Journal Description
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Gastrointestinal Disorders
is an international, open access, peer-reviewed journal on gastroenterology, published quarterly online by MDPI. The Robotic Global Surgical Society (TROGSS) is affiliated with Gastrointestinal Disorders and its members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions; authors retain copyright.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), FSTA, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Immunology and Microbiology (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 22.2 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.4 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Reliable service: rigorous peer review and professional production.
Impact Factor:
0.8 (2024)
Latest Articles
Impact of a Second E-Reminder on Fecal Immunochemical Test Uptake in the Flemish Colorectal Cancer Screening Program: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Gastrointest. Disord. 2026, 8(1), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord8010014 - 4 Mar 2026
Abstract
Background: Flanders (Belgium) offers a fecal immunochemical test (FIT) biennially to citizens aged 50–74 years, but uptake is suboptimal (~50%). This study evaluated the impact of a second e-reminder on FIT uptake. Methods: We conducted a quasi-experimental study comparing FIT uptake
[...] Read more.
Background: Flanders (Belgium) offers a fecal immunochemical test (FIT) biennially to citizens aged 50–74 years, but uptake is suboptimal (~50%). This study evaluated the impact of a second e-reminder on FIT uptake. Methods: We conducted a quasi-experimental study comparing FIT uptake in individuals who received a first e-reminder during June 2023–May 2024 and a second e-reminder five weeks later (intervention cohort) with those who received a first e-reminder in June 2021–May 2022 without a second reminder (historical control). The study outcome was FIT uptake within one year after the first e-reminder. Analyses were stratified by screening history (regular vs. irregular participants). Results: The study population consisted of 54,734 regular (27,522 control and 27,212 intervention); and 18,492 irregular participants (8565 control and 9927 intervention). Median age was slightly lower in the intervention group (regular: 57 vs. 59 years; irregular: 62 vs. 64 years). Gender distribution was balanced (≈50% men). Regular participants receiving a second e-reminder had 80% higher probability of participation than controls (OR 1.80; 95% CI 1.73–1.86; p < 0.0001); with uptake increasing from 29.5% to 43.7%. Irregular participants with a second e-reminder had a 91% higher probability of participation compared with no second e-reminder (OR 1.91; 95% CI 1.74–2.09; p < 0.0001), with uptake increasing from 9.4% to 18.4%. Conclusions: A second e-reminder significantly increased FIT uptake among both regular and irregular participants in the Flemish colorectal cancer screening program. These findings support its use as a low-cost strategy to improve population-level screening participation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Gastrointestinal Disorders in 2025–2026)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
The Evolving Landscape of Advanced Therapies in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Current Evidence and Emerging Targets
by
Daniele Balducci, Marta Mosca, Sabrina Monaco, Susanna Faenza, Stefano Fabiani, Fabio Cortellini, Nicola Cesaro, Gianpiero Stefanelli, Salvatore Paba, Maddalena Pecchini, Michele Montori and Marco Valvano
Gastrointest. Disord. 2026, 8(1), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord8010013 - 24 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background: Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), including Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), are chronic conditions that affect the gastrointestinal tract. Since the initial approval of infliximab (IFX), a monoclonal antibody targeting TNF-α, numerous novel therapeutic targets have been identified, and many
[...] Read more.
Background: Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), including Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), are chronic conditions that affect the gastrointestinal tract. Since the initial approval of infliximab (IFX), a monoclonal antibody targeting TNF-α, numerous novel therapeutic targets have been identified, and many new therapies have been approved for the treatment of IBD. Methods: We conducted a narrative review of the literature using major biomedical databases, including EMBASE, Scopus, PubMed, CENTRAL, and ClinicalTrials.gov (last search date: 10 December 2025). Results: This review summarizes the current evidence on therapies approved for IBD (both CD and UC) and provides an overview of investigational agents currently being evaluated in ongoing phase II and III clinical trials. Conclusions: Moderate optimism arises from the expanding array of therapeutic targets under investigation and from emerging treatment strategies. However, only through a deeper understanding of the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying IBD will substantial improvements in treatment outcomes be achieved for conditions that continue to impose a significant burden on patients’ quality of life.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Novel Therapies for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Systemic IgG/IgA Balance and Antigen-Specific Seroreactivity as Predictors of the Topographic Distribution of Helicobacter pylori-Associated Gastritis
by
Nebojsa Manojlovic, Ivana Tufegdzic, Elizabeta Ristanović, Nemanja Rancic and Stevan Manojlovic
Gastrointest. Disord. 2026, 8(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord8010012 - 18 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Helicobacter pylori infection induces a systemic humoral immune response that reflects both bacterial virulence and host immune regulation. While anti-H. pylori IgG is widely used as a marker of infection, its ability to predict the topographic distribution and biological activity of
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Helicobacter pylori infection induces a systemic humoral immune response that reflects both bacterial virulence and host immune regulation. While anti-H. pylori IgG is widely used as a marker of infection, its ability to predict the topographic distribution and biological activity of gastritis is limited. The objective of this study was to evaluate whether the relative predominance of systemic IgG versus IgA antibodies, IgG subclasses, and antigen-specific IgG reactivity could better reflect the features and topography of gastric inflammation. Methods: A total of 123 patients with dyspeptic symptoms, confirmed H. pylori infection, and histologically verified gastritis were included. Anti-H. pylori IgG and IgA levels were measured by ELISA, IgG1 and IgG2 subclasses by subclass-specific assays, and antigen-specific IgG reactivity (CagA, VacA, UreB66, 30 kDa, and UreA 26 kDa) by Western blot. Histopathological parameters of the antral and corpus mucosa were graded according to the updated Sydney system. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis and univariate and multivariate logistic regression were applied to identify predictors of gastritis topography. Results: Anti-H. pylori IgG levels correlated with the grade and activity of inflammation in the antrum, whereas IgA correlated with inflammatory parameters in the corpus. IgG1 and IgG2 showed limited associations with antral inflammatory activity. IgA showed the best diagnostic performance for pangastritis/corpus-predominant gastritis, while IgG2 best identified antrum-predominant gastritis. The combined serological profile defined as IgG > IgA together with 30 kDa antigen positivity was independently associated with antrum-predominant gastritis in multivariate analysis (OR 2.516; 95% CI 1.004–6.308). Conclusions: The systemic balance between IgG and IgA responses reflects the topographic distribution of H. pylori-associated gastritis. IgG predominance combined with 30 kDa antigen seropositivity represents an independent serological predictor of antrum-predominant gastritis and may improve non-invasive stratification of gastric inflammation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Ultrastructural Features of Amoeboid Tumor Cell–Unmyelinated Nerve Fiber Interactions in Early Gastric Cancer: A Case Report Within the Context of Cancer Neuroscience
by
Valerio Caruso, Luciana Rigoli and Rosario Caruso
Gastrointest. Disord. 2026, 8(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord8010011 - 10 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Perineural invasion (PNI) is a recognized pathway for cancer spread and is associated with poor outcomes in gastric cancer. However, the initial morphological characteristics of tumor–nerve interactions in early gastric cancer, particularly at the ultrastructural level, remain insufficiently defined. Case Presentation
[...] Read more.
