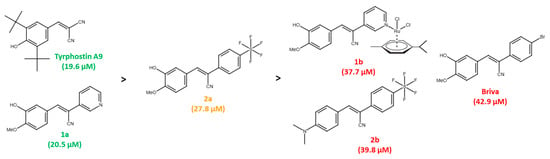
Figure 6.
Activity ranking of tyrphostins against p53-wt HCT-116 cells (green: compounds with highest activities; orange: compound with mediocre activity; red: compounds with lowest activities; IC50 values in brackets).
Since preclinical data of tyrphostin A9 in CRC are scarce, the results obtained for this tyrosine kinase inhibitor in KRAS-mutant HCT-116 CRC cells in the present study add to its well-known portfolio of anticancer activities. The selectivity of tyrphostin A9 for KRAS-mutant and p53-wt CRC cells is noteworthy. The induction of MEK1 and MEK2 mRNA expression in tyrphostin A9-treated HCT-116 cells can be a cellular response to the tyrosine kinase inhibitory activities of tyrphostin A9 and a mechanism to bypass and circumvent the action of tyrphostin A9 on PDGFR and the newly discovered dual EGFR/VEGFR-2 targeting [31]. Tyrphostin A9 was shown before to activate ERK1/2, the downstream factors of MEKs, in neuroblastoma cells and in an in vivo model [32]. It should be mentioned that both HCT-116 and HT-29 cells also have hyper-activating PIK3CA mutations (H1047R in HCT-116 cells, and P449T in HT-29 cells) [27]. The consequently upregulated PI3K signaling pathway is crucial for the development of resistance to drugs targeting RAS-MAPK signaling, and PIK3CAH1047R tumors were especially resistant to anti-EGFR antibody therapy, which renders the activity of tyrphostin A9 against HCT-116 cells more intriguing [10,33,34].
To our knowledge, this is the first description of a dual EGFR/VEGFR-2 inhibition by tyrphostin A9. Since resistance to RAS-MAPK inhibitors included upregulation of RTKs such as PDGFR, EGFR, and VEGFR-2, the multi-target approach was shown to be a promising strategy for the treatment of certain cancers dependent on dysregulated RAS-MAPK signaling [10]. Recently, tyrphostin A9 led to inhibition of macropinocytosis in KRAS-mutant pancreatic ductal carcinoma cells, which was accompanied by growth inhibition [35]. Macropinocytosis in cancer cells is activated by EGFR-induced RAS-MAPK and PI3K-AKT signaling [36]. If tyrphostin A9 also inhibits macropinocytosis in KRAS-mutant CRC cells, this remains to be shown. But it was reported that KRAS-mutant CRC cells under nutrient deprivation conditions induce macropinocytosis [37]. Moreover, macropinocytosis was upregulated in HCT-116 cells independent of the p53 status (wildtype vs. p53-knockout cells), indicating the vital role of mutant KRAS for this process in CRC cells. The anthelminthic salicylanilide drug niclosamide, which acts as a STAT3 inhibitor and as a protonophor on mitochondria, strongly suppressed macropinocytosis in HCT-116 cells by inhibition of the amino acid transporter SLC38A5 [38]. Notably, tyrphostin A9 was also reported to be a mitochondria-damaging protonophor and STAT3 inhibitor in cancer cells [17,39].
Tyrphostin A9 activated caspase 3 and induced DNA fragmentation in HCT-116 p53-wt cells, which are hallmarks of apoptotic cell death. But it cannot be excluded that further cell death mechanisms also contribute to the activity of tyrphostin A9. Caspase 3 is an important effector caspase and crucial for the induction of apoptosis. In CRC tissues, caspase 3 was downregulated in comparison with marginal colon tissues [40]. Increased levels of activated (cleaved) caspase 3 in colorectal tumor stroma were a sign of a good prognosis [41]. Apoptosis induction by tyrphostin A9 can be correlated with its kinase inhibitory activity; however, tyrphostin A9 was also described as a potent mitochondria-damaging agent [42,43,44]. Notably, tyrphostin A9 strongly enforced caspase 8 mRNA expression, while compound 2a significantly reduced caspase 8 mRNA levels. The relevance of these observations remains to be shown. Aside from its prominent pro-apoptotic activities, caspase 8 also has non-apoptotic properties. It was reported that caspase 8 mRNA is upregulated in CRC tissues [40]. Depending on the tumor context, caspase 8 can either promote cancer cell death or enhance malignancy [45].
