Information Systems Security
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Luis Javier Garcia Villalba
Prof. Dr. Luis Javier Garcia Villalba
 Prof. Dr. Luis Javier Garcia Villalba
Prof. Dr. Luis Javier Garcia Villalba
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Group of Analysis, Security and Systems (GASS), Universidad Complutense de Madrid (UCM), 28040 Madrid, Spain
Interests: artificial intelligence; big data; computer networks; computer security; information theory; IoT; multimedia forensics
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue in
Sensors: Advances on Resources Management for Multi-Platform Infrastructures
Topical Collection in
Entropy: Entropy-Based Applied Cryptography and Enhanced Security for Future IT Environments
Special Issue in
Entropy: Information Theory and 5G Technologies
Special Issue in
Sensors: Advances on Sensor Pattern Noise used in Multimedia Forensics and Counter Forensic
Special Issue in
Applied Sciences: Machine Learning for Cybersecurity Threats, Challenges, and Opportunities
Special Issue in
Entropy: Blockchain: Security, Challenges, and Opportunities
Special Issue in
Applied Sciences: Analytics, Privacy and Security for IoT and Big Data
Special Issue in
Applied Sciences: Machine Learning for Cybersecurity Threats, Challenges, and Opportunities Ⅱ
Special Issue in
Systems: Extended Reality Application and Management Systems
Special Issue in
Journal of Cybersecurity and Privacy: Privacy-Enhancing Technologies for User Systems to Foster a More Ethical E-society
Special Issue in
Applied Sciences: Machine Learning for Cybersecurity Threats, Challenges, and Opportunities III
Special Issue in
Applied Sciences: Network Information Theory and Its Applications in Security and Privacy
Special Issue in
Future Internet: Software-Driven Federated Learning for/in Smart Environment
Special Issue in
Applied Sciences: Cyber Security and Software Engineering
Special Issue in
Applied Sciences: Feature Review Papers in "Computing and Artificial Intelligence"
Special Issue in
Cryptography: Advances in Symmetric Cryptography and Data Integrity
Special Issue in
Applied Sciences: Advances in the Internet of Things (IoT): Attacks Detection and Privacy Protection
Special Issue in
Applied Sciences: New Challenges in Intelligent Agent Systems
Topics:
Machine and Deep Learning
Topics:
Trends and Prospects in Security, Encryption and Encoding
Topics:
Advances in Sixth Generation and Beyond (6G&B)
Topics:
Addressing Security Issues Related to Modern Software
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
The outstanding increase in both the number and complexity of computer attacks in the last few years, as well as the large profit made by them, have led to new business models based on cybercrime. This encourages the emergence of new strains, and raises the demand of defensive technologies able to confront them. However, the development of countermeasures has become a real challenge for the research community. This is mainly due to the fact that the design of defenses is lagging behind that of intruders, and new strategies for prevention, detection, and mitigation, adapted to the new trends, are required.
In order to contribute to addressing these threats, this Special Issue intends to collect the current developments and the future directions on network security. Hence, we encourage authors to submit original papers related to these fields.
Potential topics include, but are not limited to:
- Databases and big data security
- Electronic commerce security and digital currencies
- E-mail security, spam, and fraud
- Grid and cloud computing security
- Internet security and applications
- Intrusion detection and prevention
- Mobile computing security
- Multimedia forensics
- Network forensics
- Network steganography and steganalysis
- Peer-to-peer network security
- Penetration testing
- Secure system architectures
- Security protocols
- Sensor network security
- Trust and privacy
- Vehicular ad hoc networks security
Prof. Dr. Luis Javier Garcia Villalba
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Future Internet is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1800 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- computer attack
- cryptography
- cybercrime
- forensic
- internet securit
- intrusion detection
- malware
- network security
- privacy
- steganography
- trust
- vulnerability
Related Special Issues
Published Papers (30 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Ensemble Learning for Software Requirement-Risk Assessment: A Comparative Study of Bagging and Boosting Approaches
by
Chandan Kumar, Pathan Shaheen Khan, Medandrao Srinivas, Sudhanshu Kumar Jha, Shiv Prakash and Rajkumar Singh Rathore
Viewed by 1085
Abstract
In software development, software requirement engineering (SRE) is an essential stage that guarantees requirements are clear and unambiguous. However, incomplete inconsistency, and ambiguity in requirement documents often occur, which can cause project delay, cost escalation, or total failure. In response to these challenges,
[...] Read more.
In software development, software requirement engineering (SRE) is an essential stage that guarantees requirements are clear and unambiguous. However, incomplete inconsistency, and ambiguity in requirement documents often occur, which can cause project delay, cost escalation, or total failure. In response to these challenges, this paper introduces a machine learning method to automatically identify the risk levels of software requirements according to ensemble classification methods. The labeled textual requirement dataset was preprocessed utilizing conventional preprocessing techniques, label encoding, and oversampling with the synthetic minority oversampling technique (SMOTE) to handle class imbalance. Various ensemble and baseline models such as extra trees, random forest, bagging with decision trees, XGBoost, LightGBM, gradient boosting, decision trees, support vector machine, and multi-layer perceptron were trained and compared. Five-fold cross-validation was used to provide stable performance evaluation on accuracy, area under the ROC curve (AUC), F1-score, precision, recall, root mean square error (RMSE), and error rate. The bagging (DT) classifier achieved the best overall performance, with an accuracy of 99.55%, AUC of 0.9971 and an F1-score of 97.23%, while maintaining a low RMSE of 0.03 and error rate of 0.45%. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of ensemble-based classifiers, especially bagging (DT) classifiers, in accurately predicting high-risk software requirements. The proposed method enables early detection and mitigation of requirement risks, aiding project managers and software engineers in improving resource planning, reducing rework, and enhancing overall software quality.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Detecting Disinformation in Croatian Social Media Comments
by
Igor Ljubi, Zdravko Grgić, Marin Vuković and Gordan Gledec
Viewed by 1314
Abstract
The frequency with which fake news or misinformation is published on social networks is constantly increasing. Users of social networks are confronted with many different posts every day, often with sensationalist titles and content of dubious veracity. The problem is particularly common in
[...] Read more.
The frequency with which fake news or misinformation is published on social networks is constantly increasing. Users of social networks are confronted with many different posts every day, often with sensationalist titles and content of dubious veracity. The problem is particularly common in times of sensitive social or political situations, such as epidemics of contagious diseases or elections. As such messages can have an impact on democratic processes or cause panic among the population, many countries and the European Commission itself have recently stepped up their activities to combat disinformation campaigns on social networks. Since previous research has shown that there are no tools available to combat disinformation in the Croatian language, we proposed a framework to detect potentially misinforming content in the comments on social media. The case study was conducted with real public comments published on Croatian Facebook pages. The initial results of this framework were encouraging as it can successfully classify and detect disinformation content.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Database Security and Performance: A Case of SQL Injection Attacks Using Docker-Based Virtualisation and Its Effect on Performance
by
Ade Dotun Ajasa, Hassan Chizari and Abu Alam
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 4967
Abstract
Modern database systems are critical for storing sensitive information but are increasingly targeted by cyber threats, including SQL injection (SQLi) attacks. This research proposes a robust security framework leveraging Docker-based virtualisation to enhance database security and mitigate the impact of SQLi attacks. A
[...] Read more.
