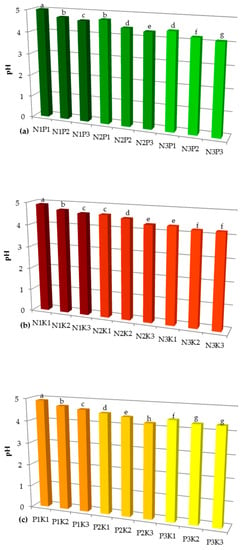
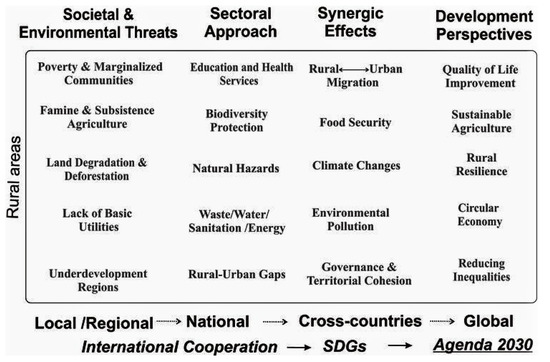
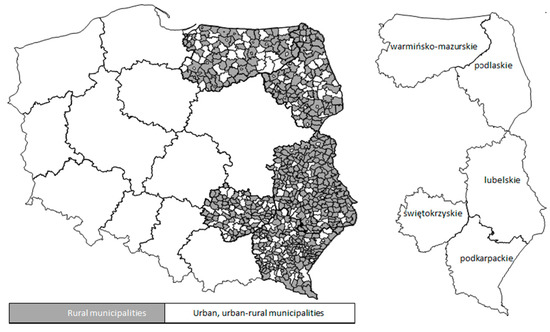
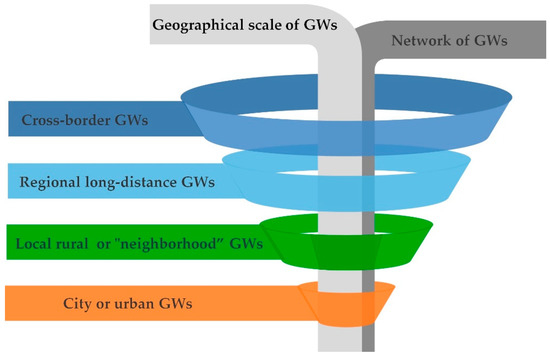
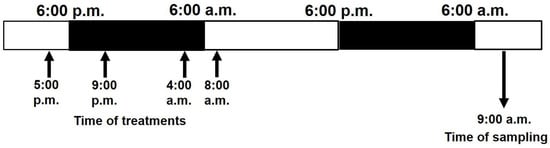
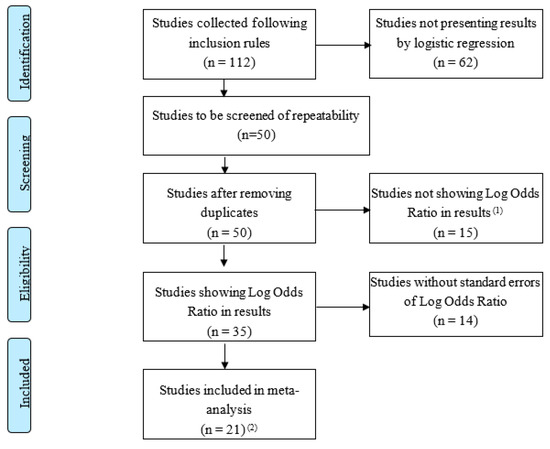
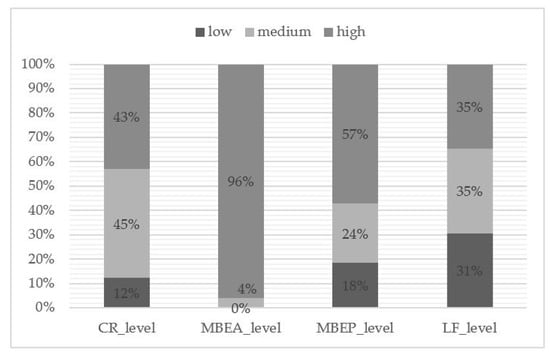
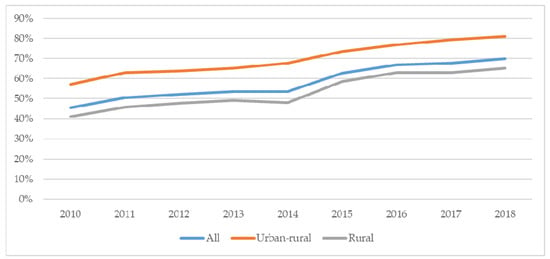
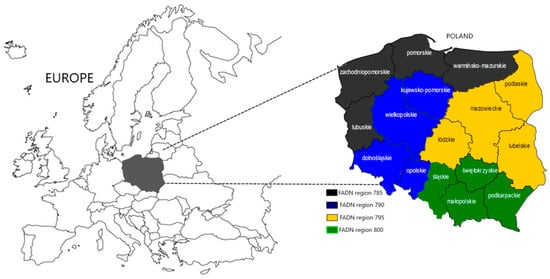
