-
 Antibiotic Elution from Cement Spacers and Its Influencing Factors
Antibiotic Elution from Cement Spacers and Its Influencing Factors -
 Greek Essential Oils Against Resistant E. coli and O157:H7
Greek Essential Oils Against Resistant E. coli and O157:H7 -
 Targeting Bacterial Biofilms on Medical Implants: Current and Emerging Approaches
Targeting Bacterial Biofilms on Medical Implants: Current and Emerging Approaches -
 Evaluating Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Methods for Cefiderocol: A Review and Expert Opinion on Current Practices and Future Directions
Evaluating Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Methods for Cefiderocol: A Review and Expert Opinion on Current Practices and Future Directions
Journal Description
Antibiotics
Antibiotics
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on all aspects of antibiotics, published monthly online by MDPI. The Croatian Pharmacological Society (CPS) is affiliated with Antibiotics and its members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Infectious Diseases) / CiteScore - Q1 (General Pharmacology, Toxicology and Pharmaceutics )
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 15 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
4.6 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.9 (2024)
Latest Articles
First Report of Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus sciuri Isolated from the Urinary Bladder of a Domestic Rabbit in Romania: A Case Study
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1089; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111089 - 29 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Staphylococcus sciuri, traditionally regarded as a commensal organism in animals and the environment, is increasingly recognized as a potential opportunistic pathogen with zoonotic significance. Its genomic reservoir of methicillin resistance homologues further raises concern regarding its role in antimicrobial resistance
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Staphylococcus sciuri, traditionally regarded as a commensal organism in animals and the environment, is increasingly recognized as a potential opportunistic pathogen with zoonotic significance. Its genomic reservoir of methicillin resistance homologues further raises concern regarding its role in antimicrobial resistance dissemination. This study describes the first documented case of S. sciuri isolated from the urinary bladder of a domestic rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) in Romania, emphasizing its clinical relevance and antimicrobial profile. Methods: A seven-year-old intact female rabbit presenting with apathy, dysuria, and hematuria underwent clinical evaluation, ultrasonography, and cystocentesis. The aspirated intravesical content was subjected to bacterial culture, MALDI-TOF MS identification, and antimicrobial susceptibility testing via the VITEK 2 system. Results: Pure colonies of Gram-positive cocci were identified as S. sciuri with high confidence. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing revealed susceptibility to β-lactams, aminoglycosides, glycopeptides, linezolid, rifampicin, fusidic acid, tigecycline, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, while resistance was observed against fluoroquinolones, macrolides, lincosamides, and tetracycline, indicating a multidrug-resistant phenotype. Treatment with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole combined with ultrasound-guided bladder lavage and supportive therapy resulted in complete clinical recovery within 10 days. Conclusions: This case highlights the pathogenic potential of S. sciuri in domestic rabbits and its capacity to exhibit multidrug resistance. The findings underscore the necessity of including rabbits in antimicrobial resistance surveillance programs and reinforce the importance of culture and sensitivity testing in guiding the therapeutic management of exotic companion animals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Veterinary Microbiology and Antimicrobial Resistance—the One Health Approach)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Retrospective Study on the Use of Daptomycin and Linezolid in Singapore General Hospital
by
Boon San Teoh, Yi Xin Liew, Yibo Wang, Shimin Jasmine Chung and Ban Hock Tan
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1088; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111088 - 28 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE) has emerged as a major nosocomial pathogen. A recent surveillance of our hospital identified a concerning rise in VRE bacteremia since 2020, despite the stable use of broad-spectrum antibiotics. This trend, coupled with the increased use of daptomycin and
[...] Read more.
Background: Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE) has emerged as a major nosocomial pathogen. A recent surveillance of our hospital identified a concerning rise in VRE bacteremia since 2020, despite the stable use of broad-spectrum antibiotics. This trend, coupled with the increased use of daptomycin and linezolid for drug-resistant Gram-positive bacteremia (GPB), prompted an evaluation of their usage beyond approved hospital indications. Methods: A retrospective analysis was carried out from 1 February 2023 to 31 July 2023, during which 100 and 195 patients received linezolid and daptomycin, respectively. Patients’ data were extracted from the hospital’s electronic medical records, and the appropriateness of the antibiotics prescribed was assessed. The amount of daptomycin and linezolid utilization during the study period was also retrieved, as was the incidence of VRE bacteremia. Results: A total of 295 courses of VRE-active agents, linezolid (n = 100) and daptomycin (n = 195), were assessed for appropriateness in this study. Linezolid and daptomycin use were judged as inappropriate 5.0% and 9.2% of the time, respectively. The primary reason for inappropriate linezolid use was overly broad empirical therapy where first-line options like cefazolin and vancomycin could have been prescribed. Daptomycin was often used inappropriately in non-VRE infections, and surgical prophylaxis or use was extended unnecessarily without microbiological justification. Conclusions: Linezolid and daptomycin were prescribed appropriately. Nevertheless, our findings suggest the need to re-evaluate the empirical treatment strategies especially in VRE-colonized patients. Implementation of robust risk-based criteria as well as in-house hospital guidelines or protocols on the initiation of VRE-active agents may help support more judicious prescribing practices of these agents.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antimicrobial Resistance in Clinical Infection and Antibiotic Stewardship)
Open AccessArticle
Implementing a Standard Operating Procedure Is Associated with Improved Vancomycin Target Attainment in Bone and Joint Infections: A Pre-Post Study
by
Moritz Diers, Juliane Beschauner, Maria Felsberg, Laura Isabell Kossack, Alexander Zeh, Karl-Stefan Delank, Natalia Gutteck and Felix Werneburg
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1087; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111087 - 28 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Intravenous vancomycin is a mainstay for prosthetic joint infections, osteomyelitis, and implant-associated infections, yet real-world dosing frequently misses PK/PD targets. We assessed whether a ward-embedded standard operating procedure (SOP) improves target attainment and dosing efficiency. Methods: Single-centre, non-randomized pre-post study
[...] Read more.