Modern database systems are critical for storing sensitive information but are increasingly targeted by cyber threats, including SQL injection (SQLi) attacks. This research proposes a robust security framework leveraging Docker-based virtualisation to enhance database security and mitigate the impact of SQLi attacks. A controlled experimental methodology evaluated the framework’s effectiveness using Damn Vulnerable Web Application (DVWA) and Acunetix databases. The findings reveal that Docker significantly reduces the vulnerability to SQLi attacks by isolating database instances, thereby safeguarding user data and system integrity. While Docker introduces a significant increase in CPU utilisation during high-traffic scenarios, the trade-off ensures enhanced security and reliability for real-world applications. This study highlights Docker’s potential as a practical solution for addressing evolving database security challenges in distributed and cloud environments.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Question–Answer Methodology for Vulnerable Source Code Review via Prototype-Based Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning
by
Pablo Corona-Fraga, Aldo Hernandez-Suarez, Gabriel Sanchez-Perez, Linda Karina Toscano-Medina, Hector Perez-Meana, Jose Portillo-Portillo, Jesus Olivares-Mercado and Luis Javier García Villalba
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2279
Abstract
In cybersecurity, identifying and addressing vulnerabilities in source code is essential for maintaining secure IT environments. Traditional static and dynamic analysis techniques, although widely used, often exhibit high false-positive rates, elevated costs, and limited interpretability. Machine Learning (ML)-based approaches aim to overcome these
[...] Read more.
In cybersecurity, identifying and addressing vulnerabilities in source code is essential for maintaining secure IT environments. Traditional static and dynamic analysis techniques, although widely used, often exhibit high false-positive rates, elevated costs, and limited interpretability. Machine Learning (ML)-based approaches aim to overcome these limitations but encounter challenges related to scalability and adaptability due to their reliance on large labeled datasets and their limited alignment with the requirements of secure development teams. These factors hinder their ability to adapt to rapidly evolving software environments. This study proposes an approach that integrates Prototype-Based Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning(Proto-MAML) with a Question-Answer (QA) framework that leverages the Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) model. By employing Few-Shot Learning (FSL), Proto-MAML identifies and mitigates vulnerabilities with minimal data requirements, aligning with the principles of the Secure Development Lifecycle (SDLC) and Development, Security, and Operations (DevSecOps). The QA framework allows developers to query vulnerabilities and receive precise, actionable insights, enhancing its applicability in dynamic environments that require frequent updates and real-time analysis. The model outputs are interpretable, promoting greater transparency in code review processes and enabling efficient resolution of emerging vulnerabilities. Proto-MAML demonstrates strong performance across multiple programming languages, achieving an average precision of
, recall of
, F1-score of
, and exact match rate of
in PHP, Java, C, and C++.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Internet of Things and Distributed Computing Systems in Business Models
by
Albérico Travassos Rosário and Ricardo Raimundo
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 3896
Abstract
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Distributed Computing Systems (DCS) is transforming business models across industries. IoT devices allow immediate monitoring of equipment and processes, mitigating lost time and enhancing efficiency. In this case, manufacturing companies use IoT sensors to
[...] Read more.
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Distributed Computing Systems (DCS) is transforming business models across industries. IoT devices allow immediate monitoring of equipment and processes, mitigating lost time and enhancing efficiency. In this case, manufacturing companies use IoT sensors to monitor machinery, predict failures, and schedule maintenance. Also, automation via IoT reduces manual intervention, resulting in boosted productivity in smart factories and automated supply chains. IoT devices generate this vast amount of data, which businesses analyze to gain insights into customer behavior, operational inefficiencies, and market trends. In turn, Distributed Computing Systems process this data, providing actionable insights and enabling advanced analytics and machine learning for future trend predictions. While, IoT facilitates personalized products and services by collecting data on customer preferences and usage patterns, enhancing satisfaction and loyalty, IoT devices support new customer interactions, like wearable health devices, and enable subscription-based and pay-per-use models in transportation and utilities. Conversely, real-time monitoring enhances security, as distributed systems quickly respond to threats, ensuring operational safety. It also aids regulatory compliance by providing accurate operational data. In this way, this study, through a Bibliometric Literature Review (LRSB) of 91 screened pieces of literature, aims at ascertaining to what extent the aforementioned capacities, overall, enhance business models, in terms of efficiency and effectiveness. The study concludes that those systems altogether leverage businesses, promoting competitive edge, continuous innovation, and adaptability to market dynamics. In particular, overall, the integration of both IoT and Distributed Systems in business models augments its numerous advantages: it develops smart infrastructures e.g., smart grids; edge computing that allows data processing closer to the data source e.g., autonomous vehicles; predictive analytics, by helping businesses anticipate issues e.g., to foresee equipment failures; personalized services e.g., through e-commerce platforms of personalized recommendations to users; enhanced security, while reducing the risk of centralized attacks e.g., blockchain technology, in how IoT and Distributed Computing Systems altogether impact business models. Future research avenues are suggested.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Impact, Compliance, and Countermeasures in Relation to Data Breaches in Publicly Traded U.S. Companies
by
Gabriel Arquelau Pimenta Rodrigues, André Luiz Marques Serrano, Guilherme Fay Vergara, Robson de Oliveira Albuquerque and Georges Daniel Amvame Nze
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 11879
Abstract
A data breach is the unauthorized disclosure of sensitive personal data, and it impacts millions of individuals annually in the United States, as reported by Privacy Rights Clearinghouse. These breaches jeopardize the physical safety of the individuals whose data are exposed and result
[...] Read more.
