Journal Description
Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on the etiology, development, and elimination of pathological processes, published quarterly online by MDPI (since Volume 21, Issue 1 - 2020). The International Society for Pathophysiology (ISP) is affiliated with Pathophysiology, serving as its official journal. Society members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, PMC, PubMed, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Pathology) / CiteScore - Q2 (Pathology and Forensic Medicine)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 27.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 6.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Impact Factor:
2.6 (2024)
Latest Articles
The Paradoxical Effect of Cannabis Use on Cognition in Chronic Psychotic Disorders
Pathophysiology 2026, 33(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology33010011 - 27 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Cannabis use has a particularly high prevalence in individuals with psychotic disorders. Although cannabis use is generally associated with cognitive impairments in the general population, its impact on cognition in psychosis remains controversial. This study aimed to investigate the association between cannabis
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Cannabis use has a particularly high prevalence in individuals with psychotic disorders. Although cannabis use is generally associated with cognitive impairments in the general population, its impact on cognition in psychosis remains controversial. This study aimed to investigate the association between cannabis use and cognitive performance in a cohort of individuals affected by psychotic disorders. Methods: A total of 105 inpatients with psychotic disorders (mean age: 40.3 years; 34 females) were recruited from the University Hospital Center “Mother Teresa” in Tirana. Data collection included socio-demographic and clinical variables. Cognitive functioning was evaluated using the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), while psychopathology was assessed with the Brief Negative Symptom Scale (BNSS), the Calgary Depression Scale for Schizophrenia (CDSS), the Psychotic Symptom Rating Scales (PSYRATS), and the Scale for the Assessment of Thought, Language, and Communication (TLC). Results: Cannabis users (CU) were more frequently male, younger, and exhibited an earlier onset of psychosis compared to non-users (No-CU). Importantly, CU demonstrated higher MoCA scores, with the most favorable outcomes observed among daily users. Conclusions: Contrary to the prevailing assumption that cannabis use exacerbates cognitive decline, our findings indicate an unexpected association between cannabis use and preserved cognitive functioning in psychosis. These results underscore the need to consider dosage, frequency, and cannabinoid composition (THC/CBD ratio) when interpreting cannabis-related cognitive outcomes in psychotic disorders.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Neurodegenerative Disorders)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Bridging the Gap Between Static Histology and Dynamic Organ-on-a-Chip Models
by
Zheyi Wang, Keiji Naruse and Ken Takahashi
Pathophysiology 2026, 33(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology33010010 - 21 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
For more than a century, pathology has served as a cornerstone of modern medicine, relying primarily on static microscopic assessment of tissue morphology—such as H&E staining—which remains the “gold standard” for disease diagnosis. However, this conventional paradigm provides only a snapshot of disease
[...] Read more.
For more than a century, pathology has served as a cornerstone of modern medicine, relying primarily on static microscopic assessment of tissue morphology—such as H&E staining—which remains the “gold standard” for disease diagnosis. However, this conventional paradigm provides only a snapshot of disease states and often fails to capture their dynamic evolution and complex functional mechanisms. Moreover, animal models are constrained by marked interspecies differences, creating a persistent gap in translational research. To overcome these limitations, we propose the concept of New Pathophysiology, a research framework that transcends purely morphological descriptions and aims to resolve functional dynamics in real time. This approach integrates Organ-on-a-Chip (OOC) technology, multi-omics analyses, and artificial intelligence to reconstruct the entire course of disease initiation and to enable personalized medicine. In this review, we first outline the foundations and limitations of traditional pathology and animal models. We then systematically summarize more than one hundred existing OOC disease models across multiple organs—including the kidney, liver, and brain. Finally, we elaborate on how OOC technologies are reshaping the study of key pathological processes such as inflammation, metabolic dysregulation, and fibrosis by converting them into dynamic, mechanistic disease models, and we propose future perspectives in the field. This review adopts a relatively uncommon classification strategy based on pathological mechanisms (mechanism-based), rather than organ-based categorization, allowing readers to recognize shared principles underlying different diseases. Moreover, the focus of this work is not on emphasizing iteration or replacement of existing approaches, but on preserving past achievements from a historical perspective, with an emphasis on overcoming current limitations and enabling new advances.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Novel Insights into the Enigmatic Genetics of Male Breast Cancer in China
by
Guan-Tian Lang, Xiao-Ling Weng, Yun Liu, Xin Hu, Zhi-Ming Shao and Zhen Hu
Pathophysiology 2026, 33(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology33010009 - 20 Jan 2026
Abstract
Objectives: The molecular characterization of male breast cancer (MaBC) has long been understudied, primarily due to its rare occurrence. Clinical management of MaBC remains profoundly challenging, with current therapeutic strategies largely extrapolated from female breast cancer protocols. Methods: Through panel-based sequencing targeting BRCA1
[...] Read more.
