- Article
The Effectiveness and Safety of a New Nutraceutical in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Pilot Study
- Cristina Vocca,
- Vincenzo Rania and
- Luca Gallelli
- + 8 authors
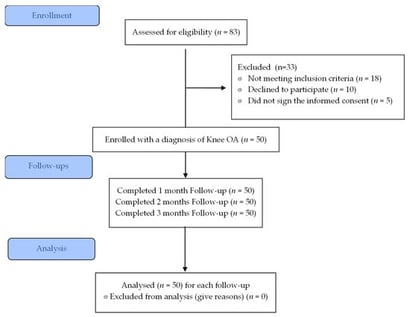
Background: Nutraceuticals are increasingly used in clinical practice for their anti-inflammatory, antiproliferative, and antioxidant properties. This study aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a fixed nutraceutical combination containing chondroitin sulfate, α-lipoic acid, astaxanthin, lycopene, escin, and omega-3 fatty acids (eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid) in improving pain and quality of life in patients with chronic knee osteoarthritis (OA). Methods: This observational study included patients with chronic knee OA who were referred to the ambulatory pain clinic at Dulbecco University Hospital, Catanzaro, Italy. Participants received one tablet daily for three months. Quality of life was assessed using the 36-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36), and adverse drug reactions (ADRs) were evaluated using the Naranjo scale. Results: Fifty patients (20 men and 30 women; mean age, 63.6 ± 11.4 years; range, 26–88 years; mean body mass index, 26.9 ± 3.7 kg/m2) were enrolled. Pain symptoms demonstrated a statistically significant improvement over time (p < 0.01). No ADRs were reported during the study period. Conclusions: The fixed nutraceutical combination improved pain and quality of life in patients with chronic knee OA and demonstrated an excellent safety profile.
5 February 2026