- Case Report
Analysis of the Psychophysiological Effect of a Bull Horn Wound in a Professional Bullfighter: A Case Report
- Luis Teba-del-Pino,
- Luis Suárez-Arrones and
- Eduardo Sáez de Villarreal
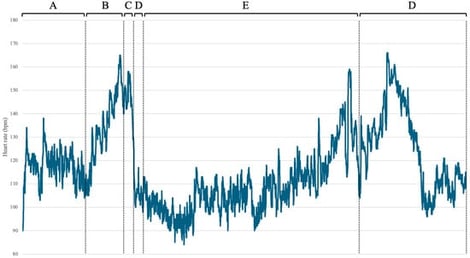
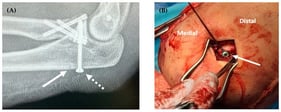
Goring during bullfights represents a penetrating trauma with a high risk of muscular, vascular, and vital injuries. Despite its frequency and severity, limited information is available on the immediate physiological response of the bullfighter at the moment of trauma. This case report describes the heart rate of a professional bullfighter who was gored during a bullfight, underwent surgery, and returned to fight the next bull. During the first fight, the bullfighter suffered a penetrating goring wound to the inner side of the lower third of his right thigh and a fracture of the ninth rib with intercostal rupture. Upon standing, he experienced a marked drop in heart rate and a feeling of loss of consciousness, possibly associated with vasovagal presyncope. He was transferred to the infirmary in hemodynamically stable condition. He was given local anesthesia, followed by surgical exploration, cleaning, and layered closure of the wound. After surgery, the bullfighter experienced a gradual increase in heart rate upon standing, possibly due to postural changes and postoperative sympathetic activation. He then returned to the bullring to resume activity. This case report highlights a possible vasovagal response to penetrating trauma, which may be relevant for trauma care, as a vasovagal or parasympathetic-predominant autonomic response could influence early clinical assessment.
28 January 2026