- Article
The Evolution of Mechatronics Engineering and Its Relationship with Industry 3.0, 4.0, and 5.0
- Eusebio Jiménez López,
- Juan Enrique Palomares Ruiz and
- José Guadalupe Castro Lugo
- + 3 authors
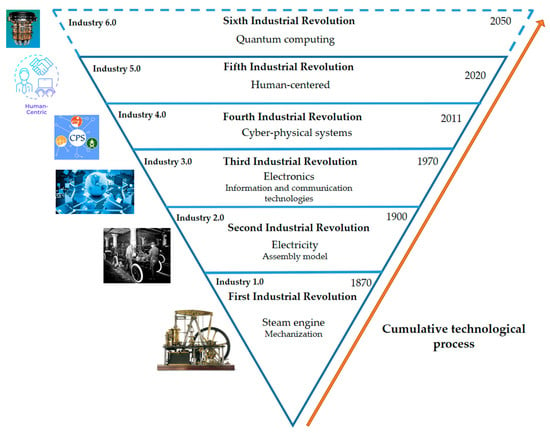
Mechatronics developed under the influence of the Third Industrial Revolution and was a discipline that provided methods and tools for the development of industrial robots, advanced machine tools, mobile phones, and automobiles, among other sophisticated products. With the emergence of Industry 4.0 in 2011, mechatronics has become indispensable, as traditional production systems are being transformed into cyber-physical systems (CPS), some of which are composed of sophisticated technologies such as Digital Twins (DT) and sophisticated robots, among others. In 2020, the Fifth Industrial Revolution began, giving rise to so-called Human Cyber-Physical Systems (HCPS) and promoting the use of Cobots in industries. Because today’s industrial world is influenced by three active industrial revolutions and two transitions, it is possible to find machines and production systems that were designed with different principles and for different purposes, making it necessary to propose a classification that allows each system to be located according to the premises of its respective industrial revolution. This article analyzes the evolution of mechatronics and proposes a classification of machines and production systems based on the premises of each industrial revolution. The objective is to determine the influence of mechatronics on the different types of machines that exist today and analyze its implications.
26 January 2026