Simple Summary
The Marburg virus (MARV) causes a deadly hemorrhagic fever that can kill up to 100% of infected people. Following the first-ever Marburg virus disease outbreaks in the Kagera region of Tanzania, an ecological investigation was conducted between October 2023 and December 2024 to map Egyptian fruit bat (Rousettus aegyptiacus) populations, the known reservoir host of the Marburg virus. Five large cave-dwelling colonies (with approximately 100,000 individual Egyptian fruit bats) were identified within defined geospatial coordinates in the Kagera River Basin ecosystem. In collaboration with local authorities, we identified conservation threats and MARV transmission risks in the surveyed bat colonies. Confirmation of bat species was achieved through DNA barcoding of mitochondrial genes. This study represents the first molecular confirmation of R. aegyptiacus in major roosts. Bats roosting in cave mines face heightened threats due to human activities, particularly fumigation from burning tyres. These findings underscore the need for integrated conservation and public health strategies to mitigate MARV spillover risks and preserve bat populations.
Abstract
The Marburg virus (MARV) is a zoonotic pathogen that causes a high case fatality rate of up to 100% in humans. In response to Marburg virus disease (MVD) outbreaks in the Kagera region, an ecological investigation was initiated to map the population and ecological threat to the reservoir host of MARV: Egyptian fruit bats. The investigation conducted from October 2023 to December 2024 included interviews with local authorities to locate all known autochthonous bat colonies in the region. Bat species confirmation was performed using high-resolution melting analysis (HRMA) and DNA barcoding, targeting two mitochondrial genes: cytochrome oxidase 1 (COI) and 16S rRNA. We found five considerably large cave-dwelling Egyptian fruit bat colonies (with approximately 100,000 individuals) at the geolocations between 1°06′04.2″ and 2°26′35.8″ S latitude and 30°40′49.7″ and 31°51′19.8″ E longitude. The study also provides the first confirmed identification of Egyptian fruit bats (Rousettus aegyptiacus) (accession numbers: PV700530-PV700534) in major bat colonies in the Kagera River Basin ecosystem. Cave-dwelling Egyptian fruit bats in mines face higher risks, and thus, attention is needed to prevent this species from becoming more vulnerable to extinction. The loss of bat roosting sites and subsequent population declines are primarily driven by the destructive practice of burning car tyres and logs, a method used to eliminate colonies through toxic smoke and heat. The collection of guano and partially eaten fruits in mining caves, as well as daily contact with Egyptian fruit bats in mines, homes, and churches, have become major potential risk factors for MARV transmission to humans. Increased threats to bats in the Kagera region warrant the implementation of conservation strategies that ensure the survival of the bat populations and inform policies on MVD risk reduction in Tanzania and the broader East African region.
1. Introduction
The Marburg virus disease (MVD) is a zoonotic hemorrhagic fever with a case fatality rate ranging from 23% to 100%, caused by either the Marburg virus (MARV) or the Ravn virus, which are both recognized as having high pandemic potential [1,2,3]. The Egyptian fruit bat (Rousettus aegyptiacus) serves as the natural reservoir of MARV, with transmission occurring through direct contact with infected animals, humans, or contaminated materials [4]. Historically, MARV was first identified in 1967 during simultaneous outbreaks in Germany and Serbia, which were traced to laboratory contamination from African green monkeys (Cercopithecus aethiops) imported from Uganda for vaccine production [5]. Owing to its high lethality, rapid transmissibility, and absence of a licenced vaccine or specific treatment, MVD represents a substantial public health and biosecurity threat to humans, animals, and environmental health [6]. Current control strategies focus primarily on preventive measures, including community engagement to reduce contact between humans and reservoir hosts, supportive care and isolation of patients, and proper waste management [7]. Notably, several experimental interventions such as antiviral agents, monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies, vaccine candidates, and novel therapeutics, including small interfering RNA (siRNA) and interferon-β, have demonstrated potential when used alongside supportive care, highlighting the urgent need for continued research to inform effective prevention and treatment strategies [8].
The most recent outbreaks of MVD were reported in Equatorial Guinea in 2023, in Tanzania in 2023 and 2025, and in Rwanda in 2024 [7,9,10,11]. As with other MVD outbreaks in Sub-Saharan Africa, the index case of the Tanzanian MVD outbreaks appears to be linked to direct interactions with Egyptian fruit bats [3]. It is possible that consumption of fruits nibbled by Egyptian fruit bats, the collection of guano from caves, contact with domestic dogs involved in bat hunting, contact with dead bats struck by overhead electric lines and/or mining tin from caves that place humans in contact with the feces, urine and/or fomites of bats are the most likely sources of exposure from which these sporadic outbreaks occurred [12,13]. Locating Egyptian fruit bat roosting sites in the vicinity of these outbreaks could aid risk-based MARV surveillance and support bat conservation efforts against a common practice of culling [14].
Bats are important species in ecosystems as they serve as pest control, pollinators, material and nutrient distributors, and seed dispersers of economically important plants [15]. Worldwide, Egyptian fruit bats are considered pests by fruit growers and disease spreaders by miners; their roosting sites are often destroyed, and bats are killed [16,17,18]. This uncontrolled killing is perhaps intensified by widely held negative beliefs among local communities toward bats, which associate them with witchcraft, bad luck, and fear of viral zoonotic pathogens [16]. Local communities are further distressed by bat feces and urine, which often instigate roost destruction without considering the negative impacts on ecology following culling [16,19]. For instance, the largest Marburg virus-infected colony was estimated to contain over 100,000 individuals of bats at the Kitaka mine in Uganda before an extermination attempt in 2007; the population was reduced by 97.5% of the original colony size in 2012 [20,21]. Since then, the levels of active infection of Marburg virus and spillover into the human population have increased, probably due to the effects of extermination and subsequent recolonization of a pool of infected juvenile bats [20]. It is common in wildlife species that the prevalence of disease increases following the killing of the reservoir hosts as a form of disease control [22].
