Journal Description
Healthcare
Healthcare
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed, open access journal on health care systems, industry, technology, policy, and regulation, and is published semimonthly online by MDPI. The European Medical Association (EMA), Ocular Wellness & Nutrition Society (OWNS) and Italian Society of Nephrology Nurses (SIAN) are affiliated with Healthcare and their members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE and SSCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Health Policy and Services) / CiteScore - Q1 (Leadership and Management)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 21.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journals for Healthcare include: Trauma Care and European Burn Journal.
- Journal Cluster of Healthcare Sciences and Services: Geriatrics, Journal of Ageing and Longevity, Healthcare, Hospitals, Hygiene, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health and Nursing Reports.
Impact Factor:
2.7 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.8 (2024)
Latest Articles
Linking Motor and Cognitive Decline in Aging: Gait Variability and Working Memory as Early Markers of Frailty
Healthcare 2025, 13(24), 3201; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243201 (registering DOI) - 7 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Frailty is an age-related clinical syndrome characterized by diminished physiological reserves and increased vulnerability to adverse outcomes. Growing evidence suggests that frailty involves shared brain networks that regulate both gait and cognitive functions. This study aimed to examine the relationship between frailty
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Frailty is an age-related clinical syndrome characterized by diminished physiological reserves and increased vulnerability to adverse outcomes. Growing evidence suggests that frailty involves shared brain networks that regulate both gait and cognitive functions. This study aimed to examine the relationship between frailty status, spatiotemporal gait parameters, and cognitive functions in community-dwelling older adults. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted with 99 adults aged ≥70 years, classified as non-frail, prefrail, or frail according to the Fried phenotype. Gait parameters were measured under usual and fast walking conditions using the OptoGait® photoelectric system. Cognitive status was assessed with the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) and a comprehensive neuropsychological battery. Multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed to identify factors associated with transitions between frailty stages. Results: The prevalence of frailty was 9.1%, with 51.5% prefrail and 39.4% non-frail. The transition from non-frail to prefrail was associated with shorter stride length at fast pace (OR = 0.92, 95% CI: 0.88–0.96), mild cognitive impairment (OR = 3.71, 95% CI: 1.08–12.69), depressive symptoms (OR = 1.82, 95% CI: 1.26–2.62), and female sex (OR = 4.94, 95% CI: 1.20–16.77). The transition from prefrail to frail was linked to increased stride time variability at fast pace (OR = 2.94, 95% CI: 1.34–6.44) and poorer working memory (OR = 0.40, 95% CI: 0.16–0.97). Conclusions: Shorter stride length, mild cognitive impairment, and depressive symptoms emerged as key markers of the transition from non-frailty to prefrailty, whereas increased stride time variability and poorer working memory distinguished prefrail from frail individuals. These findings highlight gait- and executive-function-related markers as sensitive early indicators of vulnerability. Incorporating quantitative gait assessment and brief cognitive screening into routine geriatric evaluations may substantially enhance early detection and support targeted preventive strategies for healthy aging.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multidimensional Aging Care: Gait, Cognition, Sensory Decline, and Psychosocial Vulnerability in Later Life)
Open AccessArticle
Multidimensional Stratification of Severe Disability: Demographic, Clinical, Geographic, Socio-Economic Profiles and Healthcare Pathways in a Cross-Sectional Italian Cohort
by
Rita Chiaramonte, Tamara Civello, Giuseppe Laganga Senzio, Liberato Longo, Alessandro Santo De Caro, Fabrizio Li Gotti and Michele Vecchio
Healthcare 2025, 13(24), 3200; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243200 (registering DOI) - 7 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Individuals with severe disability require intensive and long-term healthcare, rehabilitation and social support. Updated population data are essential to inform planning and resource allocation. This study aimed to quantify—with a cross-sectional analysis conducted in 2025—the demographic, clinical, socioeconomic, and geographic characteristics
[...] Read more.
Background: Individuals with severe disability require intensive and long-term healthcare, rehabilitation and social support. Updated population data are essential to inform planning and resource allocation. This study aimed to quantify—with a cross-sectional analysis conducted in 2025—the demographic, clinical, socioeconomic, and geographic characteristics of individuals with severe disability within the Provincial Health Authority (ASP) of Catania (Sicily) in Italy, and to identify statistically significant differences across subgroups. Methods: A cross-sectional analysis was conducted on 3277 individuals officially certified as having severe disability under the Italian Ministerial Decree of 26 September 2016. Data were extracted from administrative records and stratified by age, sex, clinical classification, income level, and healthcare district. Associations were tested using chi-square statistics. Results: Participants had a mean age of 39.14 ± 28.64 years; Minors represented 33% of the disability cohort (vs. 19.4% minors in the general provincial population) with a mean age 10.28 ± 3.55. Adults accounted for 67% of the cohort (vs. 81% adults in the general population), with a mean age of 69.94 ± 24.61 years. Females constituted 43% of the sample (compared with 51% females in the provincial population), whereas males represented 57% (vs. 49% males in the general population). Most individuals (95.9% of the cohort) had an income level below €25,000/year. Conclusions: The study reveals substantial demographic, socioeconomic, and clinical heterogeneity among individuals with severe disability and highlights significant district-level disparities. Notably, minors appear markedly over-represented in the disability cohort compared with the general population, while females are under-represented, indicating potential age- and sex-related differences in disability burden, access to assessment, or underlying diagnostic patterns. These findings indicate the need for stratified, district-sensitive planning approaches, ensuring equitable access to services and optimizing allocation of healthcare and social resources.