Objectives: The molecular characterization of male breast cancer (MaBC) has long been understudied, primarily due to its rare occurrence. Clinical management of MaBC remains profoundly challenging, with current therapeutic strategies largely extrapolated from female breast cancer protocols. Methods: Through panel-based sequencing targeting BRCA1, BRCA2, and PALB2 variants, we delineated the genomic landscape of 96 MaBC cases. Subsequent whole-exome sequencing (WES) of 84 BRCA1/2- and PALB2-mutation-negative MaBC patients, compared against 4480 healthy controls, revealed compelling findings. Results: Pathogenic variants in BRCA1/2 and PALB2 were identified in 14.6% (14/96) of MaBC cases, with BRCA2 mutations predominating at 12.5% (n = 12). Notably, one patient harbored the BRCA1 c.4015G > T stop-gained mutation, while another exhibited the PALB2 c.481_482dupGA alteration. Our analysis further uncovered 170 pathogenic/likely pathogenic mutations, with RAD50, DMD, ARSA, and ABCC6 demonstrating recurrent mutations in MaBC. Conclusions: As the inaugural germline genomic investigation of MaBC in a Han Chinese population, this work reveals clinically actionable alterations with diagnostic and therapeutic implications. These discoveries not only advance our understanding of MaBC’s molecular architecture but also underscore the critical need for dedicated research into this malignancy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Feature Papers in Pathophysiology)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Cannabidiol–Ion Channel Interactions Represent a Promising Preventive and Therapeutic Strategy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
by
María de Guadalupe Chávez-López, Arturo Avalos-Fuentes, Estrella del C. Cruz-Manzo, Pedro A. Aguirre-Arriaga, Benjamín Florán, Julio Isael Pérez-Carreón, Cecilia Bañuelos and Javier Camacho
Pathophysiology 2026, 33(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology33010008 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the main type of liver cancer and one of the malignancies with the highest mortality rates worldwide. HCC is associated with diverse etiological factors including alcohol use, viral infections, fatty liver disease, and liver cirrhosis (a major risk factor
[...] Read more.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the main type of liver cancer and one of the malignancies with the highest mortality rates worldwide. HCC is associated with diverse etiological factors including alcohol use, viral infections, fatty liver disease, and liver cirrhosis (a major risk factor for HCC). Unfortunately, many patients are diagnosed at advanced stages of the disease and receive palliative treatment only. Therefore, early markers of HCC and novel therapeutic approaches are urgently needed. The endocannabinoid system is involved in various physiological processes such as motor coordination, emotional control, learning and memory, neuronal development, antinociception, and immunological processes. Interestingly, endocannabinoids modulate signaling pathways involved in cell survival, proliferation, apoptosis, autophagy, and immune response. Consistently, several cannabinoids have demonstrated potential antitumor properties in experimental models. The participation of metabotropic and ionotropic cannabinoid receptors in the biological effects of cannabinoids has been extensively described. In addition, cannabinoids interact with other targets, including several ion channels. Notably, several ion channels targeted by cannabinoids are involved in inflammation, proliferation, and apoptosis in liver diseases, including HCC. In this literature review, we describe and discuss both the endocannabinoid system and exogenous phytocannabinoids, such as cannabidiol and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, along with their canonical receptors, as well as the cannabidiol-targeted ion channels and their role in liver cancer and its preceding liver diseases. The cannabidiol-ion channel association is an extraordinary opportunity in liver cancer prevention and therapy, with potential implications for several environments that are for the benefit of cancer patients, including sociocultural, public health, and economic systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Early Rod Dysfunction Influences Cone Development in a Rhodopsin P23H Mouse Model of Retinitis Pigmentosa
by
Alicia A. Brunet, Annie L. Miller, Xin Ru Lim, Alan R. Harvey and Livia S. Carvalho
Pathophysiology 2026, 33(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology33010007 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The RhoP23H/WT mouse line is a commonly used model to study rhodopsin P23H-associated autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Previous studies in RhoP23H/WT mice have largely focused on retinal changes occurring at one month of age and later, and have indicated
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The RhoP23H/WT mouse line is a commonly used model to study rhodopsin P23H-associated autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Previous studies in RhoP23H/WT mice have largely focused on retinal changes occurring at one month of age and later, and have indicated a compensatory thickening of inner retinal layers in response to rod degeneration. However, the effect of disease processes during early postnatal retinal development remains understudied. Methods: In this study, we investigated the retinal response to rod dysfunction during early postnatal developmental ages P8–P24 in our novel RhoP23H/WT reporter line, RhoP23H.GFP, which expresses green fluorescent protein (GFP) exclusively in cone photoreceptors. Results: Histological analysis revealed no significant difference in retinal thickness in RhoP23H.GFP mice compared to healthy controls at the ages investigated. RhoP23H.GFP retinas initially exhibited a greater mislocalization of rhodopsin to the rod cell bodies at P12, though this mislocalization normalized to wildtype by P24. Most notably, flow cytometry revealed significantly increased cone photoreceptor numbers in P12 (61%), P16 (48%), and P24 (40%) RhoP23H.GFP mice compared to wildtype controls, indicating a possible compensatory response of cone photoreceptors to rod dysfunction. Additionally, cone morphology appeared altered in diseased cones. Conclusions: Our results suggest that cones may undergo a developmental compensatory adaptation in response to rod dysfunction, providing new insights into early disease mechanisms of retinitis pigmentosa.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Neurodegenerative Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Paranasal Sinus CT and Polysomnographic Findings in Adults with Cystic Fibrosis: Implications for Obstructive Sleep Apnea
by
Matthias Welsner, Sarah Dietz-Terjung, Svenja Strassburg, Dirk Westhölter, Sivagurunathan Sutharsan, Christoph Schöbel, Christian Taube, Florian Stehling, Cornelius Kürten, Cornelius Deuschl, Michael Forsting, Sebastian Zensen, Johannes Haubold, Benedikt M. Schaarschmidt and Marcel Opitz
Pathophysiology 2026, 33(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology33010006 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
Objective: To assess whether chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) severity is associated with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in adult people with cystic fibrosis (pwCF). Methods: We conducted a retrospective single-center study of 44 adults with CF who underwent overnight polysomnography (PSG), Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS)
[...] Read more.
