- Article
Leishmanicidal and Immunomodulatory Effects of Ocellatin-PT4 and Ocellatin-PT6 on Amastigotes of Leishmania amazonensis
- Mayara G. C. Oliveira,
- Vanessa da Silva Eschimith and
- Felipe T. B. Kuzniewski
- + 11 authors
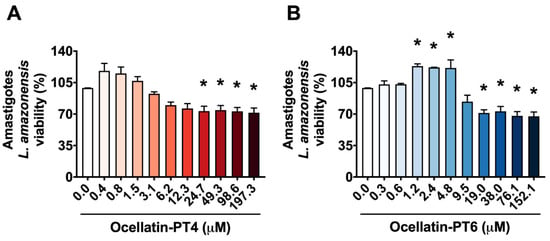
Background/Objectives: Leishmaniasis is a neglected parasitic disease with significant global impact and limited therapeutic options due to the toxicity and cost of current treatments. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) derived from amphibians, such as Ocellatin-PT4 and Ocellatin-PT6, have emerged as promising bioactive molecules due to their antimicrobial properties and low toxicity to mammalian cells. This study evaluated the leishmanicidal and immunomodulatory effects of Ocellatin-PT4 and Ocellatin-PT6 against Leishmania amazonensis amastigotes. Methods: Peptides were tested on axenic amastigotes and macrophages infected with amastigotes. Cytotoxicity was assessed using MTT (0.4–197 µM for Ocellatin-PT4 and 0.3–152.1 µM for Ocellatin-PT6) and vital dye exclusion assays. Reactive oxygen species (ROS), nitric oxide (NO), and lipid droplet (LD) production were quantified to assess immunomodulatory responses. Results: Ocellatin-PT4 and Ocellatin-PT6 significantly reduced the viability of free and intracellular amastigotes at concentrations ≥ 24.7 µM and ≥19 µM, respectively, without affecting J774 macrophage viability. Infected macrophages treated with the peptides showed reduced parasite load and decreased infection index (≥12.3 µM for Ocellatin-PT4 and ≥2.4 µM for Ocellatin-PT6). Both peptides modulated the oxidative stress response: they reduced ROS levels in infected macrophages while only slightly increasing NO production at higher concentrations. Additionally, lipid droplet accumulation, which was increased during infection, was downregulated by both peptides—particularly by Ocellatin-PT6. Conclusions: Ocellatin-PT4 and Ocellatin-PT6 exert leishmanicidal effects and modulate key macrophage functions without cytotoxicity. These peptides represent promising candidates for the development of novel therapies against cutaneous leishmaniasis.
21 December 2025


![Key components of PBPK and popPK models. PBPK models are structured around three main domains: the drug, the system, and the trial. Drug-related data comprise physicochemical and experimental or predicted ADME data. System-related data encompasses physiological and anatomical information relevant for ADME. Trial-related data include study design factors such as dosing regimen, administration route, and duration. In turn, popPK models rely primarily on analysis datasets, incorporating observed drug concentration-time data, individual covariates (e.g., age, weight, genetic markers), and study metadata (e.g., dosing history, sampling times). Adapted from [10], Springer Nature, 2016.](https://mdpi-res.com/futurepharmacol/futurepharmacol-05-00074/article_deploy/html/images/futurepharmacol-05-00074-g001-550.jpg)