- Article
An Interpretable Residual Spatio-Temporal Graph Attention Network for Multiclass Emotion Recognition from EEG
- Manal Hilali,
- Abdellah Ezzati and
- Ahmed El Badaoui
- + 1 author
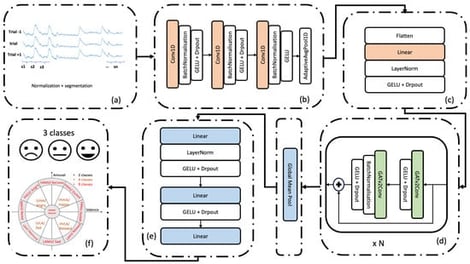
Automatic emotion recognition based on EEG has been a key research frontier in recent years, involving the direct extraction of emotional states from brain dynamics. However, existing deep learning approaches often treat EEG either as a sequence or as a static spatial map, thereby failing to jointly capture the temporal evolution and spatial dependencies underlying emotional responses. To address this limitation, we propose an Interpretable Residual Spatio-Temporal Graph Attention Network (IRSTGANet) that integrates temporal convolutional encoding with residual graph-attention blocks. The temporal module enhances short-term EEG dynamics, while the graph-attention layers learn adaptive node connectivity relationships and preserve contextual information through residual links. Evaluated on the DEAP and SEED datasets, the proposed model achieved exceptional performance on valence and arousal, as well as four-class and nine-class classification on the DEAP dataset and on the three-class SEED dataset, exceeding state-of-the-art methods. These results demonstrate that combining temporal enhancement with residual graph attention yields both improved recognition performance and interpretable insights into emotion-related neural connectivity.
5 February 2026