Objective: To assess whether chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) severity is associated with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in adult people with cystic fibrosis (pwCF). Methods: We conducted a retrospective single-center study of 44 adults with CF who underwent overnight polysomnography (PSG), Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) assessment, and sinus computed tomography (CT). CRS severity was quantified using the Lund–Mackay score (LMS) and the main nasal cavity score (MNCS). OSA was defined by Apnea–Hypopnea Index (AHI) thresholds per American Academy of Sleep Medicine criteria. Results: Participants had a mean age of 31.1 ± 8.4 years and a mean percent predicted FEV1 of 51.8 ± 15.7. Sinus CT showed radiological evidence of CRS in all participants. Mean AHI was 5.3 ± 4.4/h; 48% had AHI ≥ 5/h. There were no significant differences between pwCF with and without OSA in age, sex, BMI, lung function, total sleep time, sleep efficiency, or ESS score (all p > 0.05). Mean LMS and MNCS did not differ between OSA and non-OSA groups (both p > 0.05), and neither score correlated with PSG parameters or ESS (all p > 0.05). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis demonstrated low discriminative ability of LMS and MNCS for predicting OSA (AUCs < 0.70, p < 0.05). Conclusions: In this cohort of adults with CF, CT-based CRS severity was not associated with OSA. Given the substantial prevalence of OSA observed, PSG screening should be considered irrespective of CRS severity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Obstructive Sleep Apnea Phenotypes: First Decade of Exploration and Beyond)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Is Obesity a Modifiable Risk Factor in Multiple Sclerosis? Mechanistic Insights into Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Damage
by
Fani-Niki Varra, Olga Pagonopoulou, Michail Varras, Viktoria-Konstantina Varra and Panagiotis Theodosis-Nobelos
Pathophysiology 2026, 33(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology33010005 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune inflammatory disorder of the central nervous system (CNS) that leads to demyelination of CNS neurons and is influenced by genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, including diet and obesity. Methods: This review aims to
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune inflammatory disorder of the central nervous system (CNS) that leads to demyelination of CNS neurons and is influenced by genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, including diet and obesity. Methods: This review aims to analyze at the molecular level the relationship between obesity, as a chronic inflammatory condition, and the pathophysiology of MS, as a chronic autoimmune inflammatory disease, in order to understand the complex links between obesity and MS through a search of the PubMed and Google Scholar databases. Discussion: Chronic inflammation and OS are interconnected processes, causing a toxic state, which contributes to the development of CNS neuroinflammation and neuronal damage, resulting in neuronal demyelination and the onset of MS. Adipose tissue is a complex endocrine organ; in addition to being a lipid storage organ, it secretes cytokines and adipokines, which are involved in the regulation of hormones, metabolism, inflammation, and whole-body homeostasis. Obesity triggers chronic low-grade inflammation, disruption of the blood–brain barrier (BBB) and brain metabolism, infiltration of the CNS by immune cells, production of ROS, and generation of oxidative stress (OS). Anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory adipokines are also implicated in MS and obesity. Conclusions: Obesity affects MS through common underlying mechanisms and seems to be a modifiable risk factor. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds with multi-functional characteristics could be additional tools to slow the progression of MS and its promotion through obesity while also offering potential treatment options for both conditions via their multi-targeting characteristics.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Metabolic Syndrome-Driven Changes in Cardiac Lymphatic Endothelium: mRNA Expression and Emerging Questions
by
Ewa Jankowska-Steifer, Anna Ratajska, Aleksandra Flaht-Zabost, Dorota Magdalena Radomska-Leśniewska, Iwona Badurek, Ewelina Kiernozek, Aneta Moskalik, Barbara Majchrzak, Mateusz Bartkowiak, Krzysztof Bartkowiak, Bogdan Ciszek, Marek Kujawa and Justyna Niderla-Bielinska
Pathophysiology 2026, 33(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology33010004 - 9 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Metabolic syndrome (MetS) conditions lead to structural and functional alterations in cardiomyocytes, microvasculature, and extracellular matrix (ECM), leading to myocardial fibrosis and impaired diastolic function. Cardiac lymphatic vessels (LVs) are increasingly recognized as key regulators of myocardial homeostasis, yet their response
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Metabolic syndrome (MetS) conditions lead to structural and functional alterations in cardiomyocytes, microvasculature, and extracellular matrix (ECM), leading to myocardial fibrosis and impaired diastolic function. Cardiac lymphatic vessels (LVs) are increasingly recognized as key regulators of myocardial homeostasis, yet their response to MetS remains poorly understood. Therefore, we aimed to investigate transcriptional changes in cardiac lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) in db/db mice, a well-established model of MetS. Methods: Using flow cytometry-sorted LECs and RT-PCR, we analyzed mRNA expression of genes involved in lymphangiogenesis, metabolism, mechanotransduction, immune cell trafficking, and ECM interactions. Results: Our findings show the transcriptional plasticity of cardiac LECs in response to MetS. Conclusions: Although our study is limited by the lack of protein-level validation and functional assays, our approach provides a broader interpretative framework and identifies potential directions for future research, including functional studies and pathway-specific investigations of the identified genes to assess their impact on lymphatic flow and cardiac function. Understanding LEC responses to metabolic stress may uncover novel therapeutic targets for heart failure associated with MetS.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Sleep Disorders in Climacteric Women: Glutathione, Glutathione S-Transferase P1 and Gut Microbiome Interrelation
by
Natalya Semenova, Nadezhda Garashchenko, Olga Nikitina, Sergey Kolesnikov, Natalia Belkova, Elizaveta Klimenko, Nadezhda Smurova, Elizaveta Novikova, Irina Madaeva and Liubov Kolesnikova
Pathophysiology 2026, 33(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology33010003 - 26 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Menopause, a critical period during a woman’s life, is characterized by various changes, including disturbances in their oxidative balance and circadian rhythm. Currently, the gut microbiome is suggested as an important participant in these processes. Methods: This study involved 96
[...] Read more.