Full article
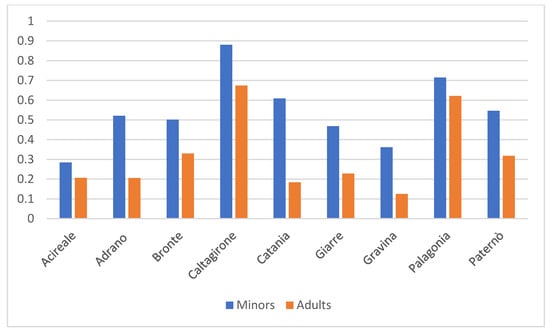
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Intelligent Patient Management in Viral Diseases: An Integrated Regression Model and Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Approach to Convalescent Plasma Transfusion
by
Thura J. Mohammed, Ahmed S. Albahri, Alhamzah Alnoor, Khai Wah Khaw, Xin Ying Chew and Shiuh Tong Lim
Healthcare 2025, 13(24), 3199; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243199 (registering DOI) - 6 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Viral diseases remain a major threat to global public health, particularly during outbreaks when limited therapeutic resources must be rapidly and fairly distributed to large populations. Although Convalescent Plasma (CP) transfusion has shown clinical promise, existing allocation frameworks treat patient prioritization, donor
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Viral diseases remain a major threat to global public health, particularly during outbreaks when limited therapeutic resources must be rapidly and fairly distributed to large populations. Although Convalescent Plasma (CP) transfusion has shown clinical promise, existing allocation frameworks treat patient prioritization, donor selection, and validation as separate processes. This study proposes a credible, converged smart framework integrating multicriteria decision-making (MCDM) and regression-based validation within a telemedicine environment to enable transparent, data-driven CP allocation. Methods: The proposed framework consists of three stages: (i) Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) for weighting five clinically relevant biomarkers, (ii) dual prioritization of patients and donors using Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) and Višekriterijumsko Kompromisno Rangiranje (VIKOR) with Group Decision-Making (GDM), and (iii) regression-based model selection to identify the most robust prioritization model. An external dataset of 80 patients and 80 donors was used for independent validation. Results: The external GDM AHP-VIKOR prediction model demonstrated strong predictive performance and internal consistency, with R2 = 0.971, MSE = 0.0010, RMSE = 0.032, and MAE = 0.025. Correlation analysis confirmed biomarker behavior consistency and stability in ranking, thereby reinforcing the reliability of the prioritization outcomes. Conclusions: The proposed patient–donor matching framework is accurate, interpretable, and timely. This work presents an initial step toward realizing safe AI-enabled transfusion systems within telemedicine, supporting transparent and equitable CP allocation in future outbreak settings.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Physical Activity Interventions in Colorectal Cancer Survivors: An Evidence Evaluation Attempt Across Racial/Ethnic Groups
by
Yves Paul Vincent Mbous, Rowida Mohamed, George A. Kelley and Kimberly Michelle Kelly
Healthcare 2025, 13(24), 3198; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243198 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
Aims: Recommendations for cancer survivors concur regarding physical activity (PA), and elucidating factors governing PA uptake among colorectal cancer (CRC) survivors is needed. This study examined the impact of PA interventions and investigated the variation in PA across several characteristics, including race/ethnicity. Design:
[...] Read more.
Aims: Recommendations for cancer survivors concur regarding physical activity (PA), and elucidating factors governing PA uptake among colorectal cancer (CRC) survivors is needed. This study examined the impact of PA interventions and investigated the variation in PA across several characteristics, including race/ethnicity. Design: We performed a systematic review and aggregate data meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of PA interventions. Data Sources: We used studies from CENTRAL, PubMed (NCBI), PsycINFO (EBSCOhost), CINAHL (EBSCOhost) with full text, Scopus (ELSEVIER), and the Web of Science (CLARIVATE) (1 May 1993–1 September 2023). Methods: For the meta-analysis, the inverse variance heterogeneity (IVhet) model was used to pool standardized mean difference effect sizes (Hedge’s g) for our primary outcome, changes in PA. Results: Sixteen studies representing 1668 participants were included in the meta-analysis. A moderate, statistically significant increase in PA was observed (g = 0.44, 95% CI 0.12–0.76; p = 0.01). However, a large amount of inconsistency was observed (I2 = 80.8%, 95% CI, 36.1% to 90.9%), as well as major asymmetry suggestive of small-study effects (publication bias, LFK = 3.04). Only 28% of trials reported race/ethnicity, limiting equity analyses. Subgroups comparing atheoretical vs. theory-based interventions did not differ statistically. Meta-regression results suggested associations with specific behavior change theories and delivery features. Based on the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) assessment, the overall certainty of evidence was considered low. Conclusions: There is low-certainty evidence that PA interventions may improve PA among CRC survivors. Future trials should (i) recruit and report diverse samples in a clear and transparent manner, (ii) explicitly map theory constructs to techniques and test mechanisms, and (iii) report fidelity and clinically meaningful thresholds alongside behavioral outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Physical Activity, Healthy Lifestyle and Well-Being Across the Lifespan: Second Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control, Mental Health and Self-Management in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial
by
Rocío Romero-Castillo, Manuel Pabón-Carrasco, Shakira Kaknani-Uttumchandani and José Antonio Ponce-Blandón
Healthcare 2025, 13(24), 3197; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243197 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Adults with type 1 diabetes (T1D) often experience psychological distress that interferes with their ability to maintain optimal self-care. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of the Diabself-care, a nurse-led structured diabetes self-management education (DSME) intervention
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Adults with type 1 diabetes (T1D) often experience psychological distress that interferes with their ability to maintain optimal self-care. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of the Diabself-care, a nurse-led structured diabetes self-management education (DSME) intervention designed to improve glycemic control, self-care practices and mental health among adults with T1D. Methods: A total of 224 adults with type 1 diabetes were randomized and final analyses included 110 participants in the intervention group and 106 in the control group. The intervention group received the Diabself-care program, consisting of five daily 90 min sessions integrating education, skill training, self-management and coping strategies in addition to usual care. The control group received standard diabetes care. Outcomes were assessed at baseline, 1 month and 3 months. The primary measure was glycemic control and secondary outcomes including self-management, anxiety and depressive symptoms. Results: The intervention group achieved a significant increase in time in range at both 1 and 3 months. Self-management adherence improved significantly in the intervention group (p < 0.001). Anxiety and depression scores decreased significantly in the intervention group at 1 and 3 months, while they remained unchanged in controls. Regression analyses identified depressive symptoms as the strongest predictor of anxiety (OR = 4.34, 95% CI = 2.99–6.28, p < 0.001), while female sex, older age, and low self-management were predictors of depression. Belonging to the intervention group was strongly protective against depression (OR = 0.11, 95% CI = 0.05–0.24, p < 0.001). Conclusions: The Diabself-care program significantly improved glycemic control, self-management, and psychological outcomes in adults with T1D. These findings highlight the dual clinical and mental health benefits of structured nurse-led DSME, supporting its integration into routine diabetes care. The trial is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov, ID: NCT05159843.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Chronic Care)
