Abstract
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common chronic gastrointestinal disorder that greatly influences patients’ quality of life and represents a growing public health concern. Characterized by typical and atypical symptoms, GERD encompasses a range of clinical phenotypes and is associated with complications such as erosive esophagitis and Barrett’s esophagus. This review intends to provide a thorough overview of current scientific knowledge on the etiological factors, risk determinants, and pathophysiology of GERD, while exploring diagnostic challenges and therapeutic approaches. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) remain the mainstay of medical therapy; however, concerns regarding their long-term safety have encouraged interest in adjunctive and alternative strategies. Emerging pharmacological agents, plant-based treatments, and integrative approaches rooted in traditional medicine offer promising modalities for enhanced management. Additionally, dietary and lifestyle modifications such as weight control, meal timing, and avoidance of trigger foods, are essential components of effective care. A multidisciplinary framework incorporating pharmacological, nutritional, and behavioral strategies is emphasized as the most reliable path toward personalized and sustainable GERD management. This review further aims to synthesize current therapeutic modalities and evolving perspectives in the treatment of GERD.
1. Introduction
1.1. Definition and Prevalence
GERD refers to a chronic gastrointestinal disorder characterized by a recurrent retrograde flow of gastric contents into the esophagus, and sometimes into the oropharynx. Esophageal reflux is normally due to disturbances in gastrointestinal motility and either due to intrinsic functional abnormality or a structural defect that impairs barrier function of the esophagogastric junction (EGJ) [1].
The three main symptoms of GERD that are seen in the clinic are heartburn, regurgitation, and chest pain. Aside from these classical symptoms, patients may report atypical or extra-esophageal symptoms that can include chronic cough, hoarseness, or the sensation of a lump in the throat (the globus sensation) [1,2]. GERD is one of the most common gastrointestinal disorders in the USA, resulting in substantial direct and indirect costs in healthcare and negatively affecting quality of life. The worldwide incidence of GERD symptoms is close to 14.8%, as per recent meta-analyses. There are important differences between countries in the prevalence of GERD. This estimated prevalence ranges from as low as 2.5% in certain Chinese populations to as high as 52.1% in Greece. In Europe and North America, the rates are generally between 10% and 20%. Studies in Asia report a prevalence of about 10%, while those in Central America report about 19.6%. All this indicates one thing: the dietary habits, lifestyle, genetics, and socio-economic conditions affect the expression of the disease [2,3,4].
Several well-established risk factors for GERD have been identified [2,3]. Advancing age is positively associated with GERD prevalence; individuals over the age of 50 report a prevalence of 17.3%, compared to 14.0% in younger populations. Female sex is also linked to a higher confirmed prevalence of GERD. Smoking is a significant risk factor, with current smokers showing a prevalence of 19.6% versus 15.9% among non-smokers. The use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is similarly associated with increased GERD risk. Obesity represents one of the strongest risk factors, with a prevalence of 22.1% among obese individuals compared to 14.2% in those of normal weight. Socioeconomic factors, including lower income and educational attainment, are also correlated with higher GERD prevalence [2].
If left untreated, GERD can progress to serious complications, including erosive esophagitis, esophageal strictures, and Barrett’s esophagus, a recognized precursor to esophageal adenocarcinoma. Diagnosis is primarily based on clinical evaluation, including a detailed history of symptom frequency, duration, and severity. Accurate diagnosis and differentiation from other gastrointestinal disorders are crucial for successful management. Improving patient education, expanding treatment options, and implementing targeted local prevention strategies are critical components in controlling the burden of GERD [2,3,4].
1.2. Etiology and Pathophysiology
GERD is a chronic condition caused by the dysfunction of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which normally serves as a barrier to prevent gastric contents from refluxing into the esophagus. When this muscle valve becomes transiently relaxed, weakened, or structurally compromised, it fails to maintain its barrier function, allowing acid and other gastric materials to contact and damage the esophageal mucosa [1,2,3,4,5].
The primary symptoms of GERD are heartburn and regurgitation, which reflect the direct impact of acid on the esophageal lining. A key physiological mechanism underlying GERD is the occurrence of transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxations (TLESRs). These are spontaneous, short-term relaxations of the LES not associated with swallowing, typically lasting 10 to 35 s. TLESRs facilitate reflux by temporarily equalizing LES and intragastric pressures. They are primarily triggered by gastric distension, activating vagal afferent pathways, and are regulated by multiple factors, including cholecystokinin, nitric oxide, high-fat diets, and mechanical stretch. Conversely, agents such as GABA agonists (e.g., baclofen), loxiglumide, nitric oxide antagonists, morphine, and environmental factors like cold ambient temperatures have been shown to reduce the frequency and duration of TLESRs [5,6,7,8].
Recent research highlights the role of esophageal hypomotility disorders in GERD, particularly when EGJ function is impaired. While LES integrity is critical for reflux prevention, normal esophageal peristalsis is equally important for acid clearance. Disorders such as ineffective esophageal motility (IEM) or nonspecific esophageal motility disorder (NSEMD) are associated with prolonged acid exposure due to delayed clearance. Patients with these motility disorders typically exhibit shorter, weaker LES pressure and altered EGJ morphology. Data from 1006 GERD patients undergoing 24 h pH monitoring indicate that impaired esophageal motility is linked not only to increased reflux frequency but also to longer reflux episodes, more severe mucosal damage, and higher prevalence of complications such as Barrett’s esophagus. These findings underscore the role of EGJ dysfunction and esophageal hypomotility in the pathogenesis and progression of GERD [9,10].
Additionally, ineffective clearance of refluxate, compromised gastroesophageal barrier integrity, and alterations in refluxate composition all contribute to mucosal injury. However, mucosal injury may occur even in the absence of visible erosions, underlining the significance of microscopic changes [1,5,6,7]. Chronic exposure leads to cellular and structural changes in the esophageal mucosa, increasing susceptibility to complications such as erosive esophagitis, strictures, and intestinal metaplasia [5,11]. Another contributing factor is the postprandial gastric acid pocket (PPGAP), a zone of unbuffered acid that accumulates in the proximal stomach after meals. In GERD patients, the PPGAP is typically larger, more acidic, and longer in duration than in healthy individuals. In the presence of a hiatal hernia, the PPGAP may be displaced above the LES, promoting reflux and explaining postprandial symptoms in many patients [12,13].
GERD is a multifactorial disorder influenced by anatomical, physiological, lifestyle, and psychological factors. LES pressure is modulated by numerous hormones and neurotransmitters. Agents such as gastrin, motilin, substance P, and cholinergic agonists increase LES tone, while cholecystokinin, secretin, glucagon, and progesterone decrease it. Several pharmacological agents and substances—including nitrates, calcium channel blockers, theophylline, diazepam, and barbiturates—can also reduce LES pressure, exacerbating reflux [13].
Obesity is a major risk factor for GERD, as increased intra-abdominal pressure promotes reflux. Diets rich in fatty, spicy, or sugary foods stimulate acid secretion and prolong LES relaxation. Smoking diminishes LES tone, while alcohol consumption impairs mucosal defenses. Supine positioning shortly after meals further facilitates reflux due to the loss of gravitational resistance [1,14]. Chronic exposure of the esophagus to acidic gastric contents leads to inflammation (esophagitis) and potential complications such as strictures and Barrett’s esophagus, the latter characterized by intestinal metaplasia of the esophageal lining and increased risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma [15]. Structural abnormalities like hiatal hernias also disrupt the anatomical relationship between the stomach and esophagus, impairing EGJ competence and promoting reflux [14]. Finally, both genetic predisposition and environmental influences contribute to inter-individual variability in GERD susceptibility, symptom expression, and response to treatment, emphasizing the complexity and heterogeneity of this disease [16].
2. Traditional Approach to GERD Treatment
2.1. Overview of Pharmacological Classes
The treatment of GERD primarily targets the reduction of gastric acid secretion and the protection of the esophageal mucosa. The main pharmacological classes include histamine-2 receptor antagonists (H2RAs), PPIs, potassium-competitive acid blockers (P-CABs), and mucosal-protective agents such as sucralfate and alginate. Each class operates through distinct mechanisms. H2RAs inhibit acid secretion by blocking histamine H2 receptors on gastric parietal cells, thereby reducing cyclic AMP-mediated stimulation of the proton pump [17]. PPIs, in contrast, provide more potent and sustained acid suppression by irreversibly inhibiting the H+/K+-ATPase enzyme in parietal cells, the final step in gastric acid secretion [18].
P-CABs represent a newer class of acid-suppressive drugs. They competitively inhibit the potassium-binding site of the H+/K+-ATPase, resulting in rapid and reversible suppression of acid secretion. Compared to PPIs, P-CABs have a faster onset of action, greater pH control, and less inter-individual variability in acid suppression [19].
While these agents primarily target acid suppression, mucosal-protective agents act through different pathways. Although they do not significantly alter gastric acid secretion, they form physical barriers over the mucosa and enhance endogenous defense mechanisms such as mucus and bicarbonate secretion, thereby protecting the esophageal lining from acid-induced injury [20].
2.1.1. PPIs: The Basis of GERD Pharmacotherapy
PPIs are among the most effective pharmacologic agents for reducing gastric acid secretion in the management of GERD. Commonly used PPIs include omeprazole, esomeprazole, and pantoprazole. These agents exert their effect by irreversibly inhibiting the H+/K+-ATPase enzyme (proton pump) located on the luminal surface of gastric parietal cells, which is responsible for the final step of hydrogen ion secretion into the gastric lumen [21]. By forming a covalent bond with the active proton pumps, PPIs prevent hydrogen ion extrusion, effectively raising intragastric pH and maintaining it at elevated levels for extended durations. This potent and prolonged acid suppression facilitates both symptom relief and mucosal healing, making PPIs the mainstay of GERD therapy [18]. The mechanism of PPI action is presented in Figure 1.
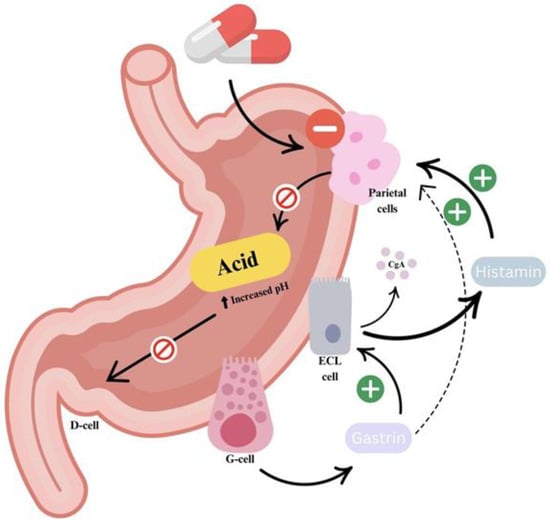
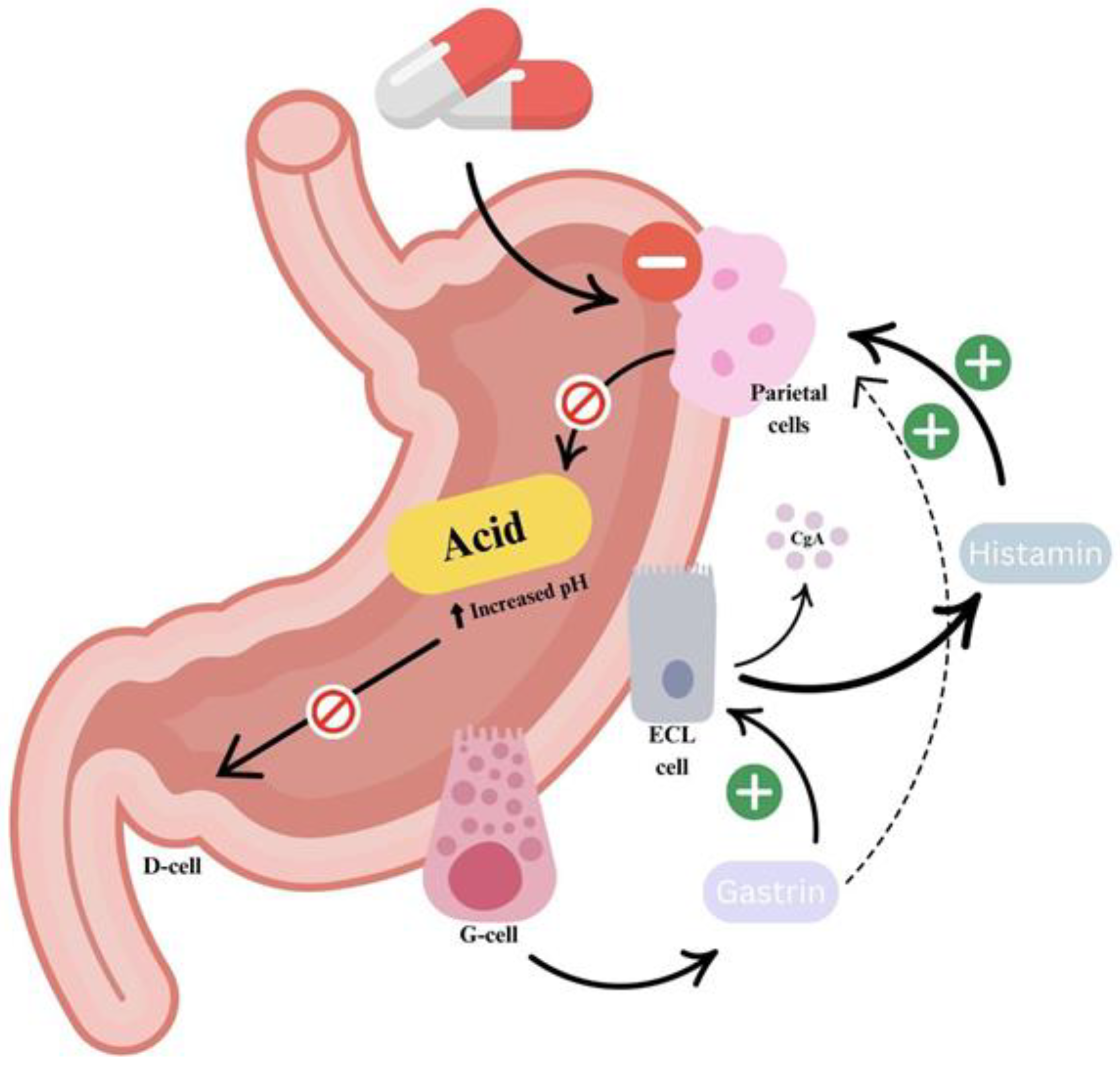
Figure 1.