Background: Intravenous vancomycin is a mainstay for prosthetic joint infections, osteomyelitis, and implant-associated infections, yet real-world dosing frequently misses PK/PD targets. We assessed whether a ward-embedded standard operating procedure (SOP) improves target attainment and dosing efficiency. Methods: Single-centre, non-randomized pre-post study in an orthopedic service. SOP mandated weight-adapted loading dose, renal function-adjusted maintenance dosing, a 15–20 mg/L trough target, and scheduled TDM. Adults receiving ≥72 h IV vancomycin were included; major renal failure and incomplete TDM were excluded. Pre-SOP data were retrospective; post-SOP data were prospective (03/2024–06/2025). Primary outcome: proportion of troughs within 15–20 mg/L (first and repeated). Repeated measures were modeled with GEE. Time to first in-range trough used Kaplan–Meier (indexed by measurement number). Results: We included 154 patients (pre-SOP n = 58; post-SOP n = 96); baseline characteristics were broadly similar. Use of a weight-based loading dose rose from 31.0% pre-SOP to 100% post-SOP (p < 0.001). At the first trough, 17.2% vs. 26.0% were within 15–20 mg/L (p = 0.238). Across 847 troughs (pre = 319; post = 528), the in-range proportion increased from 28.2% to 41.7%, with subtherapeutic values declining from 38.2% to 26.3% and supratherapeutic values remaining nearly similar (33.5% → 32.0%). Time to first in-range trough shortened from a median of 4 to 2 measurements (log-rank p < 0.001). Post-SOP measurements had higher odds of being in range (aOR 1.68, 95% CI 1.29–2.20; p < 0.001), with marginal predicted probabilities of 33.4% (pre) vs. 47.8% (post). Dose adjustments per patient decreased from a mean 4.0 to 2.48 (p < 0.001). Conclusions: A pragmatic, orthopedic ward–embedded SOP for intravenous vancomycin improved pharmacologic precision: more measurements within target, fewer subtherapeutic exposures, faster target attainment, and fewer dose changes. These data support protocol-first implementation as an immediately actionable step toward more consistent vancomycin exposure in orthopedic care. Future work should integrate AUC-guided, model-informed precision dosing and evaluate clinical endpoints and generalizability across centres.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antimicrobial Stewardship in Surgical Infection)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
“I Felt Empowered”: Patient-Reported Experience with a Pilot National Community Pharmacy-Based Urinary Tract Infection Service
by
Efi Mantzourani, Andrew Evans, Rhian Deslandes, Haroon Ahmed, Nicola Reeve, Samuel Macdonald and Rebecca Cannings-John
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1086; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111086 - 28 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: In June 2024, urinary tract infections (UTIs) were added to the list of conditions that could be treated by community pharmacists providing the national Common Ailments Service in Wales. The aim of this study was to describe patient-reported experiences of UTI management
[...] Read more.
Background: In June 2024, urinary tract infections (UTIs) were added to the list of conditions that could be treated by community pharmacists providing the national Common Ailments Service in Wales. The aim of this study was to describe patient-reported experiences of UTI management by pharmacists. Methods: A positivist research paradigm was selected, with data collection through a survey. Results: In total, 309 surveys were received between 29 June 2024 and 14 July 2025. Patients rated their experience using a scale of 1 (very poor) to 10 (excellent), with a median score of 10 (IQR = 10 to 10, range 6 to 10). High satisfaction was independent of age and provision of antibiotics, with the same median and IQR and a similar range between the groups who received and did not receive antibiotics (7–10 and 6–10, respectively). Of the 309 respondents, 297 (96.1%) stated that the next time they had a UTI, they would return to the pharmacy instead of trying to see a GP, and 253 (81.9%) that they understood why antibiotics are not always recommended. Conclusions: Community pharmacists managed patient expectations, improved patient confidence in managing current symptoms and provided information on self-care strategies for preventing future infections, demonstrating their valuable role in health promotion and antimicrobial stewardship.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pharmacist-Led Management of Antimicrobial Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Ceftazidime–Avibactam Resistance in Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Bloodstream Infections: Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes
by
Ayten Yanık and Ömer Karaşahin
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1085; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111085 - 28 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background/Introduction: Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP) bacteremia is a serious public health problem due to its high mortality rate and limited treatment options. This study aimed to identify risk factors associated with ceftazidime–avibactam (CAZ-AVI) resistance in CRKP bacteremia and to evaluate its impact on
[...] Read more.
Background/Introduction: Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP) bacteremia is a serious public health problem due to its high mortality rate and limited treatment options. This study aimed to identify risk factors associated with ceftazidime–avibactam (CAZ-AVI) resistance in CRKP bacteremia and to evaluate its impact on clinical outcomes. Methods: This retrospective single-center cohort study included adult patients with CRKP bloodstream infections treated at a tertiary hospital in Türkiye between January 2021 and December 2024. Demographic, clinical, and laboratory data were collected, and risk factors for CAZ-AVI resistance and 30-day mortality were analyzed. Results: Among 154 patients, 42.8% had CAZ-AVI-resistant strains. Resistant infections were associated with longer hospital stays and higher Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) scores. The resistance rate was lower in patients with intra-abdominal infections, while fluoroquinolone and fosfomycin use was more common in the resistant group. The overall 30-day mortality rate was 57%. Pitt bacteremia score and creatinine levels were identified as independent predictors of mortality. Discussion: CAZ-AVI resistance in CRKP bacteremia appears to develop in patients with prolonged hospitalization and high comorbidity burden. These factors likely increase exposure to resistant microorganisms and antibiotic pressure, complicating treatment outcomes. Conclusions: CAZ-AVI resistance in CRKP bacteremia is associated with specific clinical risk profiles and contributes to high mortality. Identifying high-risk patients and optimizing antimicrobial stewardship are essential to improve prognosis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Genetics and Antimicrobial Resistance in Pathogens of Hospital Importance)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
RAPID-CARE: Rapid Antibiotic Optimization in the ICU After Implementation of a Pneumonia Multiplex PCR Test—A Real-World Evaluation
by
Montserrat Rodríguez-Gómez, Fernando Martínez-Sagasti, María Calle-Romero, Andrea Prieto-Cabrera, Patricia De La Montaña-Díaz, Irene Díaz-De la Torre, Alberto Delgado-Iribarren García-Campero, Sara Domingo-Marín, Miguel Sánchez-García and Ignacio Martín-Loeches
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1084; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111084 - 27 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Lower respiratory tract infections (LRTIs) are frequent in the intensive care unit (ICU) and drive empiric broad-spectrum antibiotic use. Rapid multiplex PCR assays may improve pathogen detection and stewardship compared with conventional culture. We evaluated the real-world impact of the BioFire