Open AccessArticle
The Effectiveness of Currently Recommended Questionnaires in Identifying Scoliosis Among Chronic Back Pain Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study
by
Fabio Zaina, Tito Bassani, René Castelein, Carmelo Pulici and Stefano Negrini
Healthcare 2025, 13(24), 3196; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243196 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Low back pain (LBP) is the most prevalent musculoskeletal condition, significantly impacting quality of life and incurring high social costs. Although non-specific (without anatomical abnormalities) LBP accounts for nearly 80% of cases, LBP due to adult spinal deformities (ASDs), including scoliosis, remains
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Low back pain (LBP) is the most prevalent musculoskeletal condition, significantly impacting quality of life and incurring high social costs. Although non-specific (without anatomical abnormalities) LBP accounts for nearly 80% of cases, LBP due to adult spinal deformities (ASDs), including scoliosis, remains a major concern. Several patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs)—notably the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI), Scoliosis Research Society-22 questionnaire (SRS-22), and Core Outcome Measure Instrument (COMI)—are recommended for assessment in these populations. This study aims to verify if these PROMs can effectively distinguish between adults with scoliosis-associated LBP (SLBP) and those with non-specific LBP (LBP). Methods: subjects were categorised as either having idiopathic/degenerative scoliosis (>10° Cobb angle in the coronal plane) with LBP, or non-specific LBP. Statistical comparisons applied non-parametric tests (Wilcoxon rank-sum, Mood’s median, chi-square), Spearman’s correlation, and generalised linear regression analyses. Results: Among 1092 subjects (552 SLBP; 540 LBP), median ODI scores were similar between groups, while SRS-22 scores were modestly higher in the SLBP cohort. Females consistently reported higher ODI and lower SRS-22 scores. Significant correlations arose between ODI and COMI, with moderate inverse associations with SRS-22. Regression analysis demonstrated that pathology group, gender, age, and BMI weakly predicted PROM scores. Conclusions: ODI and SRS-22 perform comparably in assessing disability in adults with LBP regardless of scoliosis, suggesting they cannot discriminate different pathologies. These findings underscore the importance of employing multiple PROMs to capture clinical dimensions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Scoliosis Deformity—Etiological Aspects, Management and Rehabilitation)
Open AccessCase Report
Effects of Adapted Physical Activity Programs on Body Composition and Sports Performance in a Patient with Parkinson’s Disease: A Case Report
by
Luciana Zaccagni, Natascia Rinaldo, Gaetano Campanale, Antonio Pastore, Francesca Rametta and Emanuela Gualdi-Russo
Healthcare 2025, 13(24), 3195; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243195 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
The benefits of physical activity on physical and mental health are well established. Exercise can be particularly advantageous in neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s disease (PD), where progressive loss of muscle mass and impaired motor performance are common. We report the case of
[...] Read more.
The benefits of physical activity on physical and mental health are well established. Exercise can be particularly advantageous in neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s disease (PD), where progressive loss of muscle mass and impaired motor performance are common. We report the case of a 58-year-old man with PD who underwent a structured, adapted physical activity program in preparation for a relay swim across the Strait of Messina (Sicily, Italy). The aim was to evaluate changes in body composition (fat mass, fat-free mass) and performance following four months of adapted swimming training, alongside adapted physical activity in the gym and Nordic walking. The patient swam 1300 m in 42 min and 38 s in the relay, which was a marked improvement from the baseline and subsequent assessments. In conclusion, while a longer follow-up period and a larger patient sample would be necessary, the findings from this case study suggest that the adapted exercise program improved both physical fitness and body composition. This generally supports the key role of physical activity in managing Parkinson’s disease and, in particular, the positive effects of adaptive sports training.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Physical Activity, Exercise, and Sport in People with Disabilities: Strategies for Health Promotion)
Open AccessArticle
Improved Gingival Margin Stability with a Digital Workflow in Esthetic Crown Lengthening: A Single-Center, Interventional, Non-Randomized, Open-Label Comparative Clinical Study on 622 Teeth
by
Sorin Gheorghe Mihali, Dan Loloș, Andreea Raissa Hojda, Bogdan Antonio Loloș and Roxana Oancea
Healthcare 2025, 13(24), 3194; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243194 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The stability of the gingival margin after crown lengthening is a key determinant of esthetic success in anterior rehabilitation. Digital workflows have been proposed to improve surgical precision, but their long-term impact on marginal stability remains insufficiently substantiated. Methods: A
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The stability of the gingival margin after crown lengthening is a key determinant of esthetic success in anterior rehabilitation. Digital workflows have been proposed to improve surgical precision, but their long-term impact on marginal stability remains insufficiently substantiated. Methods: A total of 87 patients (622 maxillary anterior and premolar teeth) who underwent esthetic crown lengthening were retrospectively evaluated. Patients were allocated to either a digitally guided workflow (G1, n = 62) or a freehand approach (G2, n = 25). Gingival margin stability was assessed using standardized intraoral photography and calibrated digital measurements at baseline, 1–2 months, and 12 months. Recurrence, periodontal parameters, complications, and patient satisfaction (VAS) were recorded. Mixed-effects models accounted for the clustering of teeth within patients. Results: Both workflows achieved predictable crown lengthening outcomes. At 12 months, median gingival margin recurrence was significantly lower in the guided group (G1: 0.14 mm [IQR 0.10–0.19]) compared with the freehand group (G2: 0.27 mm [IQR 0.20–0.34]) (p < 0.001). Secondary surgical revision was required in 1.6% of G1 patients versus 16.0% of G2 patients (p < 0.001). Patient satisfaction was high overall but greater in G1 (mean VAS 9.65 ± 0.52) than in G2 (8.96 ± 0.73). No major biological complications occurred. Conclusions: Digitally guided crown lengthening resulted in improved gingival margin stability and reduced the need for secondary correction compared with the freehand approach. Precise control of the bone crest position relative to the planned gingival margin is critical for long-term esthetic success.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Using Machine Learning Methods to Predict Cognitive Age from Psychophysiological Tests