Mechanism of PPI action. PPIs suppress gastric acid secretion by covalently binding to and irreversibly inhibiting the active H+/K+-ATPase enzymes (proton pumps) in gastric parietal cells. This inhibition leads to a sustained increase in intragastric pH, effectively reducing acid-mediated damage. As gastric acidity decreases, the negative feedback regulation of gastrin secretion, normally mediated by somatostatin, is diminished. This results in elevated serum gastrin levels, which can exert a trophic effect on the gastric mucosa, particularly on enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cells.
PPIs reduce gastric acid secretion by irreversibly inhibiting the H+/K+-ATPase enzyme in gastric parietal cells. This leads to a sustained increase in intragastric pH, which, in turn, reduces somatostatin-mediated inhibition of gastrin release. The resulting hypergastrinemia promotes gastric mucosal proliferation, including enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cell hyperplasia. ECL cells, which are stimulated under acidic conditions, can proliferate in response to elevated gastrin levels. Despite these physiological changes, PPIs remain the cornerstone of GERD treatment due to their strong acid suppression and proven clinical efficacy. Their widespread use as first-line therapy is supported by population-based studies [22]. They are also more potent than other acid-suppressive agents, especially for long-term use.
However, their efficacy and metabolism are influenced by genetic variability, notably in the CYP2C19 enzyme, which metabolizes many PPIs. Individuals who are poor metabolizers (PMs) of CYP2C19 exhibit higher plasma concentrations of PPIs, resulting in stronger acid suppression and prolonged therapeutic effects [23,24,25]. In contrast, ultra-rapid metabolizers (UMs) metabolize PPIs quickly, often resulting in subtherapeutic levels and diminished response. The clinical effect varies by PPI: omeprazole and lansoprazole show greater variability in plasma levels across genotypes (PMs may have 5–12× higher levels than extensive metabolizers) [23]. Esomeprazole, due to reduced metabolism by CYP2C19 and increased involvement of CYP3A4, shows more stable pharmacokinetics [26], whereas rabeprazole is mainly metabolized through non-enzymatic pathways, making it potentially preferable in CYP2C19 variant carriers [27].
Clinical trials have demonstrated that PPIs heal 80–90% of erosive esophagitis within 8 weeks and provide significant symptom relief in the majority of GERD patients [28]. Accordingly, current guidelines recommend PPIs as the first-line treatment for patients with moderate to severe GERD, erosive esophagitis, or complications such as strictures or Barrett’s esophagus. Several meta-analyses indicate that esomeprazole achieves a slightly (but statistically significant) higher erosive-esophagitis healing rate than other PPIs at equivalent doses. The absolute difference is small and practical factors such as cost, availability, and patient preference still commonly guide PPI selection [29,30].
Administration timing is important: PPIs should be taken 30–60 min before breakfast, when proton pump activation is highest. Once-daily dosing controls symptoms in most patients; however, those with refractory or nocturnal symptoms may benefit from twice-daily dosing. Evidence shows that 20 mg of omeprazole taken twice daily maintains intragastric pH >4 for a longer cumulative duration compared to a single 40 mg dose, enhancing acid suppression and mucosal healing in difficult cases [31,32]. Notably, guidelines recommend a maximum of twice-daily dosing, with dosing beyond this threshold suggesting non-responsiveness to standard therapy rather than underdosing [23,24,25,26].
While PPIs are generally safe for short-term use, long-term therapy has been associated with potential adverse outcomes, including Clostridioides difficile infection, community-acquired pneumonia, osteoporotic fractures, chronic kidney disease, and micronutrient deficiencies (e.g., magnesium, calcium, vitamin B12) [33]. However, it is crucial to emphasize that most of these associations are based on observational data, and causation has not been definitively established. Patients on long-term PPI therapy often have other risk factors for these outcomes, and the overall quality of evidence remains low to moderate.
As a result, clinical guidelines now emphasize using the lowest effective dose and periodic reassessment of the indication for continued therapy [34]. After an initial 4–8-week course aimed at healing and symptom control, a step-down approach should be considered in uncomplicated cases. This may involve dose reduction, transition to on-demand or intermittent therapy, or switching to H2RAs [35]. Conversely, patients with Los Angeles (LA) grade C or D esophagitis, peptic strictures, Barrett’s esophagus, or rapid relapse after PPI withdrawal generally require long-term maintenance therapy.
For patients with non-erosive reflux disease (NERD) or mild esophagitis, on-demand PPI use has shown comparable symptom control to continuous daily use while significantly reducing overall drug exposure. Thus, PPIs remain the most effective medical therapy for GERD, but treatment should be personalized to balance maximal symptom relief with minimized risk from unnecessary long-term exposure.
2.1.2. Histamine-2 Receptor Antagonists (H2RAs)
H2RAs—such as famotidine and ranitidine—were once the mainstay of GERD treatment and continue to be useful for managing mild to moderate symptoms. They effectively reduce nocturnal gastric acid production, and many patients experience relief from heartburn by inhibiting histamine-stimulated acid secretion [36]. According to clinical trials, standard doses of H2RAs heal approximately 40% of erosive esophagitis cases over a period of 4–12 weeks, compared to placebo, which shows healing rates of around 18–20%, though this remains significantly lower than the healing rates achieved with PPIs [28]. H2RAs primarily alleviate heartburn symptoms but do not typically result in complete symptom resolution. After several months of therapy, about 50% of patients are free of heartburn, whereas more than 70% of patients using PPIs report complete symptom relief [37]. Increasing the dose of H2RAs can lead to better symptom control and faster mucosal healing; however, dosing more than twice daily provides no additional therapeutic benefit [36].
H2 blockers are often used as part of a step-up approach to GERD management, beginning with antacids or H2RAs and escalating to PPIs as needed. Conversely, they may also play a role in step-down therapy, where patients who achieve symptom control with PPIs are transitioned to H2RAs. Approximately one-third of patients without erosive esophagitis or complications can be successfully maintained on H2RA therapy after initial treatment with a PPI. However, about 40% of these patients experience relapse and require re-initiation of PPI therapy [33,34].
H2RAs may also be added at bedtime to a daytime PPI regimen to address nocturnal acid breakthrough. This combination can transiently improve overnight gastric pH control, but tachyphylaxis to H2 blockers typically develops within a week, meaning that the acid-suppressing effect is significantly reduced with continued nightly use [35,36,37,38,39,40,41].
H2 blockers are generally safe, with adverse effects being rare and usually mild, such as headache, dizziness, or diarrhea. Importantly, they are not strongly associated with serious long-term adverse events, unlike PPIs. The primary limitation of H2RAs is the development of tolerance with continuous use, which leads to diminished efficacy over time [42]. Overall, H2RAs are best suited for on-demand use in patients with intermittent symptoms or for maintenance of remission in those with mild GERD. However, they are not ideal for healing moderate to severe erosive esophagitis.
2.1.3. Potassium-Competitive Acid Blockers (P-CABs)
Potassium-competitive acid blockers (P-CABs) represent a novel class of gastric acid-suppressing agents developed to address the pharmacologic limitations of PPI. This class includes agents such as vonoprazan, tegoprazan, fexuprazan, and others, with vonoprazan being the most extensively studied and widely used. P-CABs act directly and reversibly on the H+/K+-ATPase enzyme (the gastric proton pump), inhibiting it through competitive blockade of potassium ions (K+). Unlike PPIs, they do not require activation in an acidic environment, allowing for rapid onset of action—often within hours of the first dose—and prolonged acid suppression. These pharmacodynamic advantages confer greater dosing flexibility, as administration is independent of meals or circadian timing. P-CABs have demonstrated comparable or superior efficacy to PPIs in treating GERD. Systematic reviews and randomized trials show that vonoprazan 20 mg/d is overall non-inferior to conventional PPIs, while conferring a clear healing advantage in patients with severe erosive esophagitis (LA C/D) [43,44,45,46].
Randomized controlled trials indicate that vonoprazan is non-inferior to lansoprazole for endoscopic healing of erosive reflux disease. They likewise show similar efficacy for 24-week maintenance of remission and comparable overall symptom control. In both studies, healing rates were numerically higher among patients with severe esophagitis (LA grade C/D) [47,48]. One of the key advantages of P-CABs lies in their long-lasting acid suppression regardless of dosing schedule or prandial state. These characteristics make them promising candidates for patients with incomplete symptom control on PPIs or those requiring more rapid symptomatic relief. Regarding safety, available short-term studies suggest a side-effect profile similar to that of PPIs, with no significant differences in adverse event rates. Furthermore, long-term safety data currently available are reassuring, and literature reviews have not identified any new or significant safety concerns associated with P-CABs. For instance, adverse event rates with vonoprazan were found to be comparable to those of PPIs in clinical studies [49]. Nevertheless, as P-CABs gain global regulatory approval, ongoing pharmacovigilance is warranted to detect rare or long-term adverse effects.
Recent evidence also supports the on-demand use of P-CABs in managing episodic GERD symptoms. Their rapid onset of action makes them particularly well suited for such regimens. In a randomized, double-blind trial in GERD patients, on-demand tegoprazan achieved treatment satisfaction comparable to esomeprazole (p = 0.417) and provided significantly faster symptom relief, with 26.2% of episodes resolving within 30 min versus 16.1% with esomeprazole (p < 0.05),while maintaining a favorable safety profile [50].
These findings suggest that P-CABs offer several clinical advantages over PPIs, including more rapid symptom relief, flexibility in dosing, and efficacy in severe disease. Although formal regulatory approval for on-demand use is currently lacking, the accumulating evidence underscores the versatility of P-CABs in GERD management. With ongoing global approvals, such as vonoprazan’s recent authorization for GERD indications in North America, P-CABs are expected to assume an increasingly prominent role in both conventional and innovative GERD treatment strategies.
2.1.4. Mucosal-Protective Agents: Sucralfate and Alginates
In addition to acid-suppressive therapies, there is an alternative approach to GERD management. This approach involves using agents that protect the esophageal mucosa without inhibition of acid secretion. Two of them are sucralfate (aluminum-based polysaccharide complex), and alginate-based formulations (that are often combined with antacids). Sucralfate acts by adhering to inflamed or ulcerated areas of the esophageal mucosa. They form a protective barrier against gastric acid, pepsin, and bile salts that can damage the mucosa. This barrier function facilitates mucosal healing and provides relief from symptoms. Clinical studies have demonstrated that sucralfate is more effective than placebo in healing mild erosive esophagitis in GERD (because of the coating effect in the esophagus) [51]. However, its efficacy in NERD remains unestablished, and the regimen requires frequent dosing (four times daily). This factor limits practicality in routine care.
Given the superior efficacy (and convenience) of PPIs and H2 receptor antagonists (H2RAs), sucralfate is typically reserved for special populations. It is most commonly considered in pregnant women (in whom medication options are limited), or in individuals with refractory esophagitis who do not tolerate PPIs. Sucralfate is not considered a first-line therapy and is generally recommended only as adjunctive treatment or in specific populations (PPI intolerance, pregnant woman) [51,52].
Alginates, derived from brown seaweed polysaccharides, provide a unique mechanism of mucosal protection. When ingested, alginate formulations react with gastric acid to form a viscous, gel-like “raft” that floats on the surface of the gastric contents. This mechanical barrier reduces postprandial reflux by preventing acid from reaching the esophagus (especially after meals). Although alginate-based products do not suppress acid production, they have shown clinical efficacy in reducing reflux symptoms. These positive effects are evidenced in patients with persistent postprandial complaints or regurgitation despite PPI therapy. Several studies have demonstrated that alginate–antacid combinations offer superior symptom control compared to antacids alone [53]. Given their mechanical mode of action, alginates are especially useful as adjuncts to PPI therapy in patients whose symptoms are predominantly due to reflux volume, rather than acid production itself [54].
Mucosal-protective agents such as sucralfate and alginates are associated with a favorable safety profile, primarily due to their minimal systemic absorption. Sucralfate exhibits minimal systemic bioavailability, with constipation—attributable to its aluminum content—being the most frequently reported adverse effect. Alginates are generally well tolerated, although sodium content in some formulations may be a concern for patients on sodium-restricted diets [55].
In summary, mucosal protectants are not recommended as first-line monotherapy for GERD but may play a supportive role in selected clinical scenarios. Sucralfate may be beneficial in specific populations, while alginates are best suited for those with residual regurgitation or postprandial symptoms despite acid suppression. Their role in adjunctive therapy continues to be supported by emerging scientific evidence and clinical experience.
2.2. Therapeutic Strategies and Dosing Approaches
The management of GERD should be individualized and based on the severity and frequency of symptoms. Treatment strategies range from on-demand therapy to continuous high-dose PPI regimens.
For patients with mild or infrequent symptoms, an on-demand approach may be appropriate. In this approach, the patient takes medication only during symptomatic episodes. This strategy is particularly suited for individuals with NERD or those who have achieved mucosal healing after mild erosive esophagitis. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis found that on-demand PPI therapy in such patients provided symptom control comparable to daily continuous therapy over 6–12 months. The review also found no significant differences in adverse outcomes. Also, the on-demand group used approximately 50% fewer doses, translating to reduced treatment costs and lower risk of adverse events [50].
However, on-demand PPI therapy is not suitable for all GERD patients. Those with moderate to severe esophagitis (LA grade C or D), Barrett’s esophagus, or other high-risk features typically require continuous acid suppression. In the aforementioned meta-analysis, patients with LA grade C/D esophagitis had higher relapse and treatment failure rates with on-demand therapy compared to daily regimens. Consequently, clinical guidelines recommend against non-continuous treatment in patients with severe erosive disease, with continuous PPI therapy remaining the preferred option in these cases [51,52].