The population of Egyptian fruit bats within their geographical range is fairly stable and widely distributed. For this reason, Egyptian fruit bats are classified as of least concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature’s Red List of Threatened Species [23]. However, over 3500 vertebrate species, including those listed as being of least concern, are under high human-induced threats for extinction, and approximately 900 species have become extinct over the past 500 years [24]. For bats, 15% are threatened with extinction, 18% are data-deficient, and 57% constitute unknown population patterns. If this remains unattended, it may lead to a “Passenger Pigeon Fiasco” effect whereby a common and widespread species becomes extinct over time due to continuous culling and the lack of effective legal conservation structure [18].
Accurate bat species identification is essential for effective protection and conservation, and is commonly achieved through mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) analysis due to its species-specific markers [25]. Animal mtDNA is a small, circular molecule with a total of 37 genes, including 2 for rRNAs, 13 for proteins, and 22 for tRNAs, playing a vital role in mitochondrial functioning [26]. Common genetic markers for species identification include the cytochrome b (Cyt b) gene, cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 (COI), and the hypervariable domain II of the mtDNA D-loop region. High-resolution melting analysis (HRMA), combined with qPCR-HRM, has enhanced the specificity and sensitivity of species detection by distinguishing DNA variants based on melting profiles [27]. The HRMA effectively differentiates species by exploiting sequence and GC content differences, making it a rapid and reliable tool for identifying known and unknown DNA variants [28].
The ecological status of Egyptian fruit bats is largely unknown in Tanzania [19]. The absence of well-documented Egyptian fruit bat roosts amid the recent MVD outbreaks in the Kagera region poses surveillance challenges. Thus, continued efforts to locate Egyptian fruit bat roosts in the Kagera River Basin, the richest ecosystem to span several countries in East Africa, including Uganda, where MVD outbreaks have been frequently reported, are critical for effective surveillance, the zoonotic risk assessment of MVD, and implementation of bat conservation strategies [29]. As part of this study, we mapped Egyptian fruit bat roosts in the Kagera River Basin, confirmed the identity of Egyptian fruit bats using qPCRHRM, and identified key factors that threaten the bat population. The results obtained could inform policies on MVD risk reduction and the implementation of conservation strategies that ensure the survival of bat populations across Africa.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of Study Site
With increased ecological threats to wild animals in the Kagera River Basin ecosystem, no study has been undertaken to identify emerging threats to bat roosts [30]. These threats jeopardize the ecological balance and sustainability of the ecosystem, as well as the livelihoods of communities dependent on its resources [30,31]. Effective conservation and management are essential to ensure the long-term health and sustainability of this important ecosystem. The Kagera River Basin is a significant ecosystem located in East Africa, covering approximately 60,000 km2 and spanning several countries, including Burundi, Rwanda, Tanzania, and Uganda, as reviewed by Kinimi [3]. The surveys were carried out across seven districts in the sub-Tanzania Kagera River Basin ecosystem, namely Biharamulo, Bukoba Rural, Karagwe, Kyerwa, Missenyi, Muleba, and Ngara (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
A map of Tanzania showing Egyptian fruit bat roosting sites during the survey in seven districts of the Kagera region. The Kagera region is indicated by red shading. The largest and intermediate colonies of Egyptian fruit bats are marked by red stars and green cir cles, respectively.
2.2. Bat Roosting Sites Surveys
Driving, sailing, and walking surveys were conducted in caves, mines, riverbanks, abandoned buildings, residences, hospitals, churches, factories, and trees and bridges to determine roosting sites and anthropological threats to Egyptian fruit bats (Figure 2). Evidence of bat roosts in the form of actual bats (physically visible), bat droppings, urine staining, grease marks (oily secretions from glands present on stones and shrubs), and claw and teeth marks on fruits were examined and photographed. The Egyptian fruit bats were captured using mist nets and identified as previously described [32]. Sex and age were visually evaluated based on size, pelage colour, and reproductive status. Risk factors for Marburg transmission and anthropological threats to Egyptian fruit bats’ survival were recorded through direct observation and administration of a questionnaire.

Figure 2.
Surveys of daytime inspection of Egyptian fruit bat roosting sites along the Tanzania sub-Kagera River Basin ecosystem. Evidence of bat usage was observed at (A) Kagera River; (B) riverbanks; (C) caves on the riverbanks; (D) bridges; (E) caves and mines; and (F) bats on the roof rafters of churches and abandoned buildings.
2.3. Selection of Archived Bat Tissue Samples
We sampled 50 bat liver tissue specimens from five major colonies in the Kagera region (Figure 1), with 10 samples collected from each site: Chabyondogoro and Rwamapopo Caves in Kyerwa District, Kanyangeleko Cave in Bukoba Rural District, and Makinga and Rubya Caves in Muleba District. The samples were selected from a frozen, archived collection originally collected for Marburg virus (MARV) surveillance. Approximately 30 mg of tissue was obtained from bats that tested negative for MARV, with all specimens stored at −80 °C.
2.4. DNA Extraction
Total genomic DNA extraction was performed from 50 liver tissue samples (30 mg each) using the Quick-DNATM Miniprep Plus Kit (Zymo Research, Irvine, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s protocol, as previously described by Tafur-Culqui et al. [33]. Briefly, 95 μL of water, 95 μL of Solid Tissue Buffer, and 20 μL of proteinase K were added to each tissue sample in a microcentrifuge tube. The contents were mixed thoroughly and then incubated at 55 °C for 3 h to allow complete tissue digestion. To remove insoluble debris, the mixtures were centrifuged at 12,000× g for 1 min, and the aqueous supernatant was transferred to a clean microcentrifuge tube. A total of 400 μL of Genomic Binding Buffer was added to each tube and mixed thoroughly. The mixture was transferred to a Zymo-SpinTM IC-XM Column in a collection tube and centrifuged at 12,000× g for 1 min. The collection tubes with the flow-through were discarded. A total of 400 μL of DNA Pre-Wash Buffer was added to the column in a new collection tube and centrifuged for 1 min. The flow-through was discarded; 700 μL of g-DNA Wash Buffer was added and centrifuged for 1 min, and the collection tube was emptied. Thereafter, 200 μL of g-DNA Wash Buffer was added and centrifuged for 1 min. The collection tubes with the flow through were discarded. To elute the DNA, the Zymo-SpinTM IC-XM Column was transferred to a clean microcentrifuge tube and 50 μL of the DNA Elution Buffer was added, incubated for 5 min at room temperature, and then centrifuged for 1 min. The concentration of eluted DNA extracts was measured using a NanodropTM 1000 Spectrophotometer (Waltham, MS, USA). The eluted DNA was stored at −20 °C for downstream genetic testing.