Background: Perineural invasion (PNI) is a recognized pathway for cancer spread and is associated with poor outcomes in gastric cancer. However, the initial morphological characteristics of tumor–nerve interactions in early gastric cancer, particularly at the ultrastructural level, remain insufficiently defined. Case Presentation: We report a case of a 49-year-old man diagnosed with type IIc early gastric cancer. Histological examination revealed a combined poorly cohesive carcinoma (PCC)-NOS/signet-ring cell (SRC) histotype. Tumor invasion reached the middle third of the submucosa and was accompanied by a mature desmoplastic reaction, with metastases identified in two perigastric lymph nodes (pT1bN1M0). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) revealed unmyelinated nerve fibers embedded within the submucosal desmoplastic stroma, in close proximity to infiltrating neoplastic cells. Several tumor cells exhibited cytoplasmic projections ranging from single extensions to multiple prominent pseudopods, resulting in an amoeboid morphology. Notably, an unmyelinated nerve process was observed within a cytoplasmic invagination of an individual tumor cell. Conclusions: Taken together, these ultrastructural findings provide novel and previously undescribed morphological evidence of a specific interaction between amoeboid tumor cells and peripheral unmyelinated nerve fibers within the submucosal desmoplastic stroma of early gastric cancer. The biological and clinical significance of this interaction in the early stages of perineural invasion warrants further investigation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Advances in Reversing Gastric Mucosal Atrophy: Pathological Mechanisms, Therapeutic Targets, and Clinical Strategies
by
Jianlong Chen, Huanlu Xu, Yiwen Feng and Hongzhang Shen
Gastrointest. Disord. 2026, 8(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord8010010 - 30 Jan 2026
Abstract
Chronic atrophic gastritis (CAG) is a key precursor in the Correa cascade leading to gastric cancer and is driven by long-standing Helicobacter pylori infection, autoimmune reactions, environmental exposures, and persistent inflammation. Emerging evidence indicates that mild to moderate atrophy and part of intestinal
[...] Read more.
Chronic atrophic gastritis (CAG) is a key precursor in the Correa cascade leading to gastric cancer and is driven by long-standing Helicobacter pylori infection, autoimmune reactions, environmental exposures, and persistent inflammation. Emerging evidence indicates that mild to moderate atrophy and part of intestinal metaplasia exhibit a degree of reversibility when etiological eradication, microenvironmental optimization, and regenerative stimulation are achieved. This review summarizes recent advances in the pathological basis, evaluation systems, therapeutic mechanisms, and clinical management strategies of CAG. Reversibility is closely related to residual glandular reserve, stem-cell plasticity, and effective mitigation of chronic inflammation. Current assessment tools integrate OLGA/OLGIM histological staging, high-quality endoscopy with AI assistance, and serological biomarkers. Fundamental interventions include early H. pylori eradication, mucosal protective agents, micronutrients, and small-molecule drugs targeting inflammation, oxidative stress, and epithelial regeneration. Novel strategies such as mesenchymal stem cells, exosomes, and focal endoscopic therapies demonstrate regenerative potential in preclinical studies. Traditional Chinese medicine provides multi-target regulation of inflammation, apoptosis, microecology, and stem-cell-related pathways, contributing to histological improvement. Contemporary guidelines emphasize early eradication, risk-stratified surveillance, and comprehensive intervention. Future directions focus on unified evaluation criteria, long-term prospective studies, multimodal combination regimens, and integration of AI-based risk modeling to achieve precise, cancer-preventive CAG management.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Gastrointestinal Disorders in 2025–2026)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Endoscopic and Histologic Findings in Asymptomatic Children with Iron-Deficiency Anemia: A Systematic Review and Clinical Implications
by
Abdulrahman Adel Hawari, Shaly Mohammed Aljedaani, Hanan Ismail Wasaya, Arwa Alsharif, Abdulaziz Alsharif, Reem Mohammed Rara, Aseel Alomari, Sara Abdullah Magboul and Salma Ismail Daffa
Gastrointest. Disord. 2026, 8(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord8010009 - 25 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Iron-deficiency anemia (IDA) is a common condition in children and is frequently attributed to nutritional causes. However, gastrointestinal (GI) pathology may be present even in the absence of overt GI symptoms. The diagnostic value of endoscopic evaluation in asymptomatic pediatric patients with
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Iron-deficiency anemia (IDA) is a common condition in children and is frequently attributed to nutritional causes. However, gastrointestinal (GI) pathology may be present even in the absence of overt GI symptoms. The diagnostic value of endoscopic evaluation in asymptomatic pediatric patients with IDA remains debated. This systematic review aimed to synthesize available evidence on endoscopic and histologic findings in asymptomatic children with IDA and to assess their clinical implications. Methods: A systematic review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA 2020 guidelines, and the protocol was registered in PROSPERO. MEDLINE (via PubMed) and Scopus were searched for studies involving children and adolescents (0–18 years) with confirmed iron-deficiency anemia and no gastrointestinal symptoms who underwent endoscopic evaluation. Results: Six studies met the inclusion criteria, comprising a total of 455 pediatric patients. Upper GI endoscopy was the most commonly performed procedure. Clinically significant findings were frequently identified, including histologic features consistent with celiac disease, Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis, and chronic inflammatory gastric changes. Histologic abnormalities were often present despite minimal or absent macroscopic endoscopic findings. The diagnostic yield of endoscopy was particularly high in older children and adolescents and in those with severe or refractory IDA. Conclusions: This systematic review demonstrates that asymptomatic children with IDA may harbor significant GI pathology detectable by endoscopic and histologic evaluation. These findings support the consideration of targeted endoscopic assessments in selected pediatric patients with unexplained or persistent IDA, even in the absence of GI symptoms.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pediatric Gastrointestinal Endoscopy and Surgery: Current Challenges and Future Directions)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Hydrogen and Ozone Therapies as Adjunctive Strategies for Gastrointestinal Health in Geriatric Populations
by
Joanna Michalina Jurek, Zuzanna Jakimowicz, Runyang Su, Kexin Shi and Yiqiao Qin
Gastrointest. Disord. 2026, 8(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord8010008 - 23 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Aging is accompanied by progressive gastrointestinal structural and functional decline, increased intestinal permeability, dysbiosis, and impaired mucosal immunity, collectively elevating susceptibility to infections, chronic inflammation, and multimorbidity. These age-related changes are further exacerbated by polypharmacy, metabolic disorders, and lifestyle factors, positioning the gastrointestinal
[...] Read more.
