- Article
Non-Isolated High-Voltage-Gain Step-Up DC–DC SISC Converter for Renewable Energy Applications
- Yasser Almalaq
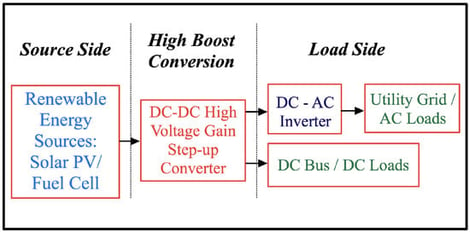
This paper presents two new step-up DC–DC converters that have high voltage gains and low voltage stresses across their main switches with respect to their output voltages. These high voltage gains are achieved with the help of voltage multiplier cells (VMCs). By inserting VMCs that are switched inductors (SIs) and switched capacitors (SCs), the voltage gains increased substantially compared to the conventional converters, such as the traditional boost converter (TBC), Luo converter, or Zeta converter. Furthermore, the TBC has a voltage stress across its main switch that equals the output voltage, while the two proposed step-up converters have voltage stresses across their main switches that are lower than their output voltages. An extended converter is obtained from the main topology, which has a higher voltage gain than the main one. This paper investigates both topologies in continuous conduction mode (CCM) operation and shows a detailed analysis deriving the voltage gain and the voltage stress between the switches. In the main topology, when the duty ratio (D) is , the output voltage equals around thirty times the input voltage. In the extended topology, when D is , the output voltage equals around sixty times the input voltage. The voltage stresses across the main switches in both topologies are half of their output voltages when D is . Simulation models using Matlab/Simulink are carried out for both the main and extended topologies, showing how these agree with the theoretical derivations.
12 February 2026