Predicting the Landscape Epidemiology of Foot-and-Mouth Disease in Endemic Regions: An Interpretable Machine Learning Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
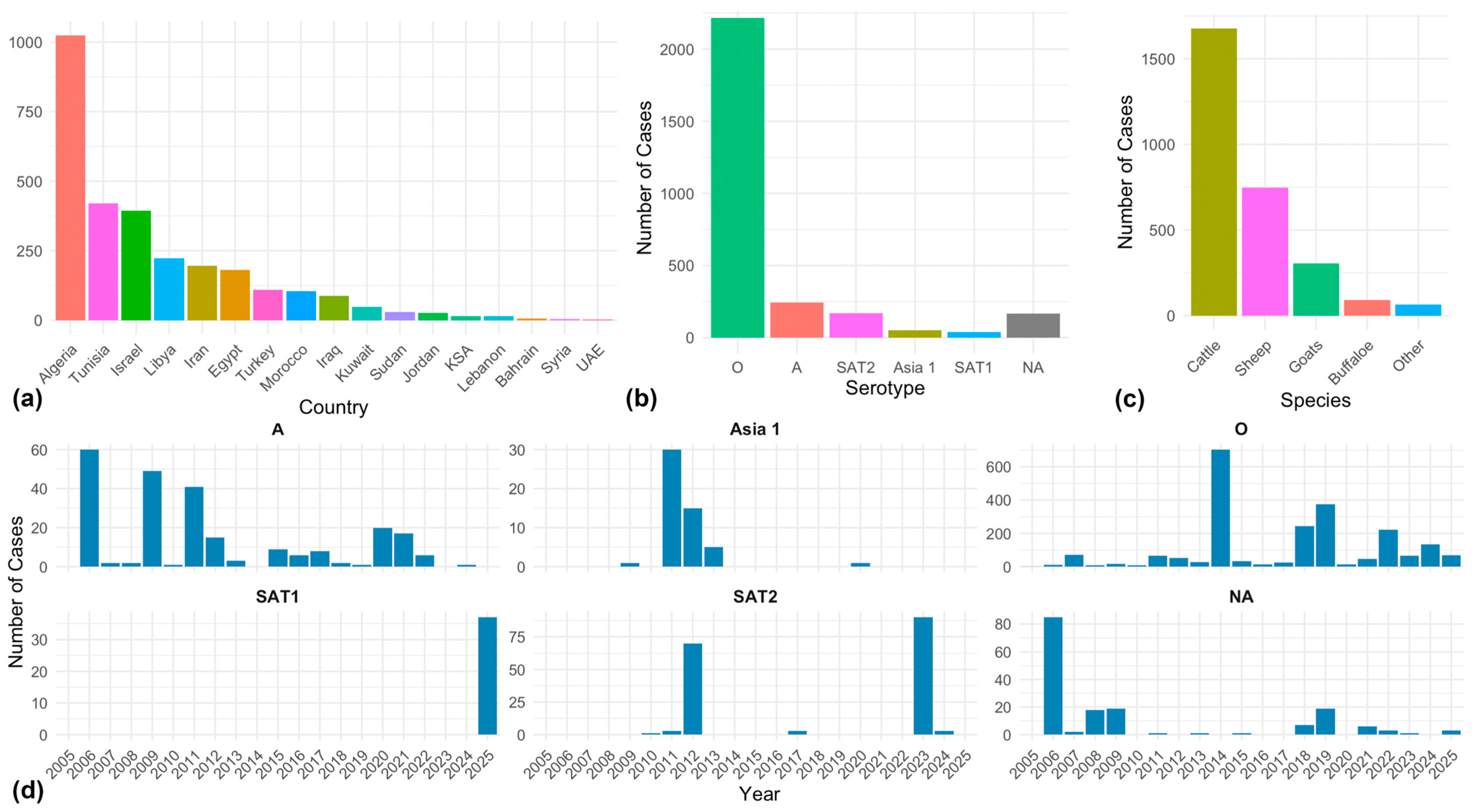
2.1. Outbreak Data
2.2. Host and Environmental Data
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. Model Training and Evaluation
2.5. Model Interpretation
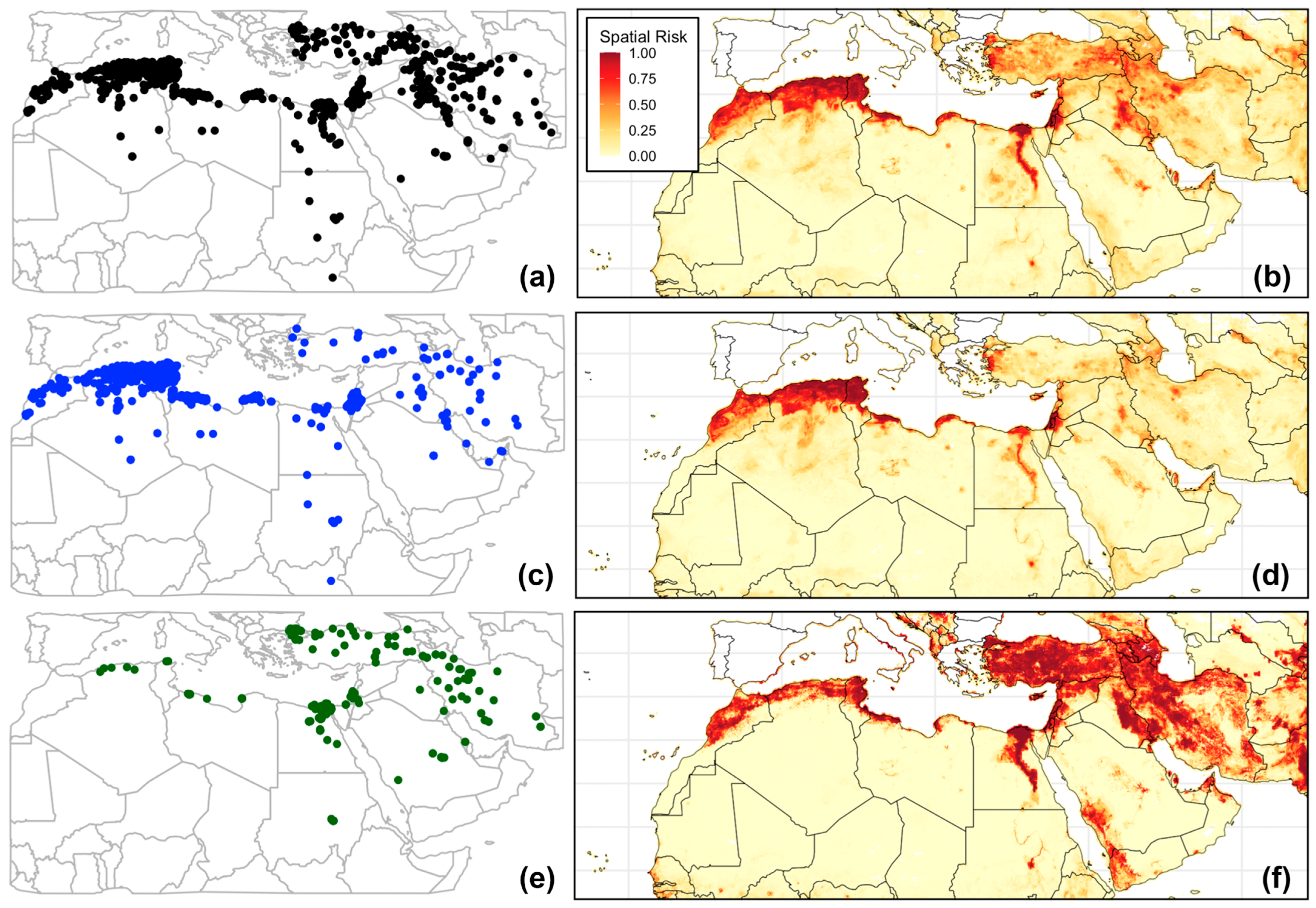
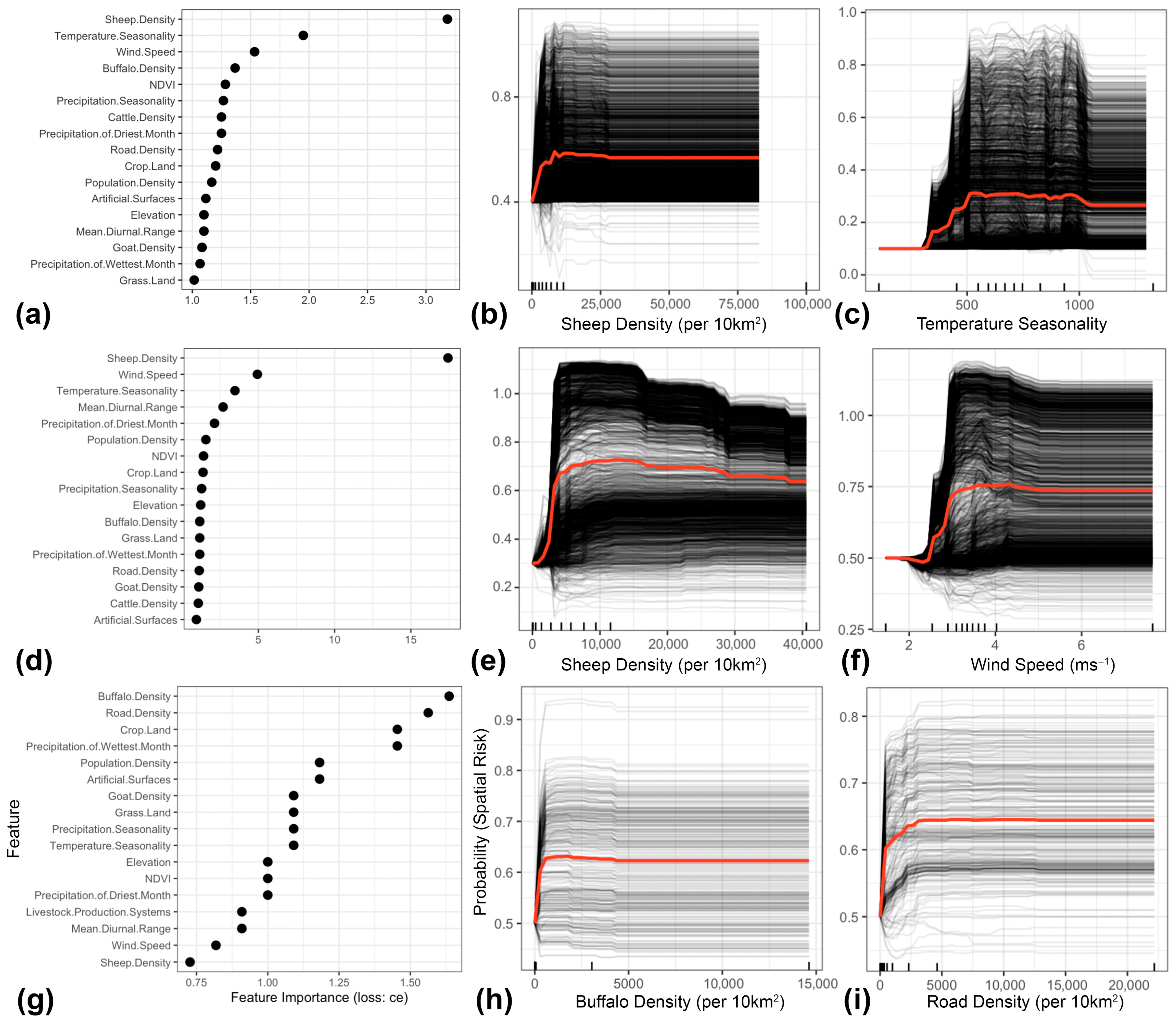
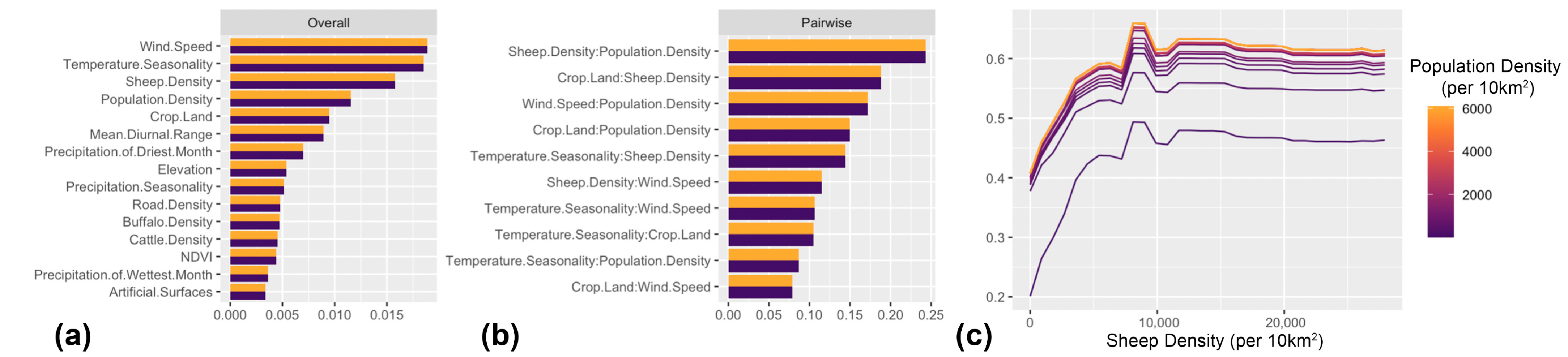
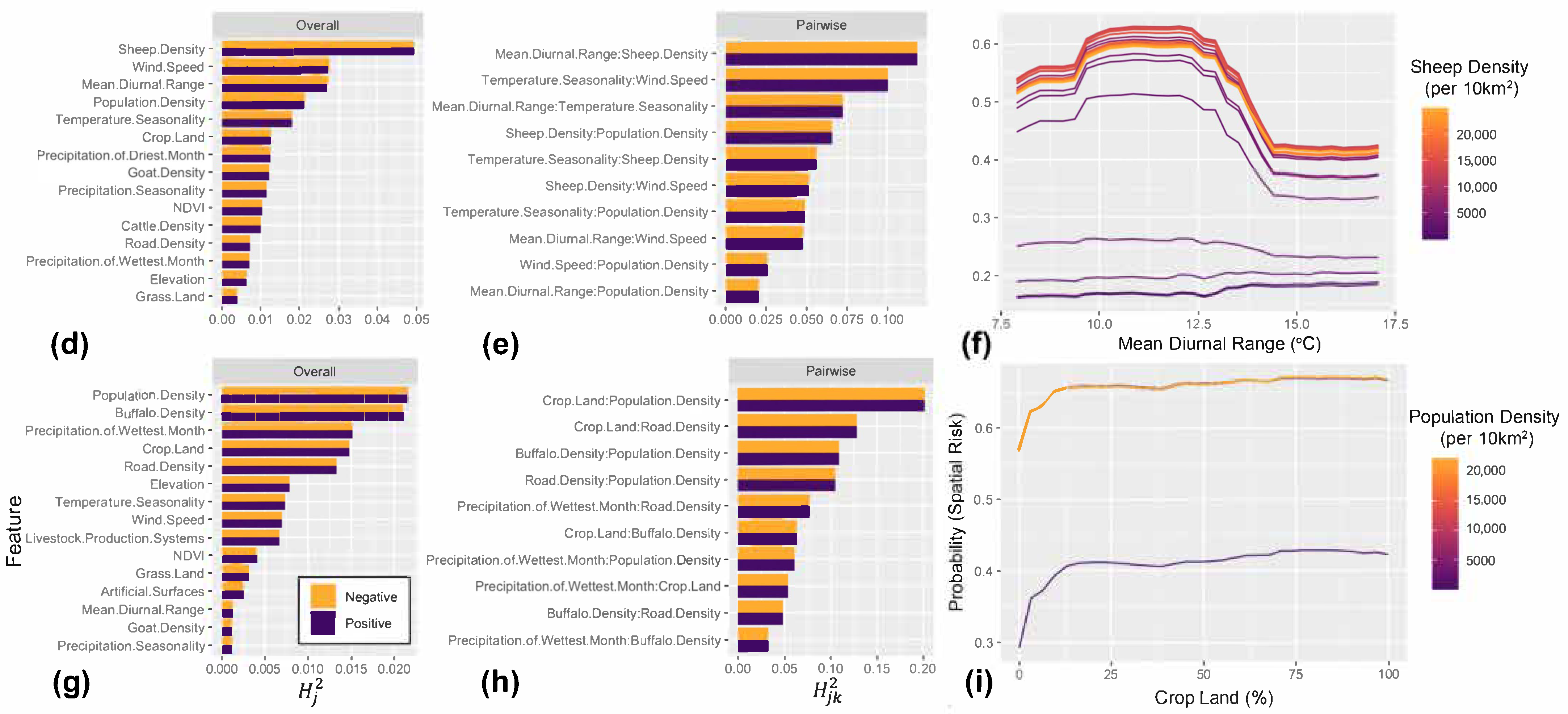
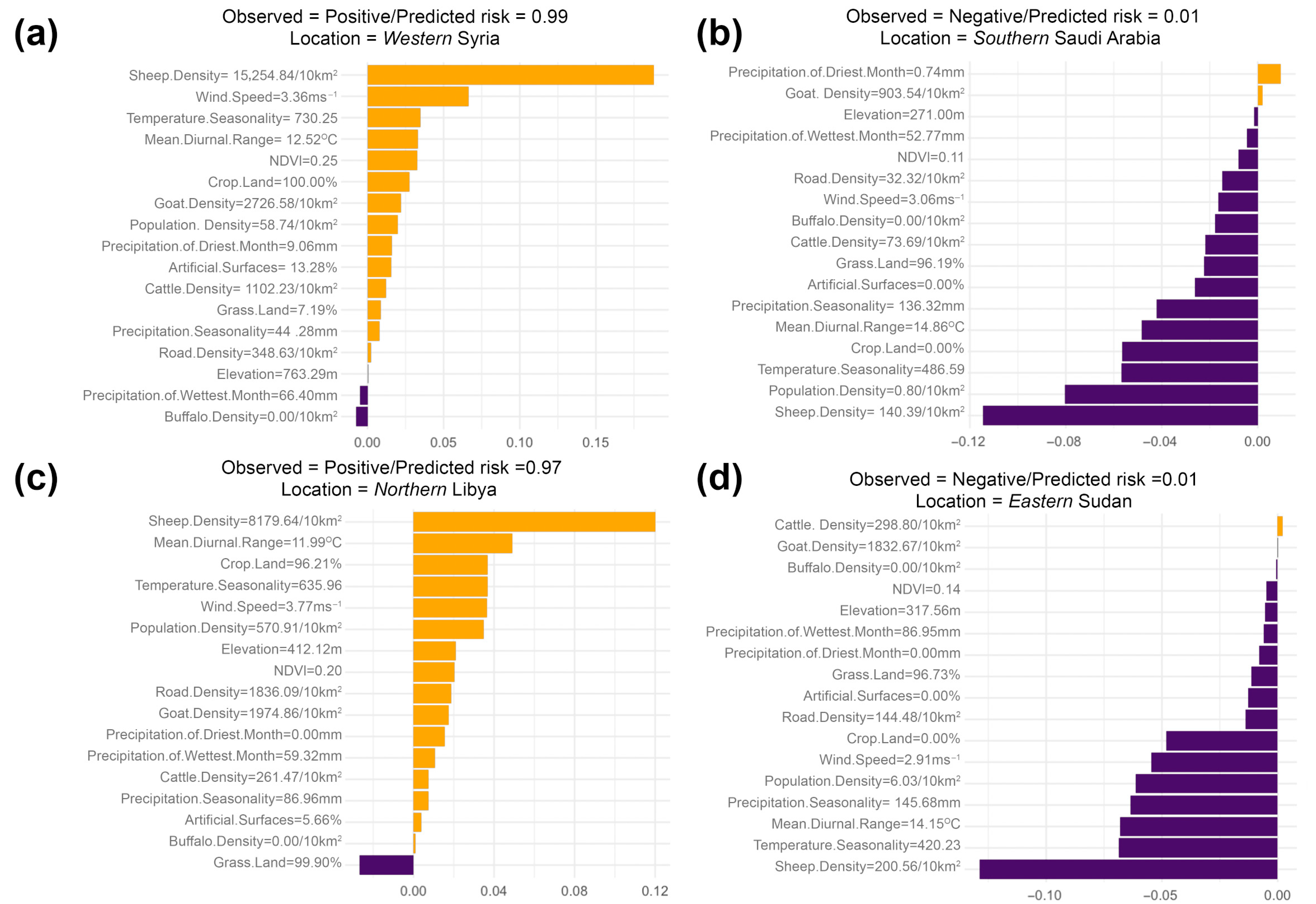
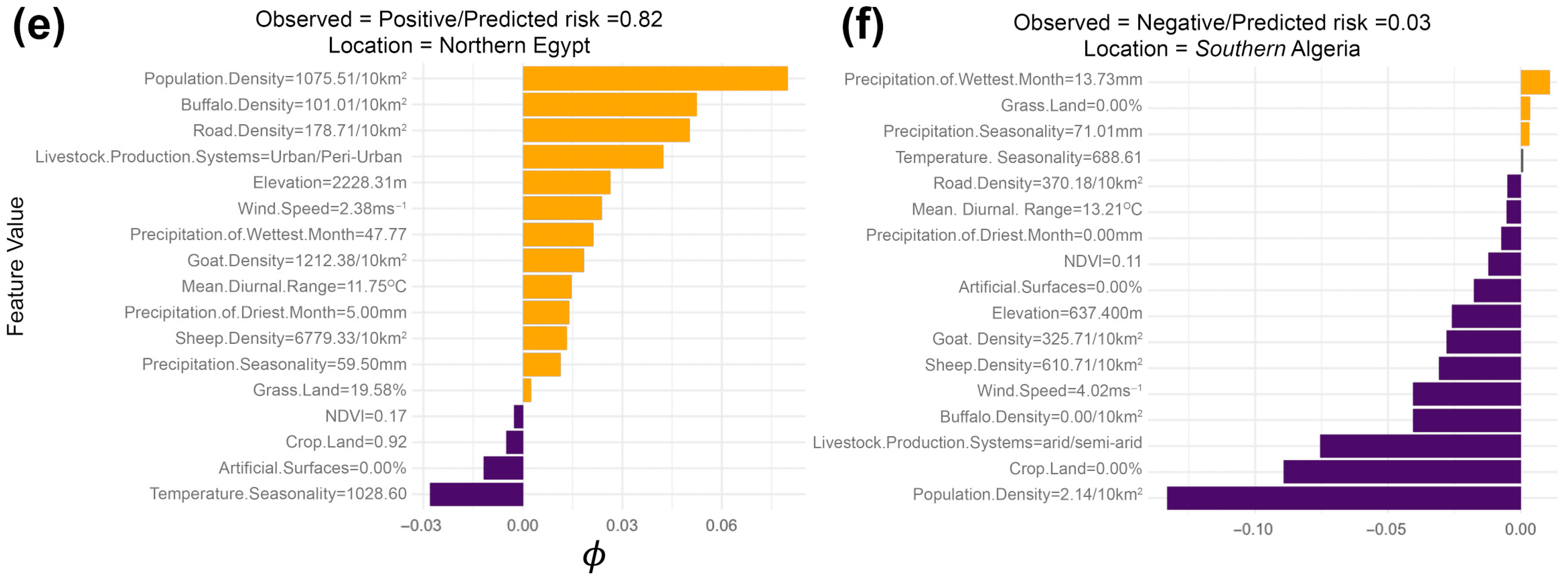
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Key Drivers of FMD in the MENA Region
4.2. Role of Host Species and Anthropogenic Factors in Shaping the Spatial Risk of FMD
4.3. Interpretation of Serotype-Specific Ecological Niches
4.4. Limitations
4.5. Implications for Risk-Based Interventions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FMD | Foot-and-Mouth Disease |
| FMDV | Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus |
| SAT1, SAT2, SAT3 | Southern African Territories serotypes of FMDV |
| MENA | Middle East and North Africa |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization (of the United Nations) |
| EMPRES-i | FAO’s Global Animal Disease Information System |
| WAHIS | World Animal Health Information System (WOAH) |
| WOAH | World Organisation for Animal Health (formerly OIE) |
| GRPS | Global Ruminant Production System |