Long-term anticancer activity of tyrphostin A9 was confirmed by inhibition of HCT-116 cell colony formation. This finding is relevant since tumors undergoing protein kinase inhibitor therapy can quickly develop drug resistance [46]. Notably, targeting of both RTK and mitochondria can suppress CRC stem cells, which is required to prevent tumor regrowth and relapse [12,47]. The effects of tyrphostin A9 on HCT-116 cells are remarkable since there is a report of the combination of the dual EGFR/VEGFR inhibitor AEE778 with the COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib, which was only active against Caco-2 CRC cells, including inhibition of stemness-related pathways, but not against KRAS-mutant HCT-116 cells [48]. It seems that tyrphostin A9 can circumvent the EGFR-inhibitor resistance mechanism of mutant KRAS in CRC cells. But its activity appears to be p53-dependent since the HCT-116 p53KO cells were less sensitive to tyrphostin A9. The p53R273H HT-29 cells were even less sensitive than the HCT-116 p53KO cells, which is in line with the previously reported p53R273H-mediated promotion of HT-29 cell survival [49]. It is conceivable that wildtype p53 contributes to the mechanism of apoptosis induction by tyrphostin A9 in HCT-116 cells as it was reported for a different acrylonitrile derivative before [50]. The transcription factor p53 is of importance in the prognosis of CRCs, and KRAS-mutant CRCs, which also have mutant p53, were associated with poor patient survival [51]. However, inhibitors of protein kinases can become useful for the therapy of such problematic CRCs, and a recent study showed that trametinib (MEK inhibitor) plus onvansertib (PLK1 inhibitor) acted synergistically in KRAS- and p53-mutant CRC [52].
MEK inhibitor resistance was accompanied by upregulation of RTKs such as EGFR; however, combination therapies with inhibitors of EGFR and MEK were inefficient in terms of apoptosis induction in lung cancer cells, while combined VEGFR and MEK inhibition effectively inhibited lung tumor growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis [53]. Hence, a combination of the pro-apoptotic dual EGFR/VEGFR-2 inhibitor tyrphostin A9 might alleviate the shortcomings of EGFR and MEK inhibitor combinations. In addition to MEK inhibitors, the relatively new class of RAS inhibitors can provide suitable combination partners for tyrphostin A9 in KRAS-mutant CRCs [54]. Moreover, several disclosed compounds inhibiting EGFR, VEGFR, and PDGFR were distinctly active against HCT-116 CRC cells, which underlines the potential of tyrphostin A9 for the therapy of KRAS-mutant CRCs [55,56].
Since tyrphostin A9 exhibited notable immunomodulatory activities, including inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase, STAT3, and NF-κB, the investigation of this compound in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors appears to be promising [19,39,57]. A triple inhibition of MEK, EGFR, and PD-L1 led to promising effects on MEK inhibitor-resistant CRC models, which supports a potential role of tyrphostin A9 as combination partner with MEK and immune checkpoint inhibitors [58].
The described activities and mechanisms of tyrphostin A9 in KRAS-mutant p53-wt CRC cells might pave the way for advanced preclinical evaluations of this compound in suitable CRC models. This is supported by the fact that tyrphostin A9, also as an oral drug, has already shown tolerability and efficacy in other in vivo models (glioblastoma and autoimmune encephalomyelitis) [32,42]. Moreover, tyrphostin A9 is not a substrate of the notorious drug efflux pump Pgp that mediates multi-drug resistance to many anticancer drugs, and it can sensitize cancer cells to other anticancer drugs, e.g., glioblastoma cells to the alkylating agent BCNU, which renders this compound a suitable co-drug for combination therapies [59,60].
