Bicarbonate Natural Mineral Water from Source “F2 Păltiniș” Facilitates Digestion—A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patients
2.2. RDQ
2.3. Subjective Assessment of Post-Prandial Fullness and the Digestion and Use of Antacids
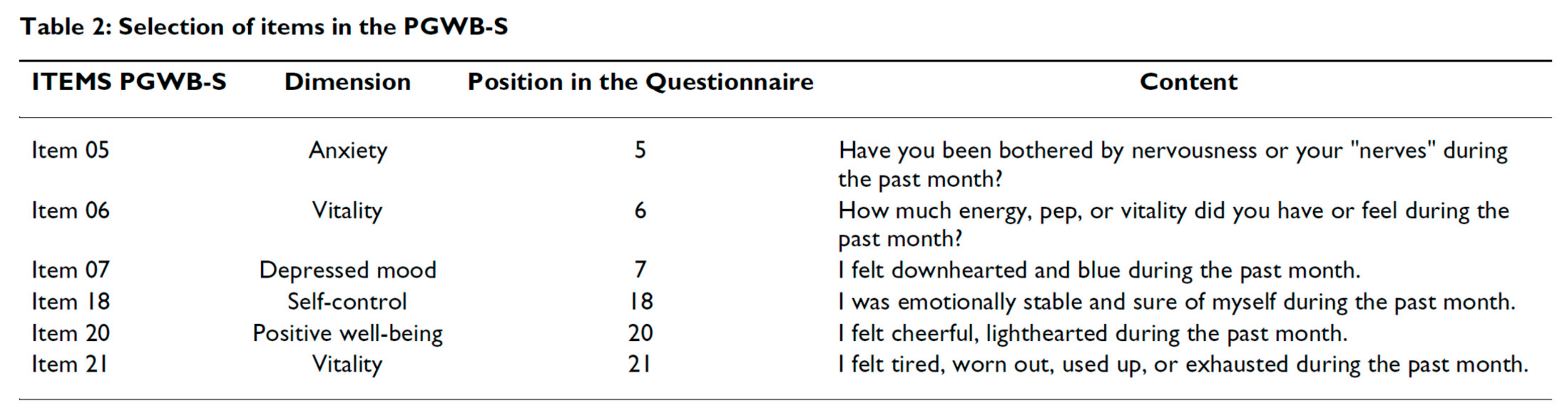
2.4. HRQoL (PGWB-S Questionnaire)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Inclusion Criteria
4.2. Exclusion Criteria
4.3. Study Design
4.4. Reflux Disease Questionnaire (RDQ)
4.5. Psychological General Well-Being Index—Short Form (PGWB-S)
4.6. Other Investigations
4.7. Endpoints
4.8. Statistical Methods
4.8.1. Sample-Size Calculation
4.8.2. Statistical Analysis
4.9. Ethics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Ford, A.C.; Marwaha, A.; Sood, R.; Moayyedi, P. Global prevalence of, and risk factors for, uninvestigated dyspepsia: A meta-analysis. Gut 2015, 64, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanghellini, V.; Chan, F.K.L.; Hasler, W.L.; Malagelada, J.R.; Suzuki, H.; Tack, J.; Talley, N.J. Gastroduodenal disorders. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshima, T. Functional dyspepsia: Current understanding and future perspective. Digestion 2024, 105, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eusebi, L.H.; Ratnakumaran, R.; Bazzoli, F.; Ford, A.C. Prevalence of dyspepsia in individuals with gastroesophageal reflux-type symptoms in the community: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 39–48.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syam, A.F.; Miftahussurur, M.; Makmun, D.; Abdullah, M.; Rani, A.A.; Siregar, G.A.; Simadibrata, M.; Zubir, N.; Wibawa, I.D.N.; Purnomo, H.D.; et al. Management of dyspepsia and Helicobacter pylori infection: The 2022 Indonesian Consensus Report. Gut Pathog. 2023, 15, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaji, M.; Fujiwara, Y.; Shiba, M.; Kohata, Y.; Yamagami, H.; Tanigawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Watanabe, T.; Tominaga, K.; Arakawa, T. Prevalence of overlaps between GERD, FD and IBS and impact on health-related quality of life. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 25, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aro, P.; Talley, N.J.; Agréus, L.; Johansson, S.-E.; Bolling-Sternevald, E.; Storskrubb, T.; Ronkainen, J. Functional dyspepsia impairs quality of life in the adult population. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 33, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, S.; Senf, W.; Häuser, W.; Tagay, S.; Grandt, D.; Heuft, G.; Gerken, G.; Talley, N.J.; Holtmann, G. Impairment of health-related quality of life in functional dyspepsia and chronic liver disease: The influence of depression and anxiety. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 27, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklund, I. Review of the quality of life and burden of illness in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dig. Dis. 2004, 22, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, B.E.; Weiser, K.T.; Kennedy, A.T.; Crowell, M.D.; Talley, N.J. Functional dyspepsia: The economic impact to patients. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 38, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, R.A.; Kleinman, N.L.; Choung, R.S.; Melkonian, A.K.; Smeeding, J.E.; Talley, N.J. Functional dyspepsia impacts absenteeism and direct and indirect costs. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, R.A.; Kleinman, N.L.; Choung, R.S.; Smeeding, J.E.; Talley, N.J. Excess comorbidity prevalence and cost associated with functional dyspepsia in an employed population. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nero, C.J.; Paine, P.A.; Agrawal, A.; Aziz, I.; Eugenicos, M.P.; Houghton, L.A.; Hungin, P.; Overshott, R.; Vasant, D.H.; Rudd, S.; et al. British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines on the management of functional dyspepsia. Gut 2022, 71, 1697–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longstreth, G.F. Functional dyspepsia-managing the conundrum. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 791–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuy, I.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Tack, J. Review article: Treatment options for functional dyspepsia. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 1134–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’souza, A.; Zink, K.; Langhorst, J.; Wildner, M.; Stupp, C.; Keil, T. How effective is drinking natural mineral water against heartburn from functional dyspepsia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, or other causes? A systematic review of clinical intervention studies. Complement. Med. Res. 2024, 31, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomiretska, N.V. Application of mineral waters in the complex treatment of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2020, 66, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, M.; Olivieri, F.; Manghetti, M.; Boccolini, E.; Bellomini, M.G.; Blandizzi, C.; Bonino, F.; Del Tacca, M. Effects of a bicarbonate-alkaline mineral water on gastric functions and functional dyspepsia: A preclinical and clinical study. Pharmacol. Res. 2002, 46, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, A.M.; Ubelhack, R.; Pohl, U. Efficacy and tolerability of hydrogen carbonate-rich water for heartburn. World J. Gasrtointest Pathophysiol. 2016, 7, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labenz, J.; Anschütz, M.; Walstab, J.; Wedemeyer, R.S.; Wolters, H.; Schug, B. Heartburn relief with bicarbonate-rich mineral water: Results of the randomised, placebo-controlled phase-III trial STOMACH STILL. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2023, 10, e001048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasbarrini, G.; Candelli, M.; Graziosetto, R.G.; Coccheri, S.; Di Iorio, F.; Nappi, G. Evaluation of thermal water in patients with functional dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome accompanying constipation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 2556–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrini, S.; Pampaloni, B.; Brandi, M.L. Natural mineral waters: Chemical characteristics and health effects. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2016, 13, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertini, M.C.; Dachà, M.; Teodori, L.; Conti, M.E. Drinking mineral waters: Biochemical effects and health implications: The state-of-the-art. Int. J. Environ. Health 2007, 1, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotti, M.; Turba, E.; Mari, C.; Lopilato, C.; Porrazzo, G.; Scalabrino, A.; Miglioli, M. Changes caused by mineral water on gastrointestinal motility in patients with chronic idiopathic dyspepsia. Minerva Med. 1999, 90, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fornai, M.; Antonioli, L.; Colucci, R.; Tuccori, M.; Awwad, O.; Serra, M.; Grasso, V.; De Giorgio, R.; Blandizzi, C. Role of crenotherapy with mineral waters in the treatment of functional disorders of digestive tract. Gazz. Med. Ital. Arch. Sci. Med. 2012, 171, 213–226. Available online: https://www.minervamedica.it/en/journals/gazzetta-medica-italiana/article.php?cod=R22Y2012N02A0213 (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Dmitrescu, M.; Iliescu, M.G.; Mazilu, L.; Micu, S.I.; Suceveanu, A.P.; Voinea, F.; Voinea, C.; Stoian, A.P.; Suceveanu, A.I. Benefits of crenotherapy in digestive tract pathology (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 23, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liska, D.; Mah, E.; Brisbois, T.; Barrios, P.L.; Baker, L.B.; Spriet, L.L. Narrative Review of Hydration and Selected Health Outcomes in the General Population. Nutrients 2019, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sharkawy, A.M.; Shaota, O.; Lobo, D.N. Acute and chronic effects of hydration status on health. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73 (Suppl 2), 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Nieuwenhoven, M.A.; Vriens, B.E.; Brummer, R.J.; Brouns, F. Effect of dehydration on gastrointestinal function at rest and during exercise in humans. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 83, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zito, P.F.; Gala, A.; Genovese, D.; Vozzella, L.; Polese, B.; Cassarano, S.; Cargiolli, M.; Andreozzi, P.; Gelzo, M.; Sarnelli, G.; et al. Mild dehydration in dyspeptic athletes is able to increase gastrointestinal symptoms: Protective effects of an appropriate hydration. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, e13520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petraccia, L.; Liberati, G.; Masciullo, S.G.; Grassi, M.; Fraioli, A. Water, mineral waters and health. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 25, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toxqui, L.; Pérez-Granados, A.M.; Blanco-Rojo, R.; Pilar Vaquero, M. A sodium-bicarbonated mineral water reduces gallbladder emptying and postprandial lipaemia: A randomised four-way crossover study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2012, 51, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuomo, R.; Grasso, R.; Sarnelli, G.; Capuano, G.; Nicolai, E.; Nardone, G.; Pomponi, D.; Budillon, G.; Ierardi, E. Effects of carbonated water on functional dyspepsia and constipation. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2002, 14, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Hong, J.H. The fundamental role of bicarbonate transporters and associated carbonic anhydrase enzymes in maintaining ion and pH homeostasis in non-secretory organs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, E.G.; de Kloet, A.D.; Flak, J.N.; Smeltzer, M.D.; Solomon, M.B.; Evanson, N.K.; Woods, S.C.; Sakai, R.R.; Herman, J.P. Hydration state controls stress responsiveness and social behavior. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 5470–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, J.T.; Rendall, R.A.; Furber, M.; Massey, H.C.; Tipton, M.J.; Young, J.S.; Corbett, J. Effects of acute or chronic heat exposure, exercise and dehydration on plasma cortisol, IL-6 and CRP levels in trained males. Citokine 2018, 110, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, K.; Davies, G. Heartburn: Influence of diet and lifestyle. Nutr. Food Sci. 2007, 38, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, M.; Fraioli, A.; Pappalardo, G.; Messina, B.; Belardinelli, L.; Guadalaxara, A. Alkalizing activity of a calcium-bicarbonate-containing water, evaluated for pH, in patients with gastroesophageal reflux. Clin. Ter. 1993, 143, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barnich, N.; Rodrigues, M.; Sauvanet, P.; Chevarin, C.; Denis, S.; Le Goff, O.; Faure-Imbert, D.; Hanh, T.; Roques, C.F.; Chassaing, B.; et al. Beneficial effects of natural mineral waters on intestinal inflammation and the mucosa-associated microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, F.; Scarlata, P.; Casini, V.; Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Porro, G.B. Validation of the reflux disease questionnaire for an Italian population of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 20, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, M.; Talley, N.J.; Beebe, T.; Rockwood, T.; Carlsson, R.; Adlis, S.; Fendrick, A.M.; Jones, R.; Dent, J.; Bytzer, P. Initial validation of a diagnostic questionnaire for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Grossi, G.; Groth, N.; Mosconi, P.; Cerutti, R.; Pace, F.; Compare, A.; Apolone, G. Development and validation of the short version of the Psychological General Well-Being Index (PGWB-S). Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2006, 4, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, S.M.; McKenna, S. A British adaptation of the general Wellbeing Index: A new tool for clinical research. Br. J. Med. Econ. 1992, 2, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, W.D. Power calculations for matched case-control studies. Biometrics 1988, 44, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, W.D.; Plummer, W.D. Power and sample size calculations: A review and computer program. Control. Clin. Trials 1990, 11, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Basal | |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| - Males | 20 (44.4%) |
| - Females | 25 (55.6%) |
| Age (years) | |
| - Mean ± SD | 50.6 ± 13.5 |
| - Range | 25–75 |
| Prevalent symptom declared by the patients | |
| - Heartburn | 22 (48.9%) |
| - Regurgitation | 17 (37.8%) |
| - Pain behind breastbone | 4 (8.9%) |