Aging is accompanied by progressive gastrointestinal structural and functional decline, increased intestinal permeability, dysbiosis, and impaired mucosal immunity, collectively elevating susceptibility to infections, chronic inflammation, and multimorbidity. These age-related changes are further exacerbated by polypharmacy, metabolic disorders, and lifestyle factors, positioning the gastrointestinal tract as a central driver of systemic physiological decline. Gut-centered interventions have emerged as critical strategies to mitigate these vulnerabilities and support healthy aging. Dietary modulation, prebiotic and probiotic supplementation, and microbiota-targeted approaches have demonstrated efficacy in improving gut microbial diversity, enhancing short-chain fatty acid production, restoring epithelial integrity, and modulating immune signaling in older adults. Beyond nutritional strategies, non-nutritional interventions such as molecular hydrogen and medical ozone offer complementary mechanisms by selectively neutralizing reactive oxygen species, reducing pro-inflammatory signaling, modulating gut microbiota, and promoting mucosal repair. Hydrogen-based therapies, administered via hydrogen-rich water or inhalation, confer antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cytoprotective effects, while ozone therapy exhibits broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, enhances tissue oxygenation, and stimulates epithelial and vascular repair. Economic considerations further differentiate these modalities, with hydrogenated water positioned as a premium wellness product and ozonated water representing a cost-effective, scalable option for geriatric gastrointestinal care. Although preclinical and early clinical studies are promising, evidence in older adults remains limited, emphasizing the need for well-designed, age-specific trials to establish safety, dosing, and efficacy. Integrating dietary, microbiota-targeted, and emerging non-nutritional gut-centered interventions offers a multimodal framework to preserve gut integrity, immune competence, and functional health, potentially mitigating age-related decline and supporting overall health span in older populations.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Serum CCL5 in Liver Transplant Candidates: A Potential Marker of Portal Hypertension, Not Cardiovascular Risk
by
Teodora Radu, Speranța M. Iacob, Ioana Manea and Liliana S. Gheorghe
Gastrointest. Disord. 2026, 8(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord8010007 - 21 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Chemokine CCL5 may drive inflammation and vascular risk in advanced liver disease, but its cardiovascular implications are unclear. Secreted by hepatic, endothelial, macrophage, and lymphocytic cells, CCL5 is involved in cytokine regulation. Its serum levels rise in acute liver injury and hepatocellular
[...] Read more.
Background: Chemokine CCL5 may drive inflammation and vascular risk in advanced liver disease, but its cardiovascular implications are unclear. Secreted by hepatic, endothelial, macrophage, and lymphocytic cells, CCL5 is involved in cytokine regulation. Its serum levels rise in acute liver injury and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but decline with fibrosis progression in end-stage liver disease (ESLD). CCL5 has also been linked to atherosclerosis. This study aimed to evaluate serum CCL5 levels in ESLD patients listed for liver transplantation (LT) and to assess their potential role as markers of cardiovascular (CV) risk and portal hypertension. Methods: We conducted an observational cohort study. Between 2019 and 2022, patients with ESLD evaluated for LT were enrolled. Data on liver pathology, CV risk, and laboratory parameters were collected. Serum CCL5 concentrations were measured using Sigma Aldrich® CCL5 ELISA kits (MilliporeSigma, St. Louis, MO, USA). The database was analyzed with IBM® SPSS® Statistics version 20 (Chicago, IL, USA). Results: Overall, 46 patients were included, 50% with viral hepatitis and 28.3% with alcohol-related liver disease. HCC was present in 37% of cases. The median CV risk scores (CAD_LT = 7, mCAD_LT = 7, CAR_OLT = 18) placed the population at moderate CV risk. Serum CCL5 levels did not vary significantly between viral vs. non-viral cirrhosis (5511.8 vs. 6272.5 pg/mL, p = 0.15) and were not influenced by the presence of HCC (6098.4 vs. 5771.3 pg/mL, p = 0.55). We did not detect a correlation with MELD score (p = 0.21) or CV risk scores (CAD_LT: p = 0.58; mCAD_LT: p = 0.70; CAR_OLT: p = 0.22). Patients with thrombocytopenia (<100,000/µL, 54.3%) or a history of esophageal variceal ligation had lower CCL5 levels (5170.9 vs. 6750.8 pg/mL, p = 0.002 and 4252.0 vs. 6237.5 pg/mL, p = 0.003, respectively). Similarly, patients with a history of previous variceal bleeding and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) had lower levels of CCL5 (4373.8 vs. 6119.9 pg/mL, p = 0.02 and 3404.3 vs. 6606.7 pg/mL, p = 0.01, respectively). We found a negative correlation between CCL5 and QTc interval duration (τ = −0.216, p = 0.037), left ventricle size (LV: τ = −0.235, p = 0.027), and pulmonary artery pressure (RV/RA gradient: τ = −0.225, p = 0.03). CCL5 correlated positively with the inflammatory markers C-reactive protein (CRP) (τ = 0.246, p = 0.018) and fibrinogen (r = 0.216, p = 0.04). Conclusions: In liver transplant candidates, serum CCL5 is not associated with cardiovascular risk scores or coronary atherosclerotic burden, but is inversely associated with clinical markers of portal hypertension severity. These findings suggest that CCL5 may serve as a potential non-invasive surrogate marker of portal hypertension rather than a cardiovascular risk biomarker in ESLD.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Usefulness of Transanal Irrigation and Colon Hydrotherapy in the Treatment of Chronic Constipation and Beyond: A Review with New Perspectives for Bio-Integrated Medicine
by
Raffaele Borghini, Francesco Borghini, Alessia Spagnuolo, Agnese Borghini and Giovanni Borghini
Gastrointest. Disord. 2026, 8(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord8010006 - 12 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Transanal Irrigation (TAI) and Colon Hydrotherapy (CHT) represent emerging therapeutic options that may complement first-line interventions or serve as rescue treatments for chronic constipation and fecal incontinence. Their clinical utility depends on patient characteristics, specific therapeutic goals, device features, and probe type, as
[...] Read more.