Background: Menopause, a critical period during a woman’s life, is characterized by various changes, including disturbances in their oxidative balance and circadian rhythm. Currently, the gut microbiome is suggested as an important participant in these processes. Methods: This study involved 96 menopausal women. Their sleep quality was assessed using three questionnaires: the Insomnia Severity Index (ISI), the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), and the Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS). The GSH and GSTP1 contents in the serum were measured by means of immunoassay methods, while the composition of the gut microbiome was determined via molecular genetic methods. Results: E. coli, K. oxytoca, S. aureus, Enterobacter spp., Shigella spp., Streptococcus spp., Prevotella spp., and M. stadmanae were found to correlate with the GSH content in different sleep groups, while the presence of K. oxytoca, S. aureus, Enterococcus spp., K. pneumoniae, and M. stadmanae is also important for the GSH level in several of these groups. F. prausnitzii, S. aureus, P. micra, Acinetobacter spp., and E. rectale are associated with GSTP1 concentration in various sleep groups, while the presence of F. nucleatum and P. micra is also relevant for the GSTP1 content in some of these groups. Conclusions: Thus, in menopausal women, the composition and structure of the gut microbiota are associated with sleep disorders. GSH and GSTP1 are associated with some gut microbiome markers in menopausal women, but these relationships differ in different sleep disorders.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Systemic Pathophysiology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Clinical Phenotypes of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Decade of Evidence Toward Personalized Management
by
William Rosales, Srija Chowdary Vanka, Harjinder Singh, Paul Bhamrah, Malti Bhamrah, Naomi Ghildiyal, Cesar Liendo, Sheila Asghar, J. Steven Alexander and Oleg Y. Chernyshev
Pathophysiology 2026, 33(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology33010002 - 22 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a heterogeneous disorder traditionally classified and stratified by the apnea–hypopnea index (AHI), which fails to capture variability in symptom burden, comorbid associations, and treatment responses. Clinical phenotyping has emerged as a promising strategy to improve disease
[...] Read more.
Background: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a heterogeneous disorder traditionally classified and stratified by the apnea–hypopnea index (AHI), which fails to capture variability in symptom burden, comorbid associations, and treatment responses. Clinical phenotyping has emerged as a promising strategy to improve disease characterization and management over the last decade. Methods: We conducted a narrative literature review of studies published between January 2014 and December 2022 that used cluster analysis to define OSA phenotypes in adults with moderate-to-severe disease (AHI ≥ 15 events/h). Eligible studies employed validated questionnaires, symptom reporting, and comorbidity profiling to identify subgroups. Findings were summarized across diverse populations, with emphasis on phenotype reproducibility, comorbidity associations, and treatment implications. Results: Across international cohorts, three reproducible symptom-based phenotypes were consistently identified: excessively sleepy (ES), disturbed sleep (DS), and minimally symptomatic (MS). Additional subtypes, such as upper airway dominant (UA) and moderately sleepy (MoS), were described in larger cohorts. Phenotypes differed in demographic profiles, comorbidity burden, and treatment adherence. ES patients exhibited the greatest symptom burden, higher cardiovascular risk, and better adherence to positive airway pressure (PAP) therapy, with significant symptomatic improvement. DS patients frequently reported insomnia symptoms, showed modest PAP-related gains, and may benefit from adjunctive insomnia-targeted interventions. MS patients, despite low symptom burden, often carried substantial comorbidity risk, specifically buildup of OSA-related cardiovascular risk. Conclusions: Symptom-based OSA phenotypes are reproducible across diverse populations and provide clinically meaningful insights beyond AHI. They allow for improved risk stratification, highlight gaps in detection of minimally symptomatic patients, and inform personalized treatment strategies. Integrating phenotyping into clinical practice has the potential to enhance diagnostic accuracy, optimize therapeutic outcomes, and refine cardiovascular risk prediction in OSA.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Obstructive Sleep Apnea Phenotypes: First Decade of Exploration and Beyond)
Open AccessArticle
Liquid Trisilanol i-Octyl POSS Achieves Rapid Hemostasis and Pneumostasis in Experimental Lung Injury
by
Michelle Tucci, Robert C. O′Brien, Joseph D. Lichtenhan, Hamed Benghuzzi and Drew Hildebrandt
Pathophysiology 2026, 33(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology33010001 - 22 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: No effective intervention currently exists for non-compressible pulmonary injury, especially in a prehospital setting. Visco-liquids like trisilanol i-octyl POSS could remedy this. POSS resists hemorrhage and activates clotting; this can be augmented with kaolin (22.5%; PK) or chitin (10%; PC). Methods
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: No effective intervention currently exists for non-compressible pulmonary injury, especially in a prehospital setting. Visco-liquids like trisilanol i-octyl POSS could remedy this. POSS resists hemorrhage and activates clotting; this can be augmented with kaolin (22.5%; PK) or chitin (10%; PC). Methods: We tested the efficacy of POSS, PK, and PC in treating incisional lung wounds in swine (39 ± 1 kg; n = 10). An incisional wound was made in the lung via a left thoracotomy, allowed to bleed freely for 30 s, and then no treatment (UNT), gauze with compression (GC), or POSS, PK, or PC was applied (1.5 mL). Each treatment was applied once per animal for a total of 5 wounds. Wounds were observed for 10 min for hemostasis and pneumostasis; GC treatments were assessed at 3 min intervals. Results: POSS and PC produced hemostasis in 8 of 10 wounds; GC: 7 (all significant from UNT); PK: 5 and UNT: 1. PK was not different from any group. POSS (2 ± 0.3 min) and PC (1.4 ± 0.4 min) clotted more quickly than GC (8 ± 3 min); PK was intermediate (3.8 ± 2 min) and not different from any other group. Pneumostasis was achieved in all POSS, PC, and PK, and only after hemostasis in the GC group. Conclusions: Because both POSS and PC provided quick and lasting hemorrhage and pneumatic control in this model, without need for compression, these results support the concept that these types of liquid POSS compounds could prove to be efficacious in prehospital treatment of non-compressible trauma wounds.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Lifestyle-Based Approaches to Cancer Prevention and Treatment: Diet, Physical Activity, and Integrative Strategies
by
Gianpiero Greco, Alessandro Petrelli, Francesco Fischetti and Stefania Cataldi
Pathophysiology 2025, 32(4), 70; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32040070 - 17 Dec 2025
Abstract
Cancer remains a leading global cause of morbidity and mortality. Modifiable lifestyle factors, including avoidance of tobacco use and excessive ultraviolet radiation, healthy dietary patterns, regular physical activity, and weight management, play key roles in prevention and care. This narrative review synthesizes evidence
[...] Read more.
