Future Pharmacotherapy for Bipolar Disorders: Emerging Trends and Personalized Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Evolving Understanding of Bipolar Pathophysiology
3.1. Genetic and Epigenetic Insights
3.2. Neuroinflammation and Immune Dysregulation
3.3. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress
3.4. Neurotransmitter and Receptor System Imbalances
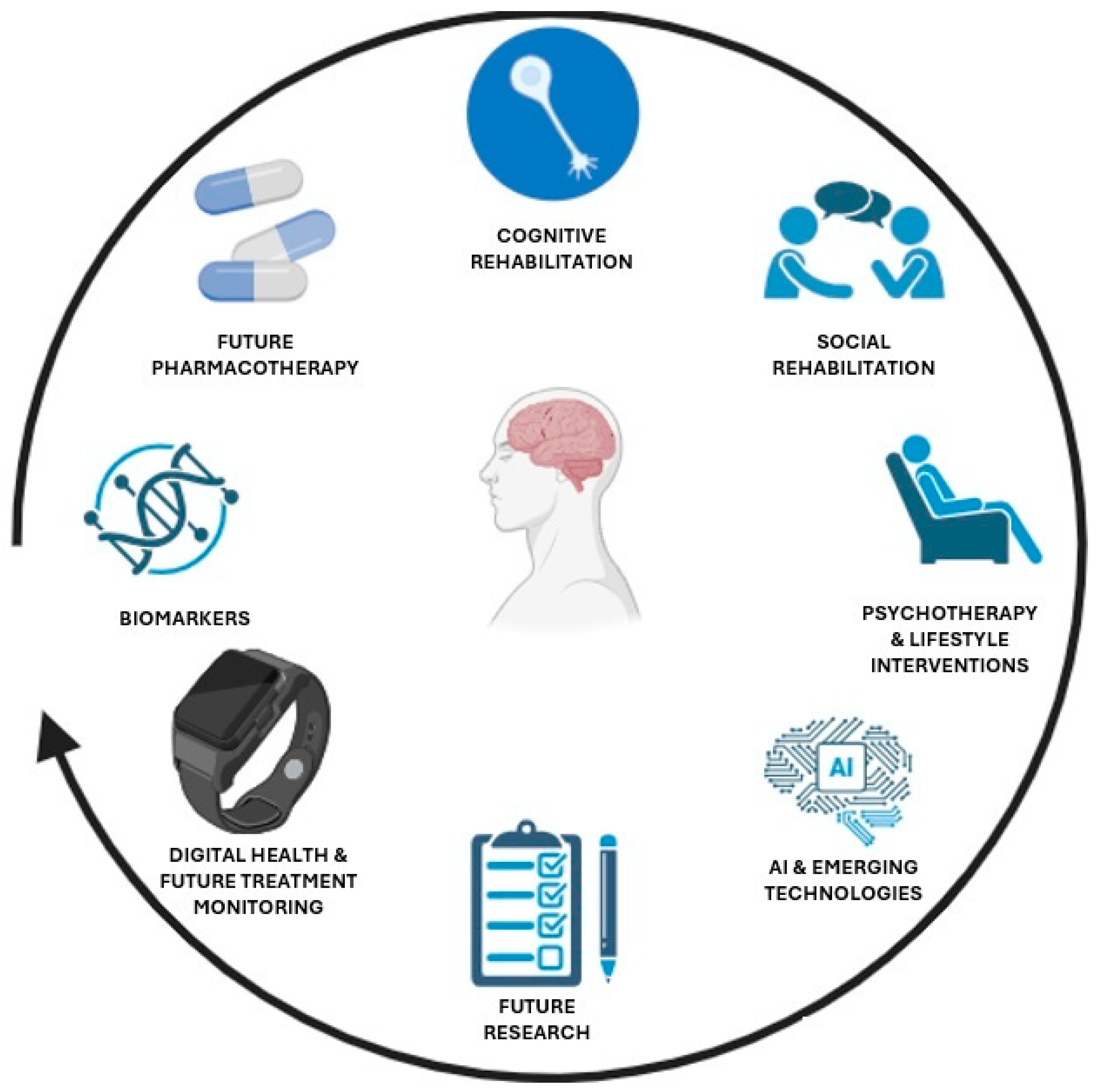
4. Future Pharmacotherapy: Emerging Drug Classes and Mechanisms
4.1. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Agents
4.2. Mitochondrial Enhancers and Oxidative Stress Modulators
4.3. Glutamatergic Modulators
4.4. Neurosteroids
4.5. Psychedelics and Novel Rapid-Acting Antidepressants
4.6. Epigenetic Drugs
4.7. Chronotherapeutic Strategies in BD
5. Digital Health and Future Treatment Monitoring
5.1. Wearable Devices and Symptom Monitoring, Relapse Prevention
5.2. Digital Applications for Monitoring Bipolar Disorder (BD)
5.3. Personalized Feedback and Interventions
5.4. Sensors for Lithium Monitoring: Emerging Technologies
5.4.1. Wearable and Continuous-Readout Biosensors
5.4.2. Saliva- or Oral Fluid-Based Sensors
5.5. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in BD Management and Precision Psychiatry
6. Integration with Psychotherapy and Lifestyle Interventions
6.1. Personalized Psychotherapy and Neurobiological Targets
6.2. Lifestyle Interventions: Sleep, Diet, and Exercise
6.3. Toward Integrated and Personalized Care
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGuffin, P.; Rijsdijk, F.; Andrew, M.; Sham, P.; Katz, R.; Cardno, A. The Heritability of Bipolar Affective Disorder and the Genetic Relationship to Unipolar Depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2003, 60, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoller, J.W.; Gardner-Schuster, E. Genetics of bipolar disorder. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2007, 9, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barnett, J.H.; Smoller, J.W. The genetics of bipolar disorder. Neuroscience 2009, 164, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Bergen, S.E.; Akula, N.; Song, J.; Hultman, C.M.; Landén, M.; Adli, M.; Alda, M.; Ardau, R.; Arias, B.; et al. Genome-wide association study of 40,000 individuals identifies two novel loci associated with bipolar disorder. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 3383–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, N.; Forstner, A.J.; O’Connell, K.S.; Coombes, B.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Qiao, Z.; Als, T.D.; Bigdeli, T.B.; Børte, S.; Bryois, J.; et al. Genome-wide association study of more than 40,000 bipolar disorder cases provides new insights into the underlying biology. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, E.A.; Breen, G.; Forstner, A.J.; McQuillin, A.; Ripke, S.; Trubetskoy, V.; Mattheisen, M.; Wang, Y.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Gaspar, H.A.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 30 loci associated with bipolar disorder. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, E.P.; Nurnberger, J.I. Molecular genetics of bipolar disorder. Genes. Brain Behav. 2006, 5, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurnberger, J.I.; Foroud, T. Genetics of bipolar affective disorder. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2000, 2, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koromina, M.; Ravi, A.; Panagiotaropoulou, G.; Schilder, B.M.; Humphrey, J.; Braun, A.; Bidgeli, T.; Chatzinakos, C.; Coombes, B.J.; Kim, J.; et al. Fine-mapping genomic loci refines bipolar disorder risk genes. Nat Neurosci. 2025, 28, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baune, B.T.; Fromme, S.E.; Aberg, M.; Adli, M.; Afantitis, A.; Akkouh, I.; Andreassen, O.A.; Angulo, C.; Barlati, S.; Brasso, C.; et al. A stratified treatment algorithm in psychiatry: A program on stratified pharmacogenomics in severe mental illness (Psych-STRATA): Concept, objectives and methodologies of a multidisciplinary project funded by Horizon Europe. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2025, 275, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, M.L.; Whittle, S.; Allen, N.B. The Role of Brain Structure and Function in the Association Between Inflammation and Depressive Symptoms. Psychosom. Med. 2016, 78, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hei, M.; Chen, P.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Xu, M.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; Duan, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, S. Effects of chronic mild stress induced depression on synaptic plasticity in mouse hippocampus. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 365, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, B.S.; Moda, R.N.; Liston, C. Glucocorticoid mechanisms of functional connectivity changes in stress-related neuropsychiatric disorders. Neurobiol. Stress 2015, 1, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liston, C.; Cichon, J.M.; Jeanneteau, F.; Jia, Z.; Chao, M.V.; Gan, W.-B. Circadian glucocorticoid oscillations promote learning-dependent synapse formation and maintenance. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanneteau, F.; Arango-Lievano, M. Linking Mitochondria to Synapses: New Insights for Stress-Related Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Neural Plast. 2016, 1, 3985063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezevic, E.; Nenic, K.; Milanovic, V.; Knezevic, N.N. The Role of Cortisol in Chronic Stress, Neurodegenerative Diseases, and Psychological Disorders. Cells 2023, 12, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, B.S.; Gianaros, P.J. Stress- and Allostasis-Induced Brain Plasticity. Annu. Rev. Med. 2011, 62, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidi, J.; Lucente, M.; Sonino, N.; Fava, G.A. Allostatic Load and Its Impact on Health: A Systematic Review. Psychother. Psychosom. 2021, 90, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fries, G.R.; Pfaffenseller, B.; Stertz, L.; Paz, A.V.C.; Dargél, A.A.; Kunz, M.; Kapczinski, F. Staging and Neuroprogression in Bipolar Disorder. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2012, 14, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, S.; McKinlay, S.; Kapczinski, F.; Pfaffenseller, B.; Wollenhaupt-Aguiar, B. Biomarkers of neuroprogression and late staging in bipolar disorder: A systematic review. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2023, 57, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barichello, T.; Giridharan, V.V.; Bhatti, G.; Sayana, P.; Doifode, T.; Macedo, D.; Quevedo, J. Inflammation as a Mechanism of Bipolar Disorder Neuroprogression; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, G.; Pardini, M.; Monacelli, F.; Orso, B.; Girtler, N.; Brugnolo, A.; Amore, M.; Nobili, F.; Disease Management Team on Dementia of the IRCCS Ospedale Policlinico San Martino. Neuroprogression as an Illness Trajectory in Bipolar Disorder: A Selective Review of the Current Literature. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos-Moreno, M.P.; Fries, G.R.; Gubert, C.; Dos Santos, B.T.M.Q.; Fijtman, A.; Sartori, J.; Ferrari, P.; Grun, L.K.; Parisi, M.M.; Guma, F.T.C.R.; et al. Telomere Length, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and BDNF Levels in Siblings of Patients with Bipolar Disorder: Implications for Accelerated Cellular Aging. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 20, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollenhaupt-Aguiar, B.; Kapczinski, F.; Pfaffenseller, B. Biological Pathways Associated with Neuroprogression in Bipolar Disorder. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinton, P.; Giorgi, C.; Siviero, R.; Zecchini, E.; Rizzuto, R. Calcium and apoptosis: ER-mitochondria Ca2+ transfer in the control of apoptosis. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6407–6418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.-H.; Lee, B.-Y.; Chen, W. Functional energetic responses and individual variance of the human brain revealed by quantitative imaging of adenosine triphosphate production rates. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2018, 38, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, M.; Gogvadze, V.; Orrenius, S.; Zhivotovsky, B. Mitochondria, oxidative stress and cell death. Apoptosis 2007, 12, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heneka, M.T.; Rodríguez, J.J.; Verkhratsky, A. Neuroglia in neurodegeneration. Brain Res. Rev. 2010, 63, 189–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, B.S. Neurobiological and Systemic Effects of Chronic Stress. Chronic Stress 2017, 1, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrea, L.T.; Batorsky, R.E.; Bowen, J.J.; Yeh, H.; Thanos, J.M.; Fu, T.; Perlis, R.H.; Sheridan, S.D. Identifying brain-penetrant small-molecule modulators of human microglia using a cellular model of synaptic pruning. Neuropsychopharmacology 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, W.; Zhang, J. A richer and more diverse future for microglia phenotypes. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, J.D.; Olschowka, J.A.; O’Banion, M.K. Neuroinflammation and M2 microglia: The good, the bad, and the inflamed. J. Neuroinflammation 2014, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wang, H.; Yin, Y. Microglia Polarization From M1 to M2 in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 815347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurga, A.M.; Paleczna, M.; Kuter, K.Z. Overview of General and Discriminating Markers of Differential Microglia Phenotypes. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2020, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellwig, S.; Heinrich, A.; Biber, K. The brain’s best friend: Microglial neurotoxicity revisited. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2013, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransohoff, R.M.; Cardona, A.E. The myeloid cells of the central nervous system parenchyma. Nature 2010, 468, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bernhardi, R.; Bernhardi, L.E.-V.; Eugenín, J. Microglial cell dysregulation in brain aging and neurodegeneration. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffenseller, B.; Fries, G.R.; Wollenhaupt-Aguiar, B.; Colpo, G.D.; Stertz, L.; Panizzutti, B.; Magalhães, P.V.; Kapczinski, F. Neurotrophins, inflammation and oxidative stress as illness activity biomarkers in bipolar disorder. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2013, 13, 827–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leboyer, M.; Soreca, I.; Scott, J.; Frye, M.; Henry, C.; Tamouza, R.; Kupfer, D.J. Can bipolar disorder be viewed as a multi-system inflammatory disease? J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 141, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapczinski, F.; Dal-Pizzol, F.; Teixeira, A.L.; Magalhaes, P.V.; Kauer-Sant’Anna, M.; Klamt, F.; Moreira, J.C.; de Bittencourt Pasquali, M.A.; Fries, G.R.; Quevedo, J.; et al. Peripheral biomarkers and illness activity in bipolar disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2011, 45, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juster, R.-P.; Smith, N.G.; Ouellet, É.; Sindi, S.; Lupien, S.J. Sexual Orientation and Disclosure in Relation to Psychiatric Symptoms, Diurnal Cortisol, and Allostatic Load. Psychosom. Med. 2013, 75, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaini, G.; Valvassori, S.S.; Diaz, A.P.; Lima, C.N.; Benevenuto, D.; Fries, G.R.; Quevedo, J. Neurobiology of bipolar disorders: A review of genetic components, signaling pathways, biochemical changes, and neuroimaging findings. Braz. J. Psychiatry 2020, 42, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, R.; Pattanayak, R.D. Potential biomarkers for bipolar disorder. Indian J. Med. Res. 2017, 145, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanova, A.; Wevers, A.; Navarro-Ledesma, S.; Pruimboom, L. Mitochondria: It is all about energy. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1114231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seager, R.; Lee, L.; Henley, J.M.; Wilkinson, K.A. Mechanisms and roles of mitochondrial localisation and dynamics in neuronal function. Neuronal. Signal. 2020, 4, NS20200008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.J.; Attwell, D. The Energetics of CNS White Matter. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.-H.; Cai, Q. Mitochondrial transport in neurons: Impact on synaptic homeostasis and neurodegeneration. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaraju, V.; Lewis, T.L., Jr.; Hirabayashi, Y.; Bergami, M.; Motori, E.; Cartoni, R.; Kwon, S.K.; Courchet, J. Pleiotropic Mitochondria: The Influence of Mitochondria on Neuronal Development and Disease. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 8200–8208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, S. Oxidative Stress and Psychological Disorders. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2014, 12, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, A.M.; McPhie, D.L.; Lange, N.T.; Punzell, S.; Elmiligy, S.; Ye, N.Z.; Froimowitz, M.P.; Hassinger, L.C.; Menesale, E.B.; Sargent, L.W.; et al. Abnormalities in Mitochondrial Structure in Cells from Patients with Bipolar Disorder. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T. Neurobiological basis of bipolar disorder: Mitochondrial dysfunction hypothesis and beyond. Schizophr. Res. 2017, 187, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, Y.; Okura, S.; Sukigara, A.; Matsunaga, A.; Maekubo, K.; Oue, T.; Ishihara, K.; Deguchi, Y.; Inoue, K. The Association Among Bipolar Disorder, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Reactive Oxygen Species. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, F.; Aggio, V.; Pratesi, M.L.; Greco, G.; Furlan, R. Neuroinflammation in Bipolar Depression. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez-Palomo, A.; Andreu, H.; de Juan, O.; Olivier, L.; Ochandiano, I.; Ilzarbe, L.; Valentí, M.; Stoppa, A.; Llach, C.D.; Pacenza, G.; et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction as a Biomarker of Illness State in Bipolar Disorder: A Critical Review. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa-Wagner, A.; Mitran, S.; Sivanesan, S.; Chang, E.; Buga, A.-M. ROS and Brain Diseases: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Oxid Med. Cell Longev. 2013, 2013, 963520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Chang, C.C.; Lin, T.T.; Liu, C.S.; Chen, P.S. Exploring the interplay between mitochondrial dysfunction, early life adversity and bipolar disorder. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 2025, 29, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.C.; Andreazza, A.C.; Young, L.T. An updated meta-analysis of oxidative stress markers in bipolar disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2014, 218, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savas, H.A.; Gergerlioglu, H.S.; Armutcu, F.; Herken, H.; Yilmaz, H.R.; Kocoglu, E.; Selek, S.; Tutkun, H.; Zoroglu, S.S.; Akyol, O. Elevated serum nitric oxide and superoxide dismutase in euthymic bipolar patients: Impact of past episodes. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 7, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwek, M.; Sowa-Kucma, M.; Styczen, K.; Misztak, P.; Szewczyk, B.; Topor-Madry, R.; Nowak, G.; Dudek, D.; Rybakowski, J.K. Thiobarbituric Acid-Reactive Substances: Markers of an Acute Episode and a Late Stage of Bipolar Disorder. Neuropsychobiology 2016, 73, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreazza, A.C.; Shao, L.; Wang, J.-F.; Young, L.T. Mitochondrial Complex I Activity and Oxidative Damage to Mitochondrial Proteins in the Prefrontal Cortex of Patients With Bipolar Disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, R.T.; Zarate, C.A., Jr.; Zanetti, M.V.; Costa, A.C.; Talib, L.L.; Gattaz, W.F.; Machado-Vieira, R. Oxidative stress in early stage Bipolar Disorder and the association with response to lithium. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2014, 50, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, I.; Fries, G.R.; Kunz, M.; Kapczinski, F. The Role of BDNF as a Mediator of Neuroplasticity in Bipolar Disorder. Psychiatry Investig. 