- Article
Impact of Harassment by Clients and Their Family Members on Psychological Health and Work Engagement: A Study of Disability Welfare Professionals in Japan
- Yanshu Li and
- Kaori Iwasaki
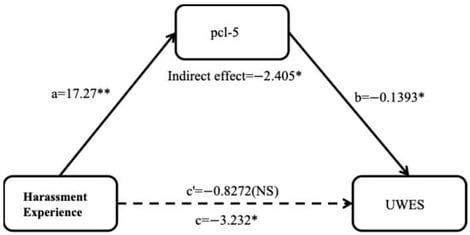
This study examined the psychological and occupational impact of harassment from clients and their family members on disability welfare professionals in Japan. Specifically, it investigated how such harassment affects post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms and work engagement, and whether PTSD mediates this relationship. A cross-sectional web-based survey was conducted among 280 disability welfare workers. All 280 participants completed the nine-item Utrecht Work Engagement Scale. Of these, 100 participants (35.71%) who reported having experienced harassment from clients or their family members also completed the PTSD Checklist for DSM-5. Results showed that 21% of participants who experienced harassment exceeded the clinical threshold for probable PTSD. Those with harassment experiences also demonstrated significantly lower work engagement. Regression analysis indicated that PTSD symptoms were a significant negative predictor of work engagement. Mediation analysis further confirmed that PTSD fully mediated the association between harassment exposure and reduced engagement, suggesting that harassment undermines work motivation primarily through its psychological impact. Harassment from clients and their family members poses a psychological risk to disability welfare professionals. Individuals with harassment experiences show higher PTSD symptoms. Future discussion should explore protective factors and interventions to support the psychological well-being and work engagement of welfare professionals.
30 January 2026