by
Daria D. Tyurina, Sergey V. Stasenko, Konstantin V. Lushnikov and Maria V. Vedunova
Healthcare 2025, 13(24), 3193; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243193 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: This paper presents the results of predicting chronological age from psychophysiological tests using machine learning regressors. Methods: Subjects completed a series of psychological tests measuring various cognitive functions, including reaction time and cognitive conflict, short-term memory, verbal functions, and color and spatial
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: This paper presents the results of predicting chronological age from psychophysiological tests using machine learning regressors. Methods: Subjects completed a series of psychological tests measuring various cognitive functions, including reaction time and cognitive conflict, short-term memory, verbal functions, and color and spatial perception. The sample included 99 subjects, 68 percent of whom were men and 32 percent were women. Based on the test results, 43 features were generated. To determine the optimal feature selection method, several approaches were tested alongside the regression models using MAE,
(This article belongs to the Special Issue AI-Driven Healthcare Insights)
Open AccessArticle
Age Matters: A Study on Perceived Discrimination Among Older Adults in Healthcare in Lithuania
by
Kristina Selli, Ramunė Kalėdienė, Skirmantė Sauliūnė, Mindaugas Stankūnas and Snieguolė Kaselienė
Healthcare 2025, 13(24), 3192; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243192 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to analyse the opinions and experiences of older adults regarding age-based discrimination in healthcare. Method: The study is based on the analysis of data from 492 older adult respondents aged 60–84, with the mean
[...] Read more.
Objective: The aim of this study was to analyse the opinions and experiences of older adults regarding age-based discrimination in healthcare. Method: The study is based on the analysis of data from 492 older adult respondents aged 60–84, with the mean age of 71.6 ± 6.6 years, who completed and returned anonymous questionnaires sent to their homes. Results: Most of the respondents (74.8%) believed that the state does not consistently improve the protection of older persons’ rights. Nearly half (42.5%) reported that healthcare services are not provided equally to younger and older people. A significant proportion of respondents (41.1%) reported experiencing age-based discrimination themselves, having responded affirmatively to at least three out of nine statements indicating discriminatory experiences. Poor health status and financial hardships emerged as the primary factors associated with multidimensional discrimination experienced by older adults. More than half (64.0%) of respondents believed that discriminatory attitudes towards older people are rooted in healthcare professionals’ internal cultural norms. Conclusions: The findings of the study indicate the need to change the attitudes of healthcare professionals towards older adults. There is an urgent need for the targeted professional education on this issue.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Aging Population and Healthcare Utilization)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Influence of Sex, Family Structure, and Access to Technology on the Motor Development of Children Aged 24 to 48 Months
by
Miguel Rebelo, Rafael Adrião, Marco Batista, Samuel Honório, Helena Mesquita, Catarina Marques and João Serrano
Healthcare 2025, 13(24), 3191; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243191 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: This study aimed to analyze the influence of sex, the presence of siblings, and the duration of exposure to technology on the development of gross and fine motor skills in children aged between 24 and 48 months, using the PDMS-2 battery
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: This study aimed to analyze the influence of sex, the presence of siblings, and the duration of exposure to technology on the development of gross and fine motor skills in children aged between 24 and 48 months, using the PDMS-2 battery as the assessment instrument. Methods: The sample comprised 193 children, distributed across three age groups: 24 months (N = 22), 36 months (N = 78), and 48 months (N = 93). The assessed skills included Postural Control, Locomotion, Object Manipulation, Fine Grasping, and Visual–Motor Integration, grouped into the domains of Gross Motor and Fine Motor development. Statistical analysis was conducted using the non-parametric Mann–Whitney and Kruskal–Wallis tests, complemented by the epsilon squared (ε2) effect size measure. Results: The results revealed statistically significant differences between sexes, with girls demonstrating superior performance in Fine Motor and Visual–Motor Integration tasks, particularly at 36 and 48 months (p < 0.05; ε2 up to 0.22). The presence of siblings showed a positive impact only at 36 months, while the duration of exposure to technology did not present a significant association with motor performance at any age group. Conclusions: The Total Motor Quotient (TMQ) varied according to the variables analyzed, reinforcing the notion that motor development is multifactorial and sensitive to familial and social contexts. These findings highlight the importance of considering both environmental and biological factors when designing motor intervention strategies in early childhood.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Impact of Physical Inactivity on Children’s Health: The Current Status of Children’s Physical Condition, Influencing Variables and Future Implications)
Open AccessArticle
Gait and Dual-Task Performance in Older Adults with Suspected Cognitive Impairment: Effects of an 8-Week Exercise Program
by
João Galrinho, Marco Batista, Marta Gonçalves-Montera, Orlando Fernandes and Ana Rita Matias
Healthcare 2025, 13(24), 3190; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243190 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Gait performance in aging relies heavily on cognitive resources, yet the extent to which short-term interventions can mitigate dual-task costs in institutionalized populations remains understudied. This study aimed to compare single and dual-task gait performance between older adults with and without suspected