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Lower respiratory tract infections (LRTIs) are frequent in the intensive care unit (ICU) and drive empiric broad-spectrum antibiotic use. Rapid multiplex PCR assays may improve pathogen detection and stewardship compared with conventional culture. We evaluated the real-world impact of the BioFire® FilmArray® Pneumonia Panel Plus (FA-PNEU®) on antimicrobial management in suspected nosocomial LRTI. Methods: This was a single-centre, prospective observational cohort study conducted in a tertiary ICU (Madrid, Spain) between April 2021 and March 2025. Adult patients with suspected hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP), ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), or ventilator-associated tracheobronchitis (VAT) were included if paired respiratory samples underwent FA-PNEU® and conventional culture (CC). Diagnostic accuracy and prescribing changes were analysed. Results: A total of 344 samples from 236 patients were included. FA-PNEU® demonstrated high sensitivity (93.4%) and negative predictive value (97.9%) but moderate specificity (65.0%) and low positive predictive value (36.5%). False positives occurred in 85.8% of patients with prior antibiotic therapy targeting the detected organism. Antibiotic management was considered directly influenced by FA-PNEU® when any prescribing decision (initiation, escalation, de-escalation, or discontinuation) explicitly followed the panel’s results rather than other clinical or microbiological information. Using this definition, FA-PNEU® directly influenced antibiotic therapy in 57.6% of cases, while in 17.7%, prescribing was instead guided by a suspected alternative infection. In patients without prior antibiotics, treatment initiation or withholding was fully concordant with FA-PNEU® results, while in those already receiving therapy, 60.8% underwent modification, two-thirds in agreement with the panel. Conclusions: In critically ill patients with suspected nosocomial LRTI, FA-PNEU® provided rapid, high-sensitivity diagnostics that substantially influenced antimicrobial prescribing. Its greatest value lies in ruling out bacterial infection and guiding stewardship, though results must be interpreted within the full clinical and microbiological context.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Antibiotics Use and Antimicrobial Stewardship)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Genotypic Characterization of Virulence Factors in Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase (ESBL)-Producing Escherichia coli Strains from Chickens in Hungary
by
Ádám Kerek, Ábel Szabó, Gergely Tornyos, Eszter Kaszab, Krisztina Bali and Ákos Jerzsele
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1083; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111083 - 27 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: The increasing attention on extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli strains isolated from poultry flocks stems from concerns about their virulence potential and zoonotic risk. Of particular significance is the identification of extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli (ExPEC) pathotypes in poultry, as these
[...] Read more.
Background: The increasing attention on extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli strains isolated from poultry flocks stems from concerns about their virulence potential and zoonotic risk. Of particular significance is the identification of extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli (ExPEC) pathotypes in poultry, as these strains pose not only animal health concerns but also serious threats to food safety and public health. Mapping the genetic background of pathogenicity and antimicrobial resistance is essential for risk assessment and the development of effective control strategies. Methods: A total of 87 E. coli isolates were isolated from tracheal and cloacal swab samples collected from healthy chickens between 2022 and 2023. Whole-genome sequencing was performed using Illumina and MGI next-generation sequencing platforms. Bioinformatic analyses were conducted to identify virulence-associated genes and pathotype markers using multiple reference databases, including VirulenceFinder. The frequency of virulence genes was summarized both in tabular form and visualized through graphical representations. Results: A substantial proportion of the isolates harbored virulence genes linked to various ExPEC pathotypes, particularly uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC), avian pathogenic E. coli (APEC), and neonatal meningitis-causing E. coli (NMEC). The most frequently detected colonization factors included members of the fim, pap, ecp, and fae gene families. Among fitness-related genes, iron acquisition systems—ent, chu, iro, iuc, fep, and ybt—were especially prevalent. Classic UPEC-associated genes such as pap and fimH, along with the APEC-related iutA and vat, were found at high frequencies. Four isolates exhibited a virulence gene profile characteristic of the NMEC pathotype (ibeA, kpsD/M/T, fimH). In contrast, hallmark genes of enteric pathotypes were absent from all isolates. Conclusions: The predominance of extraintestinal virulence factors in the examined poultry-derived E. coli strains underscores their zoonotic potential. The complete absence of enteric pathotype markers indicates that the studied poultry populations primarily harbor ExPEC-like strains. These findings highlight the critical need for ongoing genomic surveillance and targeted preventive strategies within poultry production systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Genomic Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR))
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus CC1 and CC1660 of Human and Equine Origin
by
Johanna Jahnen, Christiane Cuny, Wolfgang Witte, Ralf Ehricht, Stefan Monecke, Dennis Hanke, Tanja Ahrens, Marta Leal, Sofia S. Costa, Isabel Couto, Stefan Schwarz and Andrea T. Feßler
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1082; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111082 - 27 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Staphylococcus aureus isolates from humans and horses of the equine-associated clonal complexes (CCs) CC1 and CC1660 were comparatively investigated for their genomic relationships. Methods: A total of 91 S. aureus isolates (64 human, 27 equine) were subjected to whole-genome sequencing
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Staphylococcus aureus isolates from humans and horses of the equine-associated clonal complexes (CCs) CC1 and CC1660 were comparatively investigated for their genomic relationships. Methods: A total of 91 S. aureus isolates (64 human, 27 equine) were subjected to whole-genome sequencing (WGS), sequence analysis, and antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Results: WGS confirmed 75 CC1 and 16 CC1660 isolates, comprising nine sequence types (STs) in CC1 and four STs in CC1660. Ten spa types were present in CC1 and five in CC1660. In the arcC gene of three CC1 isolates, a 285 bp deletion was detected, and a nucleotide deletion causing a premature stop codon was found in one CC1660 isolate. Core genome (cg) MLST revealed a minimum difference of 1398/1492 alleles between the two CCs. All CC1 isolates harbored agr group III and capsule type 8 alleles, whereas all CC1660 isolates had agr group II and capsule type 5 alleles. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing revealed 18 phenotypic and 19 genotypic resistance patterns. All isolates were susceptible to vancomycin, linezolid and quinupristin–dalfopristin. Several virulence genes were detected in different combinations. The equine leukocidin genes lukP/lukQ were found in 22 isolates from horses and 38 isolates from humans, of which 35 had confirmed contact with horses. No Panton–Valentine leukocidin genes were found. Three human CC1660 isolates carried the toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 gene tst-1. Conclusions: The analysis of the 91 isolates might suggest intra- and interspecies transmission among and between humans and horses, which should be monitored in the future.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antibiotic Resistance in Bacterial Isolates of Animal Origin)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Knowledge, Perceptions, and Behaviors Regarding Antibiotic Use in a Community-Based Adult Sample in Salerno: An Observational Survey in a Province in Southern Italy
by
Emanuela Santoro, Raffaele Amelio, Roberta Manente, Giuseppina Speziga, Antonio Donato, Mario Capunzo and Giovanni Boccia
