- Article
Nutrition Label Reading and Understanding, Food Advertising Exposure, and Excess Weight Among Brazilian Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Laysa Camila Bueno,
- Luiz Felipe de Paiva Lourenção and
- Daniela Braga Lima
- + 9 authors
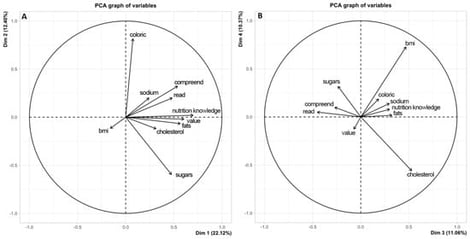
Background/Objectives: Nutrition labeling and food advertising are population-level strategies that may influence food choices. Excess weight is a recognized public health concern and a risk factor for cardiometabolic diseases; however, evidence regarding the association between label use, food advertising, and excess weight remains inconsistent. The objective of this study was to examine the associations between nutrition label reading and understanding, exposure to food advertising, food-related behaviors, and excess weight among Brazilian adults. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted with 580 adults living in the southern region of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Data were collected using a structured questionnaire addressing sociodemographic characteristics, food purchasing behaviors, exposure to food advertising, and habits related to reading and understanding nutrition labels. Excess weight was assessed using body mass index (BMI), calculated from self-reported weight and height. Logistic regression models and principal component analysis (PCA) were performed, adopting a significance level of 5%. Results: Excess weight was observed in 59.0% of participants. Regular use of nutrition labels was reported by 38.6% of respondents; among these individuals, 70.4% reported discontinuing the purchase of a food product after reading its nutritional information. In adjusted analyses, age over 30 years (p < 0.001), female sex (p = 0.006), higher number of dependents (p = 0.007), and type of media used (p = 0.005) were significantly associated with excess weight. The habit of reading nutrition labels was not independently associated with excess weight; however, better label understanding was associated with changes in food purchasing decisions. Considering the nutritional quality of foods as an important factor in food choices was associated with lower odds of having excess weight, although this association did not reach conventional levels of statistical significance (OR = 0.403; 95% CI: 0.15–1.00; p = 0.056). Conclusions: Excess weight among Brazilian adults was more strongly associated with sociodemographic and behavioral factors than with the habit of reading nutrition labels. Although nutrition labeling was not directly associated with excess weight, label understanding and perceived nutritional quality influenced food purchasing behaviors. These findings highlight the role of nutrition labeling and food advertising in shaping food choices and underscore the need for longitudinal studies to clarify their relationship with excess weight and related health outcomes.
8 February 2026