2.5. qPCR-HRM Bat Species Profiling
A total of 50 DNA extracts were analyzed for sequence variations based on their melting characteristics using real-time polymerase chain reaction high-resolution melting (qPCRHRM) for the mitochondrial (mtDNA) genes, COI, and 16S rRNA. Briefly, a reaction mixture volume of 20 μL for qPCR was prepared, each comprising 4 μL of a 5× HOT FIREPol EvaGreen HRM Mix (Solis BioDyne company, Tartu, Estonia), 0.5 μL of reverse and forward primers each, 1 μL dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), 4 μL of DNA template, and 10 μL of nuclease-free water. The primers described here were used in our previous study [27]. For internal control, each run used a negative control containing a 17 μL master mix and 3 μL of nuclease-free water. qPCR-HRM cycling was performed on a Magnetic Induction Cycler (MIC) qPCR (Biomolecular Systems, Brisbane, Australia), as previously described [34]. The qPCR-HRM on MIC had one cycle of initial activation at 95 °C for 2 min followed by 28 cycles that each comprised up to 3 steps: denaturation at 95 °C for 15 s, annealing at 56 °C for 20 s, and elongation at 72 °C for 30 s. The final elongation was performed at 72 °C for 5 min. Immediately after the qPCR amplification, the HRM step was performed with two holding times: 95 °C for 15 s and 75 °C for 30 s, followed by a gradual increase in the temperature of 0.1 °C per second up to 95 °C, while recording fluorescence every 2 s. The HRM sequence variants were differentiated by melting temperature (Tm) and the shapes of their melt curves, and samples with similar differential melting profiles were considered to constitute a group of the same species of origin. Melt curve profiles analysis was performed using MIC-qPCR Software (version 2.8). To accurately confirm high-resolution melting analysis (HRMA) results, we randomly selected two HRM variants from each of the five major bat caves for nucleotide sequencing.
2.6. Sequencing, Bat Species Authentication, and Analyses
To identify the bat species, DNA samples corresponding to selected qPCR-HRM variants were used in conventional PCR to amplify the COI gene of mtDNA. Briefly, PCR nucleotide amplification was performed using the OneTaq 2X master mix with standard buffer (M0482) (Biolabs, Hertfordshire, UK). The reaction mixture of 25 μL contained 2 μL of template DNA, 12.5 μL of OneTaq 2X Master Mix, 0.5 μL of forward primer (VF1d: TCT CAA CCA ACC ACA ARG AYA TYG G), 0.5 μL of reverse primer (VR1d: TAG ACT TCT GGG TGG CCR AAR AAY CA), and 9.5 μL of nuclease-free water in a 0.2 mL microtube. The PCR cycling conditions were designated by Ouso et al. [28]. The quality of PCR amplification products was analyzed on a 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis. The successful 750 bp amplicons were submitted for Sanger sequencing at Macrogen (Meibergdree 57, 1105 BA, Amsterdam, The Netherlands). Thereafter, PCR amplicons were purified and sequenced using the BigDye Terminator Cycle Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) with a genetic analyzer (ABI 3730xl System, Applied Biosystems). A total of 10 raw sequence datasets were analyzed using Geneious Prime software version 2024.0.5. The consensus sequences were input as nucleotide sequences to search for bat species identity in GenBank (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on: 22 April 2025) using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool for nucleotides (BLASTn). Typically, a sequence similarity of ≥99% with a top species match was used to determine the species of origin. The evolutionary history and species comparisons were determined using the Maximum Likelihood approach. In accordance with Akaike Information Criterion (AICc), the best substitution model GTR + I with an AICc value of 4553.85 was employed. Phylogenetic analyses were performed in MEGA XI with 1000 replications [35]. Data collected from the questionnaires were entered and analyzed using Microsoft Office Excel 2010 (Microsoft, Mountain View, CA, USA) and Epi Info version 7.0.8.0 (CDC, Atlanta, GA, USA).
2.7. Recruitment of Study Participants
The rationale behind this survey was explained to all participants, and verbal consent was obtained. A structured questionnaire was administered to 280 residents of the village inhabited by Egyptian fruit bats in seven districts of the Kagera region. Government officials and supervisors at the local tin mining company were consulted about appropriate questions regarding the handling of bats in the caves. Participants were first evaluated by local community health workers and village chairpersons, who determined their ability to speak and respond in Kiswahili, because some of the miners arrived from neighbouring countries (Burundi, Democratic Republic of Congo, Rwanda, Uganda, and China). Those who failed to understand Kiswahili and English were interviewed in their local dialects by a local investigative team formed during the survey. Participants were asked about their entry into and activities within the mines, caves, their exposure to fruits eaten by bats, and bat extermination attempts. We directly observed and recorded anthropological threats to bat colonies and their habitats.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Geolocations of Major Egyptian Fruit Bat Roosting Sites
A total of five considerably large colonies of Egyptian fruit bats were identified in the Kagera region (Table 1). The largest colonies were in the range of one hundred thousand individual bats. Equally, thousands of Egyptian fruit bats were found in the Kitaka mine and Python cave in Uganda, likely due to their similar equatorial climate [21,36]. On the eastern slope of Lake Victoria, we found the three largest colonies, namely in the Rubya and Makinga caves and Kanyangeleko cave, that are located in the indigenous flora of the Muleba and Bukoba rural districts, respectively (Figure 1). Interestingly, the Kanyangeleko cave was found in a village where the Marburg virus disease outbreak in Tanzania was first reported in humans, suggesting a likely source of the virus [10]. The Chabyondogoro and Rwamapopo mine caves are located in Kyerwa district, which borders Uganda in the north and Rwanda in the west on the slope of the Kagera River (Figure 1). With increasing interactions of Egyptian fruit bats between colonies and their close proximity to MARV-infected bat colonies in Uganda relative to Northwestern Tanzania, the Kagera River Basin ecosystem, with its sufficient supply of fruit trees, crops, and suitable sites for bat roosting, remains at risk of harboring infected bats with subsequent spillover to the human population [36,37].