A data breach is the unauthorized disclosure of sensitive personal data, and it impacts millions of individuals annually in the United States, as reported by Privacy Rights Clearinghouse. These breaches jeopardize the physical safety of the individuals whose data are exposed and result in substantial economic losses for the affected companies. To diminish the frequency and severity of data breaches in the future, it is imperative to research their causes and explore preventive measures. In pursuit of this goal, this study considers a dataset of data breach incidents affecting companies listed on the New York Stock Exchange and NASDAQ. This dataset has been augmented with additional information regarding the targeted company. This paper employs statistical visualizations of the data to clarify these incidents and assess their consequences on the affected companies and individuals whose data were compromised. We then propose mitigation controls based on established frameworks such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. Additionally, this paper reviews the compliance scenario by examining the relevant laws and regulations applicable to each case, including SOX, HIPAA, GLBA, and PCI-DSS, and evaluates the impacts of data breaches on stock market prices. We also review guidelines for appropriately responding to data leaks in the U.S., for compliance achievement and cost reduction. By conducting this analysis, this work aims to contribute to a comprehensive understanding of data breaches and empower organizations to safeguard against them proactively, improving the technical quality of their basic services. To our knowledge, this is the first paper to address compliance with data protection regulations, security controls as countermeasures, financial impacts on stock prices, and incident response strategies. Although the discussion is focused on publicly traded companies in the United States, it may also apply to public and private companies worldwide.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Evaluating Realistic Adversarial Attacks against Machine Learning Models for Windows PE Malware Detection
by
Muhammad Imran, Annalisa Appice and Donato Malerba
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 7826
Abstract
During the last decade, the cybersecurity literature has conferred a high-level role to machine learning as a powerful security paradigm to recognise malicious software in modern anti-malware systems. However, a non-negligible limitation of machine learning methods used to train decision models is that
[...] Read more.
During the last decade, the cybersecurity literature has conferred a high-level role to machine learning as a powerful security paradigm to recognise malicious software in modern anti-malware systems. However, a non-negligible limitation of machine learning methods used to train decision models is that adversarial attacks can easily fool them. Adversarial attacks are attack samples produced by carefully manipulating the samples at the test time to violate the model integrity by causing detection mistakes. In this paper, we analyse the performance of five realistic target-based adversarial attacks, namely Extend, Full DOS, Shift, FGSM padding + slack and GAMMA, against two machine learning models, namely MalConv and LGBM, learned to recognise Windows Portable Executable (PE) malware files. Specifically, MalConv is a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model learned from the raw bytes of Windows PE files. LGBM is a Gradient-Boosted Decision Tree model that is learned from features extracted through the static analysis of Windows PE files. Notably, the attack methods and machine learning models considered in this study are state-of-the-art methods broadly used in the machine learning literature for Windows PE malware detection tasks. In addition, we explore the effect of accounting for adversarial attacks on securing machine learning models through the adversarial training strategy. Therefore, the main contributions of this article are as follows: (1) We extend existing machine learning studies that commonly consider small datasets to explore the evasion ability of state-of-the-art Windows PE attack methods by increasing the size of the evaluation dataset. (2) To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to carry out an exploratory study to explain how the considered adversarial attack methods change Windows PE malware to fool an effective decision model. (3) We explore the performance of the adversarial training strategy as a means to secure effective decision models against adversarial Windows PE malware files generated with the considered attack methods. Hence, the study explains how GAMMA can actually be considered the most effective evasion method for the performed comparative analysis. On the other hand, the study shows that the adversarial training strategy can actually help in recognising adversarial PE malware generated with GAMMA by also explaining how it changes model decisions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Secure Partitioning of Cloud Applications, with Cost Look-Ahead
by
Alessandro Bocci, Stefano Forti, Roberto Guanciale, Gian-Luigi Ferrari and Antonio Brogi
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2103
Abstract
The security of Cloud applications is a major concern for application developers and operators. Protecting users’ data confidentiality requires methods to avoid leakage from vulnerable software and unreliable Cloud providers. Recently, trusted execution environments (TEEs) emerged in Cloud settings to isolate applications from
[...] Read more.
The security of Cloud applications is a major concern for application developers and operators. Protecting users’ data confidentiality requires methods to avoid leakage from vulnerable software and unreliable Cloud providers. Recently, trusted execution environments (TEEs) emerged in Cloud settings to isolate applications from the privileged access of Cloud providers. Such hardware-based technologies exploit separation kernels, which aim at safely isolating the software components of applications. In this article, we propose a methodology to determine safe partitionings of Cloud applications to be deployed on TEEs. Through a probabilistic cost model, we enable application operators to select the best trade-off partitioning in terms of future re-partitioning costs and the number of domains. To the best of our knowledge, no previous proposal exists addressing such a problem. We exploit information-flow security techniques to protect the data confidentiality of applications by relying on declarative methods to model applications and their data flow. The proposed solution is assessed by executing a proof-of-concept implementation that shows the relationship among the future partitioning costs, number of domains and execution times.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Online Privacy Fatigue: A Scoping Review and Research Agenda
by
Karl van der Schyff, Greg Foster, Karen Renaud and Stephen Flowerday
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 8451
Abstract
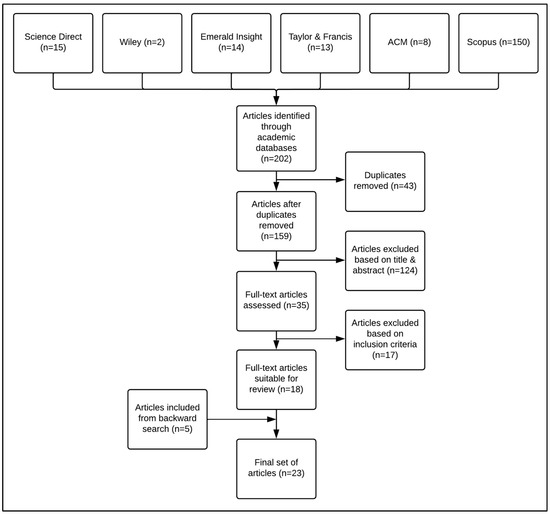
Online users are responsible for protecting their online privacy themselves: the mantra is
custodiat te (protect yourself). Even so, there is a great deal of evidence pointing to the fact that online users generally do not act to preserve the privacy of their
[...] Read more.
Online users are responsible for protecting their online privacy themselves: the mantra is
custodiat te (protect yourself). Even so, there is a great deal of evidence pointing to the fact that online users generally do not act to preserve the privacy of their personal information, consequently disclosing more than they ought to and unwisely divulging sensitive information. Such self-disclosure has many negative consequences, including the invasion of privacy and identity theft. This often points to a need for more knowledge and awareness but does not explain why even knowledgeable users fail to preserve their privacy. One explanation for this phenomenon may be attributed to
online privacy fatigue. Given the importance of online privacy and the lack of integrative online privacy fatigue research, this scoping review aims to provide researchers with an understanding of online privacy fatigue, its antecedents and outcomes, as well as a critical analysis of the methodological approaches used. A scoping review based on the PRISMA-ScR checklist was conducted. Only empirical studies focusing on online privacy were included, with nontechnological studies being excluded. All studies had to be written in English. A search strategy encompassing six electronic databases resulted in eighteen eligible studies, and a backward search of the references resulted in an additional five publications. Of the 23 studies, the majority were quantitative (74%), with fewer than half being theory driven (48%). Privacy fatigue was mainly conceptualized as a loss of control (74% of studies). Five categories of privacy fatigue antecedents were identified: privacy risk, privacy control and management, knowledge and information, individual differences, and privacy policy characteristics. This study highlights the need for greater attention to be paid to the methodological design and theoretical underpinning of future research. Quantitative studies should carefully consider the use of CB-SEM or PLS-SEM, should aim to increase the sample size, and should improve on analytical rigor. In addition, to ensure that the field matures, future studies should be underpinned by established theoretical frameworks. This review reveals a notable absence of privacy fatigue research when modeling the influence of privacy threats and invasions and their relationship with privacy burnout, privacy resignation, and increased self-disclosure. In addition, this review provides insight into theoretical and practical research recommendations that future privacy fatigue researchers should consider going forward.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of Digital Information in Storage Devices Using Supervised and Unsupervised Natural Language Processing Techniques
by
Luis Alberto Martínez Hernández, Ana Lucila Sandoval Orozco and Luis Javier García Villalba
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3299
Abstract
Due to the advancement of technology, cybercrime has increased considerably, making digital forensics essential for any organisation. One of the most critical challenges is to analyse and classify the information on devices, identifying the relevant and valuable data for a specific purpose. This
[...] Read more.