| - Epigastric pain | 2 (4.4%) |
| State of efficiency of their digestion (1–10; n = 44) | |
| - Mean ± SD | 5.9 ± 1.3 |
| - Range | 3–9 |
| Sense of post-prandial fullness (110; n = 44) | |
| - Mean ± SD | 5.7 ± 1.2 |
| - Range | 2–8 |
| Use of antacid drugs | 33 (73.3%) |
| Basal | After Wash-Out | After Alkaline Mineral Water | Alkaline Mineral Water vs. Wash-Out | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. (%) | No. (%) | p Value a | No. (%) | p Value a | p Value b | |
| Burning feeling behind breastbone | 36 (87.8%) | 34 (82.9%) | 0.500 | 32 (78.0%) | 0.625 | 1.000 |
| Pain behind breastbone | 28 (68.3%) | 26 (63.4%) | 0.500 | 18 (43.9%) | 0.008 | 0.058 |
| Burning feeling in the upper stomach | 37 (90.2%) | 37 (90.2%) | 1.000 | 29 (70.7%) | 0.008 | 0.005 |
| Pain in the upper stomach | 28 (68.3%) | 27 (65.9%) | 1.000 | 19 (46.3%) | 0.008 | 0.020 |
| Acid taste in mouth | 39 (95.1%) | 39 (95.1%) | 1.000 | 28 (68.3%) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Movement of materials | 36 (87.8%) | 36 (87.8%) | 1.000 | 27 (65.9%) | 0.004 | 0.003 |
| Heartburn | 38 (92.7%) | 36 (87.8%) | 0.500 | 33 (80.5%) | 0.375 | 0.739 |
| Dyspepsia | 38 (92.7%) | 38 (92.7%) | 1.000 | 32 (78.0%) | 0.031 | 0.014 |
| Regurgitation | 40 (97.6%) | 40 (97.6%) | 1.000 | 33 (80.5%) | 0.016 | 0.008 |
| Basal | After Wash-Out | After Alkaline Mineral Water | Alkaline Mineral Water vs. Wash-Out | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Change vs. Basal | p Value a | Mean ± SD | Change vs. End of Wash-Out | p Value a | Difference | p Value a | |
| Burning feeling behind breastbone | 5.2 ± 2.5 | 4.8 ± 2.6 | −0.4 ± 1.3 | 0.043 | 3.0 ± 2.0 | −1.8 ± 1.7 | <0.001 | −1.4 ± 2.8 | 0.003 |
| Pain behind breastbone | 3.0 ± 2.4 | 2.9 ± 2.5 | −0.1 ± 1.1 | 0.476 | 1.3 ± 1.7 | −1.6 ± 1.8 | <0.001 | −1.5 ± 2.5 | <0.001 |
| Burning feeling in the upper stomach | 5.4 ± 2.4 | 4.8 ± 2.2 | −0.6 ± 1.1 | 0.001 | 2.3 ± 1.8 | −2.5 ± 1.7 | <0.001 | −1.9 ± 2.2 | <0.001 |
| Pain in the upper stomach | 3.0 ± 2.4 | 3.1 ± 2.5 | 0.1 ± 0.9 | 0.417 | 1.2 ± 1.4 | −1.9 ± 2.1 | <0.001 | −2.0 ± 2.7 | <0.001 |
| Acid taste in mouth | 6.5 ± 2.4 | 5.7 ± 2.1 | −0.8 ± 1.5 | 0.002 | 2.6 ± 2.1 | −3.1 ± 2.3 | <0.001 | −2.3 ± 3.3 | <0.001 |
| Movement of materials | 4.9 ± 2.7 | 4.6 ± 2.6 | −0.3 ± 1.2 | 0.136 | 2.2 ± 1.9 | −2.4 ± 2.0 | <0.001 | −2.1 ± 2.8 | <0.001 |
| Heartburn | 8.2 ± 4.1 | 7.7 ± 4.4 | −0.5 ± 2.1 | 0.125 | 4.3 ± 3.3 | −3.4 ± −3.0 | <0.001 | −2.9 ± 4.6 | <0.001 |
| Dyspepsia | 8.4 ± 3.8 | 7.9 ± 3.8 | −0.5 ± 1.8 | 0.066 | 3.5 ± 2.7 | −4.3 ± 3.0 | <0.001 | −3.8 ± 4.1 | <0.001 |
| Regurgitation | 11.4 ± 4.3 | 10.3 ± 4.3 | −1.1 ± 2.3 | 0.004 | 4.8 ± 3.4 | −5.5 ± 3.6 | <0.001 | −4.4 ± 5.2 | <0.001 |
| Total score | 27.9 ± 9.9 | 25.8 ± 10.1 | −2.1 ± 5.6 | 0.005 | 12.6 ± 7.8 | −13.2 ± 7.9 | <0.001 | −11.1 ± 11.9 | <0.001 |
| Basal | After Wash-Out | After Alkaline Mineral Water | Alkaline Mineral Water vs. Wash-Out | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Change vs. Basal | p Value a | Mean ± SD | Change vs. End of Wash-Out | p Value a | Difference | p Value a | |
| State of efficiency of their digestion | 6.0 ± 1.3 | 6.2 ± 1.3 | 0.2 ± 0.5 | 0.008 | 8.0 ± 1.0 | 1.9 ± 1.2 | <0.001 | 1.6 ± 1.5 | <0.001 |
| Sense of post-prandial fullness | 5.8 ± 1.2 | 6.0 ± 1.3 | 0.2 ± 0.7 | 0.067 | 7.8 ± 1.1 | 1.8 ± 1.5 | <0.001 | 1.6 ± 1.9 | <0.001 |
| Basal | After Wash-Out | After Alkaline Mineral Water | Alkaline Mineral Water vs. Wash-Out | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Change vs. Basal | p Value a | Mean ± SD | Change vs. End of Wash-Out | p Value a | Difference | p Value a | |
| Item 05 Anxiety | 11.2 ± 4.8 | 12.1 ± 4.4 | 0.9 ± 2.3 | 0.019 | 14.1 ± 3.0 | 2.1 ± 3.5 | 0.001 | 1.2 ± 4.5 | 0.092 |
| Item 06 Vitality | 11.5 ± 2.7 | 12.2 ± 2.5 | 0.6 ± 2.2 | 0.071 | 13.4 ± 2.3 | 1.3 ± 2.4 | 0.003 | 0.6 ± 4.1 | 0.412 |
| Item 07 Depressed mood | 12.1 ± 3.3 | 11.7 ± 3.2 | −0.4 ± 3.4 | 0.667 | 13.1 ± 3.0 | 1.4 ± 4.1 | 0.005 | 1.8 ± 6.7 | 0.069 |
| Item 18 Self-control | 8.7 ± 4.2 | 8.9 ± 3.6 | 0.2 ± 2.3 | 0.627 | 8.7 ± 4.2 | -0.2 ± 4.1 | 0.772 | −0.4 ± 5.5 | 0.656 |
| Item 20 Positive well-being | 8.8 ± 4.1 | 9.2 ± 4.0 | 0.4 ± 1.5 | 0.059 | 10.3 ± 3.4 | 1.1 ± 2.7 | 0.019 | 0.6 ± 3.7 | 0.318 |
| Item 21 Tiredness | 11.4 ± 3.6 | 11.4 ± 3.6 | 0.0 ± 1.6 | 1.000 | 12.4 ± 4.2 | 1.0 ± 3.3 | 0.045 | 1.0 ± 4.3 | 0.068 |
| Total score | 63.7 ± 16.0 | 65.5 ± 13.9 | 1.8 ± 9.2 | 0.210 | 72.1 ± 11.3 | 6.6 ± 10.7 | <0.001 | 4.8 ± 16.8 | 0.079 |
| Aqueduct Tap Water (Wash-Out) | Alkaline Mineral Water | |
|---|---|---|
| Dissolved solid residual at 180 °C | 218.0 mg/L | 1.130 mg/L |
| pH at source | 8.0 UpH | 6.30 UpH |
| CO2 Free at source | N/a | 972 mg/L |
| Bicarbonates (HCO3) | 222.0 mg/L | 1310 mg/L |
| Sulfate | 20.0 mg/L | 27.7 mg/L |
| Potassium | 0.8 mg/L | 2.66 mg/L |
| Sodium | 6.53mg/L | 7.59 mg/L |
| Calcium | 50.0mg/L | 288.0 mg/L |
| Magnesium | 14.0 mg/L | 87.1 mg/L |
| Fluoride | 0.06 mg/L | 0.3 mg/L |
| Chlorides | 3.0 mg/L | <5 mg/L |
| Selenio | N/a | <20.0 µm/L |
| Sulfide | N/a | <0.05 mg/L |
| Nitrate (NO3) | 5.0 mg/L | <0.1 mg/L |
| Nitrite (NO2) | N/a | <0.01 mg/L |
| Zinc | N/a | <10.0 µm/L |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pace, F.; Morselli-Labate, A.M.; Abu Issa, A.; Zanasi, A. Bicarbonate Natural Mineral Water from Source “F2 Păltiniș” Facilitates Digestion—A Pilot Study. Gastrointest. Disord. 2025, 7, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7030047
Pace F, Morselli-Labate AM, Abu Issa A, Zanasi A. Bicarbonate Natural Mineral Water from Source “F2 Păltiniș” Facilitates Digestion—A Pilot Study. Gastrointestinal Disorders. 2025; 7(3):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7030047
Chicago/Turabian StylePace, Fabio, Antonio Maria Morselli-Labate, Aladin Abu Issa, and Alessandro Zanasi. 2025. "Bicarbonate Natural Mineral Water from Source “F2 Păltiniș” Facilitates Digestion—A Pilot Study" Gastrointestinal Disorders 7, no. 3: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7030047
APA StylePace, F., Morselli-Labate, A. M., Abu Issa, A., & Zanasi, A. (2025). Bicarbonate Natural Mineral Water from Source “F2 Păltiniș” Facilitates Digestion—A Pilot Study. Gastrointestinal Disorders, 7(3), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/gidisord7030047