5. Conclusions
The discovery of the selective activity of tyrphostin A9 against KRAS-mutant HCT-116 cells is of importance for the future development of this drug candidate as a treatment for CRC patient subgroups. The pro-apoptotic mechanism, which is probably p53-dependent, and the dual EGFR/VEGFR-2 inhibitory activity of tyrphostin A9 provide useful insights into the anticancer potential of this compound. Moreover, further tyrphostin derivatives selective for HCT-116 cells with wildtype p53 were identified, which warrant deeper investigations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/futurepharmacol5040057/s1, synthetic procedures and analysis of new compounds 2a and 2b; Figures S1 and S2: EGFR and VEGFR-2 inhibition, original graphs; Figures S3–S6: 1H and 13C NMR spectra of new compounds 2a and 2b; Figures S7 and S8: EI-MS spectra of new compounds 2a and 2b; Table S1: Sequences of primers used in the current study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.B., R.S. and L.H.T.; methodology, B.B. and L.H.T.; formal analysis, B.B. and L.H.T.; investigation, A.Y.A., M.A.H., N.A.H., K.M.S. and S.R.Y.; resources, R.S. and L.H.T.; data curation, B.B. and L.H.T.; writing—original draft preparation, B.B. and L.H.T.; writing—review and editing, A.Y.A., M.A.H., N.A.H., K.M.S., S.R.Y. and R.S.; supervision, L.H.T.; project administration, B.B. and L.H.T.; funding acquisition, L.H.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research, the Hashemite University, grant number 111/2022.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Original data associated with this article can be obtained from the authors upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BCNU | Bis-dichloroethyl-N-nitrosourea |
| BMN | Benzylidenemalononitrile |
| BRAF | B-rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma |
| CRC | Colorectal carcinoma |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MEK | MAPK/ERK kinase |
| mCRC | Metastatic colorectal cancer |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-κB |
| PDGFR | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor |
| PD-L1 | Programmed death-ligand 1 |
| Pgp | P-glycoprotein |
| PIK3CA | Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha |
| PLK1 | Polo-like kinase 1 |
| PYK2 | Proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 |
| RAS | Rat sarcoma |
| RTK | Receptor tyrosine kinase |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| VEGFR-2 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 |
References
- Hossain, M.S.; Karuniawati, H.; Jairoun, A.A.; Urbi, Z.; Ooi, D.J.; John, A.; Lim, Y.C.; Kibria, K.M.K.; Mohiuddin, A.M.; Ming, L.C.; et al. Colorectal cancer: A review of carcinogenesis, global epidemiology, current challenges, risk factors, preventive and treatment strategies. Cancers 2022, 14, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafa, M.A.; Farhat, K. Colorectal cancer in the Arab world—Screening practices and future prospects. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 7425–7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imyanitov, E.; Kuligina, E. Molecular testing for colorectal cancer: Clinical applications. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 13, 1288–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Garcia, E.; Argiles, G.; Elez, E.; Tabernero, J. BRAF mutant colorectal cancer: Prognosis, treatment, and new perspectives. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2648–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrantonio, F.; Cremolini, C.; Petrelli, F.; di Bartolomeo, M.; Loupakis, F.; Maggi, C.; Antoniotti, C.; de Braud, F.; Falcone, A.; Iacovelli, R. First-line anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies in panRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2015, 96, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardekani, G.S.; Jafarnejad, S.M.; Tan, L.; Saeedi, A.; Li, G. The prognostic value of BRAF mutation in colorectal cancer and melanoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47054. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Xu, A.T.; Zu, M.M.; Tong, J.L.; Xu, X.T.; Ran, Z.H. Predictive and prognostic roles of BRAF mutation in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer treated with anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies: A meta-analysis. J. Dig. Dis. 2013, 14, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Wu, X.Y.; Huang, Y.F.; Di, M.Y.; Zheng, D.Y.; Chen, J.Z.; Ding, H.; Mao, C.; Tang, J.L. Promising biomarkers for predicting the outcomes of patients with KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer treated with anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 1914–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassilli, E.; Cerrito, M.G. Emerging actionable targets to treat therapy-resistant colorectal cancers. Cancer Drug Resist. 