Cancer remains a leading global cause of morbidity and mortality. Modifiable lifestyle factors, including avoidance of tobacco use and excessive ultraviolet radiation, healthy dietary patterns, regular physical activity, and weight management, play key roles in prevention and care. This narrative review synthesizes evidence on lifestyle-based interventions influencing cancer risk, treatment tolerance, and survivorship. A literature search was conducted in PubMed and Scopus, supplemented by manual screening via Google Scholar. The time frame (2001–2025) was selected to reflect evidence produced within the modern era of molecular oncology and contemporary lifestyle medicine research. Eligible publications addressed carcinogen exposure (tobacco, alcohol, ultraviolet radiation), diet and nutritional strategies, physical activity, sedentary behavior, obesity, metabolic health, complementary therapies, and cancer outcomes. Evidence indicates that reducing exposure to tobacco and ultraviolet radiation remains central to cancer prevention. Adherence to predominantly plant-based diets, regular physical activity, and maintenance of healthy body weight are consistently associated with lower incidence of several cancers, including breast, colorectal, and liver cancer. Nutritional strategies such as caloric restriction, ketogenic diets, and fasting-mimicking diets show promise in improving treatment efficacy and quality of life. Complementary and mind–body therapies may alleviate treatment-related symptoms, although high-quality evidence on long-term safety and effectiveness is limited. Integrating lifestyle medicine into oncology offers a cost-effective, sustainable strategy to reduce cancer burden and enhance survivorship. Comprehensive programs combining carcinogen avoidance, dietary regulation, structured exercise, and effective radiation risk mitigation may extend healthspan, improve treatment tolerance, and help prevent recurrence.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Overview of Cancer Metabolism)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessCorrection
Correction: Al-Barazenji et al. Association Between Vitamin D Receptor BsmI Polymorphism and Low Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women in the MENA Region. Pathophysiology 2025, 32, 6
by
Tara Al-Barazenji, Asma Allouch, Nedhal Al Husaini, Sondos Yousef, Wisam Nabeel Ibrahim, Amal Al-Haidose, Hatem Zayed and Atiyeh M. Abdallah
Pathophysiology 2025, 32(4), 69; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32040069 - 3 Dec 2025
Abstract
In the original publication [...]
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation Plus Nutritional Counseling Attenuates Thigh Muscle Thickness Loss in Hospitalized Cancer Patients
by
Tatyanne L. N. Gomes, Thaís C. Borges, Jessica F. M. Ivo, Lara G. Mainardi, Renata G. C. Abadio, Benjamin T. Wall and Gustavo D. Pimentel
Pathophysiology 2025, 32(4), 68; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32040068 - 2 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background and aims: This study aimed to determine whether neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) combined with nutritional counseling promotes an increase in thigh muscle thickness (MT), as well as to assess changes in the relationship between MT and intracellular water (ICW). Body composition methods
[...] Read more.
Background and aims: This study aimed to determine whether neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) combined with nutritional counseling promotes an increase in thigh muscle thickness (MT), as well as to assess changes in the relationship between MT and intracellular water (ICW). Body composition methods such as ultrasound may overestimate muscle mass, depending on the context, because they cannot distinguish the contractile protein component from body fluids, including intra- and extracellular water. Methods: A pilot randomized parallel trial was conducted with 25 hospitalized patients with unselected cancer, who were divided into two groups: NMES + Diet and Diet. Both groups received nutritional counseling, but only one group received NMES. NMES was applied bilaterally to the origin and insertion points of the quadriceps twice daily, with a 3 h interval between sessions, for 7 consecutive days. MT and ICW were measured before and after the intervention. Food consumption was assessed using a 24 h dietary recall at baseline and at the end of the study to quantify and adjust macronutrient intake during the intervention. Results: Both treatment groups (Diet × NMES + Diet) showed similar dropout rates which means participants in the more intensive treatment did not quit more frequently, once intervention with NMES was feasible and well tolerated. In addition, both groups showed a reduction in carbohydrate intake (p = 0.012) and an increase in leucine intake (p < 0.001) post-intervention. The increase in leucine intake was significantly greater in the NMES + Diet group (p < 0.001), and the reduction in carbohydrate intake was also greater in this group (p = 0.012). In the delta analysis, the NMES + Diet group showed an increase in thigh MT, whereas the Diet group experienced a decrease (Diet group: ∆ = −2.53 ± 3.73 mm vs. NMES + Diet group: ∆ = 2.09 ± 2.27 mm, p = 0.001). Moreover, the MT/ICW ratio was higher in the NMES + Diet group post-intervention (Diet group: ∆ = −0.15 ± 0.19 mm/L vs. NMES + Diet group: ∆ = 0.11 ± 0.09 mm/L, p < 0.001), while no significant difference in ICW was observed between groups. Conclusions: short-term intervention combining nutritional counseling with NMES increased thigh MT and the MT/ICW ratio, possibly due to NMES-induced extracellular water expansion.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Modulating Role of Resveratrol in Metabolic and Inflammatory Dysregulation Caused by Surgical and Psychoemotional Stress in Rats
by
Roman Ryabushko, Heorhii Kostenko, Oleh Akimov and Vitalii Kostenko
Pathophysiology 2025, 32(4), 67; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32040067 - 1 Dec 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Objectives: This study investigates the effects of resveratrol on systemic inflammatory, oxidative, and metabolic responses in a rat model that combines surgical trauma with prior exposure to Single Prolonged Stress (SPS), an established experimental protocol for modeling post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Methods: Male
[...] Read more.