Due to the advancement of technology, cybercrime has increased considerably, making digital forensics essential for any organisation. One of the most critical challenges is to analyse and classify the information on devices, identifying the relevant and valuable data for a specific purpose. This phase of the forensic process is one of the most complex and time-consuming, and requires expert analysts to avoid overlooking data relevant to the investigation. Although tools exist today that can automate this process, they will depend on how tightly their parameters are tuned to the case study, and many lack support for complex scenarios where language barriers play an important role. Recent advances in machine learning allow the creation of new architectures to significantly increase the performance of information analysis and perform the intelligent search process automatically, reducing analysis time and identifying relationships between files based on initial parameters. In this paper, we present a bibliographic review of artificial intelligence algorithms that allow an exhaustive analysis of multimedia information contained in removable devices in a forensic process, using natural language processing and natural language understanding techniques for the automatic classification of documents in seized devices. Finally, some of the open challenges technology developers face when generating tools that use artificial intelligence techniques to analyse the information contained in documents on seized devices are reviewed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Novel Hybrid Edge Detection and LBP Code-Based Robust Image Steganography Method
by
Habiba Sultana, A. H. M. Kamal, Gahangir Hossain and Muhammad Ashad Kabir
Cited by 20 | Viewed by 5412
Abstract
In digital image processing and steganography, images are often described using edges and local binary pattern (LBP) codes. By combining these two properties, a novel hybrid image steganography method of secret embedding is proposed in this paper. This method only employs edge pixels
[...] Read more.
In digital image processing and steganography, images are often described using edges and local binary pattern (LBP) codes. By combining these two properties, a novel hybrid image steganography method of secret embedding is proposed in this paper. This method only employs edge pixels that influence how well the novel approach embeds data. To increase the quantity of computed edge pixels, several edge detectors are applied and hybridized using a logical OR operation. A morphological dilation procedure in the hybridized edge image is employed to this purpose. The least significant bits (LSB) and all LBP codes are calculated for edge pixels. Afterward, these LBP codes, LSBs, and secret bits using an exclusive-OR operation are merged. These resulting implanted bits are delivered to edge pixels’ LSBs. The experimental results show that the suggested approach outperforms current strategies in terms of measuring perceptual transparency, such as peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity index (SSI). The embedding capacity per tempered pixel in the proposed approach is also substantial. Its embedding guidelines protect the privacy of implanted data. The entropy, correlation coefficient, cosine similarity, and pixel difference histogram data show that our proposed method is more resistant to various types of cyber-attacks.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Software Design and Experimental Evaluation of a Reduced AES for IoT Applications
by
Malik Qasaimeh, Raad S. Al-Qassas and Mohammad Ababneh
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 4018
Abstract
IoT devices include RFID tags, microprocessors, sensors, readers, and actuators. Their main characteristics are their limited resources and computing capabilities, which pose critical challenges to the reliability and security of their applications. Encryption is necessary for security when using these limited-resource devices, but
[...] Read more.
IoT devices include RFID tags, microprocessors, sensors, readers, and actuators. Their main characteristics are their limited resources and computing capabilities, which pose critical challenges to the reliability and security of their applications. Encryption is necessary for security when using these limited-resource devices, but conventional cryptographic algorithms are too heavyweight and resource-demanding to run on IoT infrastructures. This paper presents a lightweight version of AES (called LAES), which provides competitive results in terms of randomness levels and processing time, operating on GF(2
4). Detailed mathematical operations and proofs are presented concerning LAES rounds design fundamentals. The proposed LAES algorithm is evaluated based on its randomness, performance, and power consumption; it is then compared to other cryptographic algorithm variants, namely Present, Clefia, and AES. The design of the randomness and performance analysis is based on six measures developed with the help of the NIST test statistical suite of cryptographic applications. The performance and power consumption of LAES on a low-power, 8-bit microcontroller unit were evaluated using an Arduino Uno board. LAES was found to have competitive randomness levels, processing times, and power consumption compared to Present, Clefia, and AES.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Securing Resource-Constrained IoT Nodes: Towards Intelligent Microcontroller-Based Attack Detection in Distributed Smart Applications
by
Andrii Shalaginov and Muhammad Ajmal Azad
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 4006
Abstract
In recent years, the Internet of Things (IoT) devices have become an inseparable part of our lives. With the growing demand for Smart Applications, it becomes clear that IoT will bring regular automation and intelligent sensing to a new level thus improving quality
[...] Read more.
In recent years, the Internet of Things (IoT) devices have become an inseparable part of our lives. With the growing demand for Smart Applications, it becomes clear that IoT will bring regular automation and intelligent sensing to a new level thus improving quality of life. The core component of the IoT ecosystem is data which exists in various forms and formats. The collected data is then later used to create context awareness and make meaningful decisions. Besides an undoubtedly large number of advantages from the usage of IoT, there exist numerous challenges attributed to the security of objects that cannot be neglected for uninterrupted services. The Mirai botnet attack demonstrated that the IoT system is susceptible to different forms of cyberattacks. While advanced data analytics and Machine Learning have proved efficiency in various applications of cybersecurity, those still have not been explored enough in the literature from the applicability perspective in the domain of resource-constrained IoT. Several architectures and frameworks have been proposed for defining the ways for analyzing the data, yet mostly investigating off-chip analysis. In this contribution, we show how an Artificial Neural Network model can be trained and deployed on trivial IoT nodes for detecting intelligent similarity-based network attacks. This article proposes a concept of the resource-constrained intelligent system as a part of the IoT infrastructure to be able to harden the cybersecurity on microcontrollers. This work will serve as a stepping stone for the application of Artificial Intelligence on devices with limited computing capabilities such as end-point IoT nodes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Security Challenges of Location Privacy in VANETs and State-of-the-Art Solutions: A Survey
by
Shawal Khan, Ishita Sharma, Mazzamal Aslam, Muhammad Zahid Khan and Shahzad Khan
Cited by 53 | Viewed by 8597
Abstract
A Vehicular Ad-hoc Network (VANET) comprises a group of moving or stationary vehicles connected by a wireless network. VANETs play a vital role in providing safety and comfort to drivers in vehicular environments. They provide smart traffic control and real-time information, event allocation.