When initiating therapy, clinicians must also decide between a step-up or step-down strategy. A step-up therapy begins with lifestyle modifications and less potent agents (e.g., antacids or H2 receptor antagonists), reserving PPIs for cases unresponsive to initial treatment. This conservative approach may prevent overtreatment in patients with mild or occasional symptoms. A step-down therapy, in contrast, starts with potent acid suppression (typically a full-dose PPI) to rapidly achieve symptom relief and mucosal healing, followed by a gradual transition to the lowest effective maintenance regimen (e.g., H2RAs or on-demand PPI).
Stepping down from an initial full-dose proton-pump inhibitor (PPI) to the lowest dose that keeps symptoms controlled is now regarded as both good clinical practice and a cost-saving measure. The 2020 Seoul Consensus explicitly endorses this approach, emphasizing that dose tapering lowers drug expenditure without sacrificing efficacy or safety [56]. Supporting data come from a Scandinavian maintenance trial in which patients on healed erosive oesophagitis received either continuous daily esomeprazole 20 mg or the same dose on demand; although sustained remission favored the daily regimen, adverse-event rates did not differ, indicating no safety penalty with less-than-daily use [57]. Similar benefits were seen in a multicentre Japanese study: reducing patients from a standard PPI dose to half-dose-maintained symptom control in roughly 80 % of cases over six months and cut total medication costs by about one-third [58]. Another randomized Japanese trial that guided tapering by symptom status reported comparable control rates and, on follow-up endoscopy, preservation of mucosal healing—outcomes superior to switching directly to an H₂-receptor antagonist [59]. Together, these findings confirm that a structured PPI step-down strategy can sustain clinical remission for most GERD patients while minimizing both drug exposure and costs.
The role of pharmacogenetics, particularly CYP2C19 polymorphisms, is increasingly recognized in tailoring PPI therapy. For instance, rapid metabolizers (RMs) exhibited a symptom recurrence rate of 88.9% following step-down to lansoprazole 15 mg/day, underscoring the potential utility of CYP2C19 genotyping in personalizing long-term GERD management [60].
Comparative efficacy between PPIs also plays a role in treatment selection. A large multicenter trial showed that esomeprazole 20 mg daily maintained remission in 83% of patients over 6 months, significantly outperforming lansoprazole 15 mg, which achieved 74% remission (p < 0.0001). Esomeprazole demonstrated superiority across all LA grades, with the most pronounced benefit observed in higher grades of severity [61]. In patients unresponsive to standard once-daily PPI therapy, a double-dose regimen is often recommended. This typically involves taking the same PPI twice daily—BID (from Latin bis in die, meaning twice a day). For example, taking omeprazole 20 mg BID instead of 40 mg once daily (QD–from Latin quaque die, meaning once a day). This approach is particularly useful in patients with refractory symptoms or extra-esophageal manifestations such as chronic cough or laryngitis. A large meta-analysis demonstrated that taking the same PPI twice daily (BID) heals reflux esophagitis more often and relieves symptoms better after 8 weeks than the conventional once-daily (QD) schedule [62]. Subsequent work showed that the average advantage is modest, but patients who remain only partially controlled on QD therapy can obtain marked additional relief when their dose is split [63]. Two randomized controlled trials provide mechanistic support for this strategy: both found that rabeprazole 10 mg BID (or similar split-dose regimens) achieved higher 24-h acid control and mucosal-healing rates than omeprazole 20 mg QD [64,65,66].
Nevertheless, failure to respond even to high-dose PPI therapy may indicate non–acid-mediated symptoms, warranting further diagnostic evaluation or alternative therapeutic strategies. In all patients on long-term high-dose PPI therapy, clinicians should periodically attempt dose de-escalation to determine the minimum effective maintenance regimen.
2.3. Adverse Effects of Long-Term Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy
PPIs are among the most commonly prescribed medications for the management of acid-related gastrointestinal disorders. While they offer substantial therapeutic benefits, especially in GERD, peptic ulcer disease, and Helicobacter pylori eradication, increasing attention has been given to the potential adverse effects associated with long-term PPI use. Chronic acid suppression by PPIs may impair the absorption of key nutrients, potentially leading to clinically significant deficiencies [66]. Gastric acid is essential for the absorption of calcium, magnesium, and vitamin B12. A reduction in gastric acidity may reduce vitamin B12 absorption, predisposing individuals—particularly the elderly—to megaloblastic anemia, cognitive impairment, peripheral neuropathies, and even neuropsychiatric disturbances [67]. Similarly, calcium malabsorption due to hypoacidity may contribute to osteoporosis and increase fracture risk, especially in patients with poor dietary intake, older adults, or those who are frail [68].
A systematic review and meta-analysis highlighted a significant association between prolonged PPI use and an increased risk of hip, spine, and forearm fractures, particularly among postmenopausal women. The data suggest a synergistic effect of estrogen deficiency and reduced acid-mediated calcium absorption on bone health [69]. Beyond nutrient malabsorption, long-term PPI therapy may compromise the gastrointestinal defence barrier, increasing susceptibility to pathogen overgrowth and infection. Hypochlorhydria may predispose to Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) [70] and small-intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) [66], both of which disturb the gut microbial ecosystem and can lead to chronic gastrointestinal symptoms. Additional observational evidence corroborates the association between chronic PPI exposure and fracture risk [71].
Renal complications have also been reported. Long-term use of PPIs has been associated with acute interstitial nephritis (AIN) and an increased risk of progression to chronic kidney disease (CKD) [71]. Cardiovascular outcomes that are linked to PPI use are not clearly defined. Observational studies have reported an elevated risk of myocardial infarction (MI) (with estimates suggesting a 16–21% increased RR). These findings have not been confirmed in randomized controlled trials, and still remain unproven [72,73]. PPI use has also been associated with the development of benign gastric polyps that may warrant monitoring in certain cases [73].
Long-term acid suppression also alters the gut microbiome. Several studies have demonstrated significant shifts in microbial composition. These include increased abundance of oral and upper gastrointestinal tract microbes, particularly Streptococcaceae. This is a reflection of the loss of gastric acid that serves as a natural microbiological barrier [74]. Recent evidence provides a more nuanced understanding, despite these risks. Risk of hip fractures increases by approximately 20–24% and are dose-dependent [75]. Observational studies suggest that patients who use PPIs and have CDI are more likely to require hospitalization [76]. A large cohort study links chronic PPI use to a 20–50 % higher risk of chronic kidney disease [77]. In contrast, RCT study found that daily pantoprazole did not raise mortality, cardio-renal events, or serious infections versus placebo, suggesting low absolute risk in appropriately selected patients [78].
These associations are statistically significant, but they must be interpreted with caution. Many studies are observational, with potential confounding factors and heterogeneity in patient populations. For most patients, especially those with persistent GERD symptoms or at risk of esophageal complications, the therapeutic benefits of PPIs outweigh the potential risks. Nevertheless, periodic reassessment of long-term PPI therapy is warranted, especially in elderly patients or those with nutritional deficiencies or renal risk factors. A key objective should be to use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary. This will help avoid long-term harms while achieving symptom control and disease prevention.
3. Limitations and Challenges in PPI Therapy
3.1. PPI-Refractory Heartburn Diagnosis: GERD vs. Functional Disorders
Despite their widespread use, PPIs fail to fully control symptoms in approximately 40–45% of patients diagnosed with GERD, a phenomenon commonly termed PPI-refractory GERD [79]. Recent evidence suggests that in a large number of instances, it is not that the acid reflux is refractory, rather that it is misdiagnosed [80]. Research using esophageal pH monitoring or MII-pH has shown that most PPI non-responders have functional heartburn or reflux hypersensitivity, and not ongoing pathologic reflux [79]. Objective testing is critical in confirming the diagnosis of GERD. Proper PPI usage—administering the drug 30–60 min before meals—must first be ensured. In the absence of response, clinicians should broaden the differential diagnosis to include other conditions (eosinophilic esophagitis, delayed gastric emptying, and functional esophageal disorders) [81].
Esophageal hypersensitivity is the most common mechanism underlying PPI non-responsiveness. As such, patients with confirmed esophageal hypersensitivity may benefit more from visceral pain-targeted treatments than PPIs. Those treatments include neuromodulators (e.g., low-dose tricyclic antidepressants or SSRIs) or behavioral interventions [82]. Recent international guidelines emphasize the importance of distinguishing proven GERD from unproven or functional disorders. As per the Lyon Consensus, a standardized approach should be taken when diagnosing GERD. An actionable diagnosis is one where the evidence presented, which is usually pathological acid exposure time (AET > 6%) on 24 h pH monitoring. Other actionable evidence includes endoscopic evidence of LA grade B or higher erosive esophagitis [83,84]. In contrast, patients with normal acid exposure and either LA grade A esophagitis or NERD are unlikely to have true GERD [85].
For unproven GERD, ambulatory reflux monitoring off PPI therapy is recommended to confirm or exclude the diagnosis. Patients with proven GERD and persistent symptoms despite optimized therapy should undergo pH-impedance monitoring on PPIs to assess reflux characteristics and symptom association [86]. This approach reduces misclassification and ensures that the treatment is adequate [87].
The spectrum of reflux-related disorders now includes reflux hypersensitivity (RH). RH is defined as symptoms of heartburn or regurgitation triggered by normal-volume acid reflux or non-acid reflux. RH must also include normal AET and no mucosal damage [88]. It is classified by the Rome IV criteria as a functional esophageal disorder, driven by visceral hypersensitivity rather than acid injury [89]. Given its distinct pathophysiology, PPI therapy is typically ineffective in RH, and the PPI trial is considered unreliable for diagnosis [90]. Management of RH often necessitates alternative strategies, including neuromodulatory medications or behavioral therapies, even when symptoms mimic GERD. The 2020 Seoul Consensus considers RH part of the broader GERD umbrella, acknowledging that EGJ dysfunction can exist even in the absence of pathologic acid exposure [91]. Proper identification of RH, especially in patients with normal pH but positive symptom–reflux correlation, will prevent overtreatment. While antireflux surgery may benefit select RH patients, the condition must be clearly distinguished from acid-mediated GERD. [87].
3.2. Consequences of PPI Overuse
In recent decades, concerns have risen regarding the over-prescription and inappropriate long-term use of PPIs, particularly among patients without clear indications. Multiple studies estimate that 25–70% of PPI prescriptions are potentially inappropriate. The percentage varies depending on the patient population and clinical context [92]. In primary care, chart reviews reveal that up to 60% of patients on chronic PPI therapy lack documentation of GERD or other acid-related disorders. In hospital settings, two-thirds of PPI use may be unjustified, often initiated during inpatient care and continued indefinitely after discharge [93,94].
A major clinical study in 2018 reported that 50% of PPI prescriptions were for off-label or non-evidence-based indications [92]. Inappropriate PPI use increases the risk of adverse effects and adds unnecessary healthcare costs [94]. Current GERD management guidelines emphasize judicious use of PPI therapy, which includes the following: confirming the diagnosis with objective testing (e.g., endoscopy, pH monitoring) to establish “proven GERD” before initiating long-term treatment; using the lowest effective dose for the shortest possible duration; and deprescribing when possible, particularly in non-GERD patients or those with resolved symptoms. Identifying reflux hypersensitivity, functional disorders, and non-acid-related causes of symptoms can significantly reduce PPI overuse. By avoiding unnecessary escalation of acid suppression in these populations, clinicians can redirect care toward more effective, targeted therapies. Overall, adherence to evidence-based recommendations is essential for improving medication stewardship, optimizing patient outcomes, and minimizing unnecessary healthcare burdens associated with chronic PPI therapy.
4. Advances in Understanding Diet and Lifestyle in GERD
4.1. Weight Management and Obesity
Central obesity is a major modifiable risk factor for GERD in overweight individuals. Weight reduction, according to several studies and guidelines, greatly improves the symptoms of GERD in overweight and obese individuals and reduces esophageal acid exposure [28,91]. In a large longitudinal study including 15,295 participants, weight loss of 2 kg/m2 or more demonstrated 2.34 times increased odds of symptom improvement. In the same study, a reduction in the waist circumference ≥5 cm was associated with a significant improvement of symptoms (p < 0.00001) [95]. Abdominal fat (abdominal obesity) raises pressure on the stomach’s entry (EGGJ) and causes reflux of its contents [96]. Fat tissue releases inflammatory substances that can worsen the inflammation of the esophagus [97]. Losing weight reduces intra-abdominal pressure and inflammation throughout the body. Based on this, the recent 2022 American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) guideline strongly recommends that overweight or obese patients with GERD should definitely work on reducing weight mostly by meal planning and exercise [34]. GERD patients should be counseled by physicians to manage their weight as the first line of lifestyle intervention. Furthermore, physicians can set goals for gradual weight loss through dietary modifications and increased physical activity. Even a modest reduction in BMI of 2 kg/m2 or more has been associated with a 32% increase in the odds of symptom improvement (p < 0.05) [95].
4.2. Impact of Meal Timing and Eating Behaviors
The timing and manner of eating play a significant role in the manifestation and severity of GERD symptoms. One of the most consistently supported lifestyle modifications is the avoidance of late-night meals. Clinical guidelines advise patients to refrain from eating for at least 2–3 h before lying down or going to bed, as postprandial recumbency facilitates reflux due to gravitational and physiological factors [90]. Late evening meals are strongly associated with nocturnal reflux, particularly because the supine position taken shortly after eating promotes the retrograde movement of gastric contents. A crossover trial demonstrated that consuming dinner two hours before bedtime resulted in significantly higher nocturnal acid exposure compared to having dinner six hours before sleep, underscoring the importance of pre-bedtime fasting intervals [98]. As such, advising patients to complete their last meal at least three hours before bedtime is a practical and effective strategy to reduce nocturnal heartburn and reflux symptoms [34].