Transanal Irrigation (TAI) and Colon Hydrotherapy (CHT) represent emerging therapeutic options that may complement first-line interventions or serve as rescue treatments for chronic constipation and fecal incontinence. Their clinical utility depends on patient characteristics, specific therapeutic goals, device features, and probe type, as well as the procedural setting. This review presents the various pathophysiological contexts in which these techniques can be applied, analyzing their specific characteristics and potential pros and cons. Moreover, these interventions are also considered within a Psycho-Neuro-Endocrino-Immunological (PNEI) framework, given the potential influence of intestinal function and microbiota modulation on the bidirectional communication pathways linking the enteric nervous system, neuroendocrine regulation, immune activity, and global patient well-being. Since there is not yet enough scientific data on this topic, future research should prioritize randomized controlled trials comparing these techniques with other standard treatments (e.g., laxatives or dietary fiber) in defined patient populations. Longitudinal studies will also be essential to clarify long-term safety, potential effects on microbiota, and both risks and benefits. Standardization of technical procedures also remains a critical need, especially regarding professional competencies, operating parameters (e.g., instilled volumes and pressure ranges), and reproducible protocols. Moreover, future investigations should incorporate objective outcome measures, as colonic transit time, stool form and frequency, indices of inflammation or intestinal wall integrity, and changes to microbiome composition. In conclusion, TAI and CHT have the potential to serve as important interventions for the treatment and prevention of chronic constipation and intestinal dysbiosis, as well as their broader systemic correlates, in the setting of bio-integrated medicine.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Robotic Heller–Dor Myotomy for Esophageal Achalasia in the Elderly: Rationale, Evidence, and Future Directions in Geriatric Minimally Invasive Surgery
by
Agostino Fernicola, Murtaja Satea, Fahim Kanani, Federico Maria Mongardini, Jesus Enrique Guarecuco Castillo, Alfonso Santangelo, Felice Crocetto, Armando Calogero, José Maria Zepeda Torres, Aniello Zoretti, Luigi Ricciardelli, Michele Santangelo and Salvatore Tolone
Gastrointest. Disord. 2026, 8(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord8010005 - 2 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background: Esophageal achalasia increasingly affects elderly patients, in whom frailty and comorbidity complicate management and heighten procedural risk. Minimally invasive Heller–Dor myotomy remains the reference surgical treatment, while the advent of robotics has renewed interest in its potential advantages. Whether these refinements
[...] Read more.
Background: Esophageal achalasia increasingly affects elderly patients, in whom frailty and comorbidity complicate management and heighten procedural risk. Minimally invasive Heller–Dor myotomy remains the reference surgical treatment, while the advent of robotics has renewed interest in its potential advantages. Whether these refinements translate into meaningful benefits for older adults remains unclear. This gap is clinically significant given the distinct physiological vulnerabilities of older adults. Methods: A narrative review of the literature was conducted to examine current evidence on robotic Heller–Dor myotomy for achalasia, with specific focus on its applicability in elderly and frail patients. Comparative studies between robotic and laparoscopic approaches were analyzed and integrated with available data on achalasia management in older individuals. Results: Robotic Heller–Dor myotomy demonstrates equivalent efficacy to laparoscopic surgery, with reduced mucosal perforation rates, improved ergonomics, and comparable operative times once the learning curve is achieved. However, no published series has specifically analyzed outcomes in geriatric cohorts. Available evidence from laparoscopic studies confirms that surgery remains safe and effective in geriatric patients, suggesting that the precision of robotics could potentially further enhance safety and recovery in this subgroup. Conclusions: Robotic Heller–Dor myotomy represents a promising evolution of minimally invasive therapy for achalasia, potentially aligning technological refinements with the physiological needs of older adults. Prospective studies incorporating frailty assessment, patient-centered outcomes, and cost analyses are required to determine its true value and guide evidence-based use in the aging population.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue GastrointestinaI & Bariatric Surgery)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Can Parents Provide Accurate Proxy Reports of Self-Management Skills for Their Child with Inflammatory Bowel Disease?