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Gait performance in aging relies heavily on cognitive resources, yet the extent to which short-term interventions can mitigate dual-task costs in institutionalized populations remains understudied. This study aimed to compare single and dual-task gait performance between older adults with and without suspected cognitive impairment and to evaluate the effects of an 8-week multicomponent exercise program on functional mobility. Methods: Institutionalized older adults (n = 42) were stratified into two groups: suspected cognitive impairment (n = 26) and no suspected impairment (n = 16), based on MMSE and Clock Drawing Test screening. Participants performed the Timed Up and Go (TUG) and Dual-Task TUG (TUG-DT) at baseline and post-intervention. Results: At baseline, the suspected impairment group exhibited significantly poorer performance on both tests (p < 0.001) compared to the non-impaired group. Following the 8-week intervention, the suspected impairment group demonstrated large, significant improvements in both TUG (r = −0.73) and TUG-DT (r = −0.59), whereas the non-impaired group remained stable. Notably, while the single-task TUG showed the greatest responsiveness to the exercise program, the TUG-DT continued to reveal a significant cognitive-motor load. Conclusions: Multicomponent exercise effectively enhances functional mobility in cognitively vulnerable older adults, reversing declines in both single and dual-task conditions. Significance: These findings support the implementation of dual-task screening to unmask latent functional deficits and validate the use of accessible, short-term multicomponent exercise programs as a vital strategy to preserve autonomy in institutionalized older adults.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Cutting-Edge Approaches in Neurological Disease Treatment)
Open AccessArticle
The Path from Depressive Symptoms to Subjective Well-Being Among Korean Young Adults During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Mediating Roles of Housing Satisfaction, Social Capital, Future Achievement Readiness, and Occupational Hazards
by
Miyoung Kwon and Myongsun Cho
Healthcare 2025, 13(24), 3189; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243189 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Recent economic instability and social isolation have increased mental health vulnerabilities among young adults, highlighting the need to clarify how multiple contextual factors shape their subjective well-being. This study explored the relationship between depressive symptoms and subjective well-being among Korean young adults.
[...] Read more.
Background: Recent economic instability and social isolation have increased mental health vulnerabilities among young adults, highlighting the need to clarify how multiple contextual factors shape their subjective well-being. This study explored the relationship between depressive symptoms and subjective well-being among Korean young adults. It also investigated the mediating effects of housing satisfaction, social capital, occupational hazards, and future achievement readiness on this relationship. Methods: A parallel mediation model was used to analyze the mediating effects of housing satisfaction, social capital, future achievement readiness, and occupational hazards on the relationship between depressive symptoms and subjective well-being. The model examined direct and indirect pathways to determine the extent to which these factors influence subjective well-being in young adults. Results: Depressive symptoms were associated with reduced housing satisfaction, social capital, and future achievement readiness, as well as increased exposure to occupational hazards. All four variable associations between depressive symptoms and subjective well-being, suggesting that multiple structural and psychosocial conditions jointly shape young adults’ subjective well-being. Conclusions: The findings suggest that conventional mental health services alone may be insufficient. A multifaceted approach—including housing welfare policies, social connection support, employment and adjustment programs, and initiatives that enhance future preparedness—may help mitigate the negative effects of depressive symptoms and improve subjective well-being among young adults.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Promoting Mental Health in School and Community Settings)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Changes in Lifestyle Behaviors and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors Before and After the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Nationally Representative Study from Korea
by
Bogja Jeoung and Sunghae Park
Healthcare 2025, 13(24), 3188; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243188 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic has substantially altered lifestyle behaviors, potentially affecting cardiovascular health. This study examined changes in lifestyle behaviors—specifically physical activity, smoking, and alcohol consumption—and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors before and after the pandemic using nationally representative data from Korea. Methods:
[...] Read more.
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic has substantially altered lifestyle behaviors, potentially affecting cardiovascular health. This study examined changes in lifestyle behaviors—specifically physical activity, smoking, and alcohol consumption—and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors before and after the pandemic using nationally representative data from Korea. Methods: Data were obtained from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) from 2016 to 2023. Weighted analyses were conducted to ensure national representativeness. Descriptive and inferential statistics (t-tests, ANOVA, and correlation analyses) were used to compare health behaviors and CVD risk factors between pre-pandemic (2016–2019) and post-pandemic (2020–2023) periods. Results: Adherence to aerobic physical activity declined from 45.5% before the pandemic to 42.1% after the pandemic, and resistance exercise participation also decreased (p < 0.05). Average sedentary time increased from 8.1 ± 3.5 to 8.7 ± 3.4 h/day. Body mass index (BMI) increased from 23.9 ± 3.7 to 24.1 ± 3.5 kg/m2, and triglyceride levels similarly increased (p < 0.05). In contrast, smoking prevalence decreased from 17.2% to 16.5%, and the average number of cigarettes smoked per day declined from 13 to 11–12. Alcohol intake per occasion also decreased significantly after the pandemic (p < 0.05). However, lipid indicators such as total cholesterol and LDL-C tended to be higher in the post-pandemic period, indicating unfavorable changes rather than improvement. Correlation analyses further showed that heavy drinking was associated with higher BMI, glucose, and triglyceride levels, whereas moderate drinking showed more favorable metabolic profiles. Conclusions: The COVID-19 pandemic exerted mixed effects on lifestyle behaviors and cardiovascular risk factors among Korean adults. While reductions in physical activity and increases in sedentary time may elevate long-term health risks, concurrent decreases in smoking and alcohol intake could have mitigated some negative outcomes. Nevertheless, adverse changes in lipid profiles—including increases in LDL-C, total cholesterol, and triglycerides—suggest that metabolic health worsened overall after the pandemic. These findings underscore the urgent need for tailored public health strategies to promote balanced lifestyle behaviors and mitigate cardiovascular risks in the post-pandemic era.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Relationship Between Physical Activity, Dietary Habits and Health Status)
Open AccessArticle
Interconnected Challenges: Examining the Impact of Poverty, Disability, and Mental Health on Refugees and Host Communities in Northern Mozambique
by
Theresa Beltramo, Florence Nimoh, Sandra Sequeira and Peter Ventevogel
Healthcare 2025, 13(24), 3187; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243187 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Poverty, disability, and mental health may reinforce one another. Forced displacement can compound these challenges, yet comparable data on displaced and non-displaced groups in the same setting are scarce. This study examines associations among mental health, disability, pessimism, loneliness, self-esteem, and financial
[...] Read more.