| NDVI | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index |
| GPW | Gridded Population of the World |
| GLoBio | Global Biodiversity Model for Policy Support |
| UNSDI | United Nations Spatial Data Infrastructure |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| ENM | Ecological Niche Modelling |
| RF | Random Forest |
| XGB | Extreme Gradient Boosting |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| LR | Logistic Regression |
| MCC | Matthews Correlation Coefficient |
| AUC | Area Under the (ROC) Curve |
| sAUC | Spatially adjusted AUC (to assess spatial sorting bias) |
| PD plots | Partial Dependence plots |
| ICE/c-ICE plots | Individual Conditional Expectation (centered ICE) plots |
| ϕ (phi) | Shapley values, from game theory |
| MDR | Mean Diurnal Range (temperature metric) |
| Boruta | ML feature selection algorithm (R package) |
| R | Statistical computing environment |
| Raster (R package) | Tool for handling spatial raster data |
| Caret (R package) | Classification and Regression Training package in R |
| iml (R package) | Interpretable Machine Learning package in R |
| hstats (R package) | For H-statistic interaction measures |
References
- Humphreys, J.M.; Stenfeldt, C.; King, D.P.; Knight-Jones, T.; Perez, A.M.; VanderWaal, K.; Sanderson, M.W.; Di Nardo, A.; Jemberu, W.T.; Pamornchainavakul, N.; et al. Epidemiology and economics of foot-and-mouth disease: Current understanding and knowledge gaps. Vet. Res. 2025, 56, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubman, M.J.; Baxt, B. Foot-and-Mouth Disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 465–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight-Jones, T.J.D.; Rushton, J. The economic impacts of foot and mouth disease—What are they, how big are they and where do they occur? Prev. Vet. Med. 2013, 112, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, A.; Knowles, N.J.; Paton, D.J. Combining livestock trade patterns with phylogenetics to help understand the spread of foot and mouth disease in sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East and Southeast Asia. Rev. Sci. Et Tech. (Int. Off. Epizoot.) 2011, 30, 63–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, N.A.; Afzal, M.; Toirov, F.; Irshad, A.; Bartels, C.J.M.; Rushton, J. Economic Considerations for Advancement Through the Progressive Control Pathway: Cost-Benefit Analysis of an FMD Disease-Free Zone in Punjab Province, Pakistan. Front. Artif. Intell. 2021, 8, 703473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, N.C.; de Menezes, T.C.; Countryman, A.M.; Lopes, F.P.N.; Groff, F.H.S.; Rigon, G.M.; Gocks, M.; Machado, G. Integrating epidemiological and economic models to estimate the cost of simulated foot-and-mouth disease outbreaks in Brazil. Prev. Vet. Med. 2025, 242, 106558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gortazar, C.; Barroso, P.; Nova, R.; Caceres, G. The role of wildlife in the epidemiology and control of Foot-and-mouth-disease And Similar Transboundary (FAST) animal diseases: A review. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 2462–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qiu, S.; Lu, H.; Niu, B. Spatio-temporal analysis and risk modeling of foot-and-mouth disease outbreaks in China. Prev. Vet. Med. 2024, 224, 106120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari Ashani, M.; Alesheikh, A.A.; Lotfata, A. Nationwide spatiotemporal prediction of foot and mouth disease in Iran using machine learning (2008–2018). Spat. Inf. Res. 2024, 32, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Lv, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z.; Gao, X.; Wang, H. Global foot-and-mouth disease risk assessment based on multiple spatial analysis and ecological niche model. Vet. Q. 2025, 45, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, C. Interpretable Machine Learning: A Guide for Making Black Box Models Explainable. 2018. Available online: https://christophm.github.io/interpretable-ml-book/ (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Alkhamis, M.A.; Fountain-Jones, N.M.; Aguilar-Vega, C.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M. Environment, vector, or host? Using machine learning to untangle the mechanisms driving arbovirus outbreaks. Ecol. Appl. A Publ. Ecol. Soc. Am. 2021, 31, e02407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandersen, S.; Zhang, Z.; Donaldson, A.I.; Garland, A.J. The pathogenesis and diagnosis of foot-and-mouth disease. J. Comp. Pathol. 2003, 129, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.; Nelson, N.; Gubbins, S.; Colenutt, C. Airborne Transmission of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus: A Review of Past and Present Perspectives. Viruses 2022, 14, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenfeldt, C.; Arzt, J. The Carrier Conundrum; A Review of Recent Advances and Persistent Gaps Regarding the Carrier State of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus. Pathogens 2020, 9, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.D.; Knowles, N.J.; Wadsworth, J.; Rambaut, A.; Woolhouse, M.E. Reconstructing geographical movements and host species transitions of foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype SAT 2. mBio 2013, 4, e00591-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.P.; Di Nardo, A.; Henstock, D. WOAH-FAO FMD Reference Laboratory Network Report 2022. Available online: https://www.wrlfmd.org/sites/world/files/quick_media/WOAH-FAO%20FMD%20Ref%20Lab%20Network%20Report%202022.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- FAO-WOAH. The Global Foot-and-Mouth Disease Control Strategy. 2012. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/ba8713e/ba8713e.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Paton, D.J.; Sumption, K.J.; Charleston, B. Options for control of foot-and-mouth disease: Knowledge, capability and policy. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2657–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salihi, K.A. The epidemiology of foot-and-mouth disease outbreaks and its history in Iraq. Vet. World 2019, 12, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba Sheikh, M.; Rashid, P.A.; Raheem, Z.; Marouf, A.S.; Amin, K.M. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of foot and mouth disease virus isolates in Sulaimani province, Iraq. Vet. Res. Forum 2021, 12, 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- FAO-WOAH. Foot and Mouth Disease Reference Laboratory Network Report, January–March 2009. Available online: https://www.wrlfmd.org/sites/world/files/quick_media/OIE-FAO%20FMD%20Ref%20Lab%20Report%20Jan-Mar%202009.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Kandeil, A.; El-Shesheny, R.; Kayali, G.; Moatasim, Y.; Bagato, O.; Darwish, M.; Gaffar, A.; Younes, A.; Farag, T.; Kutkat, M.A.; et al. Characterization of the recent outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype SAT2 in Egypt. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, B.P.; Rodriguez, L.L.; Hammond, J.M.; Pinto, J.; Perez, A.M. Review of the Global Distribution of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus from 2007 to 2014. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, P.; Arter-Hazzard, M.; King, D.; Bacigalupo, S.; Perrin, L. Foot and Mouth Disease SAT1 in Iraq, Bahrain and Kuwait: Preliminary Outbreak Assessment. 2025. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/68235104eef73e50f3644a9a/Foot_and_Mouth_Disease_SAT1_in_Iraq__Bahrain_and_Kuwait_May_2025.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2025).