by
Angharad Vernon-Roberts, Francesca Musto, Marina Aloi, Nerissa Bowcock, Daniel A. Lemberg and Andrew S. Day
Gastrointest. Disord. 2026, 8(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord8010004 - 30 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Children with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are managed with multi-modal treatment strategies, including non-clinical components such as the development of self-management skills. Assessment tools have been developed to quantify such traits, and parents may be asked to provide proxy reports on behalf
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Children with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are managed with multi-modal treatment strategies, including non-clinical components such as the development of self-management skills. Assessment tools have been developed to quantify such traits, and parents may be asked to provide proxy reports on behalf of their child. The aim of this study was for child/parent dyads to complete a self-management skills assessment tool [IBD-STAR] to assess the agreement level between reports. Methods: Children aged ≥10 years with IBD, and one parent/caregiver, were recruited from three tertiary care centers in New Zealand, Australia, and Italy [translated version]. IBD-STAR is scored as completing skills independently [score = 2], with help [score = 1], or not at all [score = 0]. Individual agreement was assessed as a proportion of the maximum agreement on items, category agreement as inter-rater reliability using Gwets AC1 coefficient, and aggregate agreement as a Bland–Altman plot and correlations between child/parent percentage scores. Results: Fifty child/parent dyads participated; child mean age of 14.5 years (±2.4), 31 (62%) female, and 31 (62%) had Crohn’s disease and 19 (38%) ulcerative colitis. At the individual level, the mean proportional agreement was 0.70 (±0.15), equating to complete agreement on ≥12 IBD-STAR items. Category agreement was in the range of 44–94% for items, parents were more likely to underestimate self-management skills, and inter-rater reliability ranged from poor to very good for items, and ‘good’ overall. Aggregate agreement showed high correlation between child/parent % scores (R 0.77, p < 0.001, CI 0.63 to 0.87), and 47 (94%) of the pairs had % scores within two standard deviations of each other. No level of agreement was associated with any independent variable. Conclusions: Parental proxy reports of self-management skills using IBD-STAR had acceptable agreement. The trend towards parental underestimation should be considered when child self-report cannot be assessed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Gastrointestinal Disorders in 2025–2026)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Unrecognized Antiplatelet Effect of Mushroom Coffee: A Case of Postoperative Bleeding Following Colonic Surgery
by
Rayan Alataa, Mohamed Farag, Priscilla Lajara Hallal and Patel Harish
Gastrointest. Disord. 2026, 8(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord8010003 - 29 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Mushroom coffee—blends of coffee with “functional” mushroom powders—has surged in popularity, yet its hemostatic effects are poorly appreciated in perioperative care. We report a postoperative hemorrhage likely potentiated by a commercial mushroom coffee. A 62-year-old man with HIV, hepatitis C, and insulin-treated diabetes
[...] Read more.
Mushroom coffee—blends of coffee with “functional” mushroom powders—has surged in popularity, yet its hemostatic effects are poorly appreciated in perioperative care. We report a postoperative hemorrhage likely potentiated by a commercial mushroom coffee. A 62-year-old man with HIV, hepatitis C, and insulin-treated diabetes underwent colostomy reversal. On postoperative day 9, he developed brisk bleeding at the colonic anastomosis requiring angiography and embolization. Recurrent hemorrhage prompted a detailed supplement history, revealing daily use of mushroom coffee for two months preoperatively. The product’s labeled ingredients include an organic mushroom blend of cordyceps, lion’s mane (Hericium), reishi (Ganoderma), shiitake, turkey tail, and king trumpet, combined with arabica coffee, MCT oil, and coconut milk. Several constituents—reishi, cordyceps, lion’s mane, and chaga (Inonotus obliquus, used in some mushroom blends)—have published antiplatelet or antithrombotic activity in vitro and/or in vivo. After counseling, the patient discontinued mushroom coffee; no further bleeding occurred, and he recovered without additional intervention. This case highlights a clinically important but underrecognized risk: mushroom-based beverages can exert antiplatelet effects comparable to herbal supplements traditionally flagged in preoperative screening. We recommend that preoperative medication reconciliation explicitly query mushroom coffees and “adaptogenic” blends and that such products be held similarly to other agents with antiplatelet properties. Greater awareness among surgeons, anesthesiologists, and internists is needed as functional foods proliferate. Controlled studies are warranted to quantify bleeding risk from multi-mushroom products and to inform evidence-based perioperative guidance
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Role of Calcium Salts in Pigment Gallstones and Their Spiculated Morphology
by
Natale Calomino, Engjell Kelmendi, Gianmario Edoardo Poto, Ludovico Carbone, Matteo Zanchetta and Daniele Marrelli
Gastrointest. Disord. 2026, 8(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord8010002 - 26 Dec 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Pigment gallstones represent a heterogeneous group of concretions, classically divided into black and brown types, whose morphology and microstructure offer critical clues about their underlying pathogenesis. Gallstone formation (lithogenesis) is a complex process triggered when the physicochemical equilibrium of bile is disrupted. Background/Objectives
[...] Read more.
Pigment gallstones represent a heterogeneous group of concretions, classically divided into black and brown types, whose morphology and microstructure offer critical clues about their underlying pathogenesis. Gallstone formation (lithogenesis) is a complex process triggered when the physicochemical equilibrium of bile is disrupted. Background/Objectives: The spicules observed on the surface of certain black pigment gallstones have traditionally been attributed to the branching capacity of cross-linked bilirubin polymers. However, a growing body of experimental and spectroscopic evidence suggests that inorganic calcium salts, particularly calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate, play a central role in the formation of the distinctive spiculated or “coral-like” architecture. Materials and Methods: In our study, we examined a case series of 1350 consecutive patients with gallstone disease, identifying 81 patients who presented with solitary black pigment stones. We systematically explored the association between high calcium content, specifically calcium carbonate, and the occurrence of spiculated morphology. Our analyses demonstrated a robust correlation between an elevated concentration of calcium carbonate and the presence of well-defined spicules. Results: These results support the hypothesis that mineral elements, rather than organic bilirubin polymers, act as crucial determinants of the peculiar crystalline structure observed in a significant subset of pigment stones. Spiculated stones, due to their small size and sharp projections, have a higher likelihood of migrating, increasing the risk of potentially life-threatening complications, such as acute cholangitis and gallstone pancreatitis. Conclusions: Our findings, consistent with recent advanced crystallographic analyses, underscore the importance of considering mineral composition in the diagnosis and management of cholelithiasis. Understanding the factors that drive calcium carbonate precipitation is essential for developing new preventive and therapeutic strategies, aiming to modulate bile chemistry and reduce the risk of calcium-driven lithogenesis.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Exercise-Induced Modulation of the Gut Microbiota: Mechanisms, Evidence, and Implications for Athlete Health
by
Jan Finderle, Valentin Silvano Schleicher, Lou Marie Salome Schleicher, Antea Krsek, Tamara Braut and Lara Baticic
Gastrointest. Disord. 2026, 8(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord8010001 - 24 Dec 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The gut microbiota plays a fundamental role in human physiology by influencing metabolism, immunity, and neuroendocrine communication. Growing evidence suggests that physical exercise modulates gut microbial composition; however, study findings remain inconsistent due to variations in design, training type, and population characteristics. This
[...] Read more.