Background: Poverty, disability, and mental health may reinforce one another. Forced displacement can compound these challenges, yet comparable data on displaced and non-displaced groups in the same setting are scarce. This study examines associations among mental health, disability, pessimism, loneliness, self-esteem, and financial security for refugees and nearby host communities in Mozambique. Methods: Ultra-poor adults—refugees (n = 134) and Mozambican nationals living near the settlement (n = 314)—were identified using a World Bank poverty scorecard. Surveys captured depression (PHQ-9), anxiety (GAD-7), disability (Washington Group Short Set), and socioeconomic characteristics. Results: Symptom rates are high in both groups—depression: 34% (refugees) vs. 29% (hosts); anxiety: 25% overall—with women reporting higher levels. Disability prevalence is substantial (refugees 25%; hosts 22%). Respondents with disabilities show markedly higher rates of depression (≈2×) and anxiety (≈3×). Financial security is negatively associated with symptom scores: a one-unit-higher financial security index correlates with a 0.069 lower anxiety score (p < 0.05) and a 0.069 lower depression score (p < 0.01). Pessimism is positively associated with poorer mental health; anxiety and depression are more than 2.5× as prevalent among chronically pessimistic respondents. Loneliness shows no clear association with anxiety or depression in this sample, whereas low self-esteem is strongly associated with both; prevalence of GAD and depression is more than twice as high among those with low self-esteem. Conclusions: We document strong associations between poverty, disability, and mental health. These patterns underscore the importance of strengthening mental and public health services for both refugees and hosts, with particular attention to women and disabled individuals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Healthcare for Immigrants and Refugees)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Family-Based Tag Rugby: Acute Effects on Risk Factors for Cardiometabolic Disease and Cognition and Factors Affecting Family Enjoyment and Feasibility
by
Scarlett M. Fountain, Grace W. M. Walters, Ryan A. Williams, Caroline Sunderland, Simon B. Cooper and Karah J. Dring
Healthcare 2025, 13(24), 3186; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243186 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Physical inactivity is associated with increased cardiometabolic disease risk and poor cognition in children and their parents. Family-based physical activity offers an opportunity for children and their parents to engage in physical activity concurrently. The present study examined the effect of
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Physical inactivity is associated with increased cardiometabolic disease risk and poor cognition in children and their parents. Family-based physical activity offers an opportunity for children and their parents to engage in physical activity concurrently. The present study examined the effect of an acute bout of family-based tag rugby on risk factors for cardiometabolic disease and cognition in families. Additionally, this study qualitatively explored families’ perceptions of enjoyment and factors affecting implementation with considerations for socioeconomic status. Methods: Sixteen families (27 children, 20 parents) participated in an exercise (45 min family-based tag rugby) and resting control trial (45 min seated rest), separated by seven days. Postprandial gylcaemia, insulinaemia, lipaemia and cognitive function were measured following exercise/rest. Families also participated in whole-family focus groups and separate parent and child interviews. Results: In parents, postprandial plasma insulin concentrations were lower on the exercise trial than the rested control trial at 30 min (p = 0.004) and 120 min following the consumption of a standardised lunch (p = 0.011). In children, a significant trial*time interaction for inverse efficiency scores on the Sternberg paradigm (three-item) was exhibited (p = 0.016). In parents, a significant trial*time interaction for inverse efficiency score on the Stroop congruent test was exhibited (trial*time interaction; p = 0.012), whereby inverse efficiency scores improved immediately post-exercise, compared with the rested control trial (p = 0.016). Qualitatively, families from all socioeconomic backgrounds agreed that tag rugby is an inclusive, enjoyable mode of physical activity that families want to participate in together, which can be adapted to overcome the barriers associated with the cost of and access to local facilities. Conclusions: An acute bout of tag rugby improved postprandial insulin concentrations in parents and cognitive function in children and their parents. Tag rugby was deemed an appropriate exercise modality for families from a range of socioeconomic backgrounds.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Physical Activity Intervention for Non-Communicable Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
PERMA Well-Being Model and Profiler: Arabic Translation and Validation Among the Saudi Adult Population
by
Ebtesam Abdullah Alzeiby, Aljawharh Ibrahim Alsukah, Nourah Abdulrhman AlGadheeb, Ali Faris Alamri, Monira Abdulrahman Almeqren and Uzma Zaidi
Healthcare 2025, 13(24), 3185; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243185 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objective: Psychological scales hold significant importance, measuring cultural sensitivity, experiences, values, and emotional expressions while controlling individuals’ biases regarding certain cultures. Arabic is used in a widespread, predominantly Middle Eastern and North African region, but it has diverse expressive variations. Therefore, the value
[...] Read more.