[...] Read more.
A Vehicular Ad-hoc Network (VANET) comprises a group of moving or stationary vehicles connected by a wireless network. VANETs play a vital role in providing safety and comfort to drivers in vehicular environments. They provide smart traffic control and real-time information, event allocation. VANETs have received attention in support of safe driving, intelligent navigation, emergency and entertainment applications in vehicles. Nevertheless, these increasingly linked vehicles pose a range of new safety and security risks to both the host and its associated properties and may even have fatal consequences. Violations of national privacy and vehicle identities are a major obstacle to introducing forced contact protocols in vehicles. Location privacy refers to the privacy of the vehicle (driver) and the location of the vehicle. Whenever a vehicle sends a message, no one but authorized entities should know their real identity and location of the vehicle. All the messages sent by the vehicle must be authenticated before processing, hence location privacy is an important design aspect to be considered in VANETs operations. The novelty of this paper is that it specifically reviews location privacy in VANETs in terms of operational and safety concerns. Furthermore, it presents a critical analysis of various attacks, identity thefts, manipulation and other techniques in vogue for location privacy protection available in state-of-the-art solutions for VANETs. The efforts in this paper will help researchers to develop a great breadth of understanding pertaining to location privacy issues and various security threats encountered by VANETs and present the critical analysis of the available state-of-the- art solutions to maintain location privacy in VANETs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Methodology to Evaluate Standards and Platforms within Cyber Threat Intelligence
by
Alessandra de Melo e Silva, João José Costa Gondim, Robson de Oliveira Albuquerque and Luis Javier García Villalba
Cited by 54 | Viewed by 11200
Abstract
The cyber security landscape is fundamentally changing over the past years. While technology is evolving and new sophisticated applications are being developed, a new threat scenario is emerging in alarming proportions. Sophisticated threats with multi-vectored, multi-staged and polymorphic characteristics are performing complex attacks,
[...] Read more.
The cyber security landscape is fundamentally changing over the past years. While technology is evolving and new sophisticated applications are being developed, a new threat scenario is emerging in alarming proportions. Sophisticated threats with multi-vectored, multi-staged and polymorphic characteristics are performing complex attacks, making the processes of detection and mitigation far more complicated. Thus, organizations were encouraged to change their traditional defense models and to use and to develop new systems with a proactive approach. Such changes are necessary because the old approaches are not effective anymore to detect advanced attacks. Also, the organizations are encouraged to develop the ability to respond to incidents in real-time using complex threat intelligence platforms. However, since the field is growing rapidly, today Cyber Threat Intelligence concept lacks a consistent definition and a heterogeneous market has emerged, including diverse systems and tools, with different capabilities and goals. This work aims to provide a comprehensive evaluation methodology of threat intelligence standards and cyber threat intelligence platforms. The proposed methodology is based on the selection of the most relevant candidates to establish the evaluation criteria. In addition, this work studies the Cyber Threat Intelligence ecosystem and Threat Intelligence standards and platforms existing in state-of-the-art.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Structured Data REST Protocol for End to End Data Mashup
by
Prakash Narayan Hardaha and Shailendra Singh
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 5536
Abstract
Due to the exponential growth of the data and its services, visiting multiple webs/apps by a user raises three issues—(1) consumption of extra bytes; (2) time killing process of surfing inside the webs/apps; (3) tedious task of remembering address of webs/apps with their
[...] Read more.
Due to the exponential growth of the data and its services, visiting multiple webs/apps by a user raises three issues—(1) consumption of extra bytes; (2) time killing process of surfing inside the webs/apps; (3) tedious task of remembering address of webs/apps with their credentials. The data mashup is a set of techniques and user-friendly approaches which not only resolves above issues but also allows ordinary user to fetch required data from multiple disparate data sources and to create the integrated view in his defined digital place. In this paper, we have proposed an extension of existing REST protocol called Structured Data REST (SDRest) protocol and user-friendly novel approach which allows even ordinary users to develop end to end data mashup, using the innovative concept of Structured Data Mashup Box (SDMB) and One Time Configuration (OTC)-Any Time Access (ATA) models. Our implementation shows that pre-mashup configuration can easily be performed by an ordinary user and an integrated user interface view of end user data mashup can be created without any technical knowledge or programming. We have also evaluated the proposed work by comparing it with some of the related works and found that the proposed work has developed user friendly configurable approach using the current state of the art techniques to involve not only the ordinary user but also the mashup service provider and the data service provider to develop public, private and hybrid data mashup.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
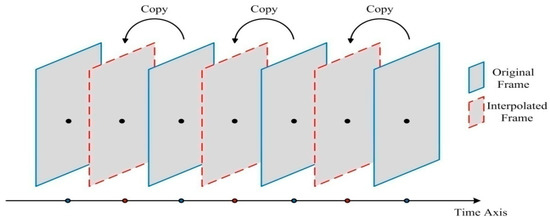
Using Noise Level to Detect Frame Repetition Forgery in Video Frame Rate Up-Conversion
by
Yanli Li, Lala Mei, Ran Li and Changan Wu
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 4794
Abstract
Frame repetition (FR) is a common temporal-domain tampering operator, which is often used to increase the frame rate of video sequences. Existing methods detect FR forgery by analyzing residual variation or similarity between video frames; however, these methods are easily interfered with by
[...] Read more.