2022, 5, 36–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biersack, B.; Tahtamouni, L.; Höpfner, M. Role and function of receptor tyrosine kinases in BRAF mutant cancers. Receptors 2024, 3, 58–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziranu, P.; Lai, E.; Schirripa, M.; Puzzoni, M.; Persano, M.; Pretta, A.; Munari, G.; Liscia, N.; Pusceddu, V.; Loupakis, F.; et al. The role of p53 expression in patients with RAS/BRAF wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer receiving irinotecan and cetuximab as later line treatment. Target. Oncol. 2021, 16, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Aranda, M.; Redondo, M. Targeting receptor kinases in colorectal cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitzki, A. Tyrphostins: Tyrosine kinase blockers as novel antiproliferative agents and dissectors of signal transduction. FASEB J. 1992, 6, 3275–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitzki, A.; Mishani, E. Tyrphostins and other tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2006, 75, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, J.; Dye, J.F.; Schachter, M.; Guillou, P.J. Inhibition of pancreatic cancer cell growth in vitro by the tyrphostin group of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Br. J. Cancer 1993, 68, 1122–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Finlay, G.A.; Hunter, D.S.; Walker, C.L.; Paulson, K.E.; Fanburg, B.L. Regulation of PDGF production and ERK activation by estrogen is associated with TSC2 gene expression. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2003, 285, C409–C418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, A.M.; Kaur, G.; Alley, M.C.; Supko, J.G.; Malspeis, L.; Grever, M.R.; Sausville, E.A. Tyrphostin AG17, [(3,5-Di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzylidene)-malononitrile], inhibits cell growth by disrupting mitochondria. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 2794–2799. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Luk, F.; Jaiswal, R.; Bebawy, M. Microparticles mediate the intercellular regulation of microRNA-503 and proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 to alter the migration and invasion capacity of breast cancer cells. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molitor, M.; Menge, A.; Mandel, S.; George, S.; Müller, S.; Knapp, S.; Hofmann, B.; Steinhilber, D.; Häfner, A.-K. Unlocking the potential: Unveiling tyrphostins with Michael-reactive cyanoacrylate motif as promising inhibitors of human 5-lipoxygenase. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2024, 476, 1913–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, T.; Lyall, R.M.; Alsina, M.M.; Persons, P.E.; Spada, A.P.; Levitzki, A.; Zilberstein, A.; Mundy, G.R. The antiproliferative effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors tyrphostins on a human squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in nude mice. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 4430–4435. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Biersack, B.; Zoldakova, M.; Effenberger, K.; Schobert, R. (Arene)Ru(II) complexes of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibiting tyrphostins with enhanced selectivity and cytotoxicity in cancer cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1972–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, K.; Al Sakhen, M.; Kanaan, S.; Yasin, S.; Höpfner, M.; Tahtamouni, L.; Biersack, B. Antitumor activity of the new tyrphostin briva against BRAFV600E-mutant colorectal carcinoma cells. Investig. New Drugs 2023, 41, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomonte, S.; Zanda, M. Synthetic chemistry and biological activity of pentafluorosulphanyl (SF5) organic molecules. J. Fluor. Chem. 2012, 143, 57–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowaileh, M.F.; Hazlitt, R.A.; Colby, D.A. Application of the pentafluorosulfanyl group as a bioisosteric replacement. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nasr, I.S.; Hanachi, R.; Said, R.B.; Rahali, S.; Tangour, B.; Abdelwahab, S.I.; Farasani, A.; Taha, M.M.E.; Bidwai, A.; Koko, W.S.; et al. p-Trifluoromethyl- and p-pentafluorothio-substituted curcuminoids of the 2,6-di[(E)-benzylidene)]cycloalkanone type: Syntheses and activities against Leishmania major and Toxoplasma gondii parasites. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 114, 105099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, D.; Eide, P.W.; Eilertsen, I.A.; Danielsen, S.A.; Eknæs, M.; Hektoen, M.; Lind, G.E.; Lothe, R.A. Epigenetic and genetic features of 24 colon cancer cell lines. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, W.; Chen, X. Mutant p53 disrupts MCF-10A cell polarity in three-dimensional culture via epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 16218–16228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granja, A.G.; Nogal, M.L.; Hurtado, C.; Salas, J.; Salas, M.L.; Carrascosa, A.L.; Revilla, Y. Modulation of p53 cellular function and cell death by African swine fever virus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 7165–7174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Ishibashi, K.; Mano, H.; Kitamoto, S.; Sato, N.; Hoshiba, K.; Kato, M.; Matsuzawa, F.; Takeuchi, Y.; Shirai, T.; et al. Mutant p53-expressing cells undergo necroptosis via cell competition with the neighboring normal epithelial cells. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 3721–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yue, L.; Xu, P.; Hu, W. An overview of agents and treatments for PDFGRA-mutated gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 927587. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Pei, M.; Long, J.; Dong, X.; Chen, Y.-L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, G.; et al. Tyrphostin A9 protects axons in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through activation of ERKs. Life Sci. 2022, 294, 120383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Tang, R.; Jiang, L.; Jia, Y. The role of PIK3CA gene mutations in colorectal cancer and the selection of treatment strategies. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1494802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sütcüoğlu, O.; Yıldırım, H.Ç.; Almuradova, E.; Günenç, D.; Yalçın, Ş. RAS mutations in advanced colorectal cancer: Mechanisms, clinical implications, and novel therapeutic approaches. Medicina 2025, 61, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambillasca, S.; Cera, M.R.; Andronache, A.; Dey, S.K.; Fagá, G.; Fancelli, D.; Frittoli, E.; Pasi, M.; Robusto, M.; Varasi, M.; et al. Novel selective inhibitors of macropinocytosis-dependent growth in pancreatic ductal carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 177, 116991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, R.; Qu, J.; Li, W. Survival strategies of cancer cells: The role of macropinocytosis in nutrient acquisition, metabolic reprogramming, and therapeutic targeting. Autophagy 2025, 21, 693–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanada, K.; Kawada, K.; Nishikawa, G.; Toda, K.; Maekawa, H.; Nishikawa, Y.; Masui, H.; Hirata, W.; Okamoto, M.; Kiyasu, Y.; et al. Dual blockade of macropinocytosis and asparagine bioavailability shows synergistic anti-tumor effects on KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2021, 522, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Sennoune, S.R.; Dharmalingam-Nandagopal, G.; Sivaprakasam, S.; Bhutia, Y.D.; Ganapathy, V. Impact of oncogenic changes in p53 and KRAS on macropinocytosis and ferroptosis in colon cancer cells and anticancer efficacy of niclosamide with differential effects on these two processes. Cells 2024, 13, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtick, U.; Vockerodt, M.; Pinkert, D.; Schoof, N.; Stürzenhofecker, B.; Kussebi, N.; Lauber, K.; Wesselborg, S.; Löffler, D.; Horn, F.; et al. STAT3 is essential for Hodgkin lymphoma cell proliferation and is a target of tyrphostin AG17 which confers sensitization for apoptosis. Leukemia 2005, 19, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, M.; Shanehbandi, D.; Kermani, T.A.; Sanaat, Z.; Zafari, V.; Hashemzadeh, S. Expression level of caspase genes in colorectal cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 1277–1280. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, P.; Vyas, M.; Al-Attar, A.; Durrant, S.; Scholefield, J.; Durrant, L. High levels of cleaved caspase-3 in colorectal tumour stroma predict good survival. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 2097–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, N.; Babu, D.; Madigubba, S.; Panigrahi, M.; Phanithi, P.B. Tyrphostin A9 attenuates glioblastoma growth by suppressing PYK2/EGFR-ERK signaling pathway. J. Neurooncol. 2023, 163, 675–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Park, Y.J.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, E.S.; Hwang, J.J.; Jin, D.-H.; Kim, J.C.; Cho, D.