- Article
Sleep Disorders in Climacteric Women: Glutathione, Glutathione S-Transferase P1 and Gut Microbiome Interrelation
- Natalya Semenova,
- Nadezhda Garashchenko and
- Olga Nikitina
- + 7 authors
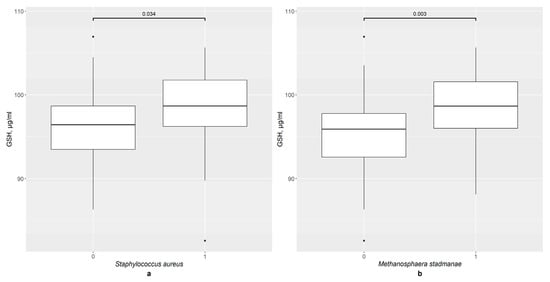
Background: Menopause, a critical period during a woman’s life, is characterized by various changes, including disturbances in their oxidative balance and circadian rhythm. Currently, the gut microbiome is suggested as an important participant in these processes. Methods: This study involved 96 menopausal women. Their sleep quality was assessed using three questionnaires: the Insomnia Severity Index (ISI), the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), and the Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS). The GSH and GSTP1 contents in the serum were measured by means of immunoassay methods, while the composition of the gut microbiome was determined via molecular genetic methods. Results: E. coli, K. oxytoca, S. aureus, Enterobacter spp., Shigella spp., Streptococcus spp., Prevotella spp., and M. stadmanae were found to correlate with the GSH content in different sleep groups, while the presence of K. oxytoca, S. aureus, Enterococcus spp., K. pneumoniae, and M. stadmanae is also important for the GSH level in several of these groups. F. prausnitzii, S. aureus, P. micra, Acinetobacter spp., and E. rectale are associated with GSTP1 concentration in various sleep groups, while the presence of F. nucleatum and P. micra is also relevant for the GSTP1 content in some of these groups. Conclusions: Thus, in menopausal women, the composition and structure of the gut microbiota are associated with sleep disorders. GSH and GSTP1 are associated with some gut microbiome markers in menopausal women, but these relationships differ in different sleep disorders.
26 December 2025