Table 1.
Geolocations of the largest colonies of Egyptian fruit bats in the Kagera region, Northwestern Tanzania.
3.2. High-Resolution Melting Profiles
The DNA melting temperature and melt curves were used to determine sequence variation across 50 bat tissue samples. The analysis of melting profiles during the HRM screening of COI and 16S rRNA amplicons revealed similar melting profiles, suggesting a single bat species. Equally, vertebrates of the same species exhibited identical melting patterns [27].
3.3. Nucleotide Amplification
Analysis of the COI PCR amplicons on agarose gel electrophoresis exhibited strong PCR bands of expected size (~750 bp), confirming successful amplification of the target DNA gene (Figure 3).

Figure 3.
Gel electrophoresis of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification products of Egyptian fruit bats captured within the Kagera River Basin ecosystem in Tanzania. The PCR amplicons indicate an expected band size of around 750 bp in line with primer targets. Please find the original figure in Figure S1.
3.4. Bat Species Authentication
The melting curves of 16 S rRNA and COI gene markers of bat tissue samples generated similar HRM profiles (peak and shape), suggesting a single bat species (Figure 4). Similarly, HRM successfully differentiated 10 domestic and 24 wildlife animal species that are common in East African illegal wildlife products [28]. The DNA sequences obtained in this study (PV700530-PV700534) matched with sequences currently available at GenBank and the Barcode of Life Data System, with a high degree of nucleotide identity up to 100%. Phylogenetic analyses of COI barcode sequences are clustered with the Egyptian fruit bat (Rousettus aegyptiacus) from Sub-Saharan Africa (Figure 5). This preliminary investigation confirms the presence of a single bat species (Rousettus aegyptiacus) inhabiting large roosts in the Kagera region. A genetic divergence of less than 2% was observed at the nucleotide level among Rousettus aegyptiacus from East Africa. In contrast, previous studies have demonstrated that the Rousettus aegyptiacus species of Mediterranean origin is often regarded as a separate and endemic species due to its 10% mtDNA divergence at the nucleotide level from Sub-Saharan populations [38]. Thus, geographical conservation and protection are required to preserve the uniqueness of bat distribution. Egyptian fruit bat authentication data are largely absent in Tanzania and across Africa. Previous studies in Tanzania elucidated the movements of fruit bats (Eidolon helvum) and seed dispersal in Eastern Tanzania, in which bats were shown to disperse 20% of the local submontane forest trees in East Usambara Mountains for long distances, three times further than African elephants [39].

Figure 4.
Differential melting profiles of bat species identified from 50 bat tissue samples using (a) 16S rRNA and (b) COI gene markers. These profiles represent sequencing results from representative DNA samples across major bat colonies in the Kagera region. Specifically, high-resolution melting profiles (a,b) correspond to Egyptian fruit bats (Rousettus aegyptiacus) upon DNA sequencing.

Figure 5.
Phylogenetic tree of the representative COI sequences derived from archived bat tissue samples collected from major bat colonies in the sub-Tanzania Kagera River Basin ecosystem (marked by shaded triangles). The phylogeny shows the clustering of COI sequences corresponding to a single bat species: Rousettus aegypticus (Egyptian fruit bat).
3.5. African Egyptian Fruit Bat Birthing Seasons
In December 2023, almost all female Egyptian fruit bats captured at the Kanyangeleko cave carried an infant, whilst bats at the Rubya and Makinga caves were pregnant. Most females had a single pup, except for five females that were found to have twins (14.7%). Equally, previous studies have caught lactating mothers in May and June and also in November for East African Egyptian fruit bats [37]. As with the East African Egyptian fruit bats, the pregnancies in this survey were evident from May to September and from October to February regarding reproductive cycles [37]. At Chabyondogoro and Rwamapopo mines, we observed a large number of juvenile Egyptian fruit bats, suggesting different birthing seasons between Egyptian fruit bats in the Kagera River Basin ecosystem. Similarly, a previous study in Uganda at the Kitaka mine showed a comparable pattern with birthing seasons observed in August and February, whilst the breeding seasons were observed in May and November [36]. In contrast, seasonal monoestry has been described in South African Egyptian fruit bats [40]. Normally, the gestation period takes 3.5 to 4 months, the pups are weaned between 6 and 10 weeks old, and they become independent of their mothers at the age of 9 months [41,42].
3.6. Study Participants at High-Risk for MARV Exposure
A total of 280 participants residing in villages inhabited by Egyptian fruit bat colonies were interviewed. Since tin deposits attract energetic young males from the surrounding villages, districts, and neighbouring countries, most participants were men (86%) aged between 21 and 48 years. Virtually all (100%) of the tin miners at Chabyondogoro and Kyerwa Syndicate mines (Rwamapopo) were males. Similarly, during the MVD survey at the gold deposits in Durba in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, over 90% of the underground miners were young males [43]. With a high proportion of infection in male miners and cave-goers without clear evidence for person-to-person transmission, this suggests that the local mines and caves are sites of primary infection with MARV, most likely through exposure to a natural reservoir, such as the Egyptian fruit bats in the DRC [43].