The gut microbiota plays a fundamental role in human physiology by influencing metabolism, immunity, and neuroendocrine communication. Growing evidence suggests that physical exercise modulates gut microbial composition; however, study findings remain inconsistent due to variations in design, training type, and population characteristics. This review summarizes current research on how different forms, intensities, and frequencies of exercise shape the gut microbiota and discusses their implications for athlete health and performance. Moderate and sustained physical activity generally promotes higher microbial diversity, increases short-chain fatty acid (SCFA)-producing bacteria, and enhances gut barrier integrity. Endurance training, particularly long-term, is most consistently associated with beneficial microbial shifts, including increases in Prevotella, Akkermansia, and Faecalibacterium. In contrast, excessive or high-intensity endurance exercise was shown to cause dysbiosis, inflammation, and greater intestinal permeability. Resistance training appears to induce milder changes but was shown to improve mucin synthesis and butyrate production, especially in older adults. Exercise frequency also plays a role, with regular daily training enriching metabolic pathways linked to gut and systemic health. Overall, the impact of exercise on the gut microbiota depends on the type, intensity, and duration of activity. Balanced, moderate exercise combined with a healthy diet emerges as the most effective strategy to enhance microbial diversity, reduce inflammation, and support overall performance and well-being in athletes.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Celiac Disease: Diagnostic Advances, Differential Challenges, and Interface with Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity
by
Vlad Alexandru Ionescu, Alice Elena Ciontu, Gabriel Ianu Ianuș, Vlad Buica, Ancuța Năstac, Ioana-Alexandra Baban, Alexandru Barbu, Loredana-Crista Tiucă, Ninel Iacobus Antonie, Gina Gheorghe and Camelia Cristina Diaconu
Gastrointest. Disord. 2025, 7(4), 79; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7040079 - 17 Dec 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Celiac disease (CeD) is an immune-mediated enteropathy triggered by gluten in genetically susceptible individuals, with a heterogeneous clinical spectrum spanning classical gastrointestinal symptoms, extraintestinal manifestations, and subclinical forms. We synthesize contemporary epidemiology, immunopathogenesis, and the updated 2025 European Society for the Study of
[...] Read more.
Celiac disease (CeD) is an immune-mediated enteropathy triggered by gluten in genetically susceptible individuals, with a heterogeneous clinical spectrum spanning classical gastrointestinal symptoms, extraintestinal manifestations, and subclinical forms. We synthesize contemporary epidemiology, immunopathogenesis, and the updated 2025 European Society for the Study of Coeliac Disease diagnostic framework. Adaptive responses to deamidated gliadin peptides presented by human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DQ2/DQ8, together with interleukin-15-driven activation of intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs), culminate in villous atrophy, crypt hyperplasia, and increased IELs. Serology centered on tissue transglutaminase immunoglobulin A (tTG-IgA) with total immunoglobulin A assessment remains first-line, complemented by standardized duodenal sampling (≥4 distal + 2 bulb biopsies) and selective HLA typing. The guidelines conditionally endorse a no-biopsy pathway for adults <45 years with tTG-IgA ≥10× upper limit of normal confirmed on a second sample, emphasizing shared decision-making and exclusion of red flags. We delineate differential diagnoses (tropical sprue, Crohn’s disease, common variable immunodeficiency, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth) and contrast CeD with non-celiac gluten sensitivity, which lacks villous atrophy, disease-specific serology, and HLA association. Emerging tools (immunohistochemistry, CD3/CD8/γδ IELs, video capsule endoscopy, confocal laser endomicroscopy) and the limitations of salivary/fecal assays are reviewed. Early detection improves quality of life and reduces healthcare utilization. Future directions include artificial intelligence-assisted imaging, molecular immunophenotyping, and non-dietary therapeutics.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Beyond the Gut: Inflammatory Bowel Disease as a Driver of Cardiovascular and Thromboembolic Risk—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 1.4 Million Patients
by
Aqsa Shoaib, Mariam Shahabi, Reyan Hussain Shaikh, Mian Muinuddin Jamshed, Syed Usama Ashraf, Faryal Jahangir, Faqeeha Arif, Soha Ali, Syed Adeel Hassan, Waqas Rasheed, Tooba Jabeen, Fatima Mansoor, Suhaira Khalid and Abubaker Khan
Gastrointest. Disord. 2025, 7(4), 78; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7040078 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is associated with systemic inflammation and potential cardiovascular complications. This meta-analysis evaluates long-term cardiovascular risks in IBD. Methods: Electronic databases were searched for studies examining cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, and thromboembolic risks in IBD. Adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs)
[...] Read more.