Objectives: This study investigates the effects of resveratrol on systemic inflammatory, oxidative, and metabolic responses in a rat model that combines surgical trauma with prior exposure to Single Prolonged Stress (SPS), an established experimental protocol for modeling post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Methods: Male Wistar rats (n = 21) were randomly assigned to three groups: (I) control (polyvinylpyrrolidone, PVP), (II) SPS + laparotomy + PVP), and (III) SPS + laparotomy + resveratrol. Resveratrol (5 mg/kg of body weight/day) or vehicle was administered intragastrically for seven days. Serum concentrations of cortisol, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-10 (IL-10), glucose, insulin, lipid fractions, and thiobarbituric acid–reactive substances (TBA-RS) were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and spectrophotometric methods. Insulin resistance was assessed using the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) index. Results: Combined SPS and surgical trauma induced a pronounced systemic inflammatory response characterized by elevated cortisol (+138%), TNF-α (+83%), IL-6 (+465%), and ceruloplasmin (+71%), as well as hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, increased HOMA-IR, and atherogenic dyslipidemia with reduced high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-CH; −64%), elevated triglycerides (TGs; +216%), and very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (VLDL-CH; +218%). Marked activation of lipid peroxidation was observed, as indicated by increased TBA-RS levels before and after incubation. Resveratrol administration significantly decreased cortisol (−45%), TNF-α (−47%), and IL-6 (−85%), normalized the IL-10/IL-6 ratio, and reduced ceruloplasmin levels (−13%). The compound improved insulin sensitivity (HOMA-IR −50%), elevated HDL-CH (+115%), and lowered TGs and VLDL-CH (−44%). It also attenuated both basal and inducible lipid peroxidation (TBA-RS −11% and −13%), indicating restoration of antioxidant capacity. Conclusions: Thus, resveratrol effectively counteracts the neuroendocrine, inflammatory, and metabolic disturbances induced by combined PTSD-like stress and surgical trauma.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Metabolic Disorders)
Open AccessArticle
Calcification in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Is Associated with Elevated GCLm and Impaired Contraction: Insights into Osteogenic Transdifferentiation and Therapeutic Approaches
by
Luisa F. Delgadillo, Nabil A. Rashdan, Hunter Hamilton, Jack H. Pattillo, Shuai Yuan, Randa S. Eshaq, Norman R. Harris, Jonathan S. Alexander and Christopher B. Pattillo
Pathophysiology 2025, 32(4), 66; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32040066 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Vascular calcification is a strong predictor of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Oxidative stress plays a key role in promoting vascular calcification. Glutathione (GSH), as a major cellular antioxidant, is produced in response to oxidative stress and is regulated by the enzyme glutamate-cysteine
[...] Read more.
Background: Vascular calcification is a strong predictor of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Oxidative stress plays a key role in promoting vascular calcification. Glutathione (GSH), as a major cellular antioxidant, is produced in response to oxidative stress and is regulated by the enzyme glutamate-cysteine ligase (GCL). In this study, we examined the role of the GCL modifier subunit (GCLm) in regulating vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) calcification. Methods: Human coronary artery VSMCs were exposed to phosphate-rich media to induce calcification. Results: Calcification led to a decrease in the GSH:GSSG ratio (reduced glutathione to oxidized glutathione), and elevated GCLm expression, coincident with mobilization of osteogenic genes and loss of contractile phenotype. KEGG pathway analysis of human unstable atherosclerotic plaques similarly showed increased GCLm expression and activation of reactive oxygen species (ROS)-related pathways. Notably, forced overexpression of GCLm in murine VSMCs (MOVAS cells) significantly accelerated calcification. These findings implicate GCLm upregulation in promoting VSMC calcification, potentially by disrupting redox homeostasis and driving phenotypic switching. Further mechanistic studies are warranted to evaluate GCLm as a potential therapeutic target in vascular calcification.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cardiovascular Pathophysiology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Clinical and Laboratory Parameters After Drowning and Diving Accidents and Their Association with Survival
by
Anne Petzold, Jan Dreßler, Anne Schrimpf and André Gries
Pathophysiology 2025, 32(4), 65; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32040065 - 19 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: The prognosis for patients admitted to emergency departments (ED) after drowning or diving accidents is often uncertain. In this study, we evaluated a range of clinical and laboratory parameters as potential indicators of survival. Many of these markers have previously been
[...] Read more.