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1081; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111081 - 27 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Antibiotic resistance represents one of the major global health emergencies, driven by the inappropriate use of antibiotics and persistent misconceptions among adults attending general medical clinics. This study, conducted on 325 participants recruited from general medical clinics in the province of
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Antibiotic resistance represents one of the major global health emergencies, driven by the inappropriate use of antibiotics and persistent misconceptions among adults attending general medical clinics. This study, conducted on 325 participants recruited from general medical clinics in the province of Salerno, aimed to assess their knowledge, perceptions, and behaviors regarding antibiotic use. Methods: A cross-sectional, quantitative observational survey was conducted using a structured questionnaire based on the WHO tool and adapted to the local context. Results: The results show that the majority of participants take antibiotics only when prescribed by a doctor (90.2%), but risky practices such as self-medication (10%) and early discontinuation of therapy (16%) persist. In addition, 72% of subjects demonstrate incomplete knowledge about the independent management of drugs, and 86% mistakenly believe that resistance is limited to the individual rather than the community. The descriptive analysis stratified by age showed higher levels of awareness among subjects under 30 years of age, compared to significant knowledge gaps and inappropriate behaviors in the over-65 age group. Conclusions: Despite a good awareness of the need for medical prescriptions and the collective importance of the phenomenon, there are still critical areas of knowledge and incorrect practices that can promote the spread of antibiotic resistance. The data collected underscore the urgency of targeted educational strategies differentiated by age group, integrated with multi-channel communication interventions, in order to promote the appropriate use of antibiotics and contain the impact of one of the most serious global health emergencies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Antibiotics Use and Antimicrobial Stewardship)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Century of Bacteriophages: Insights, Applications, and Current Utilization
by
Sadika Dkhili, Miguel Ribeiro and Karim Ben Slama
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1080; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111080 - 27 Oct 2025
Abstract
Bacteriophages or phages are viruses that exclusively target and replicate within bacteria, acting as natural predators in the biosphere. Since their discovery over a century ago, host-specific bacteriophages have been widely advocated as a cost-effective and adaptable approach to controlling and combating bacterial
[...] Read more.
Bacteriophages or phages are viruses that exclusively target and replicate within bacteria, acting as natural predators in the biosphere. Since their discovery over a century ago, host-specific bacteriophages have been widely advocated as a cost-effective and adaptable approach to controlling and combating bacterial infections. Antibiotic resistance, a growing concern and a significant global public health problem, has further underscored the importance of bacteriophages. Nevertheless, their potential applications span diverse fields, including molecular biology, phage therapy, bacterial detection, food safety, and wastewater decontamination. Furthermore, bacteriophages represent a diverse group of viruses that are relatively easy to handle, making them suitable for use in both treatments and biotechnology research. In this review, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of bacteriophage history, characteristics, and applications that have been employed to address human challenges, ranging from healthcare to environmental remediation. We will highlight key findings and outcomes, shedding light on ongoing research that will shape the future of bacteriophage applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Revolutionizing Infection Treatment: Cutting-Edge Approaches in Antimicrobial Stewardship)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluating Outer Membrane Vesicle Isolation Techniques for Borrelia burgdorferi and Their Impact on Vesicle Composition, Gene Expression Profile and Uptake
by
Jasmine Jathan, Jay M. Pandya, Mahima Jain, Tejasri Kaithalapuram, Dhara Cherukuri and Eva Sapi
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1079; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111079 - 27 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Borrelia burgdorferi, the causative agent of Lyme disease, releases outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) that may contribute to infection and modulate the host immune response. Although interest in OMVs is growing, few studies have systematically compared methods for isolating OMVs from
[...] Read more.
Background: Borrelia burgdorferi, the causative agent of Lyme disease, releases outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) that may contribute to infection and modulate the host immune response. Although interest in OMVs is growing, few studies have systematically compared methods for isolating OMVs from B. burgdorferi. Methods: In this study, we evaluated two OMV isolation techniques—standard ultracentrifugation and an ion-exchange chromatography-based ExoBacteria™ kit—and examined how serum supplements (rabbit serum vs. exosome-depleted fetal bovine serum, ED-FBS) influence Bb-OMV yield and composition. Gene expression profiles were assessed using RT-PCR, and specific protein content was identified by Western blot analyses. To assess the ability of Bb-OMVs to interact with host cells, Bb-OMVs were co-cultured with MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer cells. Results: Transmission electron microscopy confirmed that both methods produced spherical Bb-OMVs with intact membrane bilayers. Ultracentrifugation generated larger vesicles (15–180 nm), while the ExoBacteria™ kit yielded smaller vesicles (<50 nm) with a higher double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) content, and protein levels were similar across samples. Cultures grown with rabbit serum produced more Bb-OMVs and had cleaner backgrounds in the TEM images than those grown with ED-FBS. All Bb-OMV samples lacked intracellular markers (DnaK and 16S rRNA) and consistently expressed the outer surface protein OspA, confirming high purity. All isolated Bb-OMVs were taken up by the cells, as indicated by OspA expression, without detectable 16S rRNA, confirming vesicle internalization without bacterial contamination. Conclusions: These findings indicate that isolated OMVs are biologically active and capable of interacting with mammalian cells, highlighting their potential role in host–pathogen interactions and the broader relevance of OMVs in studying bacterial modulation of mammalian cell behavior. Overall, both isolation methods produced high-quality OMVs, with ultracentrifugation yielding slightly more pure vesicles, emphasizing the importance of selecting appropriate isolation methods and culture conditions for functional OMV studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles: Vehicles for Pathogenesis and Antibiotic Resistance)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Point Prevalence Survey of Antibiotic Use in Latin American Hospitals: 2022–2023
by
Paola Lichtenberger, Gabriel Levy-Hara, Robin Rojas-Cortés, Tatiana Orjuela, Jose Pablo Diaz-Madriz, Pilar Ramon-Pardo, Jose Luis Bustos, Anahí Dreser, Tania Herrera, Marcela Pilar Rojas-Diaz, Giovanna Huaquipaco, Didia Sagastume, Jose Luis Castro and on behalf of the Latin American PPS Group
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1078; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111078 - 27 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a public health challenge, exacerbated by the inappropriate use of antibiotics (ABs) and the lack of standardized surveillance in healthcare settings. Objective: The Latin American PPS aimed to provide a standardized methodology for monitoring antibiotic use, gather data
[...] Read more.