3.7. Potential Human Risk Behaviour Associated with Human–Bat Interaction
Over 88% of study participants reported direct contact with bats and that they have consumed fruits (avocado, banana, giant passion fruit, mangoes, Mivule fruit, pawpaws, and other local wild fruits) that had been partially eaten by bats, posing a risk for the transmission of zoonotic pathogens to humans (Figure 6). Previous studies demonstrated that the consumption of fruit tested by Egyptian fruit bats is a risk factor for MARV spillover into humans and susceptible wildlife animal species, as the virus remains infectious for about 6 h on discarded fruits [44,45]. A total of 157 participants (56%) had collected manure (guano) from the cave to fertilize their maize and tomato farms, or they had sold bat fertilizers to horticulture farmers in the nearby towns (Figure 6). It was reported that bat manure costs TZS 3500 (USD 1.4) per 20 L bucket. The fertilizers were collected without personal protective equipment. This underpins increased risk behaviour among study participants because Egyptian fruit bats can shed several zoonotic pathogens, including MARV [44]. We also observed dogs moving up and down in the Kanyangeleko cave, hunting for bats, which emerged from the cave contaminated with blood. Two hours later, the same dog was found eating leftovers and drinking water using domestic utensils left outside of the residence near the cave, posing a high risk of contracting rabies and other zoonotic pathogens and subsequent transmission to humans. It was further observed that vervet monkeys (Chlorocebus pygerythrus) interact directly with discarded fruits by Egyptian fruit bats, which increases the possibility of zoonotic disease amplification and spillover to humans. Equally, zoonotic spillover events on nibbled fruits have been reported in Tanzania and elsewhere [14,45]. Most respondents (97%) were not aware of the importance of Egyptian fruit bats in the ecosystem and their potential in the transmission of MVD. Similarly, previous studies have shown that over half of the study participants had poor knowledge of the risk factors associated with bat exposure [46,47]. The lack of knowledge of ecosystem services that Egyptian fruit bats provide in the Kagera River Basin ecosystem may hinder the implementation of conservation efforts and drive the persecution of bat colonies.

Figure 6.
Images showing evidence of human interaction with Egyptian fruit bats, (A,B) including actual bats in the cave and in the building, respectively; (C) bat droppings, urine stains, and grease marks on shrubs in farms; (D) bat feces collected for use as a fertilizer in maize and tomato farms; and (E) claw and teeth marks on avocado fruits.
3.8. Key Anthropogenic Threats to Egyptian Fruit Bat Colonies
We recorded a large number of human-induced threats to bat populations in the Kagera region, such as habitat loss, disturbances, and persecution using burning car tyres and exploitation for food and manure (Figure 7). The loss of roosts due to mining, agriculture, and urbanization is the main threat faced by Egyptian fruit bats in the region (Figure 8). The Egyptian fruit bats are very sensitive to human-induced disturbance, habitat modification, and the destruction of their roosts, especially in communal and maternity roosts, where they form large aggregations [19]. Regrettably, the effect of deforestation on bats in Africa remains rare and data-deficient [48]. Previous studies have demonstrated that agricultural expansion remains a major threat in the IUCN’s Red List evaluations for over 55% of threatened bat species [23]. The agriculture sector reduces bat populations mainly through the constriction of foraging sites and a reduction in roosting cover for most bat species. Hunting for bushmeat was reported as the lowest threat to bats (Figure 7). This is primarily practised by non-indigenous miners, in particular, those from China, Burundi, DRC, Rwanda, and Uganda. Given the large size of Egyptian fruit bats (>300 g body mass) and accessible large colonies, hunting may intensify in the future. Recent studies have revealed that bat hunting for food has disproportionately affected half of fruit bat populations globally [49]. In addition, less-known anthropogenic threats affecting the bat population were determined, including persecution by burning car tyres and electrocution by electric lines.
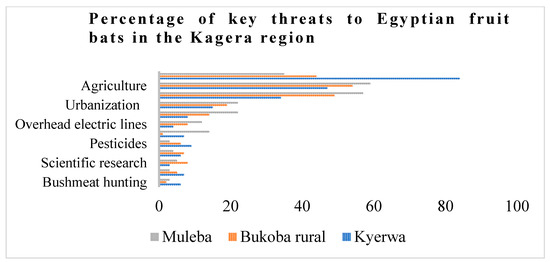
Figure 7.
The proportion of threats to Egyptian fruit bats in the Kagera region, including Muleba, Bukoba, and Kyerwa districts.

Figure 8.
Images showing ecological threats to bat roosts in the Kagera region. (A) Conversion of forested area at the cave to agricultural landscape; (B,C) replacement of natural bat fruits with timber and coffee plantations; (D) mining in caves after killing bats using burning car tyres and pesticides; (E) buildings on the top of caves; and (F) riverbank landslides.
3.9. Persecution Using Burning Car Tyres in Mines
We found Egyptian fruit bat colonies in caves and mines under intense pressure from direct threats (Figure 7). One instance was the killing of bats using burning car tyres and logs. In addition, the remaining habitats are threatened by logging and agricultural expansions (Figure 8). At the Murongo tin mine on the border of Southern Uganda, thousands of dead Egyptian fruit bats were found piled outside of two caves, and there was no evidence of bats living in them. Miners were reported to have killed them using burning car tyres and logs, and the exits were sealed with logs and soil. The destructive distillation of car tyres and logs releases intense heat and carbon monoxide, leading to hypoxia and death. Destroyed bat roosts are then converted into goat pens. However, another large colony of Egyptian fruit bats was found at Chabyondogoro cave, located about three kilometres away from the pile of dead bats, which requires immediate conservation attention. Similarly, other studies have shown that bat species that live in large numbers in caves and mines are mostly vulnerable to direct mortality threats; the loss of large roosts can have a disproportionate impact on bat ecology [19,20]. In contrast, priority habitats such as caves represent manageable and high-impact targets for conservation efforts [19]. When effectively protected, these sites can play a critical role in preventing bat species extinctions. Identifying both shared and species-specific threats and corresponding mitigation strategies enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of conservation resource allocation.