Introduction: The prognosis for patients admitted to emergency departments (ED) after drowning or diving accidents is often uncertain. In this study, we evaluated a range of clinical and laboratory parameters as potential indicators of survival. Many of these markers have previously been investigated in the context of survival prediction in both trauma-related and non-trauma-related clinical scenarios. Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of 25 patients aged >17 years who were admitted to the ED of the University Hospital Leipzig after drowning or diving accidents between 2012 and 2024. Clinical and laboratory parameters were compared between survivors and non-survivors, with survival defined as discharge from the hospital. Results: Of all cases analyzed—comprising 19 drowning and six diving incidents—10 patients (40%) survived, while 15 (60%) did not. Age, sex, or etiology of the accident were not statistically associated with survival. Compared to survivors, non-survivors were significantly more likely to have received prehospital cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR; 20% vs. 86.7%) and to have exhibited lower Glasgow Coma Scale scores and lower pH values (7.4 vs. 6.7). They were also more likely to have shown increased levels of lactate (4.3 mmol/L vs. 14.8 mmol/L), CK-MB quotient (9.7% vs. 51.8%), myoglobin (188.9 µg/L vs. 1930.9 µg/L), and blood glucose (6.6 mmol/L vs. 14.3 mmol/L). Conclusions: The need for CPR appears to be the most significant risk factor for not surviving a drowning or diving accident. Furthermore, certain laboratory parameters, such as pH and lactate, may provide supportive information regarding the severity of hypoxia and could be cautiously considered as indicators of survival likelihood in these patients. Our findings offer a rationale for future prospective studies, aiming to incorporate additional clinical and biochemical markers and potentially develop new prognostic scoring systems for patients following drowning or diving accidents. This study examines the association between clinical and laboratory parameters and survival in patients following drowning and diving accidents. A total of 25 cases from 2012 to 2024 were retrospectively analyzed. The results showed that patients who required CPR had significantly poorer outcomes. Certain laboratory markers; such as pH and lactate levels; were closely related to survival status in this patient group.
Full article
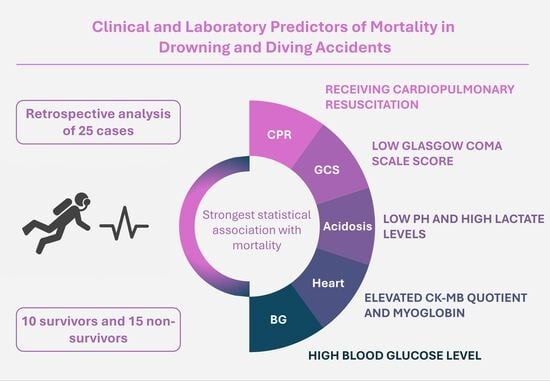
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Hyperferritinemia Is Associated with Higher Adiposity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Hepatic Dysfunction, Mainly Affecting Men: A Study in Southern Brazil
by
Késia Zanuzo, Márcia Fernandes Nishiyama, Eloá Angélica Koehnlein and Sabrina Grassiolli
Pathophysiology 2025, 32(4), 64; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32040064 - 19 Nov 2025
Abstract
Objectives: Serum ferritin (SF) reflects iron homeostasis, in addition to being an acute phase reactant protein. Since its levels are altered in the obesity state, we compared body composition, metabolic profile, liver alterations, and dietary patterns in adults stratified by SF levels
[...] Read more.
Objectives: Serum ferritin (SF) reflects iron homeostasis, in addition to being an acute phase reactant protein. Since its levels are altered in the obesity state, we compared body composition, metabolic profile, liver alterations, and dietary patterns in adults stratified by SF levels (normal vs. high). Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted using secondary data from 113 adults (≥18 years) of both sexes, attended at an outpatient nutrition clinic in southern Brazil and categorized for normal or high SF. Socioeconomic, anthropometric, blood pressure, dietary, biochemical, and liver parameters were assessed and statistical analyses performed. Results: Participants with high SF were more frequently male (p < 0.0001), married or in a civil union (p = 0.012), and had lower educational levels (p = 0.009). Moreover, higher rates of obesity (p = 0.003), cardiovascular risk (p = 0.004), increased body fat percentage (BF%; p = 0.002) and metabolic disturbances such as elevated glucose (p = 0.023), triglycerides (p = 0.003), insulin resistance (p = 0.027), hypertension (p = 0.001), and metabolic syndrome (MS) (p = 0.001) were noted in this group. Liver-related findings comprised increased ALT (p = 0.008), uric acid (p = 0.016), and indicators of steatosis (p = 0.022). Logistic regression demonstrated a higher likelihood of elevated SF among men (OR = 16.82) and individuals with increased BF% (OR = 7.5), without significant influence of diet. Conclusions: Adults with elevated SF were predominantly obese men with excess adiposity, insulin resistance, and metabolic and hepatic dysfunctions, conditions that increase the risk of MS and liver injury. These findings suggest that SF and other iron biomarkers may serve as valuable tools for diagnosing metabolic dysfunctions and obesity-related liver diseases, particularly Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Metabolic Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures
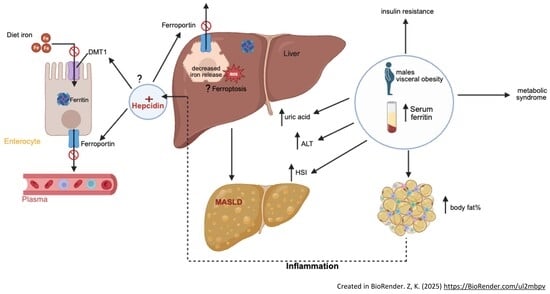
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Diffusion Tensor Tractography Shows White Matter Tract Changes in Breast Cancer Survivors with Balance Impairment
by
Alexandra Nikolaeva, Maria Pospelova, Mark Voynov, Varvara Krasnikova, Albina Makhanova, Samvel Tonyan, Aleksandr Efimtsev, Fionik Olga, Anatoliy Levchuk, Gennadiy Trufanov, Konstantin Samochernykh, Tatyana Alekseeva, Stephanie E. Combs and Maxim Shevtsov
Pathophysiology 2025, 32(4), 63; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32040063 - 19 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Objectives: Breast cancer survivors often experience long-term neurological complications, including balance impairments, following treatment. This study aimed to investigate microstructural changes in white matter tracts in breast cancer survivors with balance impairment using diffusion tensor tractography. Methods: An open, single-center, prospective
[...] Read more.