Background: Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is associated with systemic inflammation and potential cardiovascular complications. This meta-analysis evaluates long-term cardiovascular risks in IBD. Methods: Electronic databases were searched for studies examining cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, and thromboembolic risks in IBD. Adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were pooled using a random-effects model. Results: Fifty-three studies comprising 1,406,773 patients were analyzed. IBD was linked to increased risk of ischemic heart disease (aHR 1.25; p = 0.001) myocardial infarction (aHR 1.25; p = 0.01), acute coronary syndrome (aHR 1.43; p < 0.00001), heart failure (aHR 1.24; p < 0.00001), atrial fibrillation (aHR 1.20; p < 0.00001), and stroke (aHR 1.13; p < 0.00001). Elevated risks were also observed for peripheral arterial disease (aHR 1.41; p < 0.00001), diabetes mellitus (aHR 1.40; p < 0.00001), venous thromboembolism (aHR 1.98; p < 0.00001), deep vein thrombosis (aHR 2.85; p = 0.0004), and pulmonary embolism (aHR 1.98; p = 0.03). Importantly, IBD was associated with increased cardiovascular (aHR 1.14; p = 0.03) and all-cause mortality (aHR 1.53; p < 0.00001). Conclusions: IBD patients face higher risk for adverse cardiovascular outcomes, thromboembolic disease, and mortality, necessitating early cardiovascular risk assessment and targeted interventions in this population.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Beyond Digestion: The Gut Microbiota as an Immune–Metabolic Interface in Disease Modulation
by
Imran Mohammad, Md. Rizwan Ansari, Mohammed Sarosh Khan, Md. Nadeem Bari, Mohammad Azhar Kamal and Muhammad Musthafa Poyil
Gastrointest. Disord. 2025, 7(4), 77; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7040077 - 3 Dec 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
The gut microbiota has emerged as a critical immune–metabolic interface, orchestrating a complex network of interactions that extend well beyond digestion. This highly diverse community of bacteria, viruses, archaea, and eukaryotic microbes modulates host immunometabolism, metabolic reprogramming, and systemic inflammatory responses, thereby shaping
[...] Read more.
The gut microbiota has emerged as a critical immune–metabolic interface, orchestrating a complex network of interactions that extend well beyond digestion. This highly diverse community of bacteria, viruses, archaea, and eukaryotic microbes modulates host immunometabolism, metabolic reprogramming, and systemic inflammatory responses, thereby shaping human health and disease trajectories. Dysbiosis, or disruption of microbial homeostasis, has been implicated in inflammatory bowel disease, cardiometabolic disorders, neurodegeneration, dermatological conditions, and tumorigenesis. Through the biosynthesis of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), bile acid derivatives, tryptophan metabolites, and microbial-derived indoles, the gut microbiota regulates epigenetic programming, barrier integrity, and host–microbe cross-talk, thereby influencing disease onset and progression. In oncology, specific microbial taxa and oncomicrobiotics (cancer-modulating microbes) are increasingly recognized as key determinants of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) responsiveness, chemotherapeutic efficacy, and resistance mechanisms. Microbiota-targeted strategies such as fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), precision probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and engineered microbial consortia are being explored to recalibrate microbial networks and enhance therapeutic outcomes. At the systems level, the integration of multi-omics platforms (metagenomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics) combined with network analysis and machine learning-based predictive modeling is advancing personalized medicine by linking microbial signatures to clinical phenotypes. Despite remarkable progress, challenges remain, including the standardization of microbiome therapeutics, longitudinal monitoring of host–microbe interactions, and the establishment of robust ethical and regulatory frameworks for clinical translation. Future directions should prioritize understanding the causal mechanisms of microbial metabolites in immunometabolic regulation, exploring microbial niche engineering, and developing precision microbiome editing technologies (CRISPR, synthetic biology).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Gastrointestinal Disorders in 2025–2026)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Preoperative Injection of Indocyanine Green Fluorescence at the Anorectal Junction Safely Identifies the Inferior Mesenteric Artery in a Prospective Case-Series Analysis of Colorectal Cancer Patients
by
Franco Roviello, Eleonora Andreucci, Ludovico Carbone, Natale Calomino, Stefania Piccioni, Lucia Bobbio, Riccardo Piagnerelli, Andrea Fontani and Daniele Marrelli
Gastrointest. Disord. 2025, 7(4), 76; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7040076 - 28 Nov 2025
Cited by 2
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Indocyanine green (ICG)-guided surgery is an emerging technique to enhance intraoperative visualization of nodes and tumor location. However, there is no uniform protocol regarding the optimal timing, dosage, or injection site for ICG in colorectal cancer surgery. We assess the feasibility
[...] Read more.
Background: Indocyanine green (ICG)-guided surgery is an emerging technique to enhance intraoperative visualization of nodes and tumor location. However, there is no uniform protocol regarding the optimal timing, dosage, or injection site for ICG in colorectal cancer surgery. We assess the feasibility of ICG injection at the anorectal junction immediately before surgery to safely identify the inferior mesenteric artery (IMA). Methods: This was a prospective study involving robotic left hemicolectomy or anterior resection of the rectum for primary colorectal cancer in 2024 in a single center. A total of 10–20 mg was injected into the anorectal submucosa at four quadrants circumferentially using an anoscope immediately before robot docking. Results: In this first study, ICG allowed us to identify the IMA in 84.6% of 26 patients (mean age 66.5 years; BMI 26.7 kg/m2), without intraoperative medical and surgical complications. Elevated BMI correlated with failure of IMA detection (r = −0.77, p < 0.001), despite high ICG doses trending toward improved vascular visualization (p = 0.097). A mean of 22 lymph nodes was harvested after ICG injection, with yields unaffected by the quality of IMA visualization. Conclusions: Submucosal injection of ICG is a feasible and easily adoptable option for early identification of the IMA, thereby preventing major vascular injuries, particularly in patients with challenging anatomy. A standardized protocol was implemented to improve reliability.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Endobiliary Radiofrequency Ablation: Principles, Technique, and Evidence in Cholangiocarcinoma
by
Michele Montori, Daniele Balducci, Francesco Martini, Marco Valvano, Andrea Sorge, Maria Eva Argenziano, Enrico Palmeri, Giuseppe Tarantino, Marco Marzioni, Antonio Benedetti and Luca Maroni
Gastrointest. Disord. 2025, 7(4), 75; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7040075 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
Unresectable extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma remains a challenging malignancy with limited therapeutic options and poor prognosis. In this setting, effective and durable biliary drainage is crucial to prevent cholangitis, allow timely initiation and maintenance of systemic therapy, and ultimately improve survival. Endobiliary radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
[...] Read more.