- Jamal, S.M.; Khan, S.; Rahman, H.U.; Ali Shah, S.A.; Polo, N.; Wilsden, G.; Parekh, K.; Browning, C.; Wadsworth, J.; Knowles, N.J.; et al. Emergence of new sublineages of serotype O foot-and-mouth disease viruses circulating in Pakistan during 2012-2021. Virology 2025, 605, 110455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossen, M.L.; Ahmed, S.; Khan, M.F.R.; Nazmul Hussain Nazir, K.H.M.; Saha, S.; Islam, M.A.; Rahman, M.T.; Sayem, S.M.; Rahman, M.B. The emergence of foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype O PanAsia-02 sub-lineage of Middle East-South Asian topotype in Bangladesh. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2020, 7, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. FMD Situation Update—Middle East. 2025. Available online: https://www.fao.org/eufmd/global-situation/fmd-monthly-reports (accessed on 2 August 2025).
- Punyapornwithaya, V.; Klaharn, K.; Arjkumpa, O.; Sansamur, C. Exploring the predictive capability of machine learning models in identifying foot and mouth disease outbreak occurrences in cattle farms in an endemic setting of Thailand. Prev. Vet. Med. 2022, 207, 105706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulesteix, A.L.; Schmid, M. Machine learning versus statistical modeling. Biom. J. 2014, 56, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountain-Jones, N.M.; Machado, G.; Carver, S.; Packer, C.; Recamonde-Mendoza, M.; Craft, M.E. How to make more from exposure data? An integrated machine learning pipeline to predict pathogen exposure. J. Anim. Ecol. 2019, 88, 1447–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, S.E.; Hijmans, R.J. WorldClim 2: New 1-km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samy, A.M.; Peterson, A.T. Climate Change Influences on the Global Potential Distribution of Bluetongue Virus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.; Nicolas, G.; Cinardi, G.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Vanwambeke, S.O.; Wint, G.R.W.; Robinson, T.P. Global distribution data for cattle, buffaloes, horses, sheep, goats, pigs, chickens and ducks in 2010. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.P.; Thornton, P.K.; Franceschini, G.; Kruska, R.L.; Chiozza, F.; Notenbaert, A.; Cecchi, G.; Herrero, M.; Epprecht, M.; Fritz, S.; et al. Global Livestock Production Systems. 2011. Available online: https://www.fao.org/4/i2414e/i2414e.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Meijer, J.R.; Huijbregts, M.A.J.; Schotten, K.C.G.J.; Schipper, A.M. Global patterns of current and future road infrastructure. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 064006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J.; Etten, J.V.; Sumner, M.; Cheng, J.; Baston, D.; Bevan, A.; Bivand, R.; Busetto, L.; Canty, M.; Fasoli, B.; et al. Raster R Package: Geographic Data Analysis and Modeling. 2025. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/raster/raster.pdf (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Hijmans, R.J.; Elith, J. Species Distribution Models. 2021. Available online: https://rspatial.org/sdm/ (accessed on 4 October 2025).
- Kursa, M.B.; Rudnicki, W.R. Feature selection with the Boruta Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M. Building Predictive Models in R Using the caret Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 28, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J. Cross-validation of species distribution models: Removing spatial sorting bias and calibration with a null model. Ecology 2012, 93, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, C. iml: An R package for Interpretable Machine Learning. J. Open Source Softw. 2018, 3, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, A.; Kapelner, A.; Bleich, J.; Pitkin, E. Peeking Inside the Black Box: Visualizing Statistical Learning With Plots of Individual Conditional Expectation. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2015, 24, 44–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H.; Popescu, B.E. Predictive learning via rule ensembles. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2008, 2, 916–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapley, L.S. Stochastic games. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1953, 39, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.M.; Faria, N.R.; Perez, A.M.; Suchard, M.A.; Lemey, P.; Silveira, W.d.C.; Rambaut, A.; Baele, G. Spatio-temporal Dynamics of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus in South America. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.01105. [Google Scholar]