Meal size and eating pace are additional important considerations. Large meals lead to gastric distension, which transiently lowers LES tone, thereby increasing the likelihood of reflux. Patients should therefore avoid heavy, single meals, especially in the evening. Instead, consuming smaller, more frequent meals may not only reduce the frequency of reflux episodes but also help limit overall caloric intake and promote weight control—another key factor in GERD management. Although rapid eating is commonly linked to worsened GERD symptoms in anecdotal reports, objective evidence is mixed. Most studies show no statistically significant difference in reflux frequency between fast and slow eaters [94,95]. An interventional study in obese women showed that rapid ingestion markedly increased post-prandial reflux events [99]. A subsequent trial in patients with established GERD confirmed that eating quickly also heightened acid exposure and symptom severity [100]. Nonetheless, advising patients to eat mindfully, chew thoroughly, and avoid rushing through meals remains a reasonable recommendation, particularly as it may reduce overconsumption and facilitate better satiety cues. GERD patients are encouraged to avoid meals within 3 h of bedtime; eat smaller, more frequent meals rather than large, heavy ones; remain upright for several hours after eating, avoiding immediate recumbency; and eat slowly and stop before feeling completely full. These simple, non-pharmacological interventions form important elements in lifestyle management of GERD and are particularly useful in reducing reliance on long-term pharmacotherapy [34].
4.3. Dietary Triggers and Individualized Food Avoidance
Historically, patients with GERD have been advised to avoid a wide array of so-called “trigger foods”. These include spicy and acidic food, caffeine, chocolate, fatty meals, peppermint, and carbonated beverages. While widely disseminated, these recommendations were largely based on anecdotal reports rather than robust evidence. However, recent studies have demonstrated that the impact of specific foods on GERD symptoms varies significantly among individuals [92,93,94,95,96]. Many patients do not experience symptom exacerbation with all traditionally cited triggers. This suggests that blanket dietary restrictions may be unnecessarily burdensome and, in some cases, ineffective [90,97,98].
Reflecting this evolving understanding, the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2022 guidelines recommend a personalized approach to dietary management [34]. Rather than universally eliminating certain foods, the guidelines advocate for identifying and restricting only those dietary elements that reliably provoke symptoms. This is issued as a conditional recommendation, acknowledging the low quality of available evidence. It emphasizes the importance of tailoring dietary advice to patient-specific experiences and tolerances. This means that food elimination should be guided by patient symptom diaries or structured elimination-rechallenge protocols, allowing clinicians to help patients avoid unnecessary dietary restrictions while still managing symptoms effectively.
4.3.1. High-Fat and Fried Foods
Fatty foods may worsen GERD by slowing gastric emptying and decreasing LES tone. Studies have found there is an association between fat diet and reflux symptoms. While fewer controlled trials have isolated fat, reducing fat in the diet (especially greasy and fried items) is often advised. Patients who eat greasy, fried foods regularly may see improvement in symptoms after carrying out a trial of lower-fat foods. Large greasy meals are especially troublesome if scheduled in the evening because there is an increased probability of developing night-time reflux [101,102].
4.3.2. Coffee and Caffeine
Drinks containing caffeine, such as coffee, tea, and cola, are often believed to aggravate gastroesophageal reflux symptoms due to their potential to reduce lower LES pressure. A meta-analysis of all 15 case–control studies by Kim et al. [103] found no significant overall association between coffee consumption and risk of GERD. Subgroup analyses showed no significant association in studies based on symptom-defined GERD or based on different intake levels or study quality, although a slightly increased risk was observed in studies that used endoscopic diagnosis. Nonetheless, one study did report a slight increase in GERD risk with higher intake of coffee, tea, or soft drinks, especially at four or more cups per day [104]. The difference from study to study indicates that there are individual differences in the response of symptoms and that perhaps higher levels of consumption may cause effects. While current evidence does not support the restriction of caffeine, it may be individualized based on symptom response.
4.3.3. Alcohol
Alcohol consumption has been associated with an increased risk of acid reflux, particularly when intake is frequent and substantial. According to a cumulative meta-analysis of 30 observational studies, alcohol consumers had approximately 1.5-times higher odds of developing GERD than non- or occasional drinkers (p < 0.001). If a person drinks alcohol more than 3–5 times a week, there is almost double the chance of developing acid reflux conditions. Hence, the more a person drinks alcohol, the more likely they develop reflux [105]. Alcohol softens the muscle that blocks stomach acid from reaching the esophagus and can irritate the lining, worsening symptoms. People with GERD should limit or avoid intake of alcohol, as even little alcohol may trigger symptoms in sensitive individuals.
4.3.4. Acidic Foods
Many people cite acidic foods as a trigger for their heartburn. These foods include citrus fruits, such as oranges, grapefruit, and lemons, and tomato-based products. Newer studies are giving mixed results. Some observational studies note that increased daily citrus intake is linked with increased GERD symptoms or erosive disease. This is likely due to reduced LES pressure or delayed gastric emptying [106,107]. Conversely, while some people suffering from GERD may be sensitive to dietary acidity, some studies suggested that acid-sensitive individuals might tolerate citrus fruits [108]. In general, patients often complain that acidic juices (orange juice) and fruits (tomato sauce) provoke their symptoms as they feel burning or regurgitation after taking them [14]. Though these foods do not cause reflux in everyone, the acidity may worsen reflux pain if the esophagus is already irritated. People with GERD may be encouraged to reduce or dilute high-acid foods and beverages. For example, if citrus juice causes symptoms, someone who drinks it frequently may be encouraged to drink less, choose a more diluted version of the same drink or choose an alternative fruit that is not acidic/citrus. It is recommended that citrus and tomato products be avoided during active GERD flare-ups; however, complete elimination is unnecessary if these foods are tolerated in moderate amounts during controlled phases [14].
4.3.5. Spicy Foods
Chili peppers, hot spices, and capsaicin-containing foods can irritate the food pipe or esophagus and stomach lining. Even though spices do not actually relax the LES, they can stimulate mucosal pain receptors that will cause heartburn. Some patients have reflux after spicy food, while others do not [107]. Epidemiology investigations from different groups of people have recorded more cases of GERD due to more frequent and very spicy meals [109]. However, as with other triggers, individual tolerance varies. According to present instructions, it should be based on the patient’s judgment; if spicy foods constantly cause symptoms, then avoidance is a sensible decision. Otherwise, mild-to-moderate spices may be acceptable. When assessing the effects of spicy foods on the upper digestive tract, it may be helpful to distinguish between objective acid reflux and purely sensory throat burning. If the latter, it can be helpful to understand that this is likely a sensory effect. Those with GERD should probably stick to milder seasoning and avoid hot, peppery dishes, especially in the evening.
4.3.6. Chocolate
Older physiological work by Wright and Castell and later by Murphy and Castell established chocolate as a credible reflux-promoting agent. In the manometry study, ingestion of a standardized chocolate drink caused the lower-oesophageal sphincter (LES) pressure to fall by roughly one-third within minutes, and the sphincter remained hypotensive for up to an hour—long enough to facilitate retrograde flow of gastric contents [110]. Other ambulatory pH-monitoring study in symptomatic volunteers confirmed the clinical relevance of that pressure drop. After a chocolate challenge, total oesophageal acid exposure time almost doubled compared with a control meal, and most participants reported heartburn concordant with the acid peaks [111]. Both teams attributed the effect primarily to chocolate’s methylxanthines (theobromine > caffeine), which relax circular smooth muscle. Dark chocolate, being richer in methylxanthines than milk or white varieties, is therefore more likely to provoke symptoms. Translating these findings into practice, current guidance is pragmatic rather than prohibitive. Patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GERD) need not eliminate chocolate entirely, but limiting portion size and avoiding late-evening consumption are sensible first steps. Because individual sensitivity varies, a simple trial—omitting chocolate for a week, then re-introducing a small amount—can clarify personal tolerance. If symptoms improve during abstinence or worsen on re-challenge, flavour substitutes such as vanilla or fruit extracts are reasonable alternatives. These low-effort dietary tweaks, grounded in classic physiologic evidence, remain worthwhile elements of patient-centred GERD management [110,111].
4.3.7. Carbonated Beverages
Carbonated drinks and sodas introduce an excess of gas into the stomach, causing distention and belching. Belching may carry acid up into the esophagus. Carbonated drinks like cola also have caffeine and acid which can make the reflux even worse. In certain groups, studies have found carbonated drinks to be a risk factor for GERD symptoms. For instance, in a Mexican cohort, the consumption of carbonated drinks was associated with increased odds of reflux and esophagitis [106]. Some GERD patients report relief of symptoms when they eliminate carbonated drinks from the diet. It is advisable to avoid or limit carbonated beverages (including sparkling water, if it causes symptoms). Replacing carbonated drinks with water or non-carbonated drinks can minimize unnecessary bloating. Allowing carbonated beverages to become flat prior to consumption may mitigate reflux-related discomfort if such drinks are desired.
4.3.8. Fiber and Carbohydrates
Diets rich in fiber like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains have been linked to reduced risk of reflux [112]. Fiber may be beneficial in GERD as it promotes weight loss and increase gastric motility. Soluble fibers can create a gel-like substance in the stomach, which prevents acid from refluxing back [112]. A small study in NERD found that adopting a high-fiber diet significantly improved their symptom scores [113]. Although fiber did not affect acid pH indexes in the study, it enhanced patient feelings. Hence, a whole-plant fiber-rich therapeutic diet may be helpful for GERD patients as it lessens reflux and prevents the development of GERD. On the other hand, quickly digestible carbs and fermentable carbs (see FODMAP discussion below) may have an effect on reflux through gas production. Weight loss might not be necessary since early data suggest lower-carbohydrate diets improve GERD. In 2024, a systematic review and meta-analysis showed that low-carbohydrate diets reduce esophageal acid exposure time in patients [114].This means that the type and load of carbohydrate can change the reflux mechanism because of decreased gastric pressure or altered gut motility. The aforementioned studies, findings, and advice suggest that patients who have diets very “high” in refined carbs (simple sugars, white bread, etc.) may want to try moderating the intake of such foods as a first step to see if it helps ease symptoms. Choosing complex carbs and whole grains over simple sugars at the very least is a healthy approach that stands to benefit reflux.
4.3.9. FODMAP
Fermentable oligo-, di-, mono-saccharides, and polyols also known as (FODMAPs) are short-chain carbohydrates that are not well absorbed and are fermented by intestinal bacteria. They can lead to gas and bloating. They are well known to exacerbate irritable bowel syndrome. New studies have looked into whether low-fermentation-product diets could help with GERD, in patients with overlapping irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or too much belching. A single physiological study showed that in GERD patients with IBS, a high-FODMAP meal causes an increase in TLESRs [102]. In the study, a meal of wheat (high fructan) caused more reflux episodes and intestinal gas than a meal of rice (low-FODMAP). FODMAP-induced bloating in sensitive subjects can also mechanically cause reflux. In a crossover observational trial with 21 patients suffering from both GERD and IBS, postprandial reflux was significantly reduced by a low-FODMAP diet compared to standard dietary advice [102]. However, FODMAP restriction does not have much evidence for GERD in general. There was a recent open-label trial in PPI-refractory GERD which showed that a low-FODMAP diet did not offer significant benefit to patients over standard reflux diet advice in symptoms or pH measurements after four weeks [115]. Since low-FODMAP diets are restrictive and there is no consistent benefit for pure GERD, we do not recommend this as a matter of course currently. In some cases, low-FODMAP dietary therapy, for example, a GERD patient with significant bloating/IBS symptoms might be considered, but only after standard lifestyle measures have been tried. In short, the low-FODMAP diet is not the first-line management approach for GERD. However, one could try individual high-FODMAP foods, e.g., grains, onions, garlic, which should be noted by the patient in their dietary intake if there is a trigger [97,110].
4.4. Bed Elevation and Sleeping Positions
Patients who experience night-time reflux or reflux-related sleep disturbances may benefit from simply raising the head of the bed. Elevating the head of the bed by approximately 15 to 20 cm, or using a foam wedge, utilizes gravity to help prevent stomach acid from rising into the esophagus. Research has shown that elevating the head of the bed lessens acid exposure while lying on the back [104]. The ACG guidelines even recommend bed head elevation for those who have nocturnal GERD (conditional recommendation) [34]. In fact, using pillows under the head is usually ineffective (as this can kink the neck or be easily kicked off when asleep); instead, it is better to elevate the bed frame at the head or use a wedge under the mattress. People with GERD can also try sleeping on a left lateral decubitus position (left side down) as it decreases night-time reflux whereas right-side position worsens it [111,112]. Further evidence shows that remaining recumbent after a meal and using dedicated positional-therapy wedges can each lessen supine acid exposure and nocturnal symptoms [116,117]. Any patient whose GERD symptoms are worse at night or upon awakening should be counseled to practise head-of-bed elevation of approximately 30° and possibly left-side-sleeping position to reduce reflux.
4.5. Smoking Cessation
Smoking tobacco has a known harmful effect on GERD. Cigarette smoke is composed of nicotine and other things, which reduce the pressure on LES. It also harms salivary production of bicarbonates, which is required for neutralizing the refluxed acid [113,114,118]. Smoking can increase heartburn occurrences and is an independent risk factor for developing GERD [119,120]. By not smoking, reflux symptoms could become much better in time. According to one large cohort study, smokers who quit were much less likely to have frequent GERD symptoms than smokers [120]. Thus, patients with GERD who smoke should be strongly advised to quit smoking, not just to improve their reflux but also numerous other health benefits. Patients who do not have GERD can also benefit from stopping smoking as it may reduce the chance of ever developing reflux disease [121]. Clinicians should provide encouragement, information, and perhaps medication to assist individuals with GERD in quitting smoking.
4.6. Physical Activity
Normal physical activity and exercises have an indirect role in GERD mainly due to weight control and improving both esophageal and gastric motility. The evidence from studies around the world indicate that moderately exercising may lower the risk of GERD [122]. Conversely, sitting all day and high body mass are associated with more reflux. Patients should be encouraged to remain active. Activities like walking, cycling, or swimming can help with digestion and weight goals. However, timing and type of exercise matter. Strenuous exercise or bending at the waist should be avoided for at least 1–2 h postprandially. These activities increase intra-abdominal pressure and may exacerbate reflux. High-intensity exercise or heavy lifting immediately after eating may cause regurgitation. It is suggested to wait at least 1–2 h after eating before intense exercise. However, low-intensity walking in an upright position after meals may enhance gastric emptying, potentially decreasing episodes of reflux. In general, one should exercise daily but should avoid anything that compresses the abdomen after a meal, such as extreme bending, sit-ups, etc.