Unresectable extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma remains a challenging malignancy with limited therapeutic options and poor prognosis. In this setting, effective and durable biliary drainage is crucial to prevent cholangitis, allow timely initiation and maintenance of systemic therapy, and ultimately improve survival. Endobiliary radiofrequency ablation (RFA) has emerged as a promising adjunct to biliary stenting, aimed at delaying tumor ingrowth and prolonging stent patency through localized thermal ablation of malignant tissue. Several studies have reported longer stent patency and, in some cases, improved survival with RFA plus stenting compared with stenting alone. However, the literature remains heterogeneous, and recent high-quality trials have yielded conflicting results, highlighting the need for further standardization of technique and patient selection. This narrative review summarizes the current evidence on the role of endobiliary RFA in unresectable cholangiocarcinoma, with particular emphasis on mechanism of action, endoscopic technique and oncologic outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Gastrointestinal Disorders in 2025–2026)
►▼
Show Figures
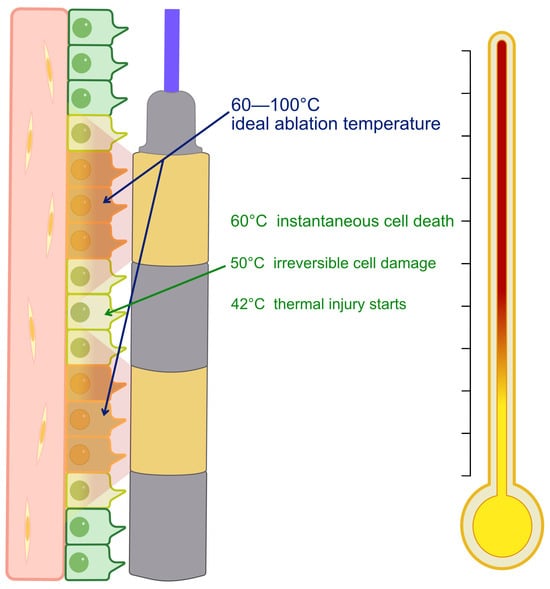
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Paraneoplastic Hypereosinophilia Revealing Disseminated Colorectal Signet Ring Cell Carcinoma
by
Saša Rink, Sabina Škrgat, Matevž Harlander and Polona Mlakar
Gastrointest. Disord. 2025, 7(4), 74; https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7040074 - 24 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Hypereosinophilia, defined as a peripheral blood eosinophil count greater than 1.5 × 109/L, can arise from allergic, infectious, autoimmune, or malignant conditions. In solid tumors, it is rare and most often linked to mucin-secreting carcinomas, while on extremely rare
[...] Read more.
Background: Hypereosinophilia, defined as a peripheral blood eosinophil count greater than 1.5 × 109/L, can arise from allergic, infectious, autoimmune, or malignant conditions. In solid tumors, it is rare and most often linked to mucin-secreting carcinomas, while on extremely rare occasions, it accompanies signet ring cell carcinoma, a highly aggressive form of adenocarcinoma. Case Presentation: A 64-year-old woman presented with dyspnea and hypereosinophilia (2.9 × 109/L). She was admitted with suspected eosinophilic pneumonia, but extensive testing was inconclusive. After bone marrow biopsy, her condition deteriorated; histology revealed metastatic signet ring cell carcinoma. PET/CT showed skeletal metastases without apparent local recurrence, although colonoscopy could not be performed to definitively rule it out. Retrospective review uncovered a 2 mm rectal polyp with signet ring cell carcinoma (SRCC) removed two years earlier. Peripheral eosinophilia progressively increased from 0.16 × 109/L ten months earlier to a peak of 4.29 × 109/L one month prior to admission. She died four weeks after discharge. Conclusions: To the best of our knowledge, this case represents one of the smallest reported primary colorectal SRCC lesions (2 mm) presenting with disseminated disease and paraneoplastic hypereosinophilia as the first diagnostic clue. Monitoring peripheral blood eosinophil counts may provide additional insight into disease activity and prognosis in solid tumors.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Diagnostics, Gastrointestinal Disorders, IJMS, JCM, Nutrients, Medicina, Pharmaceuticals
Advances in Comprehensive Management Strategies for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Topic Editors: Vito Annese, Vincenzo Villanacci, Fabiana Castiglione, Ferdinando D'Amico, Flavio CaprioliDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topic in
Cancers, Diagnostics, Gastrointestinal Disorders, JCM, Current Oncology
Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: From Laboratory to Clinical Studies, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Ioannis Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, Diamantis I. TsilimigrasDeadline: 20 August 2026
Topic in
Cancers, Diagnostics, JCM, Biomedicines, Gastrointestinal Disorders, Current Oncology, Therapeutics
Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Diseases: Novel Strategies of Diagnosis and Treatments—Second Edition
Topic Editors: Alessandro Coppola, Roberta Angelico, Chiara MazzarelliDeadline: 25 November 2026
Topic in
Biomedicines, Current Oncology, Diagnostics, JCM, Livers, Transplantology, Gastrointestinal Disorders
Advances in Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: From Physiological Mechanisms to Clinical Practice, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Davide Giuseppe Ribaldone, Gian Paolo CavigliaDeadline: 20 December 2026

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Gastrointestinal Disorders
The Interactions of Diet, Genes, Gut Microbiota and Immune System in Health and Disease
Guest Editors: Vaios Svolos, Athina A. SamaraDeadline: 20 May 2026
Special Issue in
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Novel Therapies for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Guest Editors: Angharad Vernon-Roberts, Andrew DayDeadline: 25 June 2026
Special Issue in
Gastrointestinal Disorders
GastrointestinaI & Bariatric Surgery
Guest Editors: Rodolfo Oviedo, Aman Goyal, Luigi MaranoDeadline: 25 August 2026
Special Issue in
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Minimally Invasive Surgery for Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Diseases: New Trends and Future Perspectives
Guest Editor: Giuseppe PalombaDeadline: 31 October 2026