- Fountain-Jones, N.M.; Jordan, G.J.; Burridge, C.P.; Wardlaw, T.J.; Baker, T.P.; Forster, L.; Petersfield, M.; Baker, S.C. Trophic position determines functional and phylogenetic recovery after disturbance within a community. Funct. Ecol. 2017, 31, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, M.J.; Woolhouse, M.E.; May, R.M.; Davies, G.; Grenfell, B.T. Modelling vaccination strategies against foot-and-mouth disease. Nature 2003, 421, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González Gordon, L.; Porphyre, T.; Muhanguzi, D.; Muwonge, A.; Boden, L.; Bronsvoort, B.M.d.C. A scoping review of foot-and-mouth disease risk, based on spatial and spatio-temporal analysis of outbreaks in endemic settings. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 3198–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenfeldt, C.; Eschbaumer, M.; Humphreys, J.; Medina, G.N.; Arzt, J. The pathogenesis of foot-and-mouth disease virus: Current understandings and knowledge gaps. Vet. Res. 2025, 56, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenfeldt, C.; Pacheco, J.M.; Singanallur, N.B.; Vosloo, W.; Rodriguez, L.L.; Arzt, J. Virulence beneath the fleece; a tale of foot-and-mouth disease virus pathogenesis in sheep. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0227061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.; Aktas, S.; Mohammed, H.; Roeder, P.; Sumption, K.; Tufan, M.; Slingenbergh, J. Patterns of spread and persistence of foot-and-mouth disease types A, O and Asia-1 in Turkey: A meta-population approach. Epidemiol. Infect. 2005, 133, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.; Alkheraije, K.A. The prevalence of foot-and-mouth disease in Asia. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1201578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukrishnan, M.; Singanallur Balasubramanian, N.; Villuppanoor Alwar, S. Experimental Infection of Foot and Mouth Disease in Indian Sheep and Goats. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Rahim, I.H.A.; Asghar, A.H.; Mohamed, A.M.; Fat’hi, S.M. The impact of importation of live ruminants on the epizootiology of foot and mouth disease in Saudi Arabia. Rev. Sci. Et Tech. (Int. Off. Epizoot.) 2016, 35, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, A.I.; Alexandersen, S. Predicting the spread of foot and mouth disease by airborne virus. Rev. Sci. Et Tech. (Int. Off. Epizoot.) 2002, 21, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutmoller, P.; Barteling, S.S.; Olascoaga, R.C.; Sumption, K.J. Control and eradication of foot-and-mouth disease. Virus Res. 2003, 91, 101–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, S.; Bkear, N.; Badr, Y.; Elshafey, B.; Alhag, S.K.; Al-Shuraym, L.A.; Batiha, G.; Fakhry, B.; Hamada, R. A Newly Emerging Serotype A Strain in Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus with Higher Severity and Mortality in Buffalo than in Cattle Calves in North Egypt. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardi, M.; Colucci, M.; Pozzi, A.V.; Scerri, E.M.L.; Manica, A. tidysdm: Leveraging the flexibility of tidymodels for species distribution modelling in R. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2024, 15, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, R.; Yesson, C.; Yu, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, L. Key factors for species distribution modeling in benthic marine environments. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1222382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Model | Accuracy (%) | Specificity (%) | Sensitivity (%) | MCC | sAUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Serotypes | |||||
| RF | 91.74 | 91.20 | 92.28 | 0.83 | 0.99 |
| XGB | 93.26 | 90.81 | 93.70 | 0.85 | 0.99 |
| SVM | 89.80 | 88.04 | 91.55 | 0.79 | 0.97 |
| LR | 87.20 | 83.71 | 90.68 | 0.74 | 0.94 |
| Serotype O | |||||
| RF | 94.94 | 95.44 | 94.43 | 0.89 | 0.99 |
| XGB | 94.95 | 94.90 | 93.01 | 0.89 | 0.99 |
| SVM | 94.19 | 93.84 | 94.55 | 0.88 | 0.97 |
| LR | 91.34 | 92.75 | 89.93 | 0.82 | 0.95 |
| Serotype A | |||||
| RF | 86.07 | 83.04 | 84.10 | 0.72 | 0.98 |
| XGB | 84.29 | 82.99 | 82.99 | 0.71 | 0.96 |
| SVM | 80.87 | 76.59 | 85.15 | 0.61 | 0.94 |
| LR | 82.68 | 80.89 | 84.48 | 0.65 | 0.93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alkhamis, M.A.; Abouelhassan, H.; Alateeqi, A.; Husain, A.; Humphreys, J.M.; Arzt, J.; Perez, A.M. Predicting the Landscape Epidemiology of Foot-and-Mouth Disease in Endemic Regions: An Interpretable Machine Learning Approach. Viruses 2025, 17, 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101383
Alkhamis MA, Abouelhassan H, Alateeqi A, Husain A, Humphreys JM, Arzt J, Perez AM. Predicting the Landscape Epidemiology of Foot-and-Mouth Disease in Endemic Regions: An Interpretable Machine Learning Approach. Viruses. 2025; 17(10):1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101383
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlkhamis, Moh A., Hamad Abouelhassan, Abdulaziz Alateeqi, Abrar Husain, John M. Humphreys, Jonathan Arzt, and Andres M. Perez. 2025. "Predicting the Landscape Epidemiology of Foot-and-Mouth Disease in Endemic Regions: An Interpretable Machine Learning Approach" Viruses 17, no. 10: 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101383
APA StyleAlkhamis, M. A., Abouelhassan, H., Alateeqi, A., Husain, A., Humphreys, J. M., Arzt, J., & Perez, A. M. (2025). Predicting the Landscape Epidemiology of Foot-and-Mouth Disease in Endemic Regions: An Interpretable Machine Learning Approach. Viruses, 17(10), 1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101383