4.7. Stress and the Gut–Brain Axis
According to the latest research findings, the GBA is a very complex communication system involving the GI tract and the brain. This communication is bidirectional, meaning that gut health and gut microbiota influence mental health and vice versa [123]. In addition, stress levels, which are roughly proportional to mental health status, can also influence gut function and gut microbiota [123]. The gut–brain axis is a term that refers to the highly interconnected and intertwined pathways consisting of neuroendocrine and immune pathways as well as the autonomic nervous pathways that enable signaling from the gut to the brain. The gut microbiota can influence brain function and responses to stress, mood, or emotional well-being. Dysbiosis occurs when there is a malfunction or imbalance of this microbiota. Such dysbiosis may disrupt intestinal function and foster a feedback loop that perpetuates microbial imbalance [123].
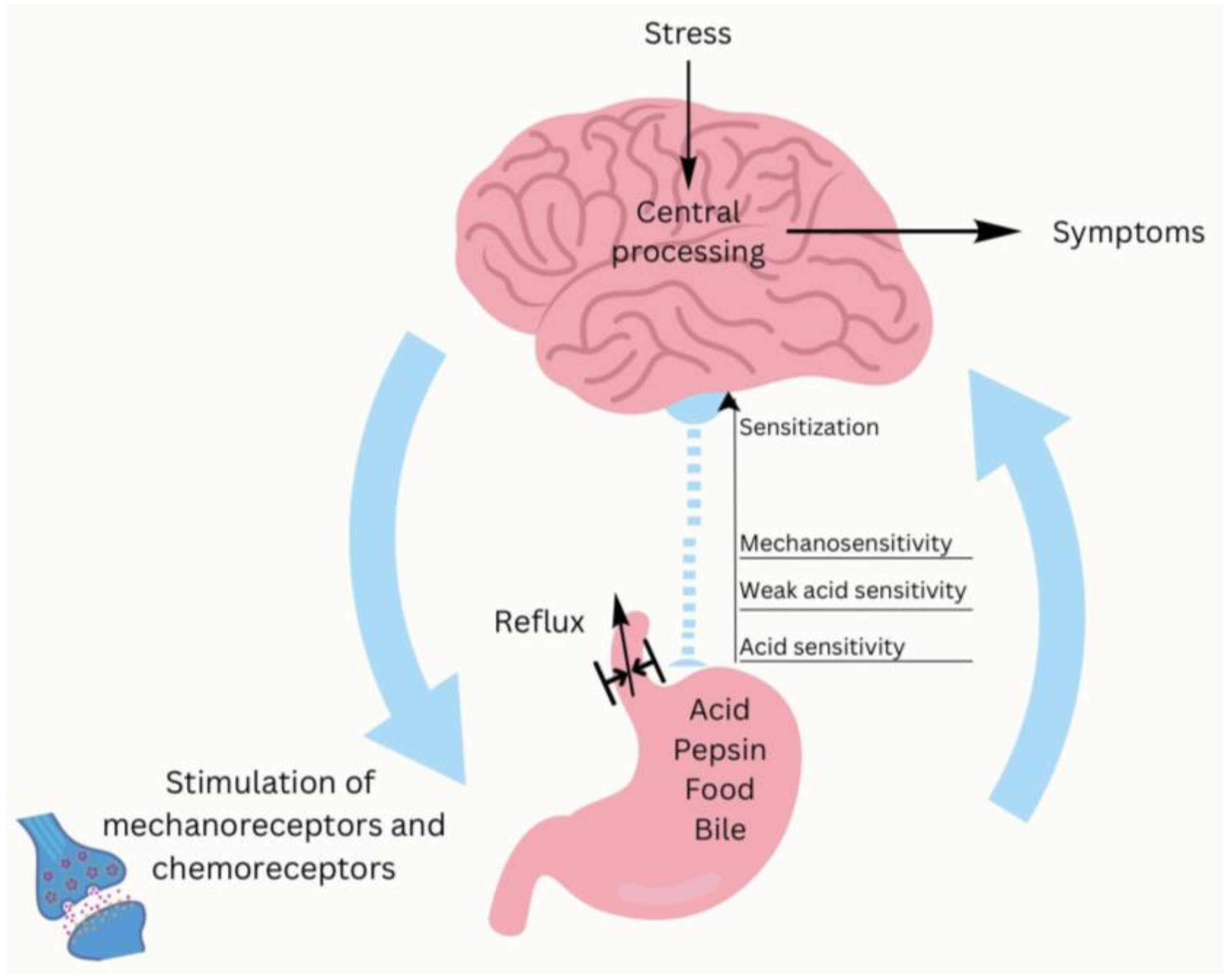
Recent scientific research shows that the gut microbiota has an influence on the stress response. Psychological stress affects how the gut moves and absorbs. The intestinal mucosa becomes more sensitive due to psychological stress. This added sensation can lead to the development of symptoms of GERD such as acid reflux and heartburn [124,125,126]. When people are under psychological stress, the body sometimes produces more stomach acid, which can trigger GERD symptoms, among others. Stress and GERD have been associated, with stress being shown to be both a triggering factor and a causative exacerbator of GERD symptoms (Figure 2).
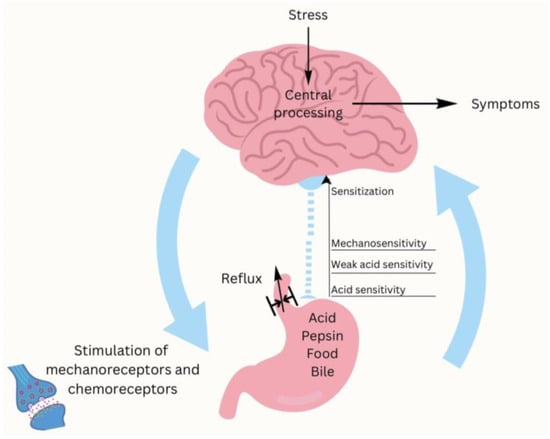
Figure 2.
Impact of stress and the gut–brain axis on GERD.
Specific commensal species produce neurotransmitters like serotonin, which modulate the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis and influence reactivity to stress [127]. On the other hand, dysbiosis is associated with increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and other metabolites. These metabolites affect brain function and increase sensitivity to stress [128,129]. In anxious or depressed patients, the perception of GERD symptoms is usually exacerbated in the general population [130]. A large number of patients report more frequent heartburn and reflux when they are under stress [131].
Psychological and emotional factors, as well as intestinal dysfunction, complicate the healing of GERD. For example, patients with increased anxiety are more aware of GERD symptoms because they are more alert to physical sensations. This, in turn, triggers a spiral of increased anxiety and worse symptoms [132]. GERD treatment can be improved through a better understanding of the gut–brain connection. Probiotics and prebiotics can restore the balance of the gut microbiota, helping to maintain gut function and mental well-being. Most probiotic strains show the potential to combat stress and improve mood CBT, mindfulness exercises and relaxation techniques, and other stress-reduction strategies can help in the psychological domain, which can exacerbate the suffering of people with GERD and alleviate symptoms [128,129,130,131,133,134,135,136]. The relationship between the gut–brain axis and the microbiota and stress contribute significantly to the pathophysiology and management of GERD. Understanding this interaction will aid providers in holistic symptom management to alleviate the physical components of GERD while addressing psychological and possibly microbiota-related issues of this potential disorder. The new method will contribute to a larger, holistic framework of the interaction between the gut, emotions, and body that provides a greater opportunity to improve clinical outcomes for patient health [124].
5. Future Perspectives and Evolving Trends in GERD Research and Recommendations
5.1. Probiotics and Prebiotics
A systematic review by Cheng and Ouwehand [137] explored the effects of probiotics on GERD and associated upper GI symptoms in adults. In total, there were 951 participants across the 13 clinical studies (14 comparisons). According to the results, 79% of the interventions showed beneficial effects, with improvement in reflux-related outcomes (heartburn and regurgitation), and dyspepsia and other upper GI discomforts (nausea, abdominal pain, and gas-related symptoms).
Particular varieties had the strongest effect, including Lactobacillus gasseri LG21 and Bifidobacterium bifidum YIT 10347 which were associated with fewer reflux symptoms and improved gastric motility. For example, L. gasseri LG21 did show gastric acid-reducing action as well as improved gastric emptying action, but B. Bifidum YIT 10347 helped with protection and controlling the immune reaction. The mechanism proposed for probiotic efficacy can involve modulation of gut microbiota, enhancement in efficacy and integrity of epithelial barrier, decrease in gastric acidity and anti-inflammatory effect, and improving GI motility. Even though many studies suggested clinical benefits, there were differences in study design, probiotic strains, dosages, and symptom assessment tools. Only five comparisons were rated as high-quality RCTs. Importantly, the Helicobacter pylori status was not assessed in any of the studies, which could have confounded GERD symptoms. The review noted that none of the trials had standardized protocols so firm conclusions cannot be made nor a meta-analysis performed. Certain strains of probiotics (like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium) may help symptoms and pathways involved in the disease, thus offering supportive benefits for GERD. However, further well-designed, large-scale, placebo-controlled studies with standardized endpoints and adequate sample sizes are essential to validate these findings and to establish optimal therapeutic strategies.
Probiotic strains (notably Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium) do offer benefits for reflux and upper GI symptoms. However, due to variability of designs, strains, outcome measures, and limited quality of RCTs, probiotics and prebiotics could be regarded as adjuncts to conventional GERD therapy.
5.2. Natural Remedies
5.2.1. Ginger
Ginger has a long history of use as a traditional remedy for gastrointestinal upset because of its anti-emetic, carminative and anti-inflammatory properties [138,139]. Evidence derived mainly from dyspepsia trials suggests that ginger can enhance gastric motility; cholinergic neurotransmission appears to underlie much of its pro-kinetic and anti-emetic activity [138]. A recent trial that gave patients 1 080 mg of Zingiber officinale extract daily for four weeks reported significant improvement in upper-gastric symptoms such as post-prandial fullness, early satiety and epigastric pain [140]. Although controlled data in GERD are sparse, systematic reviews of functional-dyspepsia and nausea studies support the use of ginger as an adjunctive therapy for upper-GI symptoms [138,141]. Its principal bioactive compounds—gingerols and shogaols—exert anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects on the gastric mucosa, which may underlie these clinical benefits [138,139].
5.2.2. Aloe Vera
Aloe vera is a useful medicinal plant as it has medicinal properties for gastrointestinal diseases. It contains bioactive anthraquinones, polysaccharides, and flavonoids with putative anti-inflammatory and gastroprotective effects [142].Aloe vera has been employed in traditional pharmacopeias for a long time, for example, in Chinese herbal medicine. Aloe vera showed similar symptom relief to omeprazole and ranitidine in pilot trial, with few reported side effects [143]. The bioactive component of aloe vera consists of anthraquinones (aloin A, aloin B, aloe-emodin), polysaccharides, and flavonoids, which may have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and gastroprotective action [144].
One interesting study on rats indicated that aloe vera, through modulation of the gut–brain axis, decreases secretion of gastric acid and increases water content of the duodenum [145]. Clinical trials show that syrup of aloe vera is effective in alleviating the symptoms of GERD such as heartburn, regurgitation, and nausea. Aloe vera, during a four-week randomized trial, was well tolerated with a significant reduction in GERD symptoms and patient-reported outcomes [146]. Also, it works on other inflammatory bowel illnesses, such as ulcerative colitis, where it reduces disease activity with minimal side effects [147].
5.2.3. Licorice Root
Licorice root is used in traditional medicine for its soothing and protective effects on the GI mucosa [148]. Modern formulations often use deglycyrrhizinated licorice (DGL) to minimize the risk of adverse effects associated with glycyrrhizin, such as hypertension and hypokalemia [149]. Licorice increases mucus production, heals esophagus mucosa, and reduces inflammation by changing prostaglandins and cytokines [148]. One study showed that licorice and its deglycyrrhizinated form (DGL) taken daily for four weeks can ameliorate GERD symptoms and enhance quality of life. Another study found that licorice root (Glycyrrhiza glabra) helps in Amlapitta, which resembles GERD, by relieving symptoms like sour belching, burning sensation in chest, nausea, and indigestion [150]. In addition, a 2-year observational study revealed that a herbal formula containing licorice showed greater symptom relief than conventional antacids in maintaining long-term control over heartburn in a small trial (58 patients) [151]. The findings support the use of licorice as a natural alternative/complement in GERD treatment, ideal for patients wanting milder, mucosa-protective options. Licorice flavonoids regenerate mucus-secreting cells in the stomach and upregulate mucins like MUC5AC and MUC6 in context of gastric ulcers. Preclinical studies have shown that licorice may activate the EGFR/ERK pathway and support gastric mucosal healing. However, its efficacy in esophageal tissue remains to be confirmed in human studies [152]. Licorice flavonoids, by enhancing mucin expression and activating the EGFR/ERK pathway involved in mucosal repair, could also aid in healing esophageal damage caused by GERD, but future clinical validation and research is needed.
5.2.4. Chamomile
Chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla L. and related Anthemis spp.) is one of the world’s most widely consumed medicinal herbs [153]. Infusions prepared from its flower heads exhibit mild antispasmodic, sedative and anti-inflammatory actions that can calm the upper-gastro-intestinal mucosa [153]. To date no randomized controlled trial has tested chamomile as a stand-alone therapy for adult gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GERD); however, an RCT in infant colic and several observational reports indicate symptomatic relief of abdominal discomfort, suggesting a potential benefit in functional dyspepsia and reflux-associated complaints [154]. Key constituents such as apigenin and α-bisabolol confer mucosal protection, inhibit prostaglandin-driven inflammation and accelerate ulcer healing in experimental models [153,155]. Chamomile is also a component of the multi-herbal liquid STW 5 (Iberogast®); pre-clinical studies show that this combination diminishes gastric acid rebound, improves mucosal blood flow and shields against stress-induced gastric injury—mechanisms thought to underlie its clinical utility in functional heartburn and reflux hypersensitivity [156]. Across clinical and laboratory investigations chamomile has demonstrated a very favourable safety profile, making it a reasonable complementary option for patients seeking herbal support alongside standard GERD therapy [153].