Objectives: Breast cancer survivors often experience long-term neurological complications, including balance impairments, following treatment. This study aimed to investigate microstructural changes in white matter tracts in breast cancer survivors with balance impairment using diffusion tensor tractography. Methods: An open, single-center, prospective study was conducted including two groups—healthy age-matched volunteers (n = 28) and breast cancer survivors (n = 35) with balance impairment. All participants underwent diffusion tensor tractography at baseline and at the end of the follow-up period of six months. Quantitative anisotropy was analyzed using DSI Studio to assess white matter integrity. Results: At baseline, patients with balance impairment exhibited significantly reduced quantitative anisotropy values in the middle cerebellar peduncles (p = 0.046) and cerebellar hemispheres (p = 0.024, 0.055) compared to healthy controls. At the end of the follow-up, quantitative anisotropy values were increased across most tracts, though some differences persisted between groups (p < 0.001). Conclusions: Breast cancer survivors with balance impairment demonstrate sustained microstructural white matter changes, particularly in cerebellar and vestibular pathways. These findings suggest that diffusion tensor tractography can provide valuable insights into central nervous system alterations contributing to post-treatment balance dysfunction and may serve as a potential tool for early diagnosis and rehabilitation planning.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Increased Mortality with Intermediate Ascitic Polymorphonuclear Cell Counts Amongst Patients with Cirrhosis: Time to Redefine the Care Approach
by
Shahid Habib, Michael Ball, Chris Thomas, Traci Murakami, Nehali Patel, Sandeep Yarlagadda, Sarah Patel, Courtney Walker, Varun Takyar, Krunal Patel, Christian Domingues and Chiu-Hsieh Hsu
Pathophysiology 2025, 32(4), 62; https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32040062 - 11 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) is a serious complication in patients with decompensated cirrhosis and ascites. Diagnosis typically relies on an ascitic polymorphonuclear (A-PMN) cell count ≥ 250 cells/high-power field (HPF). Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, 117 hospitalized patients with acute decompensation
[...] Read more.
Background: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) is a serious complication in patients with decompensated cirrhosis and ascites. Diagnosis typically relies on an ascitic polymorphonuclear (A-PMN) cell count ≥ 250 cells/high-power field (HPF). Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, 117 hospitalized patients with acute decompensation of chronic liver disease and a diagnostic paracentesis were evaluated. Clinical, laboratory, and imaging data were collected. Patients were stratified by A-PMN counts of ≤50, 51–249, or ≥250 cells/HPF. Additional analysis was performed with patients stratified by ascitic white blood cell (WBC) count and albumin. Mortality risk was assessed at 28, 90, and 365 days. Results: Patients with A-PMN ≤ 50 cells/HPF had the lowest 28-day mortality (8%). At 90 and 365 days, mortality risk was significantly higher for the A-PMN 51–249 cells/HPF group (90-day hazard ratio (HR) 3.55, p = 0.01; 365-day HR 2.43, p = 0.02), but not A-PMN ≥ 250 cells/HPF group (90-day HR 2.95, p = 0.1; 365-day HR 2.95, p = 0.2). Ascitic WBC count did not significantly predict mortality, though higher counts were associated with extraperitoneal infections. Ascitic fluid albumin ≤ 1.0 g/dL was independently associated with increased 365-day mortality (HR 3.53, p = 0.03). Conclusions: Binary SBP A-PMN thresholds may not adequately capture mortality risk in cirrhotic patients with ascites. Low ascitic albumin and intermediate A-PMN counts are associated with increased long-term mortality, suggesting the need for more nuanced diagnostic and prognostic criteria in SBP evaluation.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Cells, Organoids, Cancers, Metabolites, Pathophysiology
Overview of Cancer Metabolism
Topic Editors: Arnaud Blomme, Cyril CorbetDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topic in
Biomedicines, Clinics and Practice, Diseases, JCM, Pathophysiology, Diagnostics
Evolving Insights into Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Therapy, and Prognosis in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): From Bench to Bedside—Third Edition
Topic Editors: Denise Battaglini, Patricia Rieken Macêdo Rocco, Raffaele MerolaDeadline: 31 March 2027

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology in 2026
Guest Editor: Jonathan Steven AlexanderDeadline: 30 June 2026
Special Issue in
Pathophysiology
Cardiovascular Convergence: Bridging Basic, Translational and Clinical Research
Guest Editors: Dragan Djuric, Vladimir JakovljevicDeadline: 30 November 2026
Special Issue in
Pathophysiology
Obstructive Sleep Apnea Phenotypes: First Decade of Exploration and Beyond
Guest Editors: Jonathan Steven Alexander, Oleg ChernyshevDeadline: 15 December 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Pathophysiology
Feature Papers in Pathophysiology
Collection Editor: Jonathan Steven Alexander