Frame repetition (FR) is a common temporal-domain tampering operator, which is often used to increase the frame rate of video sequences. Existing methods detect FR forgery by analyzing residual variation or similarity between video frames; however, these methods are easily interfered with by noise, affecting the stability of detection performance. This paper proposes a noise-level based detection method which detects the varying noise level over time to determine whether the video is forged by FR. Wavelet coefficients are first computed for each video frame, and median absolute deviation (MAD) of wavelet coefficients is used to estimate the standard deviation of Gaussian noise mixed in each video frame. Then, fast Fourier transform (FFT) is used to calculate the amplitude spectrum of the standard deviation curve of the video sequence, and to provide the peak-mean ratio (PMR) of the amplitude spectrum. Finally, according to the PMR obtained, a hard threshold decision is taken to determine whether the standard deviation bears periodicity in the temporal domain, in which way FR forgery can be automatically identified. The experimental results show that the proposed method ensures a large PMR for the forged video, and presents a better detection performance when compared with the existing detection methods.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
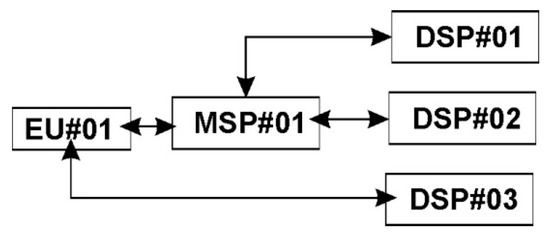
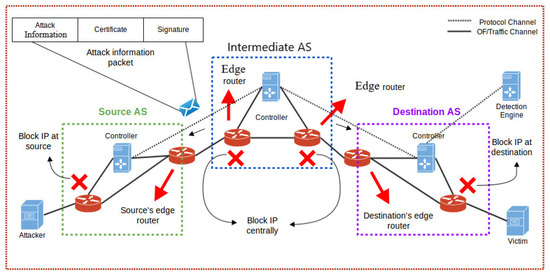
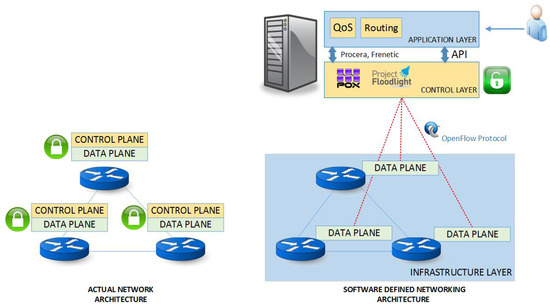
SDN Based Collaborative Scheme for Mitigation of DDoS Attacks
by
Sufian Hameed and Hassan Ahmed Khan
Cited by 71 | Viewed by 11782
Abstract
Software Defined Networking (SDN) has proved itself to be a backbone in the new network design and is quickly becoming an industry standard. The idea of separation of control plane and data plane is the key concept behind SDN. SDN not only allows
[...] Read more.
Software Defined Networking (SDN) has proved itself to be a backbone in the new network design and is quickly becoming an industry standard. The idea of separation of control plane and data plane is the key concept behind SDN. SDN not only allows us to program and monitor our networks but it also helps in mitigating some key network problems. Distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack is among them. In this paper we propose a collaborative DDoS attack mitigation scheme using SDN. We design a secure controller-to-controller (C-to-C) protocol that allows SDN-controllers lying in different autonomous systems (AS) to securely communicate and transfer attack information with each other. This enables efficient notification along the path of an ongoing attack and effective filtering of traffic near the source of attack, thus saving valuable time and network resources. We also introduced three different deployment approaches i.e., linear, central and mesh in our testbed. Based on the experimental results we demonstrate that our SDN based collaborative scheme is fast and reliable in efficiently mitigating DDoS attacks in real time with very small computational footprints.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Network Intrusion Detection through Discriminative Feature Selection by Using Sparse Logistic Regression
by
Reehan Ali Shah, Yuntao Qian, Dileep Kumar, Munwar Ali and Muhammad Bux Alvi
Cited by 35 | Viewed by 9937
Abstract
Intrusion detection system (IDS) is a well-known and effective component of network security that provides transactions upon the network systems with security and safety. Most of earlier research has addressed difficulties such as overfitting, feature redundancy, high-dimensional features and a limited number of
[...] Read more.
Intrusion detection system (IDS) is a well-known and effective component of network security that provides transactions upon the network systems with security and safety. Most of earlier research has addressed difficulties such as overfitting, feature redundancy, high-dimensional features and a limited number of training samples but feature selection. We approach the problem of feature selection via sparse logistic regression (SPLR). In this paper, we propose a discriminative feature selection and intrusion classification based on SPLR for IDS. The SPLR is a recently developed technique for data analysis and processing via sparse regularized optimization that selects a small subset from the original feature variables to model the data for the purpose of classification. A linear SPLR model aims to select the discriminative features from the repository of datasets and learns the coefficients of the linear classifier. Compared with the feature selection approaches, like filter (ranking) and wrapper methods that separate the feature selection and classification problems, SPLR can combine feature selection and classification into a unified framework. The experiments in this correspondence demonstrate that the proposed method has better performance than most of the well-known techniques used for intrusion detection.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
TSKT-ORAM: A Two-Server k-ary Tree Oblivious RAM without Homomorphic Encryption
by
Jinsheng Zhang, Qiumao Ma, Wensheng Zhang and Daji Qiao
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 7271
Abstract
This paper proposes TSKT-oblivious RAM (ORAM), an efficient multi-server ORAM construction, to protect a client’s access pattern to outsourced data. TSKT-ORAM organizes each of the server storages as a
k-ary tree and adopts XOR-based private information retrieval (PIR) and a novel delayed
[...] Read more.
This paper proposes TSKT-oblivious RAM (ORAM), an efficient multi-server ORAM construction, to protect a client’s access pattern to outsourced data. TSKT-ORAM organizes each of the server storages as a
k-ary tree and adopts XOR-based private information retrieval (PIR) and a novel delayed eviction technique to optimize both the data query and data eviction process. TSKT-ORAM is proven to protect the data access pattern privacy with a failure probability of
when system parameter
. Meanwhile, given a constant-size local storage, when
N (i.e., the total number of outsourced data blocks) ranges from
–
, the communication cost of TSKT-ORAM is only 22–46 data blocks. Asymptotic analysis and practical comparisons are conducted to show that TSKT-ORAM incurs lower communication cost, storage cost and access delay in practical scenarios than the compared state-of-the-art ORAM schemes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Review on Semi-Fragile Watermarking Algorithms for Content Authentication of Digital Images
by
Xiaoyan Yu, Chengyou Wang and Xiao Zhou
Cited by 40 | Viewed by 9108
Abstract
With the popularity of network and the continuous development of multimedia technology, saving of network bandwidth and copyright protection of multimedia content have gradually attracted people’s attention. The fragile watermark for integrity authentication of image data and protection of copyright has become a
[...] Read more.
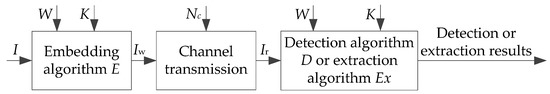
With the popularity of network and the continuous development of multimedia technology, saving of network bandwidth and copyright protection of multimedia content have gradually attracted people’s attention. The fragile watermark for integrity authentication of image data and protection of copyright has become a hotspot. In the storage and transmission process, image data must be compressed to save network bandwidth. As a result, semi-fragile watermarking techniques, which can be used to distinguish common image processing operations from malicious tampering, are emerging. In this paper, semi-fragile watermarking algorithms for image authentication are surveyed. The basic principles and characteristics about semi-fragile watermarking algorithms are introduced, and several kinds of attack behaviors are also included. Aiming at several typical image-authentication algorithms, advantages and disadvantages are analyzed, and evaluation indexes of various algorithms are compared. Finally, we analyze the key points and difficulties in the study on semi-fragile watermarking algorithms, and the direction about future development is prospected.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Survey of Denial-of-Service and Distributed Denial of Service Attacks and Defenses in Cloud Computing
by
Adrien Bonguet and Martine Bellaiche
Cited by 50 | Viewed by 12262
Abstract
Cloud Computing is a computing model that allows ubiquitous, convenient and on-demand access to a shared pool of highly configurable resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications and services). Denial-of-Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks are serious threats to the Cloud services’ availability
[...] Read more.