-H. A receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, tyrphostin A9 induces cancer cell death through Drp1 dependent mitochondria fragmentation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 408, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, H.; Noguchi, N.; Yokoyama, H.; Ise, H.; Jin, C.Z.; Kasai, S.; Taira, Z. Design and synthesis of new mitochondrial cytotoxin N-thiadiazolylanilines that inhibit tumor cell growth. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1996, 4, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupack, D.G. Caspase-8 as a therapeutic target in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 332, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabnis, A.J.; Bivona, T.G. Principles of resistance to targeted cancer therapy: Lessons from basic and translational cancer biology. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainho, M.d.A.; Siqueira, P.B.; de Amorim, Í.S.S.; Mencalha, A.L.; Thole, A.A. Mitochondria in colorectal cancer stem cells—A target in drug resistance. Cancer Drug Resist. 2023, 6, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, A.; Penarando, J.; Canas, A.; López-Sánchez, L.M.; Conde, F.; Hernández, V.; Peralbo, E.; López-Pedrera, C.; de la Haba-Rodríguez, J.; Aranda, E.; et al. Simultaneous inhibition of EGFR/VEGFR and cyclooxygenase-2 targets stemness-related pathways in colorectal cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.S.; Tiong, K.H.; Choo, H.L.; Chung, F.F.-L.; Hii, L.-W.; Tan, S.H.; Yap, I.K.S.; Pani, S.; Khor, N.T.W.; Wong, S.F.; et al. Mutant p53-R273H mediates cancer cell survival and anoikis resistance through AKT-dependent suppression of BCL2-modifying factor (BMF). Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.F.; Ibrahim, N.S.; Saddiq, A.A.; Abdelhamid, I.A. Novel 3-(pyrazol-4-yl)-2-(1H-indole-3-carbonyl)acrylonitrile derivatives induce intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic death mediated p53 in HCT116 colon carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebl, M.C.; Hofmann, T.G. The role of p53 signaling in colorectal cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-E.; Oh, H.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, Y.-B.; Kim, S.-T.; Yim, H. Synergistic two-step inhibition approach using a combination of trametinib and onvansertib in KRAS and TP53-mutated colorectal adenocarcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2025, 182, 117796. [Google Scholar]
- Kun, E.; Tsang, Y.T.M.; Ng, C.W.; Gershenson, D.M.; Wong, K.K. MEK inhibitor resistance mechanisms and recent developments in combination trials. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 92, 102137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, D.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, W.; Li, N.; Yan, X. Targeting KRAS in colorectal cancer (Review). Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 23, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allawi, M.M.; Mahmood, A.A.R.; Tahtamouni, L.H.; Saleh, A.M.; Kanaan, S.I.; Saleh, K.M.; AlSakhen, M.F.; Himsawi, N.; Yasin, S.R. Anti-proliferation evaluation of new derivatives of indole-6-carboxylate ester as receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Future Med. Chem. 2024, 16, 1313–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzahabi, H.S.A.; Nossier, E.S.; Khalifa, N.M.; Alasfoury, R.A.; El-Manawaty, M.A. Anticancer evaluation and molecular modeling of multi-targeted kinase inhibitors based pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidine scaffold. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2018, 33, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, A.R.; Bradley, R.; Ganju, R.K. LPS-induced MCP-1 expression in human microvascular endothelial cells is mediated by the tyrosine kinase, Pyk2 via the p38 MAPK/NF-κB dependent pathway. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, S.; Matrone, N.; Muddassir, A.L.; Martini, G.; Sorokin, A.; de Falco, V.; Giunta, E.F.; Ciardiello, D.; Martinelli, E.; Belli, V.; et al. Triple blockade of EGFR, MEK and PD-L1 has antitumor activity in colorectal cancer models with constitutive activation of MAPK signaling and PD-L1 overexpression. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, R.; Furqan, M.; Ullah, R.; Mithani, A.; Saleem, R.S.Z.; Faisal, A. A cell-based high-throughput screen identifies inhibitors that overcome P-glycoprotein (Pgp)-mediated multidrug resistance. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.C.; Ullyatt, E. Chemosensitization of glioblastoma cells to bis-dichloroethyl-nitrosourea with tyrphostin AG17. Clin. Cancer Res. 1998, 4, 773–781. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).