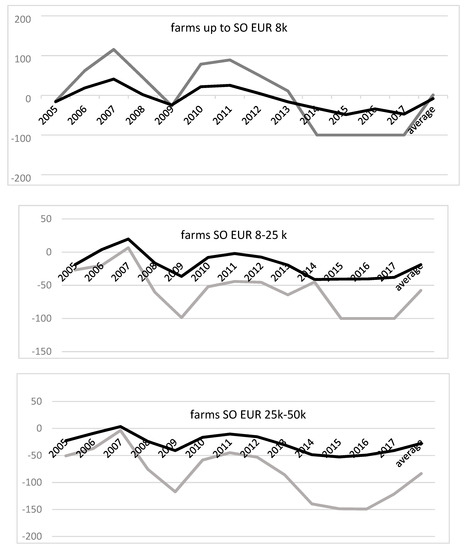
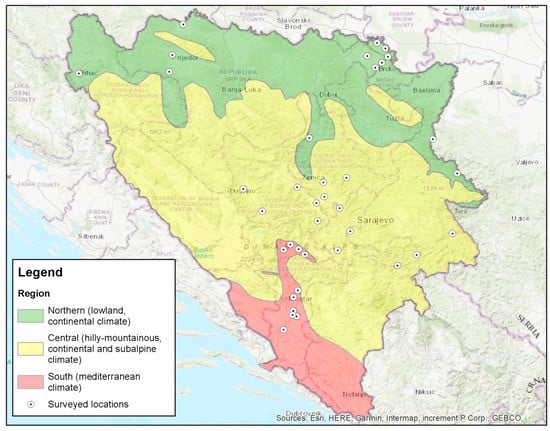
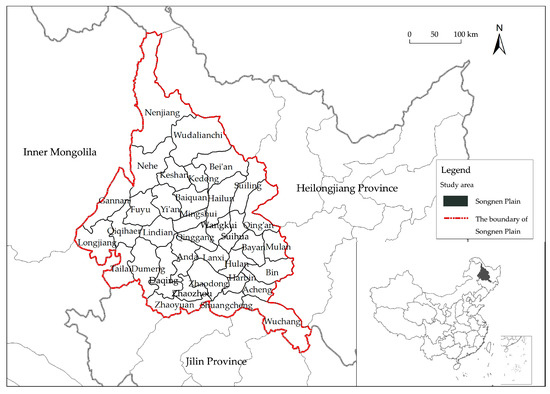
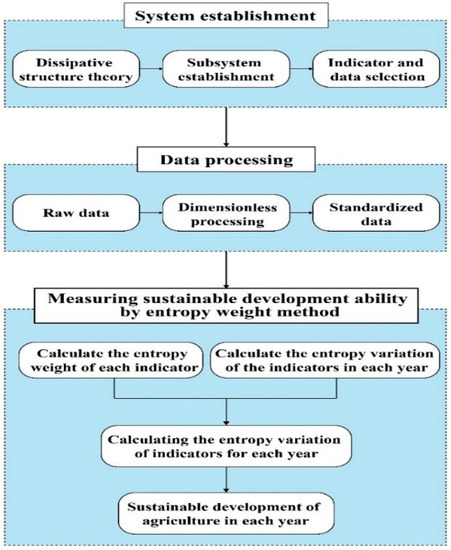
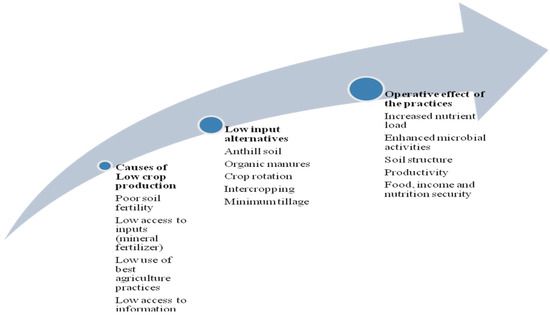
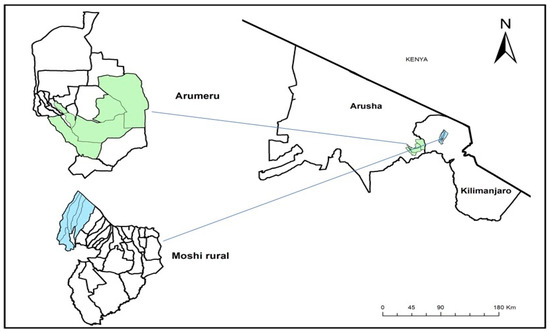
Sustainable Development of Rural Areas and Agriculture
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050).