5.2.5. Rose Oil Vera (Rosa Damascena)
Essential oils with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties are gaining interest as adjunctive options in the management of acid-related disorders. Among these, Rosa damascena oil has shown particularly promising early evidence. In a randomized, double-blind pilot trial, 100 mg soft-gel capsules of rose oil administered twice daily for six weeks led to significant improvement in heartburn, regurgitation, and GERD-related quality of life scores—comparable to omeprazole 20 mg daily—with no notable adverse effects reported [157]. Mechanistic studies support this clinical potential: extracts of R. damascena have been shown to inhibit NF-κB–mediated inflammation, protect gastric epithelial cells from Helicobacter pylori-induced damage, and demonstrate broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity [158]. Furthermore, a polyherbal formulation containing R. damascena, Glycyrrhiza glabra (liquorice), and Nardostachys jatamansi significantly promoted mucosal healing in an ethanol-induced gastric ulcer model in rats, suggesting synergistic repair effects that could enhance standard GERD therapy [159].
5.2.6. Melatonin
Melatonin, best known as the body’s “sleep hormone,” is also synthesised in large quantities by enterochromaffin cells of the gastrointestinal tract, where it modulates motility, curbs acid output, boosts gastrin and nitric-oxide release, and strengthens mucosal defences against oxidative and inflammatory injury [160]. Early clinical data are encouraging: small pilot RCTs and open-label studies report heartburn, regurgitation, and GERD-HRQL improvements that approach the efficacy of once-daily omeprazole, but the overall evidence base is still limited—a gap highlighted by an ongoing systematic review and meta-analysis protocol [161]. Experimental work in stress-induced gastric and oesophageal injury models shows that exogenous melatonin markedly reduces lesion size and accelerates healing [160,162]. Given its simultaneous benefits for sleep quality and nocturnal acid suppression, melatonin appears a promising, well-tolerated adjunct for patients whose reflux symptoms worsen at night or who have co-existing sleep disturbances; however, larger, high-quality trials are warranted before routine use can be recommended.
5.2.7. Traditional Chinese Herbal Formula
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) formulas used alongside standard Western drugs are emerging as a plausible integrative strategy for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. A registered systematic-review protocol will soon pool all available randomised and quasi-randomised trials to judge whether adding TCM preparations to proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) or other conventional therapies improves healing rates, symptom control and safety [163]. Mechanistic animal work lends biological credibility. In rats sensitised with ovalbumin and then exposed to acid, the classical Heweijiangni-decoction preserved tight-junction architecture, kept mitochondria intact and limited epithelial shedding, thereby protecting the oesophageal mucosa from combined allergen- and acid-induced injury [164]. Another study showed that Zhujie Hewei Granules not only buffered gastric acidity but also modulated gastrointestinal hormones and curtailed inflammatory damage, restoring both structural and functional alterations in reflux oesophagitis models [165]. These pre-clinical findings, together with the forthcoming systematic review of human data, suggest that carefully selected Chinese herbal formulas could complement PPIs—potentially enhancing efficacy and allowing dose reductions—yet high-quality clinical trials are still required before firm recommendations can be made.
6. Holistic Approach to GERD Treatment
An effective and all-encompassing treatment for GERD uses a combination of PPIs, acid suppression, and individualized dietary and lifestyle management. PPIs are important in reducing gastric acid production and promoting intestinal mucosal healing. However, long-term PPI use carries risks of nutrient malabsorption and increased susceptibility to infection. Therefore, modifying the diet by avoiding trigger foods (fatty, spicy or acidic, caffeine, and alcohol) and possibly trying the low-FODMAP diet can have an impact on how severe the symptoms are. Implementing a structured exercise program to maintain a healthy body weight may reduce obesity-related reflux episodes by regulating intra-abdominal pressure. Making small dietary and lifestyle modifications, such as consuming smaller, more frequent meals; avoiding large or heavy meals before bedtime; elevating the head of the bed during sleep; and remaining upright after eating, can reduce postprandial reflux episodes by leveraging gravitational forces to minimize gastric content reflux. Cognitive behavioral therapy and mindfulness-based stress-reduction interventions, together with targeted prebiotic and probiotic supplementation, may modulate the gut–brain axis to decrease the frequency and severity of GERD episodes. Natural remedies may provide additional symptom relief with a potentially lower risk of adverse effects compared to conventional pharmacologic therapies. When used as complementary approaches alongside standard treatments, certain natural agents such as herbal supplements, dietary modifications, and lifestyle interventions may enhance therapeutic outcomes, improve patient adherence, and support long-term management of symptoms. However, their efficacy and safety should be evaluated through clinical studies to ensure evidence-based integration into treatment plans.
7. Conclusions
In summary, PPIs are highly effective in reducing gastric acid secretion and remain the first-line treatment for conditions such as GERD, erosive esophagitis, and peptic ulcer disease. Despite their efficacy, concerns about potential long-term side effects, including impaired absorption of nutrients like magnesium, calcium, and vitamin B12, as well as an increased risk of gastrointestinal infections, highlight the importance of ongoing clinical monitoring and reassessment. Additionally, treatment resistance may occur due to factors such as incorrect diagnosis, suboptimal patient adherence, or individual genetic differences affecting drug metabolism. The frequent overuse of PPIs highlights the need for careful and appropriate prescribing by healthcare providers. A more personalized management approach that emphasizes dietary and lifestyle modifications such as avoiding known trigger foods, optimizing meal timing, maintaining a healthy body weight, and elevating the head during sleep can significantly enhance symptom control. Combining conventional therapies with evidence-based natural remedies may offer complementary benefits while minimizing side effects. Furthermore, incorporating stress reduction techniques and interventions that support gut microbiota balance, including targeted use of prebiotics and probiotics, may strengthen treatment outcomes by addressing the gut–brain axis, a key player in gastrointestinal health. This integrative strategy may provide more comprehensive and sustainable relief for GERD patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.I.B., T.B., A.K., V.S. and L.B.; writing—original draft preparation, J.I.B. and A.K.; writing—review and editing, J.I.B., T.B., A.K., V.S. and L.B.; visualization, A.K.; supervision, T.B., V.S. and L.B.; funding acquisition, L.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This work was written up as part of the scientific project “uniri-iskusni-biomed-23-88-3035: In-fluence of elective primary coronary intervention and coronary artery bypass grafting on the beating heart on endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inflammatory response in patients with is-chemic heart disease” and “uniri-iskusni-biomed-23-100: Nectin-2 and nectin-4 expression in different laryngeal carcinoma stages”. As this is a Review paper, the approval by the Ethics Committee is waived.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to Marko Dolibasic for his hard work and help with the technical editing of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chen, J.; Brady, P. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Gastroenterol. Nurs. 2019, 42, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eusebi, L.H.; Ratnakumaran, R.; Yuan, Y.; Solaymani-Dodaran, M.; Bazzoli, F.; Ford, A.C. Global prevalence of, and risk factors for, gastro-oesophageal reflux symptoms: A meta-analysis. Gut 2018, 67, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, W.M.; Lai, K.C.; Lam, K.F.; Hui, W.M.; Hu, W.H.C.; Lam, C.L.K.; Xia, H.H.X.; Huang, J.Q.; Chan, C.K.; Lam, S.K.; et al. Prevalence, clinical spectrum and health care utilization of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in a Chinese population: A population-based study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 18, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spantideas, N.; Drosou, E.; Bougea, A.; Assimakopoulos, D. Gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms in the Greek general population: Prevalence and risk factors. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2016, 9, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Shang, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, X.; Xin, C.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, R.; Huang, J.; et al. Current Advancement on the Dynamic Mechanism of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 4154–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, R.; Vaezi, M.F. Esophageal Motility Disorders and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1961–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariah, R.A.; Goo, T.; Lee, R.H. Mechanism and Pathophysiology of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 30, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Xu, X.; Yu, L.; Ding, H.; Pan, J.; Yu, Y.; Shi, C.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, M.; Lv, H.; et al. Randomised clinical trial: Gabapentin vs baclofen in the treatment of suspected refractory gastro-oesophageal reflux-induced chronic cough. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, U.; Patti, M.G.; Molena, D.; Fisichella, P.M.; Way, L.W. Esophageal dysmotility and gastroesophageal reflux disease. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2001, 5, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettura, F.; Bronzini, F.; Campigotto, M.; Lambiase, C.; Pancetti, A.; Berti, G.; Marchi, S.; de Bortoli, N.; Zerbib, F.; Savarino, E.; et al. Refractory Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Management Update. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 765061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, S.; Ishimura, N.; Mikami, H.; Okimoto, E.; Tamagawa, Y.; Mishiro, T.; Kinoshita, Y.; Ishihara, S. Evaluations of Gastric Acid Pocket Using Novel Vertical 8-Channel pH Monitoring System and Effects of Acid Secretion Inhibitors. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 27, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFarlane, B. Management of gastroesophageal reflux disease in adults: A pharmacist’s perspective. Integr. Pharm. Res. Pract. 2018, 7, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, M. Gastrointestinal hormones and regulation of gastric emptying. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2019, 26, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidarzadeh-Esfahani, N.; Soleimani, D.; Hajiahmadi, S.; Moradi, S.; Heidarzadeh, N.; Nachvak, S.M. Dietary Intake in Relation to the Risk of Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2021, 26, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.F.; Spechler, S.J. Mechanisms and pathophysiology of Barrett oesophagus. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdiana, Y. Functional Food in Relation to Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD). Nutrients 2023, 15, 3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y. Comparative effectiveness of histamine-2 receptor antagonists as short-term therapy for gastro-esophageal reflux disease: A network meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 54, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, M.M.; Sachs, G. Acid suppression: Optimizing therapy for gastroduodenal ulcer healing, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and stress-related erosive syndrome. Gastroenterology 2000, 118 (Suppl. 1), S9–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K.; Carlsson, E. Potassium-competitive acid blockade: A new therapeutic strategy in acid-related diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 108, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weberg, R.; Berstad, A. Symptomatic effect of a low-dose antacid regimen in reflux oesophagitis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1989, 24, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Clarke, J.O. Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPI). In StatPearls Internet; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al Ghadeer, H.A.; Alabbad, Z.E.; AlShaikh, S.B.; Ahmed, S.U.; Bu-Khamseen, A.A.; Alhashem, A.T. Prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease and associated risk factors in the Eastern Region, Saudi Arabia. Cureus 2021, 13, e19599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Rouby, N.; Lima, J.J.; Johnson, J.A. Proton pump inhibitors: From CYP2C19 pharmacogenetics to precision medicine. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2018, 14, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, F.; Xiong, M.; Jiang, L.; Tang, K.; Fu, M.; Wu, Y.; He, B. Effects of CYP2C19 genetic polymorphisms on the cure rates of H. pylori in patients treated with the proton pump inhibitors: An updated meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 938419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Tan, Q.; Guo, D.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, C.; Guo, W. Patients carrying CYP2C19 loss of function alleles have a reduced response to clopidogrel therapy and a greater risk of in-stent restenosis after endovascular treatment of lower extremity peripheral arterial disease. J. Vasc. Surg. 2014, 60, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaartinen, T.J.K.; Tornio, A.; Tapaninen, T.; Launiainen, T.; Isoherranen, N.; Niemi, M.; Backman, J.T. Effect of High-Dose Esomeprazole on CYP1A2, CYP2C19, and CYP3A4 Activities in Humans: Evidence for Substantial and Long-lasting Inhibition of CYP2C19. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 108, 1254–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, Y.B. Exploring Differences in Pharmacometrics of Rabeprazole between Genders via Population Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Modeling. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weijenborg, P.W.; Cremonini, F.; Smout, A.J.; Bredenoord, A.J. PPI therapy is equally effective in well-defined non-erosive reflux disease and in reflux esophagitis: A meta-analysis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 24, 747–757, e350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gralnek, I.M.; Dulai, G.S.; Fennerty, M.B.; Spiegel, B.M. Esomeprazole versus other proton pump inhibitors in erosive esophagitis: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fass, R. Healing erosive esophagitis with a proton pump inhibitor: The more the merrier? Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 531–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, J.; Schmidt, B. Effect of Splitting the Dose of Esomeprazole on Gastric Acidity and Nocturnal Acid Breakthrough. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 19, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilder-Smith, C.; Röhss, K.; Bokelund Singh, S.; Sagar, M.; Nagy, P. The effects of dose and timing of esomeprazole administration on 24-h, daytime and night-time acid inhibition in healthy volunteers. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 32, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehra, A.K.; Alexander, J.A.; Loftus, C.G.; Nehra, V. Proton Pump Inhibitors: Review of Emerging Concerns. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2018, 93, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, P.O.; Dunbar, K.B.; Schnoll-Sussman, F.H.; Greer, K.B.; Yadlapati, R.; Spechler, S.J. ACG Clinical Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 117, 27–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.W.; Vela, M.F.; Peterson, K.A.; Carlson, D.A. AGA Clinical Practice Update on the Diagnosis and Management of Extraesophageal Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Expert Review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 1414–1421.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fackler, W.K.; Ours, T.M.; Vaezi, M.F.; Richter, J.E. Long-term effect of H2RA therapy on nocturnal gastric acid breakthrough. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabesin, S.M.; Berlin, R.G.; Humphries, T.J.; Bradstreet, D.C.; Walton-Bowen, K.L.; Zaidi, S. Famotidine relieves symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease and heals erosions and ulcerations. Results of a multicenter, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study. Arch. Intern. Med. 1991, 151, 2394–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inadomi, J.M.; Jamal, R.; Murata, G.H.; Hoffman, R.M.; Lavezo, L.A.; Vigil, J.M.; Swanson, K.M.; Sonnenberg, A. Step-down management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology 2001, 121, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tougas, G.; Armstrong, D. Efficacy of H2 receptor antagonists in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease and its symptoms. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 11 (Suppl. B), 51B–54B. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Hussein, M.; Freeman, J.; Castell, D. Concomitant Administration of a Histamine2 Receptor Antagonist and Proton Pump Inhibitor Enhances Gastric Acid Suppression. Pharmacotherapy 2015, 35, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainie, I.; Tutuian, R.; Castell, D.O. Addition of a H2 receptor antagonist to PPI improves acid control and decreases nocturnal acid breakthrough. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2008, 42, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabesin, S.M. Safety Issues Relating to Long-Term Treatment with Histamine H2-Receptor Antagonists. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1993, 7 (Suppl. S2), 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Tan, X.; Dai, Y.; Xie, C.; Li, X.; Lu, Q.; Kou, F.; Jiang, H.; Li, J. Direct Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Vonoprazan Versus Proton-Pump Inhibitors for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, H.; Igarashi, A.; Takeuchi, T.; Teng, L.; Uda, A.; Deguchi, H.; Higuchi, K.; Tango, T. Vonoprazan versus proton-pump inhibitors for healing gastroesophageal reflux disease: A systematic review. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 1316–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhou, X.; Jia, X.; Zhang, M.; Tan, N.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, J.; Xiao, Y. Comparative Efficacy of P-CAB vs Proton Pump Inhibitors for Grade C/D Esophagitis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 119, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, H.; Igarashi, A.; Teng, L.; Uda, A.; Deguchi, H.; Tango, T. Systematic review with network meta-analysis: Indirect comparison of the efficacy of vonoprazan and proton-pump inhibitors for maintenance treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Dai, N.; Fei, G.; Goh, K.L.; Chun, H.J.; Sheu, B.S.; Chong, C.F.; Funao, N.; Zhou, W.; et al. Phase III, randomised, double-blind, multicentre study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of vonoprazan compared with lansoprazole in Asian patients with erosive oesophagitis. Gut 2020, 69, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, T.; Arai, E.; Taki, M.; Kondo, T.; Tomita, T.; Fukui, H.; Watari, J.; Miwa, H. Randomised clinical trial: Vonoprazan versus lansoprazole for the initial relief of heartburn in patients with erosive oesophagitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Bai, Z.; Shang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wong, Y.; Qi, X. Incidence and Type of Adverse Events in Patients Taking Vonoprazan: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2023, 16, 17562848231167858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Moon, H.S.; Sung, J.K.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, K.B.; Lee, S.W.; Cho, Y.S.; Bang, K.B.; Song, K.H. Assessment of the efficacy of on-demand tegoprazan therapy in gastroesophageal reflux disease through a randomized controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Simon, B.; Ravelli, G.P.; Goffin, H. Sucralfate gel versus placebo in patients with non-erosive gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1996, 10, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.A.R.; Hassan, J.; Egan, L.J. Review of Recent Evidence on the Management of Heartburn in Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohof, W.O.; Bennink, R.J.; Smout, A.J.; Thomas, E.; Boeckxstaens, G.E. An alginate-antacid formulation localizes to the acid pocket to reduce acid reflux in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 1585–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savarino, E.; de Bortoli, N.; Zentilin, P.; Martinucci, I.; Bruzzone, L.; Furnari, M.; Marchi, S.; Savarino, V. Alginate controls heartburn in patients with erosive and nonerosive reflux disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 4371–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudaravalli, P.; Patel, P.; John, S. Sucralfate. In StatPearls Internet; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.K.; Tae, C.H.; Song, K.H.; Kang, S.J.; Park, J.K.; Gong, E.J.; Shin, J.E.; Lim, H.C.; Lee, S.K.; Jung, D.H.; et al. 2020 Seoul Consensus on the Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 27, 453–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöstedt, S.; Befrits, R.; Sylvan, A.; Harthon, C.; Jörgensen, L.; Carling, L.; Modin, S.; Stubberöd, A.; Toth, E.; Lind, T. Daily treatment with esomeprazole is superior to that taken on-demand for maintenance of healed erosive oesophagitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 22, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzuki, T.; Okada, H.; Kawahara, Y.; Takenaka, R.; Nasu, J.; Ishioka, H.; Fujiwara, A.; Yoshinaga, F.; Yamamoto, K. Proton pump inhibitor step-down therapy for GERD: A multi-center study in Japan. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mine, S.; Iida, T.; Tabata, T.; Kishikawa, H.; Tanaka, Y. Management of symptoms in step-down therapy of gastroesophageal reflux disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 20, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, T.; Sugimoto, M.; Kodaira, C.; Nishino, M.; Yamade, M.; Ikuma, M.; Shirai, N.; Watanabe, H.; Umemura, K.; Kimura, M.; et al. CYP2C19 genotype is associated with symptomatic recurrence of GERD during maintenance therapy with low-dose lansoprazole. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 65, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritsen, K.; Devière, J.; Bigard, M.A.; Bayerdörffer, E.; Mózsik, G.; Murray, F.; Kristjánsdóttir, S.; Savarino, V.; Vetvik, K.; De Freitas, D.; et al. Esomeprazole 20 mg and lansoprazole 15 mg in maintaining healed reflux oesophagitis: Metropole study results. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 17 (Suppl. 1), 24, discussion 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Hongo, M.; Japan TWICE Study Group. Efficacy of twice-daily rabeprazole for reflux esophagitis patients refractory to standard once-daily administration of PPI: The Japan-based TWICE study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fass, R.; Sontag, S.J.; Traxler, B.; Sostek, M. Treatment of patients with persistent heartburn symptoms: A double-blind, randomized trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delchier, J.C.; Cohen, G.; Humphries, T.J. Rabeprazole, 20 mg once daily or 10 mg twice daily, is equivalent to omeprazole, 20 mg once daily, in the healing of erosive gastrooesophageal reflux disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 35, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galmiche, J.P.; Zerbib, F.; Ducrottè, P.; Fournet, J.; Rampal, P.; Avasthy, N.; Humphries, T.J. Decreasing oesophageal acid exposure in patients with GERD: A comparison of rabeprazole and omeprazole. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 15, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, T.; Roberts, D.N.; Tierney, W.M. Long-term safety concerns with proton pump inhibitors. Am. J. Med. 2009, 122, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Elzen, W.P.; Groeneveld, Y.; de Ruijter, W.; Souverijn, J.H.; le Cessie, S.; Assendelft, W.J.; Gussekloo, J. Long-term use of proton pump inhibitors and vitamin B12 status in elderly individuals. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 27, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X.; Lewis, J.D.; Epstein, S.; Metz, D.C. Long-term proton pump inhibitor therapy and risk of hip fracture. JAMA 2006, 296, 2947–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, T.F.; de Camargo, B.G.; Pereira, M.E.; de Oliveira, C.S.; Guiloski, I.C. Increased Risk of Fractures and Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors in Menopausal Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Chen, C.X.; Wang, M.; Liao, H.R.; Wang, M.X.; Hua, S.Z.; Huang, B.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Xu, Y.L. Updated meta-analysis of controlled observational studies: Proton-pump inhibitors and risk of Clostridium difficile infection. J. Hosp. Infect. 2018, 98, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayyedi, P.; Cranney, A. Hip fracture and proton pump inhibitor therapy: Balancing the evidence for benefit and harm. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 2428–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.H.; LePendu, P.; Bauer-Mehren, A.; Ghebremariam, Y.T.; Iyer, S.V.; Marcus, J.; Nead, K.T.; Cooke, J.P.; Leeper, N.J. Proton Pump Inhibitor Usage and the Risk of Myocardial Infarction in the General Population. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Poly, T.N.; Walther, B.A.; Dubey, N.K.; Anggraini Ningrum, D.N.; Shabbir, S.A.; Jack Li, Y.C. Adverse outcomes of long-term use of proton pump inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 30, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, M.A.; Goodrich, J.K.; Maxan, M.E.; Freedberg, D.E.; Abrams, J.A.; Poole, A.C.; Sutter, J.L.; Welter, D.; Ley, R.E.; Bell, J.T.; et al. Proton pump inhibitors alter the composition of the gut microbiota. Gut 2016, 65, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poly, T.N.; Islam, M.M.; Yang, H.C.; Wu, C.C.; Li, Y.J. Proton pump inhibitors and risk of hip fracture: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Osteoporos. Int. 2019, 30, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tleyjeh, I.M.; Bin Abdulhak, A.A.; Riaz, M.; Alasmari, F.A.; Garbati, M.A.; AlGhamdi, M.; Al-Tannir, M.; Alasmari, A.M.; Alshamrani, M.M.; Baddour, L.M.; et al. Association between proton pump inhibitor therapy and Clostridium difficile infection: A contemporary systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, B.; Chen, Y.; Wilson, F.P.; Sang, Y.; Chang, A.R.; Coresh, J.; Grams, M.E. Proton Pump Inhibitor Use and the Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moayyedi, P.; Eikelboom, J.W.; Bosch, J.; Connolly, S.J.; Dyal, L.; Shestakovska, O.; Leong, D.; Anand, S.S.; Störk, S.; Branch, K.R.H.; et al. Safety of Proton Pump Inhibitors Based on a Large, Multi-Year, Randomized Trial of Patients Receiving Rivaroxaban or Aspirin. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 682–691.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, J.; George, N.; Yamasaki, T.; Ganocy, S.; Fass, R. Most Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Who Failed Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy Also Have Functional Esophageal Disorders. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 1073–1080.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadlapati, R.; DeLay, K. Proton Pump Inhibitor-Refractory Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 103, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Yadlapati, R. Diagnosis and Management of Refractory Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 17, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ostovaneh, M.R.; Saeidi, B.; Hajifathalian, K.; Farrokhi-Khajeh-Pasha, Y.; Fotouhi, A.; Mirbagheri, S.S.; Emami, H.; Barzin, G.; Mirbagheri, S.A. Comparing omeprazole with fluoxetine for treatment of patients with heartburn and normal endoscopy who failed once daily proton pump inhibitors: Double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyawali, C.P.; Yadlapati, R.; Fass, R.; Katzka, D.; Pandolfino, J.; Savarino, E.; Sifrim, D.; Spechler, S.; Zerbib, F.; Fox, M.R.; et al. Updates to the Modern Diagnosis of GERD: Lyon Consensus 2.0. Gut 2024, 73, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visaggi, P.; Del Corso, G.; Gyawali, C.P.; Ghisa, M.; Baiano Svizzero, F.; Stefani Donati, D.; Venturini, A.; Savarino, V.; Penagini, R.; Zeki, S.; et al. Ambulatory pH-Impedance Findings Confirm That Grade B Esophagitis Provides Objective Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 118, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, R.I.; Fox, M.R.; Tucker, E.; Zeki, S.; Dunn, J.M.; Jafari, J.; Warburton, F.; Wong, T. Validation of the Lyon classification for GORD diagnosis: Acid exposure time assessed by prolonged wireless pH monitoring in healthy controls and patients with erosive oesophagitis. Gut 2021, 70, 2230–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyawali, C.P.; Fass, R. Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spechler, S.J.; Hunter, J.G.; Jones, K.M.; Lee, R.; Smith, B.R.; Mashimo, H.; Sanchez, V.M.; Dunbar, K.B.; Pham, T.H.; Murthy, U.K.; et al. Randomized Trial of Medical versus Surgical Treatment for Refractory Heartburn. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarino, E.; Marabotto, E.; Savarino, V. Recent insights on functional heartburn and reflux hypersensitivity. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2022, 38, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, Q.; Fass, R.; Gyawali, C.P.; Miwa, H.; Pandolfino, J.E.; Zerbib, F. Functional Esophageal Disorders. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1368–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzka, D.A.; Pandolfino, J.E.; Kahrilas, P.J. Phenotypes of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Where Rome, Lyon, and Montreal Meet. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyawali, C.P.; Kahrilas, P.J.; Savarino, E.; Zerbib, F.; Mion, F.; Smout, A.J.P.M.; Vaezi, M.; Sifrim, D.; Fox, M.R.; Vela, M.F.; et al. Modern diagnosis of GERD: The Lyon Consensus. Gut 2018, 67, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F. Proton pump inhibitor utilisation and potentially inappropriate prescribing analysis: Insights from a single-centred retrospective study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e040473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidelbaugh, J.J.; Kim, A.H.; Chang, R.; Walker, P.C. Overutilization of Proton-Pump Inhibitors: What the Clinician Needs to Know. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2012, 5, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.Y.; Sun, L.N.; Zhang, X.H.; Li, Y.Q.; Yu, L.; Yuan, Z.Q.; Meng, L.; Zhang, H.W.; Wang, Y.Q. A Review of the Novel Application and Potential Adverse Effects of Proton Pump Inhibitors. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 1070–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.K.; Lee, T.; Yang, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Sohn, C.I.; Ryu, S.; Park, D.I. Weight loss and waist reduction is associated with improvement in gastroesophageal disease reflux symptoms: A longitudinal study of 15,295 subjects undergoing health checkups. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29, e13009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandolfino, J.E.; El-Serag, H.B.; Zhang, Q.; Shah, N.; Ghosh, S.K.; Kahrilas, P.J. Obesity: A challenge to esophagogastric junction integrity. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahima, R.S.; Flier, J.S. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 11, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piesman, M.; Hwang, I.; Maydonovitch, C.; Wong, R.K. Nocturnal reflux episodes following the administration of a standardized meal. Does timing matter? Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 2128–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bor, S.; Erdogan, A.; Bayrakci, B.; Yildirim, E.; Vardar, R. The impact of the speed of food intake on gastroesophageal reflux events in obese female patients. Dis. Esophagus 2017, 30, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valitova, E.R.; Bayrakçı, B.; Bor, S. The effect of the speed of eating on acid reflux and symptoms of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 24, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Satia, J.A.; Rabeneck, L. Dietary intake and the risk of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: A cross sectional study in volunteers. Gut 2005, 54, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaidum, S.; Patcharatrakul, T.; Promjampa, W.; Gonlachanvit, S. The Effect of Fermentable, Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols (FODMAP) Meals on Transient Lower Esophageal Relaxations (TLESR) in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Patients with Overlapping Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). Nutrients 2022, 14, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Oh, S.W.; Myung, S.K.; Kwon, H.; Lee, C.; Yun, J.M.; Lee, H.K.; Korean Meta-analysis (KORMA) Study Group. Association between coffee intake and gastroesophageal reflux disease: A meta-analysis. Dis. Esophagus 2014, 27, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ness-Jensen, E.; Lindam, A.; Lagergren, J.; Hveem, K. Weight loss and reduction in gastroesophageal reflux. A prospective population-based cohort study: The HUNT study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Cen, L.; Chen, W.; Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Shen, Z. Alcohol Consumption and the Risk of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Alcohol Alcohol. 2019, 54, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Colombo, A.; Pacio-Quiterio, M.S.; Jesús-Mejenes, L.Y.; Rodríguez-Aguilar, J.E.; López-Guevara, M.; Montiel-Jarquín, A.J.; López-Alvarenga, J.C.; Morales-Hernández, E.R.; Ortiz-Juárez, V.R.; Ávila-Jiménez, L. Risk factors associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease relapse in primary care patients successfully treated with a proton pump inhibitor. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2017, 82, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, O.; Shahraki, M.; Bahari, A.; Shahraki, T. Dietary habits and obesity indices in patients with gastro-esophageal reflux disease: A comparative cross-sectional study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017, 17, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, A.; Block, G.; Quesenberry, C.P., Jr.; Buffler, P.; Corley, D.A. Dietary guideline adherence for gastroesophageal reflux disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariri, A.M.; Darraj, M.A.; Wassly, A.; Arishi, H.A.; Lughbi, M.; Kariri, A.; Madkhali, A.M.; Ezzi, M.I.; Khawaji, B. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Southwestern Saudi Arabia. Cureus 2020, 12, e6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, L.E.; Castell, D.O. The adverse effect of chocolate on lower esophageal sphincter pressure. Am. J. Dig. Dis. 1975, 20, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.W.; Castell, D.O. Chocolate and heartburn: Evidence of increased esophageal acid exposure after chocolate ingestion. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1988, 83, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- DiSilvestro, R.A.; Verbruggen, M.A.; Offutt, E.J. Anti-heartburn effects of a fenugreek fiber product. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, S.; Isakov, V.; Konovalova, M. Fiber-enriched diet helps to control symptoms and improves esophageal motility in patients with non-erosive gastroesophageal reflux disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 2291–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakananurak, N.; Pitisuttithum, P.; Susantitaphong, P.; Patcharatrakul, T.; Gonlachanvit, S. The Efficacy of Dietary Interventions in Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Intervention Studies. Nutrients 2024, 16, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivière, P.; Vauquelin, B.; Rolland, E.; Melchior, C.; Roman, S.; Bruley des Varannes, S.; Mion, F.; Gourcerol, G.; Sacher-Huvelin, S.; Zerbib, F. Low FODMAPs diet or usual dietary advice for the treatment of refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease: An open-labeled randomized trial. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 33, e14181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, L.C.; Just, R.; Castell, D.O. Body position affects recumbent postprandial reflux. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 1994, 18, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allampati, S.; Lopez, R.; Thota, P.N.; Ray, M.; Birgisson, S.; Gabbard, S.L. Use of a positional therapy device significantly improves nocturnal gastroesophageal reflux symptoms. Dis. Esophagus 2017, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennish, G.W.; Castell, D.O. Inhibitory effect of smoking on the lower esophageal sphincter. N. Engl. J. Med. 1971, 284, 1136–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahrilas, P.J.; Gupta, R.R. The effect of cigarette smoking on salivation and esophageal acid clearance. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1989, 114, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ness-Jensen, E.; Lindam, A.; Lagergren, J.; Hveem, K. Tobacco smoking cessation and improved gastroesophageal reflux: A prospective population-based cohort study: The HUNT study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ness-Jensen, E.; Hveem, K.; El-Serag, H.; Lagergren, J. Lifestyle Intervention in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 175–182.e1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, M.; Johnsen, R.; Ye, W.; Hveem, K.; Lagergren, J. Lifestyle related risk factors in the aetiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux. Gut 2004, 53, 1730–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, A.; Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K. Stress, depression, diet, and the gut microbiota: Human-bacteria interactions at the core of psychoneuroimmunology and nutrition. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2019, 28, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, M.; Nishida, K.; Kataoka-Kato, A.; Gondo, Y.; Ishikawa, H.; Suda, K.; Kawai, M.; Hoshi, R.; Watanabe, O.; Igarashi, T.; et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota relieves stress-associated symptoms by modulating the gut-brain interaction in human and animal models. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 28, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krsek, A.; Baticic, L. Neutrophils in the Focus: Impact on Neuroimmune Dynamics and the Gut–Brain Axis. Gastrointest. Disord. 2024, 6, 557–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Guan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Li, W.; Guo, S.; Zhang, A. The communication mechanism of the gut-brain axis and its effect on central nervous system diseases: A systematic review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyte, J.M.; Gheorghe, C.E.; Goodson, M.S.; Kelley-Loughnane, N.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Clarke, G. Gut-brain axis serotonergic responses to acute stress exposure are microbiome-dependent. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e13881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafavi Abdolmaleky, H.; Zhou, J.R. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Epigenetic Alterations in Metabolic Diseases. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.; Song, X.; Qian, Y.; Liao, Z.; Sui, L.; Ai, L.; Xia, Y. Understanding the Connection between Gut Homeostasis and Psychological Stress. J. Nutr. 2023, 153, 924–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungin, A.P.; Yadlapati, R.; Anastasiou, F.; Bredenoord, A.J.; El Serag, H.; Fracasso, P.; Mendive, J.M.; Savarino, E.V.; Sifrim, D.; Udrescu, M.; et al. Management advice for patients with reflux-like symptoms: An evidence-based consensus. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 36, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, N.; Devanarayana, N.M. Unveiling the intricacies: Insight into gastroesophageal reflux disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2025, 31, 98479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Duan, H.; Wang, Q.; Dong, P.; Zhou, X.; Sun, K.; Tang, F.; Wang, X.; Lin, L.; Long, Y.; et al. Analyzing the correlation between gastroesophageal reflux disease and anxiety and depression based on ordered logistic regression. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X. Probiotics Regulate Gut Microbiota: An Effective Method to Improve Immunity. Molecules 2021, 26, 6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandran, S.; Raman, R.; Kishor, M.; Nandeesh, H.P. The effectiveness of mindfulness meditation in relief of symptoms of depression and quality of life in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 38, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Jin, H.; Kwok, L.Y.; Sun, Z.; Liong, M.T.; Zhang, H. Probiotic consumption relieved human stress and anxiety symptoms possibly via modulating the neuroactive potential of the gut microbiota. Neurobiol. Stress 2021, 14, 100294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald-Haile, J.; Bradley, L.A.; Bailey, M.A.; Schan, C.A.; Richter, J.E. Relaxation training reduces symptom reports and acid exposure in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology 1994, 107, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Ouwehand, A.C. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Probiotics: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkhah Bodagh, M.; Maleki, I.; Hekmatdoost, A. Ginger in gastrointestinal disorders: A systematic review of clinical trials. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 7, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Anh, N.H.; Kim, S.J.; Long, N.P.; Min, J.E.; Yoon, Y.C.; Lee, E.G.; Kim, M.; Kim, T.J.; Yang, Y.Y.; Son, E.Y.; et al. Ginger on Human Health: A Comprehensive Systematic Review of 109 Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2020, 12, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aregawi, L.G.; Shokrolahi, M.; Gebremeskel, T.G.; Zoltan, C. The Effect of Ginger Supplementation on the Improvement of Dyspeptic Symptoms in Patients With Functional Dyspepsia. Cureus 2023, 15, e46061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palatty, P.L.; Haniadka, R.; Valder, B.; Arora, R.; Baliga, M.S. Ginger in the prevention of nausea and vomiting: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, A.K.; Gupta, A.; Bishayee, A.; Pandey, A.K. Therapeutic potential of Aloe vera-A miracle gift of nature. Phytomedicine 2019, 60, 152996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, A.; Ceramella, J.; Iacopetta, D.; Marra, M.; Conforti, F.; Lupi, F.R.; Gabriele, D.; Borges, F.; Sinicropi, M.S. Aloe vera—An Extensive Review Focused on Recent Studies. Foods 2024, 13, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yu, M.; Kong, X.Y.; Chen, T.T.; Zou, Z.M. In vivo metabolism combined network pharmacology to identify anti-constipation constituents in Aloe barbadensis Mill. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319 Pt 1, 117200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarzi, Z.; Rezapour, T.M.; Vatanchian, M.; Zare Hesari, M.; Nabizade Haghighi, H.; Izanlu, M.; Sabaghian, M.; Shahveisi, K. The effects of aqueous extract of Aloe vera leaves on the gastric acid secretion and brain and intestinal water content following acetic acid-induced gastric ulcer in male rats. Avicenna J. Phytomedicine 2014, 4, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Panahi, Y.; Khedmat, H.; Valizadegan, G.; Mohtashami, R.; Sahebkar, A. Efficacy and safety of Aloe vera syrup for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease: A pilot randomized positive-controlled trial. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2015, 35, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, L.; Feakins, R.M.; Goldthorpe, S.; Holt, H.; Tsironi, E.; De Silva, A.; Jewell, D.P.; Rampton, D.S. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of oral aloe vera gel for active ulcerative colitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 19, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorino, G.; Cornara, L.; Soares, S.; Rodrigues, F.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Liquorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra): A phytochemical and pharmacological review. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2323–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedegaard, S.B.; Svart, M.V. Licorice induced pseudohyperaldosteronism, severe hypertension, and long QT. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2019, 2019, 19-0109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, S.M.; Patel, B.R. A comparative clinical study of Jethimala (Taverniera nummularia Baker.) and Yashtimadhu (Glycyrrhiza glabra Linn.) in the management of Amlapitta. Ayurveda 2015, 36, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, A.M.; Golianu, B. Integrative Treatment of Reflux and Functional Dyspepsia in Children. Children 2014, 1, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Huang, T.; Huang, D.; Liu, L.; Shen, C.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Liang, P.; et al. Licorice flavonoid alleviates gastric ulcers by producing changes in gut microbiota and promoting mucus cell regeneration. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 169, 115868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, J.K.; Shankar, E.; Gupta, S. Chamomile: A herbal medicine of the past with bright future. Mol. Med. Rep. 2010, 3, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crotteau, C.A.; Wright, S.T.; Eglash, A. Clinical inquiries. What is the best treatment for infants with colic? J. Fam. Pract. 2006, 55, 634–636. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baser, K.H.; Demirci, B.; Iscan, G.; Hashimoto, T.; Demirci, F.; Noma, Y.; Asakawa, Y. The essential oil constituents and antimicrobial activity of Anthemis aciphylla BOISS. var. discoidea BOISS. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayyal, M.T.; Seif-El-Nasr, M.; El-Ghazaly, M.A.; Okpanyi, S.N.; Kelber, O.; Weiser, D. Mechanisms involved in the gastro-protective effect of STW 5 (Iberogast) and its components against ulcers and rebound acidity. Phytomedicine 2006, 13 (Suppl. 5), 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel Mehraban, M.S.; Shirzad, M.; Ahmadian-Attari, M.M.; Shakeri, R.; Taghizadeh Kashani, L.M.; Tabarrai, M.; Shirbeigi, L. Effect of rose oil on Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in comparison with omeprazole: A double-blind controlled trial. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2021, 43, 101361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, S.F.; Muhammad, J.S.; Shahryar, S.; Usmanghani, K.; Gilani, A.H.; Jafri, W.; Sugiyama, T. Anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective effects of selected Pakistani medicinal plants in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 141, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memariani, Z.; Hajimahmoodi, M.; Minaee, B.; Khodagholi, F.; Yans, A.; Rahimi, R.; Amin, G.; Moghaddam, G.; Toliyat, T.; Sharifzadeh, M. Protective Effect of a Polyherbal Traditional Formula Consisting of Rosa damascena Mill., Glycyrrhiza glabra L. And Nardostachys jatamansi DC., Against Ethanol-induced Gastric Ulcer. Iran J. Pharm. Res. 2017, 16, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Konturek, S.J.; Konturek, P.C.; Brzozowski, T. Melatonin in gastroprotection against stress-induced acute gastric lesions and in healing of chronic gastric ulcers. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2006, 57 (Suppl. 5), 51–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jha, L.K.; Fass, R.; Gadam, R.; Maradey-Romero, C.; Nasrollah, L.; Hershcovici, T.; Quan, S.F.; Dickman, R. The Effect of Ramelteon on Heartburn Symptoms of Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Chronic Insomnia: A Pilot Study. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 50, e19–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konturek, S.J.; Zayachkivska, O.; Havryluk, X.O.; Brzozowski, T.; Sliwowski, Z.; Pawlik, M.; Konturek, P.C.; Cześnikiewicz-Guzik, M.; Gzhegotsky, M.R.; Pawlik, W.W. Protective influence of melatonin against acute esophageal lesions involves prostaglandins, nitric oxide and sensory nerves. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2007, 58, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Huang, G.; Liu, X.; Lin, H.; Zhou, H.; Feng, C.; Wang, T.; Liang, R. Efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese herbal formula combined with western medicine for gastroesophageal reflux disease: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e22454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, B.Y.; Xie, C.E.; Wang, Z.B.; Pei, W.J.; Li, X.H.; Shi, L.; Liu, J.L.; Han, Y.F.; Tan, X.; Ding, P.H.; et al. The effect of Heweijiangni-decoction on esophageal morphology in a rat model of OVA-induced visceral hypersensitivity followed by acid exposure. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2019, 65, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Hu, J.L.; Zhao, C.C.; Zhang, J.Q.; Wu, F.; Ma, B.L.; Feng, Y.; Ruan, K.F. Zhujie Hewei Granules Ameliorated Reflux Esophagitis in Rats. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 1392020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).