- Article
Comparison Between Helpful and Missing Resources Identified by Patients with End-Stage Liver Disease and Their Caregivers: A Content Analysis
- Susan J. Rosenkranz,
- Shirin O. Hiatt and
- Lissi Hansen
- + 2 authors
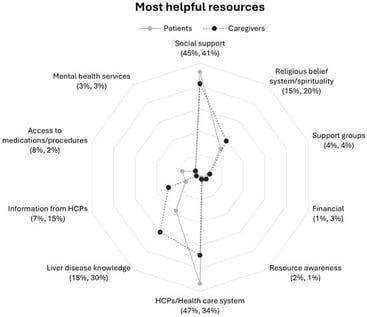
Patients with end-stage liver disease (ESLD) and their caregivers experience extensive physical, psychological, and social burdens and needs for resources. However, empirical evidence on patients’ and caregivers’ specific reported use of resources to help manage ESLD is lacking. Understanding the type and helpfulness of resources used could strengthen clinical care to address individual needs for resources. Aim: To examine and compare resources patients and caregivers identified as being most helpful in managing ESLD in relation to resources they felt would be helpful. Methods: Patients with ESLD and their caregivers responded in writing to two open-ended questions as part of a survey: (1) What resources have you found most helpful in dealing with patient’s liver disease? and (2) What resources would be helpful in dealing with patient’s liver disease? Conventional content analysis was used to identify resource categories. Results: A total of 192 patients and 198 caregivers completed surveys. We identified two major resource domains—medical and non-medical—and five categories within each. Analysis revealed participant group- and disease severity-based differences in helpful resources. Conclusions: Proactively engaging patients and caregivers early in the course of illness to identify relevant resources that might facilitate ability to manage ESLD. An interprofessional care approach would facilitate efforts supporting financial, social, spiritual, emotional, and mental health needs. Future longitudinal research of unique resource needs along the disease trajectory may help to develop effective interventions.
9 March 2026