Viewed by 459468Editor
Interests: sustainable development; sustainable development of rural areas and agriculture; education for sustainable development; rural advisory services; agricultural knowledge and innovation systems (AKIS); diffusion and adoption of innovations in rural areas; multifunctional development of rural areas; entrepreneurship; non-agricultural entrepreneurship in rural areas; horizontal and vertical integration in the food sector and agriculture; formation and operation of agricultural producer groups
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
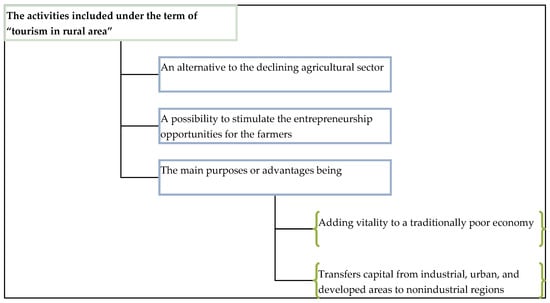
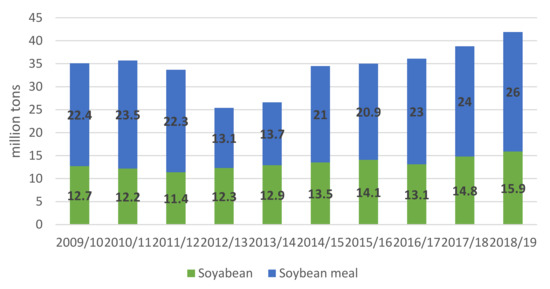
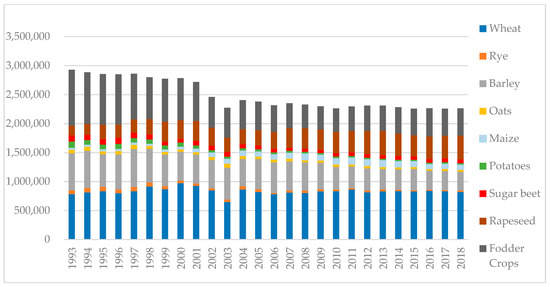
Rural areas and agriculture play a significant role in the economy around the world. They are the settings for the life and work of a large part of society, and such areas produce food, as well as the non-food raw materials used in many branches of industry and in the energy sectors. Unfortunately, the development of rural areas and agriculture has generated many problems related to the lack of balance of economic, social, and ecological factors.
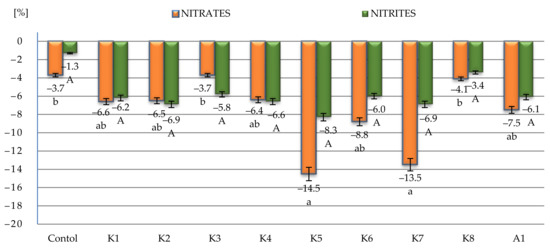
The rapid development of industrial agriculture in highly developed countries has created ecological threats and social problems. This type of agriculture has contributed to the generation and accumulation of environmental pollution. Among the consequences of increased agricultural production, including the increased use of chemical fertilizers and chemical plant protection products, is the accumulation of their residues throughout the food chain and, consequently, in food consumed by people. Nitrogen emissions in groundwater, rivers, and lakes have led to their eutrophication. The introduction of field monocultures has resulted in the impoverishment of biological diversity. Work-saving techniques and production technologies have undermined the economic existence of small farms. Economic conditions and quality of life have deteriorated in many rural communities, which has led to a negative migration balance in and depopulation of many rural areas.
The contemporary picture of agriculture and rural areas will undergo subsequent changes. The evolutionary nature of their development is a natural process, caused by the need to adapt to the changing reality, as well as the economic and social environment. It is important, therefore, due to the close connection between agriculture and natural resources, for this Special Issue to become a collection of scientific papers and valuable recommendations that will help to design and propose a model for the sustainable development of rural areas and agriculture that will guarantee economic development in equilibrium and harmony with social expectations and the requirements of the natural environment.
Prof. Dr. Piotr Prus
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Sustainable development of rural areas
- Sustainable agriculture
- Organic agriculture
- Agricultural biodiversity
- Climate change
- Mitigation of climate change
- Adaptation to climate change
- R&D programs for sustainable development of rural areas and agriculture
- Public policies for development of rural areas and agriculture
- The role of rural advisory services in supporting the sustainable development of rural areas and agriculture
- The role of agricultural knowledge and innovation systems (AKIS) in facilitating the sustainable development of rural areas and agriculture
- The role of ecological education (at the vocational and university level, as well as formal and informal programs) for the sustainable development of rural areas
- Sustainable food production
- Sustainable production of agricultural non-food raw materials
- Sustainable production of agricultural energy resources
- Sustainable yield increase
- Markets and the preservation of agricultural diversity
- Sustainable food marketing and new product development
- Consumer behavior and food sustainability