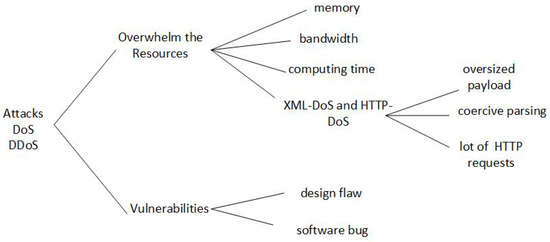
Cloud Computing is a computing model that allows ubiquitous, convenient and on-demand access to a shared pool of highly configurable resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications and services). Denial-of-Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks are serious threats to the Cloud services’ availability due to numerous new vulnerabilities introduced by the nature of the Cloud, such as multi-tenancy and resource sharing. In this paper, new types of DoS and DDoS attacks in Cloud Computing are explored, especially the XML-DoS and HTTP-DoS attacks, and some possible detection and mitigation techniques are examined. This survey also provides an overview of the existing defense solutions and investigates the experiments and metrics that are usually designed and used to evaluate their performance, which is helpful for the future research in the domain.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Security Enhancement for Data Migration in the Cloud
by
Jean Raphael Ngnie Sighom, Pin Zhang and Lin You
Cited by 31 | Viewed by 9172
Abstract
In today’s society, cloud computing has significantly impacted nearly every section of our lives and business structures. Cloud computing is, without any doubt, one of the strategic directions for many companies and the most dominating infrastructure for enterprises as long as end users.
[...] Read more.
In today’s society, cloud computing has significantly impacted nearly every section of our lives and business structures. Cloud computing is, without any doubt, one of the strategic directions for many companies and the most dominating infrastructure for enterprises as long as end users. Instead of buying IT equipment (hardware and/or software) and managing it themselves, many organizations today prefer to buy services from IT service providers. The number of service providers increase dramatically and the cloud is becoming the tools of choice for more cloud storage services. However, as more personal information and data are moved to the cloud, into social media sites, DropBox, Baidu WangPan, etc., data security and privacy issues are questioned. Daily, academia and industry seek to find an efficient way to secure data migration in the cloud. Various solution approaches and encryption techniques have been implemented. In this work, we will discuss some of these approaches and evaluate the popular ones in order to find the elements that affect system performance. Finally, we will propose a model that enhances data security and privacy by combining Advanced Encryption Standard-256, Information Dispersal Algorithms and Secure Hash Algorithm-512. Our protocol achieves provable security assessments and fast execution times for medium thresholds.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Feature-Based Image Watermarking Algorithm Using SVD and APBT for Copyright Protection
by
Yunpeng Zhang, Chengyou Wang, Xiaoli Wang and Min Wang
Cited by 20 | Viewed by 7978
Abstract
Watermarking techniques can be applied in digital images to maintain the authenticity and integrity for copyright protection. In this paper, scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) is combined with local digital watermarking and a digital watermarking algorithm based on SIFT, singular value decomposition (SVD), and
[...] Read more.
Watermarking techniques can be applied in digital images to maintain the authenticity and integrity for copyright protection. In this paper, scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) is combined with local digital watermarking and a digital watermarking algorithm based on SIFT, singular value decomposition (SVD), and all phase biorthogonal transform (APBT) is proposed. It describes the generation process of the SIFT algorithm in detail and obtains a series of scale-invariant feature points. A large amount of candidate feature points are selected to obtain the neighborhood which can be used to embed the watermark. For these selected feature points, block-based APBT is carried out on their neighborhoods. Moreover, a coefficients matrix of certain APBT coefficients is generated for SVD to embed the encrypted watermark. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed watermarking algorithm has stronger robustness than some previous schemes. In addition, APBT-based digital watermarking algorithm has good imperceptibility and is more robust to different combinations of attacks, which can be applied for the purpose of copyright protection.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Towards Incidence Management in 5G Based on Situational Awareness
by
Lorena Isabel Barona López, Ángel Leonardo Valdivieso Caraguay, Jorge Maestre Vidal, Marco Antonio Sotelo Monge and Luis Javier García Villalba
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 9938
Abstract
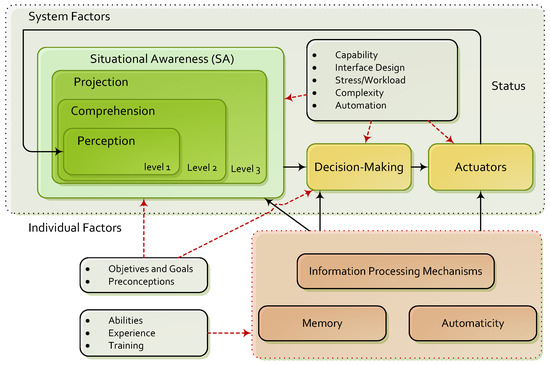
The fifth generation mobile network, or 5G, moves towards bringing solutions to deploying faster networks, with hundreds of thousands of simultaneous connections and massive data transfer. For this purpose, several emerging technologies are implemented, resulting in virtualization and self-organization of most of their
[...] Read more.
The fifth generation mobile network, or 5G, moves towards bringing solutions to deploying faster networks, with hundreds of thousands of simultaneous connections and massive data transfer. For this purpose, several emerging technologies are implemented, resulting in virtualization and self-organization of most of their components, which raises important challenges related to safety. In order to contribute to their resolution, this paper proposes a novel architecture for incident management on 5G. The approach combines the conventional risk management schemes with the Endsley Situational Awareness model, thus improving effectiveness in different aspects, among them the ability to adapt to complex and dynamical monitoring environments, and countermeasure tracking or the role of context when decision-making. The proposal takes into account all layers for information processing in 5G mobile networks, ranging from infrastructure to the actuators responsible for deploying corrective measures.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Key Technologies in the Context of Future Networks: Operational and Management Requirements
by
Lorena Isabel Barona López, Ángel Leonardo Valdivieso Caraguay, Marco Antonio Sotelo Monge and Luis Javier García Villalba
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 9781
Abstract
The concept of Future Networks is based on the premise that current infrastructures require enhanced control, service customization, self-organization and self-management capabilities to meet the new needs in a connected society, especially of mobile users. In order to provide a high-performance mobile system,
[...] Read more.