Background/Objective: Psychological scales hold significant importance, measuring cultural sensitivity, experiences, values, and emotional expressions while controlling individuals’ biases regarding certain cultures. Arabic is used in a widespread, predominantly Middle Eastern and North African region, but it has diverse expressive variations. Therefore, the value of translating and validating scales lies in their compatibility with cultural norms. This study focuses on measuring the psychometric properties and factorial structure of the widely used PERMA-Profiler to assess the general well-being of the Saudi adult population. Methods: Using stratified sampling, (N = 2927) Saudi adults were recruited via various electronic and social media. Results: The confirmatory factor analysis showed strong evidence of the instrument’s validity, confirming well-being as a single latent factor composed of five dimensions with an acceptable degree of reliability. The correlation coefficients indicate considerable internal consistency for numerous factors, including positive emotions, engagement, relationships, meaning, accomplishment, health, and happiness (α = 0.83, 0.79, 0.77, 0.84, 0.80, 0.69, 0.71), respectively. The Split-Half coefficient demonstrated significant reliability (0.87). Conclusions: The validity and reliability of the scale are supported, confirming that PERMA can be applied to measure the well-being of Saudi society. Furthermore, the Arabic version of PERMA can be utilized in counseling and psychotherapy practice as well as in research studies. It could be a helpful tool for exploring and preventing mental health issues and improving well-being within the community.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Can a Generative Artificial Intelligence Model Be Used to Create Mass Casualty Incident Simulation Scenarios? A Feasibility Study
by
Sergio M. Navarro, Angie G. Atkinson, Ege Donagay, Maxwell Jabaay, Sarah Lund, Myung S. Park, Erica A. Loomis, John M. Zietlow, T. N. Diem Vu, Mariela Rivera and Daniel Stephens
Healthcare 2025, 13(24), 3184; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243184 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
Introduction: Mass casualty incident (MCI) simulation scenarios are developed based on detailed review and planning by multidisciplinary trauma teams. This study aimed to assess the feasibility of using generative artificial intelligence (AI) in developing mass casualty trauma simulation scenarios. The study evaluated a
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Mass casualty incident (MCI) simulation scenarios are developed based on detailed review and planning by multidisciplinary trauma teams. This study aimed to assess the feasibility of using generative artificial intelligence (AI) in developing mass casualty trauma simulation scenarios. The study evaluated a range of mass casualty trauma simulation scenarios generated from a public generative artificial intelligence platform based on publicly available data with a validated objective simulation scoring tool. Methods: Using a large language model (LLM) platform (ChatGPT4, OpenAI, San Francisco, CA, USA), 10 complex MCI trauma simulation scenarios were generated based on publicly available US reported trauma data. Each scenario was evaluated by two Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS) certified raters based on the Simulation Scenario Evaluation Tool (SSET), a validated scoring tool out of 100 points. The tool scoring is based on learning objectives, tasks for performance, clinical progression, debriefing criteria, and resources. Two publicly available mass casualty trauma scenarios were similarly evaluated as controls. Revision and recommended feedback was provided for the scenarios, with review time recorded. Post-revision scenarios were evaluated. Interrater reliability was calculated based on Intraclass Correlation Coefficients (2, k) (ICCs). For the scenarios, scores and review times were reported as medians with interquartile range (IQR) as 25th and 75th percentiles. Results: Ten mass casualty trauma simulation scenarios were generated by an LLM, producing a total of 62 simulated patients. The initial LLM-generated scenarios demonstrated a median SSET score of 78.5 (IQR 74–82), substantially lower than the median score of 94 (IQR 93–95) observed in publicly available scenarios. The interrater reliability ICC for the LLM-generated scenarios was 0.965 and 1.00 for publicly available scenarios. Following secondary human revision and iterative refinement, the LLM-generated scenarios improved, achieving a median SSET score of 94 (IQR 93–96) with an interrater reliability ICC of 0.7425. Conclusions: The feasibility study suggests that a structured, collaborative workflow combining LLM-based generation with expert human review may enable a new approach to mass casualty trauma simulation scenario creation. LLMs hold promise as a scalable tool for the development of MCI training materials. However, consistent human oversight, quality assurance processes, and governance frameworks remain essential to ensure clinical accuracy, safety, and educational value.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Generative AI and Interdisciplinary Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
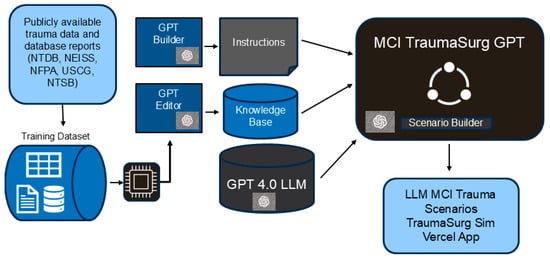
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Perceptions and Awareness of Healthcare Professionals Regarding FAIR Data Principles and Health Data Sharing in Saudi Arabia
by
Ebtisam Ali Alharbi and Abdulmajeed Fahad Alrefaei
Healthcare 2025, 13(24), 3183; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13243183 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: The FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) data principles are guidelines for managing data assets. While applied globally, no prior research has examined healthcare professionals’ perceptions and awareness of FAIR principles in Saudi Arabia’s healthcare context—a critical knowledge gap requiring investigation.