2010, 7, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maletic, V.; Raison, C. Integrated Neurobiology of Bipolar Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2014, 5, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, M.; Behl, T.; Sachdeva, M.; Arora, S. Role of brain derived neurotropic factor in obesity. Obes. Med. 2020, 17, 100189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunçel, Ö.K.; Sarisoy, G.; Çetin, E.; Tunçel, E.K.; Bilgici, B.; Karaustaoğlu, A. Neurotrophic factors in bipolar disorders patients with manic episode. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 50, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.R.; Singh, N.; Whitaker, E.; de Brito, M.; Lewis, A.M.; Vieta, E.; Churchill, G.C.; Geddes, J.R.; Goodwin, G.M. Altered plasma glutathione levels in bipolar disorder indicates higher oxidative stress; a possible risk factor for illness onset despite normal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels. Psychol. Med. 2014, 44, 2409–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ino, H.; Honda, S.; Yamada, K.; Horita, N.; Tsugawa, S.; Yoshida, K.; Noda, Y.; Meyer, J.H.; Mimura, M.; Nakajima, S.; et al. Glutamatergic Neurometabolite Levels in Bipolar Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Studies. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2023, 8, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmond, D.E. Cerebrospinal Fluid Amine Metabolites. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1986, 43, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiste, A.K.; Arango, V.; Ellis, S.P.; Mann, J.J.; Underwood, M.D. Norepinephrine and serotonin imbalance in the locus coeruleus in bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2008, 10, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, L.; Carballo, J.J.; Grunebaum, M.F.; Burke, A.K.; Zalsman, G.; Huang, Y.Y.; Mann, J.J.; Oquendo, M.A. A prospective study of the association of cerebrospinal fluid monoamine metabolite levels with lethality of suicide attempts in patients with bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2006, 8, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, M.; Nishino, S.; Numata, Y.; Okubo, Y.; Sato, T. The noradrenaline metabolite MHPG is a candidate biomarker between the depressive, remission, and manic states in bipolar disorder I: Two long-term naturalistic case reports. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgs, B.W.; Elashoff, M.; Richman, S.; Barci, B. An online database for brain disease research. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, A.H.; Marques, T.R.; Jauhar, S.; Nour, M.M.; Goodwin, G.M.; Young, A.H.; Howes, O.D. The dopamine hypothesis of bipolar affective disorder: The state of the art and implications for treatment. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, M.; Dodd, S.; Kauer-Sant’anna, M.; Malhi, G.S.; Bourin, M.; Kapczinski, F.; Norman, T. Dopamine dysregulation syndrome: Implications for a dopamine hypothesis of bipolar disorder. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2007, 116, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rossum, I.; Tenback, D.; van Os, J. Bipolar disorder and dopamine dysfunction: An indirect approach focusing on tardive movement syndromes in a naturalistic setting. BMC Psychiatry 2009, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laje, G.; Cannon, D.M.; Allen, A.S.; Klaver, J.M.; Peck, S.A.; Liu, X.; Manji, H.K.; Drevets, W.C.; McMahon, F.J. Serotonin Transporter Binding in Bipolar Disorder Assessed using [11C]DASB and Positron Emission Tomography. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 60, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oquendo, M.A.; Hastings, R.S.; Huang, Y.Y.; Simpson, N.; Ogden, R.T.; Hu, X.Z.; Goldman, D.; Arango, V.; Van Heertum, R.L.; Mann, J.J.; et al. Brain Serotonin Transporter Binding in Depressed Patients With Bipolar Disorder Using Positron Emission Tomography. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2007, 64, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lan, M.J.; Zanderigo, F.; Pantazatos, S.P.; Sublette, M.E.; Miller, J.; Ogden, R.T.; Mann, J.J. Serotonin 1A Receptor Binding of [11C]CUMI-101 in Bipolar Depression Quantified Using Positron Emission Tomography: Relationship to Psychopathology and Antidepressant Response. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022, 25, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniele, S.; Da Pozzo, E.; Abelli, M.; Panighini, A.; Pini, S.; Gesi, C.; Lari, L.; Cardini, A.; Cassano, G.B.; Martini, C. Platelet uptake of GABA and glutamate in patients with bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2012, 14, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gos, T.; Steiner, J.; Bielau, H.; Dobrowolny, H.; Günther, K.; Mawrin, C.; Krzyżanowski, M.; Hauser, R.; Brisch, R.; Bernstein, H.G.; et al. Differences between unipolar and bipolar I depression in the quantitative analysis of glutamic acid decarboxylase-immunoreactive neuropil. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2012, 262, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullumsmith, R.E.; Kristiansen, L.V.; Beneyto, M.; Scarr, E.; Dean, B.; Meador-Woodruff, J.H. Decreased NR1, NR2A, and SAP102 transcript expression in the hippocampus in bipolar disorder. Brain Res. 2007, 1127, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayed, N.; Andrés, E.; Viguera, L.; Modrego, P.J.; Garcia-Campayo, J. Higher Glutamate + Glutamine and Reduction of N-acetylaspartate in Posterior Cingulate According to Age Range in Patients with Cognitive Impairment and/or Pain. Acad. Radiol. 2014, 21, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, D.L.; Uzenoff, S.R.; Perkins, D.; Mueser, K.T.; Hamer, R.; Waldheter, E.; Saade, S.; Cook, L. A pilot investigation of the Graduated Recovery Intervention Program (GRIP) for first episode psychosis. Schizophr. Res. 2011, 125, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques-Deak, A.; Cizza, G.; Sternberg, E. Erratum: Brain-immune interactions and disease susceptibility. Mol. Psychiatry 2005, 10, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Tomar, J.S. Elevated Brain Glutamate Levels in Bipolar Disorder and Pyruvate Carboxylase-Mediated Anaplerosis. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 640977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirvonen, M.; Laakso, A.; Någren, K.; Rinne, J.O.; Pohjalainen, T.; Hietala, J. Erratum: C957T polymorphism of the dopamine D2 receptor (DRD2) gene affects striatal DRD2 availability in vivo. Mol. Psychiatry 2005, 10, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Ohnishi, T.; Hashimoto, R.; Nemoto, K.; Moriguchi, Y.; Noguchi, H.; Nakabayashi, T.; Hori, H.; Harada, S.; Saitoh, O.; et al. Progressive changes of white matter integrity in schizophrenia revealed by diffusion tensor imaging. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2007, 154, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigante, A.D.; Bond, D.J.; Lafer, B.; Lam, R.W.; Young, L.T.; Yatham, L.N. Brain glutamate levels measured by magnetic resonance spectroscopy in patients with bipolar disorder: A meta-analysis. Bipolar Disord. 2012, 14, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Sastre, P.; Gómez-Sánchez-Lafuente, C.; Martín-Martín, J.; Herrera-Imbroda, J.; Mayoral-Cleries, F.; Santos-Amaya, I.; Rodríguez de Fonseca, F.; Guzmán-Parra, J.; Rivera, P. Pharmacotherapeutic value of inflammatory and neurotrophic biomarkers in bipolar disorder: A systematic review. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 134, 111056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanaatfar, F.; Ghanaatfar, A.; Isapour, P.; Farokhi, N.; Bozorgniahosseini, S.; Javadi, M.; Gholami, M.; Ulloa, L.; Coleman-Fuller, N.; Motaghinejad, M. Is lithium neuroprotective? An updated mechanistic illustrated review. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 37, 4–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa, E.L.M. Lithium as a Neuroprotective Agent for Bipolar Disorder: An Overview. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 42, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakrajda, K.; Szczepankiewicz, A. Inflammation-Related Changes in Mood Disorders and the Immunomodulatory Role of Lithium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, D.; Beaulieu, J.M. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3 by lithium, a mechanism in search of specificity. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1028963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hong, W.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, C.; Li, Z.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z.; Fang, Y. IL-23 and TGF-β1 levels as potential predictive biomarkers in treatment of bipolar I disorder with acute manic episode. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 174, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.; Phillips, C.; Fahimi, A.; McNerney, M.W.; Salehi, A. Mechanisms of action and clinical efficacy of NMDA receptor modulators in mood disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 80, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.N.; Greenwald, M.S.; Henter, I.D.; Kraus, C.; Mkrtchian, A.; Clark, N.G.; Park, L.T.; Gold, P.; Zarate, C.A., Jr.; Kadriu, B. Inflammation, stress and depression: An exploration of ketamine’s therapeutic profile. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkheslat, N. Targeting inflammation in depression: Ketamine as an anti-inflammatory antidepressant in psychiatric emergency. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2021, 18, 100383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Newman, L.E.; Gold, P.W.; Luckenbaugh, D.A.; Yuan, P.; Machado-Vieira, R.; Zarate, C.A., Jr. Change in cytokine levels is not associated with rapid antidepressant response to ketamine in treatment-resistant depression. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2017, 84, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soczynska, J.K.; Kennedy, S.H.; Alsuwaidan, M.; Mansur, R.B.; Li, M.; McAndrews, M.P.; Brietzke, E.; Woldeyohannes, H.O.; Taylor, V.H.; McIntyre, R.S. A pilot, open-label, 8-week study evaluating the efficacy, safety and tolerability of adjunctive minocycline for the treatment of bipolar I/II depression. Bipolar Disord. 2017, 19, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitz, J.B.; Teague, T.K.; Misaki, M.; Macaluso, M.; Wurfel, B.E.; Meyer, M.; Drevets, D.; Yates, W.; Gleason, O.; Drevets, W.C.; et al. Treatment of bipolar depression with minocycline and/or aspirin: An adaptive, 2×2 double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase IIA clinical trial. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Xiong, R.; Gong, X. Memantine, NMDA Receptor Antagonist, Attenuates ox-LDL-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via Activation of BDNF/TrkB Signaling Pathway in HUVECs. Inflammation 2021, 44, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.B.; Chen, S.L.; Lee, S.Y.; Chang, Y.H.; Chen, S.H.; Chu, C.H.; Tzeng, N.S.; Lee, I.H.; Chen, P.S.; Yeh, T.L.; et al. Neuroprotective and neurogenesis agent for treating bipolar II disorder: Add-on memantine to mood stabilizer works. Med. Hypotheses 2012, 79, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Chen, S.L.; Chang, Y.H.; Chen, P.S.; Huang, S.Y.; Tzeng, N.S.; Wang, Y.S.; Wang, L.J. The Effects of Add-On Low-Dose Memantine on Cytokine Levels in Bipolar II Depression. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2014, 34, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Wang, T.Y.; Chen, S.L.; Chang, Y.H.; Chen, P.S.; Huang, S.Y.; Tzeng, N.S.; Wang, L.J.; Lee, I.H.; Chen, K.C.; et al. Add-On Memantine Treatment for Bipolar II Disorder Comorbid with Alcohol Dependence: A 12-Week Follow-Up Study. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Wang, T.Y.; Chen, S.L.; Chang, Y.H.; Chen, P.S.; Huang, S.Y.; Tzeng, N.S.; Wang, L.J.; Lee, I.H.; Chen, K.C.; et al. Combination of dextromethorphan and memantine in treating bipolar spectrum disorder: A 12-week double-blind randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Bipolar Disord. 2020, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.B.; Wang, T.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Chang, Y.H.; Chen, S.L.; Tsai, T.Y.; Chen, P.S.; Huang, S.Y.; Tzeng, N.S.; Lee, I.H.; et al. Add-on memantine may improve cognitive functions and attenuate inflammation in middle- to old-aged bipolar II disorder patients. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 279, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybakowski, J.K. Mood Stabilizers of First and Second Generation. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Lee, S.Y.; Chang, Y.H.; Chen, P.S.; Lee, I.H.; Wang, T.Y.; Chen, K.C.; Yang, Y.K.; Hong, J.S.; Lu, R.B. Therapeutic effects of add-on low-dose dextromethorphan plus valproic acid in bipolar disorder. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansur, R.B.; Subramaniapillai, M.; Lee, Y.; Pan, Z.; Carmona, N.E.; Shekotikhina, M.; Iacobucci, M.; Rodrigues, N.; Nasri, F.; Rashidian, H.; et al. Leptin mediates improvements in cognitive function following treatment with infliximab in adults with bipolar depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2020, 120, 104779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, R.S.; Subramaniapillai, M.; Lee, Y.; Pan, Z.; Carmona, N.E.; Shekotikhina, M.; Rosenblat, J.D.; Brietzke, E.; Soczynska, J.K.; Cosgrove, V.E.; et al. Efficacy of Adjunctive Infliximab vs Placebo in the Treatment of Adults With Bipolar I/II Depression. JAMA Psychiatry 2019, 76, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Mansur, R.B.; Brietzke, E.; Carmona, N.E.; Subramaniapillai, M.; Pan, Z.; Shekotikhina, M.; Rosenblat, J.D.; Suppes, T.; Cosgrove, V.E.; et al. Efficacy of adjunctive infliximab vs. placebo in the treatment of anhedonia in bipolar I/II depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 88, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salatin, S.; Shafiee-Kandjani, A.R.; Hamidi, S.; Amirfiroozi, A.; Kalejahi, P. Individualized psychiatric care: Integration of therapeutic drug monitoring, pharmacogenomics, and biomarkers. Per Med. 2025, 22, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitz, J.; Preskorn, S.; Teague, T.K.; Drevets, D.; Yates, W.; Drevets, W. Minocycline and aspirin in the treatment of bipolar depression: A protocol for a proof-of-concept, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 2 × 2 clinical trial. BMJ Open. 2012, 2, e000643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, S.; Baig, N.; Decker, K.; Halaris, A. Systemic Inflammatory Response Index (SIRI) at Baseline Predicts Clinical Response for a Subset of Treatment-Resistant Bipolar Depressed Patients. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, S.; Murphy, M.; Hoppensteadt, D.; Fareed, J.; Welborn, A.; Halaris, A. Effects of adjunctive inflammatory modulation on IL-1β in treatment resistant bipolar depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edberg, D.; Hoppensteadt, D.; Walborn, A.; Fareed, J.; Sinacore, J.; Halaris, A. Plasma MCP-1 levels in bipolar depression during cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor combination treatment. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2020, 129, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edberg, D.; Hoppensteadt, D.; Walborn, A.; Fareed, J.; Sinacore, J.; Halaris, A. Plasma C-reactive protein levels in bipolar depression during cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor combination treatment. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 102, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kargar, M.; Yousefi, A.; Mojtahedzadeh, M.; Akhondzadeh, S.; Artounian, V.; Abdollahi, A.; Ahmadvand, A.; Ghaeli, P. Effects of celecoxib on inflammatory markers in bipolar patients undergoing electroconvulsive therapy: A placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomised study. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2014, 144, w13880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, D.E.; Schinagle, M.; Gao, K.; Conroy, C.; Ganocy, S.J.; Ismail-Beigi, F.; Calabrese, J.R. PPAR-γ Agonism as a Modulator of Mood: Proof-of-Concept for Pioglitazone in Bipolar Depression. CNS Drugs 2014, 28, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletti, S.; Zanardi, R.; Mandelli, A.; Aggio, V.; Finardi, A.; Lorenzi, C.; Borsellino, G.; Carminati, M.; Manfredi, E.; Tomasi, E.; et al. Low-dose interleukin 2 antidepressant potentiation in unipolar and bipolar depression: Safety, efficacy, and immunological biomarkers. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 118, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslahi, H.; Shakiba, M.; Saravani, M.; Payandeh, A.; Shahraki, M. The effects of omega 3 fatty acids on the serum concentrations of pro inflammatory cytokines anddepression status in patients with bipolar disorder: A randomized double-blind controlled clinical trial. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2023, 28, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabouri, S.; Esmailzadeh, M.; Sadeghinejad, A.; Shahrbabaki, M.E.; Asadikaram, G.; Nikvarz, N. The Effect of Adjunctive Probiotics on Markers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Bipolar Disorder: A Double-blind, Randomized, Controlled Trial. J. Psychiatr. Pract. 2022, 28, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malewska-Kasprzak, M.; Sikorski, M.; Dmitrzak-Weglarz, M.; Rybakowski, F. Diagnostic potential of P2X7, NACHT, and iL-6 as immune biomarkers in bipolar disorder. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2025, 26, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuperberg, M.; Greenebaum, S.L.A.; Nierenberg, A.A. Targeting mitochondrial dysfunction for bipolar disorder. In Bipolar Disorder: From Neuroscience to Treatment; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 61–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nierenberg, A.A.; Kansky, C.; Brennan, B.P.; Shelton, R.C.; Perlis, R.; Iosifescu, D.V. Mitochondrial modulators for bipolar disorder: A pathophysiologically informed paradigm for new drug development. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2013, 47, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berk, M.; Copolov, D.L.; Dean, O.; Lu, K.; Jeavons, S.; Schapkaitz, I.; Anderson-Hunt, M.; Bush, A.I. N-Acetyl Cysteine for Depressive Symptoms in Bipolar Disorder—A Double-Blind Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 64, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grings, M.; Moura, A.P.; Parmeggiani, B.; Pletsch, J.T.; Cardoso, G.M.F.; August, P.M.; Matté, C.; Wyse, A.T.S.; Wajner, M.; Leipnitz, G. Bezafibrate prevents mitochondrial dysfunction, antioxidant system disturbance, glial reactivity and neuronal damage induced by sulfite administration in striatum of rats: Implications for a possible therapeutic strategy for sulfite oxidase deficiency. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 2135–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Örzsik, B.; Yalin, N.; Simpson, I.; Nwaubani, P.; Pinna, A.; De Marco, R.; Sharp, H.; Kartar, A.; Singh, N.; et al. Altered oxidative neurometabolic response to methylene blue in bipolar disorder revealed by quantitative neuroimaging. J Affect Disord. 2024, 362, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoffroy, P.A.; Etain, B.; Lajnef, M.; Zerdazi, E.H.; Brichant-Petitjean, C.; Heilbronner, U.; Hou, L.; Degenhardt, F.; Rietschel, M.; McMahon, F.J.; et al. Circadian genes and lithium response in bipolar disorders: Associations with PPARGC1A(PGC-1 α) and RORA. Genes. Brain Behav. 2016, 15, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colle, R.; de Larminat, D.; Rotenberg, S.; Hozer, F.; Hardy, P.; Verstuyft, C.; Fève, B.; Corruble, E. PPAR-γ Agonists for the Treatment of Major Depression: A Review. Pharmacopsychiatry 2016, 50, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyse, A.T.S.; Grings, M.; Wajner, M.; Leipnitz, G. The Role of Oxidative Stress and Bioenergetic Dysfunction in Sulfite Oxidase Deficiency: Insights from Animal Models. Neurotox Res. 2019, 35, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhu, X.M.; Zhang, Q.E.; Cheng, G.; Cai, D.B.; He, J.; Ng, C.H.; Ungvari, G.S.; Peng, X.J.; Ning, Y.P.; et al. Adjunctive minocycline for major mental disorders: A systematic review. J. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 33, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shultz, R.; Zhong, Y. Minocycline targets multiple secondary injury mechanisms in traumatic spinal cord injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, O.D.; Coronado, N.G.; Sethi, R.; Berk, M.; Dodd, S. Putative neuroprotective pharmacotherapies to target the staged progression of mental illness. Early Interv. Psychiatry 2019, 13, 1032–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuni, Y.; Goldstein, S.; Dean, O.M.; Berk, M. The chemistry and biological activities of N-acetylcysteine. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-General. Subj. 2013, 1830, 4117–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.; Chavarria, V.; Vian, J.; Ashton, M.M.; Berk, M.; Marx, W.; Dean, O.M. Mitochondrial Agents for Bipolar Disorder. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 21, 550–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, M.; Turner, A.; Malhi, G.S.; Ng, C.H.; Cotton, S.M.; Dodd, S.; Samuni, Y.; Tanious, M.; McAulay, C.; Dowling, N.; et al. A randomised controlled trial of a mitochondrial therapeutic target for bipolar depression: Mitochondrial agents, N-acetylcysteine, and placebo. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neergheen, V.; Chalasani, A.; Wainwright, L.; Yubero, D.; Montero, R.; Artuch, R.; Hargreaves, I. Coenzyme Q10 in the Treatment of Mitochondrial Disease. J. Inborn. Errors Metab. Screen. 2017, 5, 232640981770777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantle, D.; Hargreaves, I. Coenzyme Q10 and Degenerative Disorders Affecting Longevity: An Overview. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; Anderson, G.; Berk, M.; Maes, M. Coenzyme Q10 Depletion in Medical and Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Potential Repercussions and Therapeutic Implications. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 48, 883–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M.; Mihaylova, I.; Kubera, M.; Uytterhoeven, M.; Vrydags, N.; Bosmans, E. Lower plasma Coenzyme Q10 in depression: A marker for treatment resistance and chronic fatigue in depression and a risk factor to cardiovascular disorder in that illness. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2009, 30, 462–469. [Google Scholar]
- Forester, B.P.; Harper, D.G.; Georgakas, J.; Ravichandran, C.; Madurai, N.; Cohen, B.M. Antidepressant Effects of Open Label Treatment With Coenzyme Q10 in Geriatric Bipolar Depression. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2015, 35, 338–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrpooya, M.; Yasrebifar, F.; Haghighi, M.; Mohammadi, Y.; Jahangard, L. Evaluating the Effect of Coenzyme Q10 Augmentation on Treatment of Bipolar Depression. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 38, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J.; Rosales-Corral, S.; Tan, D.X.; Jou, M.J.; Galano, A.; Xu, B. Melatonin as a mitochondria-targeted antioxidant: One of evolution’s best ideas. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3863–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuna-Castroviejo, D. Melatonin role in the mitochondrial function. Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nováková, M.; Praško, J.; Látalová, K.; Sládek, M.; Sumová, A. The circadian system of patients with bipolar disorder differs in episodes of mania and depression. Bipolar Disord. 2015, 17, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishi, T.; Nomura, I.; Sakuma, K.; Kitajima, T.; Mishima, K.; Iwata, N. Melatonin receptor agonists—Ramelteon and melatonin—For bipolar disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trials. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2019, 15, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diazgranados, N.; Ibrahim, L.; Brutsche, N.E.; Newberg, A.; Kronstein, P.; Khalife, S.; Kammerer, W.A.; Quezado, Z.; Luckenbaugh, D.A.; Salvadore, G.; et al. A Randomized Add-on Trial of an N-methyl-D-aspartate Antagonist in Treatment-Resistant Bipolar Depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarate, C.A., Jr.; Brutsche, N.E.; Ibrahim, L.; Franco-Chaves, J.; Diazgranados, N.; Cravchik, A.; Selter, J.; Marquardt, C.A.; Liberty, V.; Luckenbaugh, D.A. Replication of Ketamine’s Antidepressant Efficacy in Bipolar Depression: A Randomized Controlled Add-On Trial. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 71, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- aan het Rot, M.; Collins, K.A.; Murrough, J.W.; Perez, A.M.; Reich, D.L.; Charney, D.S.; Mathew, S.J. Safety and efficacy of repeated-dose intravenous ketamine for treatment-resistant depression. Safety and Efficacy of Repeated-Dose Intravenous Ketamine for Treatment-Resistant Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrough, J.W.; Perez, A.M.; Pillemer, S.; Stern, J.; Parides, M.K.; aan het Rot, M.; Collins, K.A.; Mathew, S.J.; Charney, D.S.; Iosifescu, D.V. Rapid and Longer-Term Antidepressant Effects of Repeated Ketamine Infusions in Treatment-Resistant Major Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Chen, S.L.; Chang, Y.H.; Chen, S.H.; Chu, C.H.; Huang, S.Y.; Tzeng, N.S.; Wang, C.L.; Lee, I.H.; Yeh, T.L.; et al. The DRD2/ANKK1 gene is associated with response to add-on dextromethorphan treatment in bipolar disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 138, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.F.; Lieberman, D.Z. The utility of the combination of dextromethorphan and quinidine in the treatment of bipolar II and bipolar NOS. J. Affect. Disord. 2014, 167, 333–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkerly, A.; Leader, L.D.; Cooke, E.; VandenBerg, A. Review of Allopregnanolone Agonist Therapy for the Treatment of Depressive Disorders. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2021, 15, 3017–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Botella, G.; Salituro, F.G.; Harrison, B.L.; Beresis, R.T.; Bai, Z.; Blanco, M.J.; Belfort, G.M.; Dai, J.; Loya, C.M.; Ackley, M.A.; et al. Neuroactive Steroids. 2. 3α-Hydroxy-3β-methyl-21-(4-cyano-1 H-pyrazol-1′-yl)-19-nor-5β-pregnan-20-one (SAGE-217): A Clinical Next Generation Neuroactive Steroid Positive Allosteric Modulator of the (γ-Aminobutyric Acid) A Receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 7810–7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, A.; Jaggi, A.S. Multifunctional aspects of allopregnanolone in stress and related disorders. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 48, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüscher, B.; Möhler, H. Brexanolone, a neurosteroid antidepressant, vindicates the GABAergic deficit hypothesis of depression and may foster resilience. F1000Research 2019, 8, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz-Bruce, H.; Kanes, S.J.; Zorumski, C.F. Trial of SAGE-217 in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, M.G.; Bhat, K.M.; Preti, A. GABAergic neuroactive steroids: A new frontier in bipolar disorders? Behav. Brain Funct. 2012, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, C.E.; Stevens, R.D.; Shampine, L.J.; Uzunova, V.; Trost, W.T.; Butterfield, M.I.; Massing, M.W.; Hamer, R.M.; Morrow, A.L.; Lieberman, J.A. Neuroactive Steroids are Altered in Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder: Relevance to Pathophysiology and Therapeutics. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 31, 1249–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.S.; Park, J.; Marx, C.E.; Hynan, L.S.; Gardner, C.; Davila, D.; Nakamura, A.; Sunderajan, P.; Lo, A.; Holmes, T. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Pregnenolone for Bipolar Depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014, 39, 2867–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passie, T.; Seifert, J.; Schneider, U.; Emrich, H.M. The pharmacology of psilocybin. Addict. Biol. 2002, 7, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutt, D.; Erritzoe, D.; Carhart-Harris, R. Psychedelic Psychiatry’s Brave New World. Cell 2020, 181, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carhart-Harris, R.L.; Friston, K.J. REBUS and the Anarchic Brain: Toward a Unified Model of the Brain Action of Psychedelics. Pharmacol. Rev. 2019, 71, 316–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carhart-Harris, R.; Giribaldi, B.; Watts, R.; Baker-Jones, M.; Murphy-Beiner, A.; Murphy, R.; Martell, J.; Blemings, A.; Erritzoe, D.; Nutt, D.J. Trial of Psilocybin versus Escitalopram for Depression. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.K.; Barrett, F.S.; May, D.G.; Cosimano, M.P.; Sepeda, N.D.; Johnson, M.W.; Finan, P.H.; Griffiths, R.R. Effects of Psilocybin-Assisted Therapy on Major Depressive Disorder. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblat, J.D.; Meshkat, S.; Doyle, Z.; Kaczmarek, E.; Brudner, R.M.; Kratiuk, K.; Mansur, R.B.; Schulz-Quach, C.; Sethi, R.; Abate, A.; et al. Psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy for treatment resistant depression: A randomized clinical trial evaluating repeated doses of psilocybin. Med 2024, 5, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, J.A.; Guimarães, F.S.; Campos, A.C.; Zuardi, A.W. Translational Investigation of the Therapeutic Potential of Cannabidiol (CBD): Toward a New Age. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartim, A.G.; Guimarães, F.S.; Joca, S.R.L. Antidepressant-like effect of cannabidiol injection into the ventral medial prefrontal cortex—Possible involvement of 5-HT1A and CB1 receptors. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 303, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.V.; Crippa, J.A.S.; Ceresér, K.M.; Vianna-Sulzbach, M.F.; Silveira Júnior, É.M.; Santana da Rosa, G.; Testa da Silva, M.G.; Hizo, G.H.; Simão Medeiros, L.; Santana de Oliveira, C.E.; et al. Cannabidiol as an Adjunctive Treatment for Acute Bipolar Depression: A Pilot Study: Le cannabidiol comme traitement d’appoint de la dépression bipolaire aiguë: Une étude pilote. Can. J. Psychiatry 2024, 69, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, R.S.; Rosenblat, J.D.; Nemeroff, C.B.; Sanacora, G.; Murrough, J.W.; Berk, M.; Brietzke, E.; Dodd, S.; Gorwood, P.; Ho, R.; et al. Synthesizing the Evidence for Ketamine and Esketamine in Treatment-Resistant Depression: An International Expert Opinion on the Available Evidence and Implementation. Am. J. Psychiatry 2021, 178, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.N.; Kadriu, B.; Kraus, C.; Henter, I.D.; Zarate, C.A. Ketamine in neuropsychiatric disorders: An update. Neuropsychopharmacology 2024, 49, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Chang, L.; Hashimoto, K. A historical review of antidepressant effects of ketamine and its enantiomers. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2020, 190, 172870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.B.; Daly, E.J.; Mathews, M.; Fedgchin, M.; Popova, V.; Hough, D.; Drevets, W.C. Approval of esketamine for treatment-resistant depression. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Osso, B.; Martinotti, G. Exploring the potential of Esketamine in the treatment of bipolar depression. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2023, 77, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, S.; Cubała, W.J.; Fagiolini, A.; Ramos-Quiroga, J.A.; Souery, D.; Young, A.H. Practical recommendations for the management of treatment-resistant depression with esketamine nasal spray therapy: Basic science, evidence-based knowledge and expert guidance. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 22, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryst, J.; Kawalec, P.; Pilc, A. Efficacy and safety of intranasal esketamine for the treatment of major depressive disorder. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2020, 21, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia-Melo, F.S.; Leal, G.C.; Vieira, F.; Jesus-Nunes, A.P.; Mello, R.P.; Magnavita, G.; Caliman-Fontes, A.T.; Echegaray, M.V.F.; Bandeira, I.D.; Silva, S.S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of adjunctive therapy using esketamine or racemic ketamine for adult treatment-resistant depression: A randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority study. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 264, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, N.A.; Joseph, B.; Kumar, R.; Douka, I.; Miola, A.; Prokop, L.J.; Mickey, B.J.; Singh, B. An Update on the Efficacy of Single and Serial Intravenous Ketamine Infusions and Esketamine for Bipolar Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, C.; Ji, F.; Tian, H.; Wang, L.; Jia, F.; Jiang, D.; Chen, C.; Zhou, C.; Lin, X.; Zhu, J. Transient effects of multi-infusion ketamine augmentation on treatment-resistant depressive symptoms in patients with treatment-resistant bipolar depression—An open-label three-week pilot study. Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkowska, A.; Włodarczyk, A.; Gałuszko-Węgielnik, M.; Wiglusz, M.S.; Cubała, W.J. Intravenous Ketamine Infusions in Treatment-Resistant Bipolar Depression: An Open-Label Naturalistic Observational Study. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2021, 17, 2637–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhou, Y.L.; Liu, W.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhan, Y.N.; Lan, X.F.; Zhang, B.; Ning, Y.P. A preliminary study of adjunctive ketamine for treatment-resistant bipolar depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 275, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfino, R.S.; Del-Porto, J.A.; Surjan, J.; Magalhães, E.; Sant, L.C.D.; Lucchese, A.C.; Tuena, M.A.; Nakahira, C.; Fava, V.A.R.; Steglich, M.S.; et al. Comparative effectiveness of esketamine in the treatment of anhedonia in bipolar and unipolar depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 278, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fancy, F.; Rodrigues, N.B.; Di Vincenzo, J.D.; Chau, E.H.; Sethi, R.; Husain, M.I.; Gill, H.; Tabassum, A.; Mckenzie, A.; Phan, L. Real-world effectiveness of repeated ketamine infusions for treatment-resistant bipolar depression. Bipolar Disord. 2023, 25, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, J.M.; Bustos, R.H.; Lechtig-Wassermann, S.; Beltran, S.; Zarate, C.A., Jr. Ketamine in clinical practice: Transitioning from anesthetic agent to psychiatric therapeutic. CNS Spectr. 2025, 30, e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard, E.D.; Wills, K.; Lally, N.; Richards, E.M.; Luckenbaugh, D.A.; Walls, T.; Ameli, R.; Niciu, M.J.; Brutsche, N.E.; Park, L.; et al. Anhedonia as a clinical correlate of suicidal thoughts in clinical ketamine trials. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 218, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkowska, A.; Wiglusz, M.S.; Gałuszko-Wegielnik, M.; Włodarczyk, A.; Cubała, W.J. Antianhedonic Effect of Repeated Ketamine Infusions in Patients With Treatment Resistant Depression. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 704330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Voort, J.L.V.; Riva-Posse, P.; Pazdernik, V.M.; Frye, M.A.; Tye, S.J. Ketamine-Associated Change in Anhedonia and mTOR Expression in Treatment-Resistant Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 93, e65–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banwari, G.; Desai, P.; Patidar, P. Ketamine-induced affective switch in a patient with treatment-resistant depression. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2015, 47, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollenweider, F.X.; Preller, K.H. Psychedelic drugs: Neurobiology and potential for treatment of psychiatric disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 21, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, B.; Fong, J.; Galvez, V.; Shelker, W.; Loo, C.K. Side-effects associated with ketamine use in depression: A systematic review. Lancet Psychiatry 2018, 5, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, R.S.; Alsuwaidan, M.; Baune, B.T.; Berk, M.; Demyttenaere, K.; Goldberg, J.F.; Gorwood, P.; Ho, R.; Kasper, S.; Kennedy, S.H.; et al. Treatment-resistant depression: Definition, prevalence, detection, management, and investigational interventions. World Psychiatry 2023, 22, 394–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peedicayil, J.; Kumar, A. Epigenetic Drugs for Mood Disorders. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2018, 157, 151–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negelspach, D.; Kennedy, K.E.R.; Huskey, A.; Cha, J.; Alkozei, A.; Killgore, W.D.S. Mapping the Neural Basis of Wake Onset Regularity and Its Effects on Sleep Quality and Positive Affect. Clocks Sleep. 2025, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torous, J.; Bucci, S.; Bell, I.H.; Kessing, L.V.; Faurholt-Jepsen, M.; Whelan, P.; Carvalho, A.F.; Keshavan, M.; Linardon, J.; Firth, J. The growing field of digital psychiatry: Current evidence and the future of apps, social media, chatbots, and virtual reality. World Psychiatry 2021, 20, 318–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaesu, Y. Circadian rhythm in bipolar disorder: A review of the literature. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 72, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagum, P. Digital biomarkers of cognitive function. NPJ Digit. Med. 2018, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faurholt-Jepsen, M.; Munkholm, K.; Frost, M.; Bardram, J.E.; Kessing, L.V. Electronic self-monitoring of mood using IT platforms in adult patients with bipolar disorder: A systematic review of the validity and evidence. BMC Psychiatry 2016, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onnela, J.-P.; Rauch, S.L. Harnessing Smartphone-Based Digital Phenotyping to Enhance Behavioral and Mental Health. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 1691–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.; Glenn, T.; Geddes, J.; Gitlin, M.; Grof, P.; Kessing, L.V.; Monteith, S.; Faurholt-Jepsen, M.; Severus, E.; Whybrow, P.C. Smartphones in mental health: A critical review of background issues, current status and future concerns. Int. J. Bipolar Disord. 2020, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faurholt-Jepsen, M.; Bauer, M.; Kessing, L.V. Smartphone-based objective monitoring in bipolar disorder: Status and considerations. Int. J. Bipolar Disord. 2018, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardram, J.E.; Frost, M.; Szántó, K.; Faurholt-Jepsen, M.; Vinberg, M.; Kessing, L.V. Designing mobile health technology for bipolar disorder. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Paris, France, 27 April–2 May 2013; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 2627–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, A.L.; Mallinson, S.; Griffiths, M.; Morriss, R.; Jones, S.H.; Lobban, F. Users’ experiences of an online intervention for bipolar disorder: Important lessons for design and evaluation. Evid. Based Ment. Health 2017, 20, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myin-Germeys, I.; Klippel, A.; Steinhart, H.; Reininghaus, U. Ecological momentary interventions in psychiatry. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2016, 29, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Peng, S.; He, S.; Tang, S.Y.; Goda, K.; Wang, C.H.; Li, M. Wearable Electrochemical Biosensors for Advanced Healthcare Monitoring. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2411433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosman, A.W.; Sczupak, C.A.; Pakes, G.E. Correlation between saliva and serum lithium levels in manic-depressive patients. Am. J. Hosp. Pharm. 1980, 37, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, G.M.; McCarthy, M.J.; Thein, S.H.; Piccerillo, H.L.; Warikoo, N.; Granger, D.A.; Thomas, E.A. Saliva Testing as a Means to Monitor Therapeutic Lithium Levels in Patients with Psychiatric Disorders: Identification of Clinical and Environmental Covariates, and Their Incorporation into a Prediction Model. Bipolar Disord. 