The concept of Future Networks is based on the premise that current infrastructures require enhanced control, service customization, self-organization and self-management capabilities to meet the new needs in a connected society, especially of mobile users. In order to provide a high-performance mobile system, three main fields must be improved: radio, network, and operation and management. In particular, operation and management capabilities are intended to enable business agility and operational sustainability, where the addition of new services does not imply an excessive increase in capital or operational expenditures. In this context, a set of key-enabled technologies have emerged in order to aid in this field. Concepts such as Software Defined Network (SDN), Network Function Virtualization (NFV) and Self-Organized Networks (SON) are pushing traditional systems towards the next 5G network generation.This paper presents an overview of the current status of these promising technologies and ongoing works to fulfill the operational and management requirements of mobile infrastructures. This work also details the use cases and the challenges, taking into account not only SDN, NFV, cloud computing and SON but also other paradigms.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
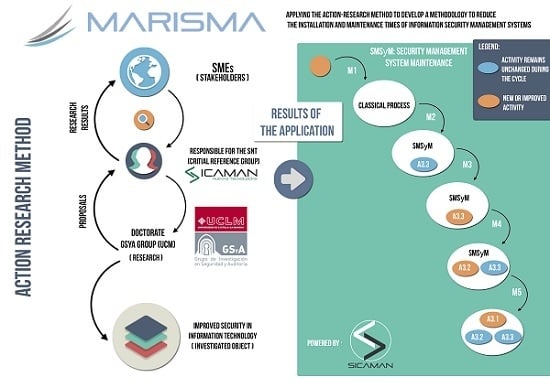
Open AccessArticle
Applying the Action-Research Method to Develop a Methodology to Reduce the Installation and Maintenance Times of Information Security Management Systems
by
Antonio Santos-Olmo, Luis Enrique Sánchez, David G. Rosado, Eduardo Fernández-Medina and Mario Piattini
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 8736
Abstract
Society is increasingly dependent on Information Security Management Systems (ISMS), and having these kind of systems has become vital for the development of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs). However, these companies require ISMS that have been adapted to their special features and have
[...] Read more.
Society is increasingly dependent on Information Security Management Systems (ISMS), and having these kind of systems has become vital for the development of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs). However, these companies require ISMS that have been adapted to their special features and have been optimized as regards the resources needed to deploy and maintain them, with very low costs and short implementation periods. This paper discusses the different cycles carried out using the ‘Action Research (AR)’ method, which have allowed the development of a security management methodology for SMEs that is able to automate processes and reduce the implementation time of the ISMS.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
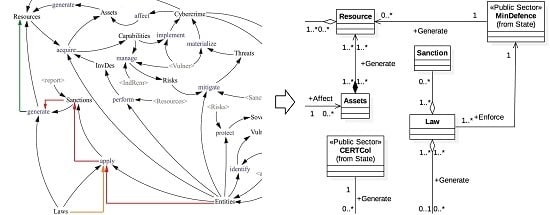
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of Dynamic Complexity of the Cyber Security Ecosystem of Colombia
by
Angélica Flórez, Lenin Serrano, Urbano Gómez, Luis Suárez, Alejandro Villarraga and Hugo Rodríguez
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 9493
Abstract
This paper presents two proposals for the analysis of the complexity of the Cyber security Ecosystem of Colombia (CEC). This analysis shows the available knowledge about entities engaged in cyber security in Colombia and the relationships between them, which allow an understanding of
[...] Read more.
This paper presents two proposals for the analysis of the complexity of the Cyber security Ecosystem of Colombia (CEC). This analysis shows the available knowledge about entities engaged in cyber security in Colombia and the relationships between them, which allow an understanding of the synergy between the different existing components. The complexity of the CEC is detailed from the view of the Influence Diagram of System Dynamics and the Domain Diagram of Software Engineering. The resulting model makes cyber security evident as a strategic component of national security.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
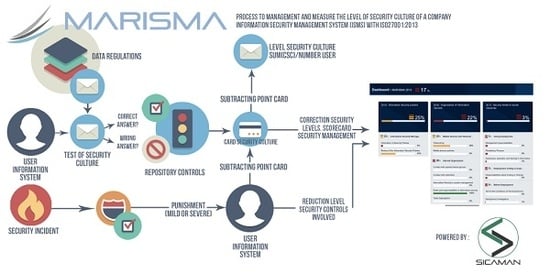
Open AccessArticle
The Importance of the Security Culture in SMEs as Regards the Correct Management of the Security of Their Assets
by
Antonio Santos-Olmo, Luis Enrique Sánchez, Ismael Caballero, Sara Camacho and Eduardo Fernandez-Medina
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 10995
Abstract
The information society is increasingly more dependent on Information Security Management Systems (ISMSs), and the availability of these kinds of systems is now vital for the development of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs). However, these companies require ISMSs that have been adapted to
[...] Read more.
The information society is increasingly more dependent on Information Security Management Systems (ISMSs), and the availability of these kinds of systems is now vital for the development of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs). However, these companies require ISMSs that have been adapted to their special features, and which are optimized as regards the resources needed to deploy and maintain them. This article shows how important the security culture within ISMSs is for SMEs, and how the concept of security culture has been introduced into a security management methodology (MARISMA is a Methodology for “Information Security Management System in SMEs” developed by the Sicaman Nuevas Tecnologías Company, Research Group GSyA and Alarcos of the University of Castilla-La Mancha.) for SMEs. This model is currently being directly applied to real cases, thus allowing a steady improvement to be made to its implementation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
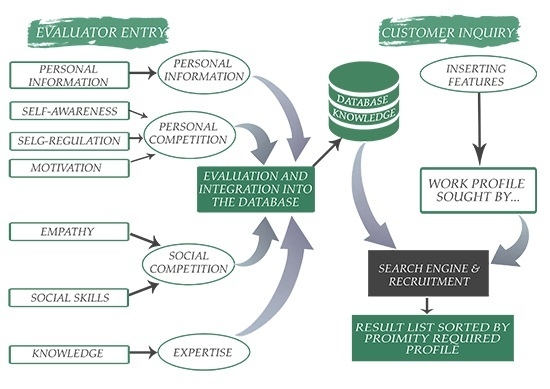
Development of an Expert System for the Evaluation of Students’ Curricula on the Basis of Competencies
by
Luis Enrique Sánchez, Antonio Santos-Olmo, Esther Álvarez, Monica Huerta, Sara Camacho and Eduardo Fernández-Medina
Cited by 21 | Viewed by 8473
Abstract
The concept of competence, which emerged during the reform of computer engineering degrees, has not brought benefits to companies when attempting to select the most suitable candidates for their jobs. This article aims to show some of the research that has been conducted
[...] Read more.
The concept of competence, which emerged during the reform of computer engineering degrees, has not brought benefits to companies when attempting to select the most suitable candidates for their jobs. This article aims to show some of the research that has been conducted to determine why companies have not found these skills useful and how both can be aligned. Finally, we show the development of an Expert System that will enable companies to select the most suitable candidates for their jobs, considering personal and social skills, along with technical knowledge. This prototype will serve as a basis to align the competencies defined in the curricula with professional requirements, thus allowing a true alignment between degree courses and the needs of professional companies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures