- Article
Three Staphylococcus Bacteriophages Isolated from Swine Farm Environment in Quebec, Canada, Infecting S. chromogenes
- Mousumi Sarker Chhanda,
- Rébecca E. St-Laurent and
- Steve J. Charette
- + 6 authors
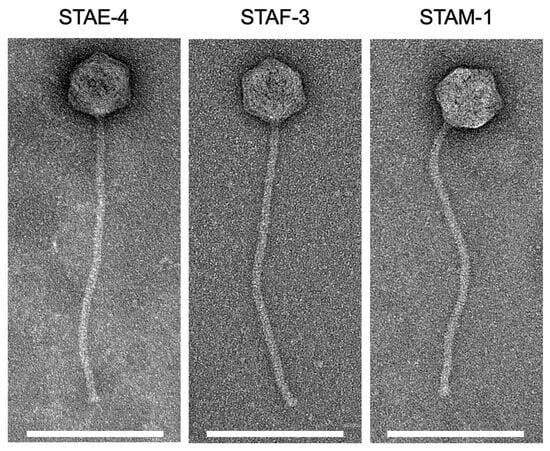
Exudative epidermitis (EE), caused by Staphylococcus hyicus, represents an issue for swine production, particularly due to antimicrobial resistance. In this project, we isolated bacteriophages using S. hyicus as host and studied them as a potential alternative to antibiotic treatment in Quebec, Canada. Three phages, STAE-4, STAF-3, and STAM-1, were isolated from swine farm samples using a single S. hyicus strain (SC366) as the host. Transmission electron microscopy revealed that all three phages exhibited a siphovirus-like morphology, and RAPD-PCR profiling indicated that the phages were genetically distinct. Whole genome sequencing confirmed these differences and showed that the three phages were closely related to each other, and, more importantly, highly similar to phages previously described as infecting Staphylococcus chromogenes, a species closely related to S. hyicus. Host range analysis confirmed that the three phages preferentially infected the S. chromogenes strains included in the study, exhibiting minimal to no lytic activity against other strains of S. hyicus or Staphylococcus agnetis, another closely related species. The only exception was the host S. hyicus strain SC366, which was effectively infected by all three phages, albeit less efficiently than the most sensitive S. chromogenes strain (SC385). Adsorption tests further supported these observations, showing that phages bound to strain SC366 much more quickly than to SC385, despite the lower lytic activity observed. Taken together, these results highlight that while the phages retain some capacity to infect S. hyicus, their biological properties point to a stronger adaptation to S. chromogenes, indicating that they are not suitable candidates for controlling EE.
22 January 2026