2021, 23, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudin, A.; Maatoug, R.; Bourla, A.; Ferreri, F.; Bonnot, O.; Millet, B.; Schoeller, F.; Mouchabac, S.; Adrien, V. Digital Phenotyping: Data-Driven Psychiatry to Redefine Mental Health. J. Med. Internet Res. 2023, 25, e44502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milic, J.; Zrnic, I.; Grego, E.; Jovic, D.; Stankovic, V.; Djurdjevic, S.; Sapic, R. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Managing Bipolar Disorder: A New Frontier in Patient Care. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, N.C.; Weingarden, H.; Wilhelm, S. Digital biomarkers of mood disorders and symptom change. NPJ Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklowitz, D.J.; Schneck, C.D.; Walshaw, P.D.; Singh, M.K.; Sullivan, A.E.; Suddath, R.L.; Forgey Borlik, M.; Sugar, C.A.; Chang, K.D. Effects of Family-Focused Therapy vs Enhanced Usual Care for Symptomatic Youths at High Risk for Bipolar Disorder: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2020, 77, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, K.-J.; Tsai, J.-C.; Liu, D.; Lin, C.-H.; Chiu, H.-L.; Chou, K.-R. Efficacy of cognitive-behavioral therapy in patients with bipolar disorder: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moot, W.; Crowe, M.; Inder, M.; Eggleston, K.; Frampton, C.; Porter, R.J. Domain-Based Functional Improvements in Bipolar Disorder After Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 767629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orhan, M.; Korten, N.; Mans, N.; van Schaik, D.; Kupka, R.; Stek, M.; Steenhuis, D.; van Dijk, M.; Swartz, H.A.; van Oppen, P.; et al. Feasibility and Acceptability of Group Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy for Recurrent Mood Disorders: A Pilot Study. Am. J. Psychother. 2024, 77, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktaş, Y. Effectiveness of interpersonal social rhythm therapy applied to individuals with bipolar disorder: A systematic review. J. Psychiatr. Nurs. 2024, 15, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein-Piekarski, A.N.; Ball, T.M.; Samara, Z.; Staveland, B.R.; Keller, A.S.; Fleming, S.L.; Grisanzio, K.A.; Holt-Gosselin, B.; Stetz, P.; Ma, J.; et al. Mapping Neural Circuit Biotypes to Symptoms and Behavioral Dimensions of Depression and Anxiety. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 91, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, A.G.; Soehner, A.M.; Kaplan, K.A.; Hein, K.; Lee, J.; Kanady, J.; Li, D.; Rabe-Hesketh, S.; Ketter, T.A.; Neylan, T.C.; et al. Treating insomnia improves mood state, sleep, and functioning in bipolar disorder: A pilot randomized controlled trial. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2015, 83, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swainson, J.; Reeson, M.; Malik, U.; Stefanuk, I.; Cummins, M.; Sivapalan, S. Diet and depression: A systematic review of whole dietary interventions as treatment in patients with depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 327, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford-Smith, D.E.; Anthony, D.C. Prebiotic and Probiotic Modulation of the Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis in Depression. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marano, G.; Mazza, M.; Lisci, F.M.; Ciliberto, M.; Traversi, G.; Kotzalidis, G.D.; De Berardis, D.; Laterza, L.; Sani, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. The Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis: Psychoneuroimmunological Insights. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marano, G.; Rossi, S.; Sfratta, G.; Traversi, G.; Lisci, F.M.; Anesini, M.B.; Pola, R.; Gasbarrini, A.; Gaetani, E.; Mazza, M. Gut Microbiota: A New Challenge in Mood Disorder Research. Life 2025, 15, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvia, L.G.; Ametrano, R.M.; Nierenberg, A.A. Exercise Treatment for Bipolar Disorder: Potential Mechanisms of Action Mediated through Increased Neurogenesis and Decreased Allostatic Load. Psychother. Psychosom. 2010, 79, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkintoni, E.; Vassilopoulos, S.P.; Nikolaou, G.; Boutsinas, B. Digital and AI-Enhanced Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia: Neurocognitive Mechanisms and Clinical Outcomes. J Clin Med. 2025, 14, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, J.; Marx, W.; Dash, S.; Carney, R.; Teasdale, S.B.; Solmi, M.; Stubbs, B.; Schuch, F.B.; Carvalho, A.F.; Jacka, F.; et al. The Effects of Dietary Improvement on Symptoms of Depression and Anxiety: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Psychosom. Med. 2019, 81, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marano, G.; Rossi, S.; Sfratta, G.; Acanfora, M.; Anesini, M.B.; Traversi, G.; Lisci, F.M.; Rinaldi, L.; Pola, R.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Gut Microbiota in Women with Eating Disorders: A New Frontier in Pathophysiology and Treatment. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalakshmi, B.; Maurya, N.; Lee, S.-D.; Kumar, V.B. Possible Neuroprotective Mechanisms of Physical Exercise in Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyman, E.; Gamelin, F.X.; Goekint, M.; Piscitelli, F.; Roelands, B.; Leclair, E.; Di Marzo, V.; Meeusen, R. Intense exercise increases circulating endocannabinoid and BDNF levels in humans—Possible implications for reward and depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2012, 37, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Intervention | Clinical Objective | Neurobiological Target |
|---|---|---|
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | Reduce depressive/manic symptoms, improve adherence and cognitive regulation | Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, amygdala |
| Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy (IPSRT) | Stabilize circadian and social rhythms, prevent relapses | Suprachiasmatic nucleus, HPA axis |
| Psychoeducation | Increase illness awareness, improve compliance | Cognitive modulation, indirect neuroplasticity |
| Family-Focused Therapy (FFT) | Reduce family stress and negative emotional expression | Ventromedial prefrontal cortex, limbic circuits |
| CBT for Insomnia (CBT-I) | Improve sleep quality, reduce mood instability | Medial prefrontal cortex, HPA axis regulation |
| Nutritional Interventions | Reduce inflammation, improve neurochemical balance | Gut-brain axis, microglia, cytokines |
| Aerobic Exercise | Enhance mood, cognition, and neuroplasticity | BDNF, hippocampus, systemic inflammation reduction |
| Digital Monitoring Tools | Personalize treatment, improve symptom tracking | Functional regulation via biofeedback and behavioral data |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marano, G.; Lisci, F.M.; Boggio, G.; Marzo, E.M.; Abate, F.; Sfratta, G.; Traversi, G.; Mazza, O.; Pola, R.; Sani, G.; et al. Future Pharmacotherapy for Bipolar Disorders: Emerging Trends and Personalized Approaches. Future Pharmacol. 2025, 5, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5030042
Marano G, Lisci FM, Boggio G, Marzo EM, Abate F, Sfratta G, Traversi G, Mazza O, Pola R, Sani G, et al. Future Pharmacotherapy for Bipolar Disorders: Emerging Trends and Personalized Approaches. Future Pharmacology. 2025; 5(3):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5030042
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarano, Giuseppe, Francesco Maria Lisci, Gianluca Boggio, Ester Maria Marzo, Francesca Abate, Greta Sfratta, Gianandrea Traversi, Osvaldo Mazza, Roberto Pola, Gabriele Sani, and et al. 2025. "Future Pharmacotherapy for Bipolar Disorders: Emerging Trends and Personalized Approaches" Future Pharmacology 5, no. 3: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5030042
APA StyleMarano, G., Lisci, F. M., Boggio, G., Marzo, E. M., Abate, F., Sfratta, G., Traversi, G., Mazza, O., Pola, R., Sani, G., Gaetani, E., & Mazza, M. (2025). Future Pharmacotherapy for Bipolar Disorders: Emerging Trends and Personalized Approaches. Future Pharmacology, 5(3), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/futurepharmacol5030042