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) data principles are guidelines for managing data assets. While applied globally, no prior research has examined healthcare professionals’ perceptions and awareness of FAIR principles in Saudi Arabia’s healthcare context—a critical knowledge gap requiring investigation. Methods: To address this gap, this two-part mixed-methods study assessed practitioners’ awareness, perceptions, and expectations regarding the implementation of FAIR principles within the Saudi healthcare system. The first stage involved administering a cross-sectional survey to a random sample of 153 healthcare professionals working in the Saudi health sector. The second stage comprised three follow-up focus group discussions that further explored insights derived from the survey data. Results: The survey revealed that over half of the participants (52.9%) were unfamiliar with the FAIR data principles and 84.3% had not applied them in managing health data. Thematic analysis identified three key themes: awareness of FAIR data principles, perceived benefits and drivers of implementation, and challenges in current data management practices. Conclusions: This study provides the first theoretically grounded examination of FAIR adoption in Saudi healthcare. The findings offer actionable insights for policymakers to strengthen data governance, promote a culture of data stewardship, and align national digital health strategies with FAIR principles—thereby supporting sustainable, interoperable, and responsible data practices across the Saudi healthcare system.
Full article
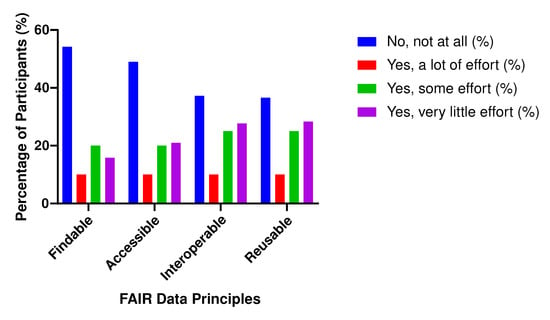
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Detecting Burnout Among Undergraduate Computing Students with Supervised Machine Learning
by
Eldar Yeskuatov, Lee Kien Foo and Sook-Ling Chua
Healthcare 2025, 13(23), 3182; https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13233182 - 4 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Academic burnout significantly impacts students’ cognitive and psychological well-being and may result in adverse behavioral changes. An effective and timely detection of burnout in the student population is crucial as it enables educational institutions to mobilize necessary support systems and implement intervention
[...] Read more.
Background: Academic burnout significantly impacts students’ cognitive and psychological well-being and may result in adverse behavioral changes. An effective and timely detection of burnout in the student population is crucial as it enables educational institutions to mobilize necessary support systems and implement intervention strategies. However, current survey-based detection methods are susceptible to response biases and administrative overhead. This study investigated the feasibility of detecting academic burnout symptoms using machine learning trained exclusively on university records, eliminating reliance on psychological surveys. Methods: We developed models to detect three burnout dimensions—exhaustion, cynicism, and low professional efficacy. Five machine learning algorithms (i.e., logistic regression, support vector machine, naive Bayes, decision tree, and extreme gradient boosting) were trained using features engineered from administrative data. Results: Results demonstrated considerable variability across burnout dimensions. Models achieved the highest performance for exhaustion detection, with logistic regression obtaining an F1 score of 68.4%. Cynicism detection showed moderate performance, while professional efficacy detection has the lowest performance. Conclusions: Our findings showed that automated detection using passively collected university records is feasible for identifying signs of exhaustion and cynicism. The modest performance highlights the challenges of capturing psychological constructs through administrative data alone, providing a foundation for future research in unobtrusive student burnout detection.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Technologies to Promote Psychosocial and Occupational Well-Being in University Students and Healthcare Workers: Innovation and Public Health Challenges)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Healthcare Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Urban Science, Medicina, Atmosphere, Buildings, Applied Sciences, Aerobiology, Healthcare
Impacts of Air Quality on Environment and Human Health
Topic Editors: Marco Dettori, Antonella Arghittu, Giovanna DeianaDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
Applied Sciences, IJERPH, JCM, JPM, Technologies, Healthcare
Smart Healthcare: Technologies and Applications, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Gang Kou, Shuai Ding, Li Luo, Tian Lu, Yogesan KanagasingamDeadline: 20 January 2026
Topic in
Brain Sciences, IJERPH, JAL, Nursing Reports, Nutrients, Healthcare
Healthy, Safe and Active Aging, 2nd EditionTopic Editors: Antonella Lopez, Andrea Bosco, Alessandro Oronzo Caffò, Elisabetta Ricciardi, Giuseppina Spano, Luigi TinellaDeadline: 28 February 2026
Topic in
JFMK, Medicina, Therapeutics, Healthcare, JCM, Rheumato
New Trends in Physiotherapy Care: Improvements in Functionality, Pain Management, and Quality of Life
Topic Editors: Carlos Bernal-Utrera, Ernesto Anarte-Lazo, Juan José González GerezDeadline: 3 March 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Healthcare
Family Care and Mental Health Delivery to Improve Welfare of Children and Parents
Guest Editor: Leonor Rivera-RiveraDeadline: 15 December 2025
Special Issue in
Healthcare
Nursing, Coaching, Oncology and Chronic Diseases: Future Insights and Perspectives
Guest Editors: Elsa Vitale, Karen AvinoDeadline: 15 December 2025
Special Issue in
Healthcare
The Impact of Exercise and Physical Activity on Quality of Life
Guest Editor: Frontini RobertaDeadline: 15 December 2025
Special Issue in
Healthcare
The Role of Physical Fitness in Effective Health Management
Guest Editor: Tiago Rodrigues De LimaDeadline: 15 December 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Healthcare
Health Economics & Finance and Global Public Health
Collection Editor: Mustafa Z. Younis
Topical Collection in
Healthcare
Mindfulness in Healthcare
Collection Editors: Helen Noble, Ian Walsh
Topical Collection in
Healthcare
Aging and Chronic Disease: Experiences, Holisitic Care and Quality of Life
Collection Editor: Jose Granero-Molina
Topical Collection in
Healthcare
Integrative, Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM) in Healthcare
Collection Editors: Manoj Sharma, Kavita Batra