3.10. Electrocution by Overhead Electric Lines
We found 24 dead bats due to electrocution by overhead electric lines passing over the Kanyangeleko cave (Figure 8). Previous studies have demonstrated the impact of overhead electric lines on different bat species [16,50,51]. Thus, a larger field survey on bat electrocution is needed to properly estimate daily electrocution rates in Tanzania and elsewhere. Exploring how long dead bats persist in hanging from electric wires, the proportion of dead bats falling to the ground, and their removal by scavengers, as well as seasonal variations in mortality rates, are central issues for bat preservation.
4. Conclusions
This study provides the first confirmed identification of Rousettus aegyptiacus within major roosting sites and systematically documents key ecological threats to bat populations in the Kagera River Basin ecosystem of Tanzania. Thus, it is very important to identify threats, increase conservation education campaigns, develop effective policies, and forge ethical conservation strategies for species both designated as threatened and species of lowest concern that may be exposed to emerging threats. Future research should inform our present understanding of the extent of threats and their impacts on each bat species, their vulnerabilities across species and habitats, their distribution, and persistence in roosts. A larger field study is needed to better quantify the level of threats to each bat species and assess their zoonotic potential.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/zoonoticdis5040030/s1, Figure S1: The original figure of Figure 3.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.K. and G.M.; methodology, E.K.; software, E.K.; validation, E.K.; formal analysis, E.K. and G.M.; investigation, E.K., G.M., L.J.-Y., L.J.-S., L.H.-Y., and M.S.Y.; resources, L.J.-Y., L.J.-S., L.H.-Y., and M.S.Y.; data curation, E.K. and G.M.; writing—original draft preparation, E.K. and G.M.; writing—review and editing, L.J.-Y., L.J.-S., L.H.-Y., and M.S.Y.; visualization, E.K. and G.M.; supervision, G.M., L.J.-Y., L.J.-S., L.H.-Y., and M.S.Y.; project administration, G.M., L.J.-Y., L.J.-S., L.H.-Y., and M.S.Y.; funding acquisition, G.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Korea National Institute of Health, with a grant awarded to the SACIDS Foundation for One Health of the Sokoine University of Agriculture (Grant No. KNIH-SACIDS 2023).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Research clearance for mapping Egyptian fruit bat roosting sites and conducting sampling in the Kagera region was granted by the Sokoine University of Agriculture on behalf of the Tanzania Commission for Science and Technology (Reference Number: SUA/DPRTC/R/160/24), approved on: 10 October 2023. The involvement of human subjects received ethical approval from the Tanzania Medical Research Coordinating Committee of the National Institute for Medical Research (Ref.: NIMR: HQ/R.8a/Vo1.IX/3891), approved on: 26 January 2022.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was sought from local government officials, supervisors at the local tin mining company, and participating villagers after the study’s purpose was explained and translated into local languages. Informed consent was obtained was obtained from all subjects involved in this study.
Data Availability Statement
The bat nucleotide datasets sequenced in this study are publicly available at GenBank (accession numbers: PV700530-PV700534) and can be accessed from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their sincere gratitude to the Korea National Institute of Health (KNIH) for funding provided to the SACIDS Foundation for One Health to support surveillance of epidemic viral hemorrhagic fevers in the Kagera River Basin ecosystem. Special thanks go to Mark Rweyemamu, the SACIDS Executive Director, and the late Leonard Mboera for pioneering Korean research collaborations. We are indebted to Jacqueline Weyer and Janusz T. Paweska for their valuable guidance on the significance of Marburg virus surveillance in Egyptian fruit bats within Marburg virus disease hotspots. We also extend our sincere thanks to the International Livestock Research Institute through the Capacitating One Health in Eastern and Southern Africa Initiatives for providing permission to Zikankuba Sijali to participate in the identification and sampling of Egyptian fruit bats in the Kagera River Basin ecosystem. We are thankful to our research team, Baraka Ngingo, Kato Elias, Medes Antony, and Jovin Burchard, as well as animal health community workers, for assisting with bat netting. Our thanks also go to Ramadhani Amiri for his long-hour drive of the 4 × 4-wheel drive Mobile Genomic Laboratory during bat roost searches and sampling. We are grateful to Népomuscène Hakizimana for his valuable assistance in map preparation and Mwinyi Masala for his technical support in the laboratory during bat species identification. We are thankful to Mariam Makange, Ester Kasisi and Lawrence Mapunda for their involvement in laboratory logistics and testing of MARV from bat tissue samples. We are also grateful to government officials in the Kagera region for their security support and endorsement to carry out mapping of Egyptian fruit bat roosting sites and subsequent sampling in their areas of jurisdiction.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors report no potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Shifflett, K.; Marzi, A. Marburg Virus Pathogenesis—Differences and Similarities in Humans and Animal Models. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedenkopf, N.; Bukreyev, A.; Chandran, K.; Di Paola, N.; Formenty, P.B.H.; Griffiths, A.; Hume, A.J.; Mühlberger, E.; Netesov, S.V.; Palacios, G.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Filoviridae 2024. J. Gen. Virol. 2024, 105, 001955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinimi, E. Marburg Virus Disease in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Review of Currently Available Comprehensive Genomic Data up to 2024. Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauburger, K.; Hume, A.J.; Mühlberger, E.; Olejnik, J. Forty-Five Years of Marburg Virus Research. Viruses 2012, 4, 1878–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luby, J.P.; Sanders, C.V. Green Monkey Disease (“Marburg Virus” Disease): A New Zoonosis. Ann. Intern. Med. 1969, 71, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, D.; Kutikuppala, L.V.S.; Shanker, P.; Sahoo, R.N.; Pattnaik, G.; Dash, R.; Kandi, V.; Ansari, A.; Mishra, S.; Desai, D.N.; et al. The Neglected Continuously Emerging Marburg Virus Disease in Africa: A Global Public Health Threat. Health Sci. Rep. 2023, 6, e1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muvunyi, C.M.; Ngabonziza, J.C.S.; Bigirimana, N.; Ndembi, N.; Siddig, E.E.; Kaseya, J.; Ahmed, A. Evidence-Based Guidance for One Health Preparedness, Prevention, and Response Strategies to Marburg Virus Disease Outbreaks. Diseases 2024, 12, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musafiri, S.; Siddig, E.E.; Nkuranga, J.B.; Rukundo, A.; Mpunga, T.; Sendegeya, A.; Twagirumugabe, T.; Ahmed, A.; Muvunyi, C.M. Emerging Strategies and Progress in the Medical Management of Marburg Virus Disease. Pathogens 2025, 14, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butera, Y.; Mutesa, L.; Parker, E.; Muvunyi, R.; Umumararungu, E.; Ayitewala, A.; Musabyimana, J.P.; Olono, A.; Sesonga, P.; Ogunsanya, O.; et al. Genomic and Transmission Dynamics of the 2024 Marburg Virus Outbreak in Rwanda. Nat. Med. 2024, 31, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mmbaga, V.; Mrema, G.; Ngenzi, D.; Magoge, W.; Mwakapasa, E.; Jacob, F.; Matimba, H.; Beyanga, M.; Samweli, A.; Kiremeji, M.; et al. Epidemiological Description of Marburg Virus Disease Outbreak in Kagera Region, Northwestern Tanzania. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0309762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezie, K.N.; Takoutsing, B.D.; Modeste, D.; Ines, M.Z.; Sybile, T.N.L.; Caleb, N.M.; Esene, I.N. Marburg Virus Outbreak in Equatorial Guinea: Need for Speed. Ann. Glob. Health 2024, 90, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amman, B.R.; Jones, M.E.B.; Sealy, T.K.; Uebelhoer, L.S.; Schuh, A.J.; Bird, B.H.; Coleman-McCray, J.D.; Martin, B.E.; Nichol, S.T.; Towner, J.S. Oral Shedding of Marburg Virus in Experimentally Infected Egyptian Fruit Bats (Rousettus aegyptiacus). J. Wildl. Dis. 2015, 51, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugavel, B.; Kandula, S.; Somanathan, H.; Kelber, A. Home Ranges, Directionality and the Influence of Moon Phases on the Movement Ecology of Indian Flying Fox Males in Southern India. Biol. Open 2023, 12, bio059513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecino-Latorre, D.; Goldstein, T.; Gilardi, K.; Wolking, D.; Van Wormer, E.; Kazwala, R.; Ssebide, B.; Nziza, J.; Sijali, Z.; Cranfield, M.; et al. Reproduction of East-African Bats May Guide Risk Mitigation for Coronavirus Spillover. One Health Outlook 2020, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasso, M.; Balakrishnan, M. Ecological and Economic Importance of Bats (Order Chiroptera). Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 2013, 187415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’shea, T.J.; Cryan, P.M.; Hayman, D.T.S.; Plowright, R.K.; Streicker, D.G. Multiple Mortality Events in Bats: A Global Review. Mammal Rev. 2016, 46, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, C.C.; Kingston, T. Bats in the Anthropocene. In Bats in the Anthropocene: Conservation of Bats in a Changing World; Voigt, C.C., Kingston, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–9. ISBN 978-3-319-25220-9. [Google Scholar]
- Tanalgo, K.; Tabora, J.A.; Hughes, A. Bat Cave Vulnerability Index (BCVI): A Holistic Rapid Assessment Tool to Identify Priorities for Effective Cave Conservation in the Tropics. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, W.F.; Kingston, T.; Flanders, J. A Review of the Major Threats and Challenges to Global Bat Conservation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1469, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amman, B.R.; Nyakarahuka, L.; McElroy, A.K.; Dodd, K.A.; Sealy, T.K.; Schuh, A.J.; Shoemaker, T.R.; Balinandi, S.; Atimnedi, P.; Kaboyo, W.; et al. Marburgvirus Resurgence in Kitaka Mine Bat Population after Extermination Attempts, Uganda. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1761–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towner, J.S.; Amman, B.R.; Sealy, T.K.; Carroll, S.A.R.; Comer, J.A.; Kemp, A.; Swanepoel, R.; Paddock, C.D.; Balinandi, S.; Khristova, M.L.; et al. Isolation of Genetically Diverse Marburg Viruses from Egyptian Fruit Bats. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ham, C.; Donnelly, C.A.; Astley, K.L.; Jackson, S.Y.B.; Woodroffe, R. Effect of Culling on Individual Badger Meles Meles Behaviour: Potential Implications for Bovine Tuberculosis Transmission. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 56, 2390–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korine, C. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species: Rousettus Aegyptiacus. In IUCN Red List Threatened Species; International Union for Conservation of Nature: Gland, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ceballos, G.; Ehrlich, P.R.; Barnosky, A.D.; García, A.; Pringle, R.M.; Palmer, T.M. Accelerated Modern Human–Induced Species Losses: Entering the Sixth Mass Extinction. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1400253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaout, Y.; Djelouadji, Z.; Robardet, E.; Cappelle, J.; Cliquet, F.; Touzalin, F.; Jimenez, G.; Hurstel, S.; Borel, C.; Picard-Meyer, E. Genetic Identification of Bat Species for Pathogen Surveillance across France. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boore, J.L. Animal Mitochondrial Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dule, E.J.; Kinimi, E.; Bakari, G.G.; Max, R.A.; Lyimo, C.M.; Mushi, J.R. Species Authentication in Meat Products Sold in Kilosa District in Tanzania Using HRM-Enhanced DNA Barcoding. J. Für Verbraucherschutz Leb. 2025, 20, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouso, D.O.; Otiende, M.Y.; Jeneby, M.M.; Oundo, J.W.; Bargul, J.L.; Miller, S.E.; Wambua, L.; Villinger, J. Three-Gene PCR and High-Resolution Melting Analysis for Differentiating Vertebrate Species Mitochondrial DNA for Biodiversity Research and Complementing Forensic Surveillance. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasso, G.; Grodus, M.; Valencia, E.; DeJesus, V.; Liang, E.; Delwel, I.; Bortz, R.H.; Lupyan, D.; Ehrlich, H.Y.; Castellanos, A.A.; et al. Decoding the Blueprint of Receptor Binding by Filoviruses through Large-Scale Binding Assays and Machine Learning. Cell Host Microbe 2025, 33, 294–313.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, M.; Ma, B.; Wang, B. Grid-Scale Impact of Climate Change and Human Influence on Soil Erosion within East African Highlands (Kagera Basin). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolo, C.U.; Majule, E.A.; Perfect, J. Changing Trends of Natural Resources Degradation in Kagera Basin: Case Study of Kagera Sub-Basin, Uganda. Nat. Resour. 2012, 3, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingdon, J. The Kingdon Pocket Guide to African Mammals, 2nd ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-0-691-20352-2. [Google Scholar]
- Tafur-Culqui, J.; Calderon, M.S.; Bustamante, D.E. Identification of Commercial Meats from Amazonas, Peru Using PCR-RFLP of Mitochondrial 12S rRNA Gene. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2020, 23, e2019274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suluba, E.; Masaganya, J.; Liang, W.; Masala, M.; Mbugi, E.; Mselle, T.; Majani, N.; Kubhoja, S.; Mutayoba, B.M.; Shuwei, L. TBX 5 Gene Mutation Analysis among Tanzanian Children with Congenital Heart Diseases Using High-Resolution Melting Assays. Anat. J. Afr. 2022, 11, 2240–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amman, B.R.; Carroll, S.A.; Reed, Z.D.; Sealy, T.K.; Balinandi, S.; Swanepoel, R.; Kemp, A.; Erickson, B.R.; Comer, J.A.; Campbell, S.; et al. Seasonal Pulses of Marburg Virus Circulation in Juvenile Rousettus Aegyptiacus Bats Coincide with Periods of Increased Risk of Human Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okia, N.O. Reproductive Cycles of East African Bats. J. Mammal. 1987, 68, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benda, P.; Vallo, P.; Hulva, P.; Horáček, I. The Egyptian Fruit Bat Rousettus Aegyptiacus (Chiroptera: Pteropodidae) in the Palaearctic: Geographical Variation and Taxonomic Status. Biologia 2012, 67, 1230–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seltzer, C.E.; Ndangalasi, H.J.; Cordeiro, N.J. Seed Dispersal in the Dark: Shedding Light on the Role of Fruit Bats in Africa. Biotropica 2013, 45, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, R.T.F.; Tsita, J.N. Seasonally Monoestrous Reproduction in the Molossid Bat, Tadarida Aegyptiaca from Low Temperate Latitudes (33°S) in South Africa. S. Afr. J. Zool. 1995, 30, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutere, F.A. The Breeding Biology of the Fruit Bat Rousettus Aegyptiacus E. Geoffroy Living at o Degrees 22’S. Acta Trop. 1968, 25, 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg, M.; Nissan, Y.; Yovel, Y. Egyptian Fruit Bat Rousettus Aegyptiacus (Geoffroy, 1810). In Handbook of the Mammals of Europe; Hackländer, K., Zachos, F.E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–26. ISBN 978-3-319-65038-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bausch, D.G.; Nichol, S.T.; Muyembe-Tamfum, J.J.; Borchert, M.; Rollin, P.E.; Sleurs, H.; Campbell, P.; Tshioko, F.K.; Roth, C.; Colebunders, R.; et al. Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever Associated with Multiple Genetic Lineages of Virus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amman, B.R.; Schuh, A.J.; Albariño, C.G.; Towner, J.S. Marburg Virus Persistence on Fruit as a Plausible Route of Bat to Primate Filovirus Transmission. Viruses 2021, 13, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randhawa, N.; Bird, B.H.; VanWormer, E.; Sijali, Z.; Kilonzo, C.; Msigwa, A.; Ekiri, A.B.; Samson, A.; Epstein, J.H.; Wolking, D.J.; et al. Fruit Bats in Flight: A Look into the Movements of the Ecologically Important Eidolon Helvum in Tanzania. One Health Outlook 2020, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musila, S.; Prokop, P.; Gichuki, N. Knowledge and Perceptions of, and Attitudes to, Bats by People Living around Arabuko-Sokoke Forest, Malindi-Kenya. Anthrozoös 2018, 31, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninsiima, L.R.; Nyakarahuka, L.; Kisaka, S.; Atuheire, C.G.K.; Mugisha, L.; Odoch, T.; Romano, J.S.; Klein, J.; Mor, S.M.; Kankya, C. Knowledge, Perceptions, and Exposure to Bats in Communities Living around Bat Roosts in Bundibugyo District, Uganda: Implications for Viral Haemorrhagic Fever Prevention and Control. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, C.F.J.; Struebig, M.J.; Willig, M.R. Responses of Tropical Bats to Habitat Fragmentation, Logging, and Deforestation. In Bats in the Anthropocene: Conservation of Bats in a Changing World; Voigt, C.C., Kingston, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 63–103. ISBN 978-3-319-25220-9. [Google Scholar]
- Mickleburgh, S.; Waylen, K.; Racey, P. Bats as Bushmeat: A Global Review. Oryx 2009, 43, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tella, J.L.; Hernández-Brito, D.; Blanco, G.; Hiraldo, F. Urban Sprawl, Food Subsidies and Power Lines: An Ecological Trap for Large Frugivorous Bats in Sri Lanka? Diversity 2020, 12, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidemann, C.R.; Nelson, J.E. Life Expectancy, Causes of Death and Movements of the Grey-Headed Flying-Fox (Pteropus Poliocephalus) Inferred from Banding. Acta Chiropterologica 2011, 13, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).