Background: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a public health challenge, exacerbated by the inappropriate use of antibiotics (ABs) and the lack of standardized surveillance in healthcare settings. Objective: The Latin American PPS aimed to provide a standardized methodology for monitoring antibiotic use, gather data on antibiotic prescription practices, and support initiatives for antimicrobial stewardship (AMS). Methodology: Using a Spanish-adapted version of the WHO PPS methodology, a point prevalence survey (PPS) was conducted between 2022 and 2023 in 67 hospitals across five Latin American countries. Results: A total of 11,094 patients were surveyed, of which 47.9% received at least one AB; surgical and intensive care units displayed the highest prevalence. Most prescribed AB were third-generation cephalosporins (3GC) (22.0%), carbapenems (12.1%), glycopeptides (9.2%), and penicillin combinations (8.6%). A substantial use of agents classified under the WHO’s “Watch” group was found, with notable variances across countries. A multilevel logistic regression model identified that patient age, ICU admission, recent hospitalization, the presence of a catheter, and intubation were significantly associated with higher odds of AB use. In contrast, patients admitted to obstetric or pediatric wards had lower odds of receiving antibiotics. The model revealed considerable heterogeneity between countries, even after adjusting clinical and demographic factors. Conclusions: This study highlights AMS opportunities through targeted interventions, such as optimizing surgical prophylaxis, reducing the use of 3GC, carbapenems, and glycopeptides, and improving adherence to CPGs. These findings provide a comprehensive framework for policymakers and healthcare facilities to develop AMS strategies tailored to the Latin American context.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antibiotic Resistance: A One-Health Approach, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
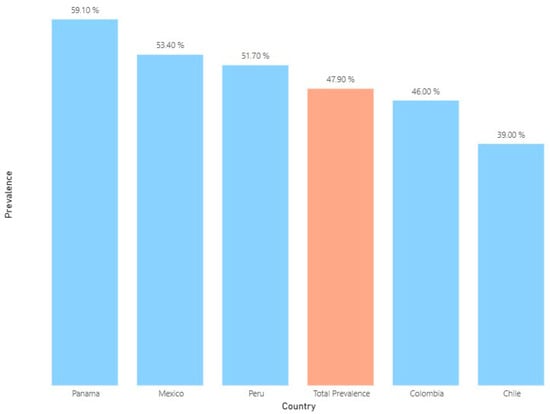
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sequence Permutation Generated Lysine and Tryptophan-Rich Antimicrobial Peptides with Enhanced Therapeutic Index
by
Kuang-Li Peng, Yu-Hsuan Wu, Hsuan-Che Hsu and Jya-Wei Cheng
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1077; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111077 - 26 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are promising therapeutic agents due to their broad-spectrum activity against bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Unlike traditional antibiotics, AMPs target microbial membranes directly and are less likely to induce resistance. They also possess immunomodulatory and wound-healing properties. However, clinical application
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are promising therapeutic agents due to their broad-spectrum activity against bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Unlike traditional antibiotics, AMPs target microbial membranes directly and are less likely to induce resistance. They also possess immunomodulatory and wound-healing properties. However, clinical application remains limited by factors such as salt sensitivity, low bioavailability, and poor stability. To address these challenges, researchers have turned to structural optimization strategies. Recently, artificial intelligence (AI) has facilitated peptide drug design by rapidly screening large peptide libraries. Still, AI struggles to predict how subtle sequence changes affect peptide structure and function. Traditional sequence permutation offers a complementary approach by analyzing structural and functional effects without altering amino acid composition. Methods: In this study, we applied a clockwise sequence permutation strategy to the AMP W5K/A9W, generating derivative peptides with identical molecular weight, net charge, and hydrophobicity. We aimed to investigate how lysine and tryptophan distribution affects antimicrobial activity, membrane permeability, and selectivity. We assessed the secondary structures using circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy and evaluated in vitro antimicrobial activity, salt resistance, membrane-permeabilizing ability, hemolysis, and wound healing effects. Results: The results revealed that the sequence arrangement of key residues significantly impacts peptide bioactivity and therapeutic index. Conclusions: This study highlights the importance of sequence order in determining AMP function. It also supports integrating permutation strategies with AI-based design to enhance AMP discovery. Together, these approaches offer new opportunities to combat drug-resistant pathogens and advance next-generation anti-infective therapies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antimicrobial Peptides: Mechanisms, Engineering, and Therapeutic Development)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Measuring Contamination Levels and Incubation Results of Hatching Eggs Sanitized with Essential Oils
by
Vinícius Machado dos Santos, Gabriel da Silva Oliveira, Pedro Henrique Gomes de Sá Santos, Liz de Albuquerque Cerqueira, José Luiz de Paula Rôlo Jivago, Susana Suely Rodrigues Milhomem Paixão, Márcio Botelho de Castro and Concepta McManus
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1076; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111076 - 26 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Making sustainable choices and transforming guidelines into effective bacterial control practices for viable and safe hatching eggs is a challenge for many researchers. Gradually, scientific findings are strengthening the case for using antibacterial protocols with essential oils (EOs) for hatching eggs,
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Making sustainable choices and transforming guidelines into effective bacterial control practices for viable and safe hatching eggs is a challenge for many researchers. Gradually, scientific findings are strengthening the case for using antibacterial protocols with essential oils (EOs) for hatching eggs, which could lead to changes in traditional egg sanitization management and stimulate new research. The present study aimed to measure the contamination levels and incubation outcomes of hatching eggs sanitized with Zingiber officinale (ZOEO), Cymbopogon flexuosus (CFEO), and Rosmarinus officinalis (ROEO) essential oils. Methods: Hatching eggs from commercial broiler breeders were sanitized with solutions of ZOEO, CFEO, and ROEO prepared in grain alcohol and compared with formaldehyde and non-sanitized eggs. Bacterial contamination, eggshell integrity, incubation parameters, embryonic trachea histology, genotoxicity, and irritation potential were evaluated under commercial conditions. Results: It has been demonstrated that these EOs significantly reduce eggshell and yolk sac contamination, promote hatchability rates above 93% with good-quality chicks, and do not cause alterations in the embryonic trachea or potential genetic damage to the chicks. Conclusions: ZOEO, CFEO, and ROEO can be recommended as sanitizers for hatching eggs.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Occurrence and Antibiotic Resistance Risk Burden of Vibrio mimicus Isolates from Seafood and Aquatic Environments
by
Temitope C. Ekundayo and Frederick T. Tabit
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1075; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111075 - 26 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Emerging antimicrobial resistance in Vibrio mimicus (Vm) associated with seafood may exacerbate infections in patients. Method: This study investigated the prevalence of antibiotic resistance and its cross-sample/territory risk burden in Vm from seafood and aquatic environment using hierarchical mixed-effects and antimicrobial resistance
[...] Read more.
Background: Emerging antimicrobial resistance in Vibrio mimicus (Vm) associated with seafood may exacerbate infections in patients. Method: This study investigated the prevalence of antibiotic resistance and its cross-sample/territory risk burden in Vm from seafood and aquatic environment using hierarchical mixed-effects and antimicrobial resistance risk index (ARRI) modelling. Results: Among the Vm isolates, resistance was highest to amoxicillin (83.7%, 5.3–99.8) and streptomycin (54.6%, 95% CIs: 15.8–88.5), with generally high resistance to penicillins (58.0–98.0%), macrolides (17.2–65.8%), and colistin sulphate (80.2%). Resistance to aminoglycosides, cephalosporins, tetracyclines, and fluoroquinolones varied widely, with seafood and environmental water sources showing similar trends. Notably, resistance to nalidixic acid (47.2%, 17.3–79.4) and doxycycline (59.4%, 3.6–98.3) was prominent. Carbapenem resistance remained low, especially in seafood. Chloramphenicol resistance (32.3%, 2.7–89.0) was higher in environmental water. Trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole resistance was relatively low (5.8%, 0.7–36.1). Ampicillin–sulbactam resistance (43.3%, 5.1–91.5) exceeded that of amoxicillin–clavulanic acid (31.8%, 0.8–96.3). The current data reveal antibiotic resistance burdens (ARBs) of Vm in seafood (ARRI ≈ 50) and waters (ARRI ≈ 46) exceeded that of human isolates (ARRI ≈ 0.01) greatly. Also, it identified Nigeria (ARRI = 7.78)/India (ARRI = 7.35) and Asia (ARRI = 56.91)/Africa (ARRI = 40.12) as hotspots of Vm ARBs. Conclusions: Overall, Vm exhibited diverse antimicrobial resistance patterns across sources with high resistance concerns and high rates against penicillins, cephalosporins, macrolides, and sometimes polymyxins. Thus, it is recommended that stricter regulations on antibiotic use in aquaculture are enforced; wastewater treatment is improved, one-health surveillance is implemented; and education of stakeholders about resistance risks, use of alternatives, and proper cooking of seafood to mitigate Vm-resistant impact is promoted.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Through the Pharmacist’s Lens: A Qualitative Study of Antibiotic Misuse and Antimicrobial Resistance in Brazilian Communities
by
Timo J. Lajunen, Líria Souza Silva and Mark J. M. Sullman
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1074; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111074 - 25 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: AMR causes a large global health burden, with approximately 4.95 million deaths linked to bacterial AMR in 2019, 1.27 million due to AMR directly. Although Brazil mandated prescriptions for systemic antibiotics in 2010/2011, self-medication and access without prescriptions continue, with community
[...] Read more.
Background: AMR causes a large global health burden, with approximately 4.95 million deaths linked to bacterial AMR in 2019, 1.27 million due to AMR directly. Although Brazil mandated prescriptions for systemic antibiotics in 2010/2011, self-medication and access without prescriptions continue, with community pharmacists playing a vital part in antimicrobial stewardship (AMS). This study examined antibiotic misuse and AMR in Brazil through community pharmacists’ perspectives, emphasising their dual role as professional actors and frontline observers of public behaviour. Methods: We conducted 20 semi-structured interviews with community pharmacists and performed reflexive thematic analysis of their accounts, repeating five independent analytic cycles to confirm thematic robustness. Results: Six themes were consistently identified as recounted by pharmacists in their practice contexts: Access and Self-Medication; Relationships with Healthcare Professionals; Knowledge and Beliefs about Antibiotics; Use and Adherence; Healthcare System Barriers; and Regulation and Enforcement. Pharmacists mentioned regular requests for antibiotics without prescriptions, drug reuse, and significant impact from community, i.e., from relatives, and peers. The common misunderstanding was that antibiotics treat viral illnesses. Structural issues, for instance GP appointment costs and long waits, made patients seek help from pharmacies. Due to regulation being applied inconsistently, pharmacies struggled to refuse unsuitable requests. Conclusions: Framed through pharmacists’ dual vantage as professionals and frontline observers, the findings highlight intertwined factors underpinning inappropriate antibiotic use in Brazil and support a multi-pronged intervention spanning health system strengthening, professional education, economic considerations, and community engagement.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antibiotic Use in the Communities—2nd Edition)
Open AccessArticle
Risk Factors Associated with Community-Onset Infections Due to Multidrug-Resistant Organisms
by
Rafail Matzaras, Dimitrios Biros, Sissy Foteini Sakkou, Diamantina Lymperatou, Sempastian Filippas-Ntekouan, Anastasia Prokopidou, Revekka Konstantopoulou, Valentini Samanidou, Lazaros Athanasiou, Anastasia Christou, Petros-Spyridonas Adamidis, Amalia Despoina Koutsogianni, George Liamis, Haralampos Milionis, Matilda Florentin and Eirini Christaki
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1073; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111073 - 25 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) and the emergence of multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) represent major public health threats. Although traditionally linked to hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), MDROs are becoming gradually more prevalent in community-onset infections. Objectives: The objective of this study is to identify
[...] Read more.
Background: Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) and the emergence of multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs) represent major public health threats. Although traditionally linked to hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), MDROs are becoming gradually more prevalent in community-onset infections. Objectives: The objective of this study is to identify major risk factors associated with community-onset MDRO infections among patients admitted to the hospital. Methods: This is a retrospective study of patients admitted to the Internal Medicine Departments of the University General Hospital of Ioannina from July 2022 to August 2023 and had a microbiologically confirmed infection. Patients with HAIs were excluded. Data were extracted from both electronic and paper-based medical records and included variables such as demographics, baseline comorbidities, previous antibiotic use, previous hospitalizations, the type of MDRO and infection, and clinical outcomes. Statistical analysis included descriptive statistics, univariate analyses, and subsequently multiple binary regression models. Each regression model was adjusted for age and sex. Results: Our cohort included 125 participants with a mean age of 77.9 years, with the majority (58.4%) being female. The overall prevalence of MDRO infections was 43.2% (54/125). Notably, the presence of a permanent urinary catheter was associated with a nearly fourfold increase in the risk of community-onset MDRO infections (OR = 3.69; 95% CI: 1.35–10.05; p = 0.011), while prior hospitalization (OR = 3.33; 95% CI: 1.48–7.51; p = 0.004), the Charlson index score (OR = 3.08; 95% Cl: 1.1–8.68; p = 0.033) and previous antibiotic use (OR = 2.18; 95% CI: 0.98–4.84; p = 0.057) were also significant potential risk factors. Conclusions: The identification of key risk factors associated with community-onset MDRO infections in patients admitted to the hospital can assist clinicians in early stratification and rational selection of initial empirical antimicrobial treatment, support antimicrobial stewardship programs, promote targeted public health interventions, and encourage more judicious antibiotic use.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Healthcare-Associated Infections (HAIs): Prevention, Control and Surveillance)
►▼
Show Figures
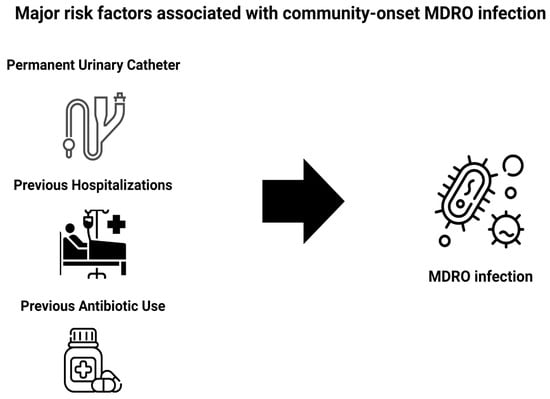
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Treatment Duration in Bacterial Prosthetic Joint Infections: A Narrative Review of Current Evidence
by
Hajer Harrabi, Christel Mamona-Kilu, Eloïse Meyer, Emma d’Anglejan Chatillon, Nathalie Dournon, Frédérique Bouchand, Clara Duran, Véronique Perronne, Karim Jaffal and Aurélien Dinh
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1066; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111066 - 25 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The optimal duration of antibiotic therapy for bacterial prosthetic joint infections (PJI) remains a topic of considerable debate. Current recommendations are often based on limited evidence and expert consensus. Emerging data suggest that shorter antibiotic courses may be as effective as prolonged
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The optimal duration of antibiotic therapy for bacterial prosthetic joint infections (PJI) remains a topic of considerable debate. Current recommendations are often based on limited evidence and expert consensus. Emerging data suggest that shorter antibiotic courses may be as effective as prolonged treatments in select cases. Shortening the duration of therapy offers several advantages, including a reduced risk of bacterial resistance, fewer adverse events, and cost savings. However, this approach must be carefully balanced with the individual patient’s risk of treatment failure. This narrative review aims to synthesize current evidence regarding the duration of antibiotic therapy in PJIs, according to surgical strategies—DAIR (debridement, antibiotics, and implant retention), one-stage exchange, two-stage exchange, and resection without reimplantation—and to identify parameters that may guide individualized and potentially shortened regimens. Methods: We conducted a comprehensive search of PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases through January 2025, including observational studies, randomized controlled trials, and international guidelines. Reference lists of key articles were also screened. Results: Studies on DAIR suggest that longer regimens (e.g., 8–12 weeks) are necessary, especially in staphylococcal infections, as confirmed by the DATIPO trial, which showed higher failure rates with 6 weeks compared to 12 weeks. Evidence on one-stage exchange is limited but increasingly suggests that 6 weeks may be sufficient in selected patients; however, no dedicated trial has confirmed this. In two-stage exchange, small retrospective series report successful outcomes with short antibiotic therapy combined with local antibiotics, but randomized trials show trends favoring longer regimens. For patients treated with permanent resection arthroplasty, arthrodesis, or amputation, antibiotic durations are highly variable, with few robust data. Across all strategies, most studies are limited by methodological weaknesses, including small sample sizes, retrospective design, lack of microbiological stratification, and heterogeneous outcome definitions. Conclusions: Despite growing interest in shortening antibiotic durations in PJIs, high-quality evidence remains limited. Until additional randomized trials are available—particularly in one- and two-stage exchange settings—12 weeks remains the safest reference duration for most patients, especially those with retained hardware. Future studies should incorporate stratification by infection type, causative organism, and host factors to define tailored and evidence-based antibiotic strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Orthopedic Infections: Epidemiology and Antimicrobial Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure A1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Existing Evidence from Economic Evaluations of Antimicrobial Resistance—A Systematic Literature Review
by
Sajan Gunarathna, Yongha Hwang and Jung-Seok Lee
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1072; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111072 - 24 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Although antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is recognized as a critical global health threat across human, animal, and environmental domains, evidence from AMR economic evaluations remains limited. This study systematically reviewed available studies, emphasizing existing evidence and reported limitations in AMR-related economic evaluations.
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Although antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is recognized as a critical global health threat across human, animal, and environmental domains, evidence from AMR economic evaluations remains limited. This study systematically reviewed available studies, emphasizing existing evidence and reported limitations in AMR-related economic evaluations. Methods: A comprehensive review of peer-reviewed empirical studies was conducted, including publications up to July 2023 without temporal restrictions, but limited to English-language articles. Literature searches were undertaken in PubMed and Cochrane using a search strategy centered on the terms “economic evaluations” and “antimicrobial resistance.” Screening and data extraction were performed by two reviewers independently, with disagreements resolved through consensus or consultation with a third reviewer. Findings were synthesized narratively. Results: Of the 3682 records screened, 93 studies were included. Evidence gaps were identified across income and geographic regions, particularly in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) and the African, Southeast Asian, and Eastern Mediterranean regions. Studies were comparatively more numerous in high-income countries (HICs) and the European and Americas regions. Substantial gaps also existed in one health approach and community-based evaluations. Nine major study limitations were identified, with many interlinked. The most frequent issues included limited generalizability primarily due to inadequate sampling approaches (n = 16), and single-center studies (n = 11), alongside errors in cost estimation (n = 4), and lack of consideration for essential features or information (n = 3). Conclusions: The review highlights persistent evidence gaps and recurring methodological shortcomings in AMR economic evaluations. Addressing these limitations, particularly in LMICs, will strengthen the evidence base and better inform policy implementation to combat AMR effectively.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Antibiotic Use in the Community in Spain: A National Surveillance System Within the Framework of the Spanish Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance
by
Rocío Fernández-Urrusuno, Carmen Marina Meseguer-Barros, María García-Gil, Itxasne Lekue-Alkorta, María Belén Pina-Gadea, María Ana Prado-Prieto, Natalia Alzueta-Isturiz, Lucía Jamart-Sánchez, Laura Villar-Gómara and Antonio López-Navas
Antibiotics 2025, 14(11), 1071; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics14111071 - 24 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) remains a critical major public health challenge, largely driven by the inappropriate use of antibiotics in the community. In Spain, the National Action Plan on AMR (PRAN) emphasizes the need for robust surveillance systems based on standardized indicators and
[...] Read more.
Background: Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) remains a critical major public health challenge, largely driven by the inappropriate use of antibiotics in the community. In Spain, the National Action Plan on AMR (PRAN) emphasizes the need for robust surveillance systems based on standardized indicators and high-quality data sources. Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the feasibility of calculating PRAN prescribing indicators using the National Electronic Database for Pharmacoepidemiological Research in Primary Care (BIFAP) and to validate BIFAP as a data source for national antimicrobial prescribing surveillance. Methods: A population-based cross-sectional study was conducted using 2018 data from 9.4 million individuals. Results: Overall, 23.3% received at least one antibiotic prescription during the year, with an average of 1.8 treatments per patient. First-line recommended antibiotics represented 26.5% of total dispensed defined daily doses. Notable age-related variability in prescribing patterns was observed: children predominantly received first-line narrow-spectrum antibiotics, whereas older adults were more frequently prescribed broad-spectrum agents. Discusion: BIFAP-based indicators closely aligned with PRAN data while allowing for the calculation of additional metrics, such as prevalence of use, treatments per patient-year, and variations by age and sex. The findings underscore the importance of patient-level monitoring to identify demographic-age-specific priorities for targeted interventions aimed at optimizing antibiotic use in Primary Care. Conclusions: This study confirms the feasibility of using BIFAP to strengthen antibiotic consumption monitoring and policy evaluation efforts in Spain.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antibiotic Stewardship in Ambulatory Care Settings)

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Antibiotics Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Antibiotics, JPM, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Medicines
Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Modelling in Drug Discovery and Development
Topic Editors: Inaki F. Troconiz, Victor Mangas Sanjuán, Maria Garcia-Cremades MiraDeadline: 31 October 2025
Topic in
Agriculture, Animals, Veterinary Sciences, Antibiotics, Zoonotic Diseases
Animal Diseases in Agricultural Production Systems: Their Veterinary, Zoonotic, and One Health Importance, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Ewa Tomaszewska, Beata Łebkowska-Wieruszewska, Tomasz Szponder, Joanna Wessely-SzponderDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topic in
Antibiotics, IJMS, Microbiology Research, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Nanomaterials, Microorganisms
Challenges and Future Prospects of Antibacterial Therapy, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Kwang-Sun Kim, Zehra EdisDeadline: 30 November 2026
Topic in
Biomolecules, IJMS, Micro, Molecules, Antibiotics, Nanomaterials, Microorganisms, JFB
Antimicrobial Agents and Nanomaterials—2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Vasco D. B. Bonifácio, Sandra PintoDeadline: 31 December 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Antibiotics
Revolutionizing Infection Treatment: Cutting-Edge Approaches in Antimicrobial Stewardship
Guest Editors: Jacob Myles Keck, Aleksandra BaracDeadline: 30 October 2025
Special Issue in
Antibiotics
Diagnosis and Antimicrobial Therapy of Osteoarticular Infection
Guest Editor: Janet D. ConwayDeadline: 31 October 2025
Special Issue in
Antibiotics
Biofilms and Urinary Tract Infections
Guest Editors: Dino Sgarabotto, Anabela BorgesDeadline: 31 October 2025
Special Issue in
Antibiotics
ESKAPE and MDRO Pathogens: Infections and Antimicrobial Treatment
Guest Editor: Carlo PallottoDeadline: 31 October 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Antibiotics
Antimicrobial Prescribing and Antimicrobial Use in Healthcare Settings
Collection Editors: Masayuki Maeda, Yuichi Muraki
Topical Collection in
Antibiotics
Antibiotics in Ophthalmology Practice
Collection Editor: Sanjay Marasini
Topical Collection in
Antibiotics
Staphylococcus— Molecular Pathogenesis, Virulence Regulation and Antibiotics Resistance
Collection Editor: Ewa Szczuka
Topical Collection in
Antibiotics
Editorial Board Members' Collection Series: Structural Aspects of AMPs and Antimicrobials
Collection Editors: J. Michael Conlon, Marc Maresca, Bong-Jin Lee, Aurélie Tasiemski








