In Vitro Chronic Hyperinsulinemia Induces Remodelling of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells from Young Men and Women in a Sex Hormone Independent Manner
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Culturing of Human Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
2.2. Pretreatment with High Insulin Levels and Sexual Hormones
2.3. Quantitve 3D Confocal Microscopy
2.4. Determination of the Cell Volume
2.5. Loading with the Calcium, Glutathione, and ROS Fluorescent Probes
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
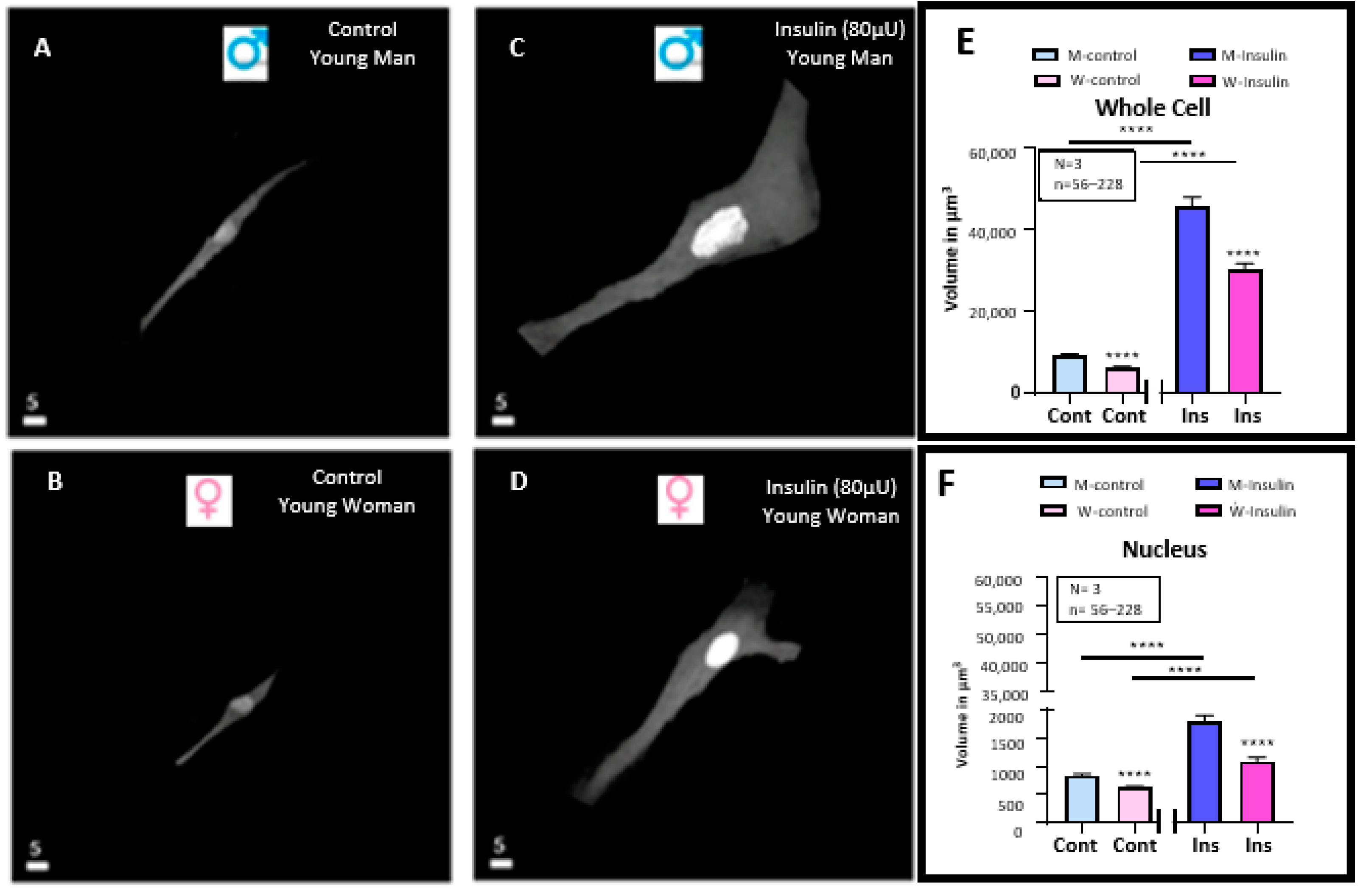
3.1. Effect of a 48 h Treatment of Hyperinsulinemia (80 μU/mL) on the Volume of VSMCs from Men and Women
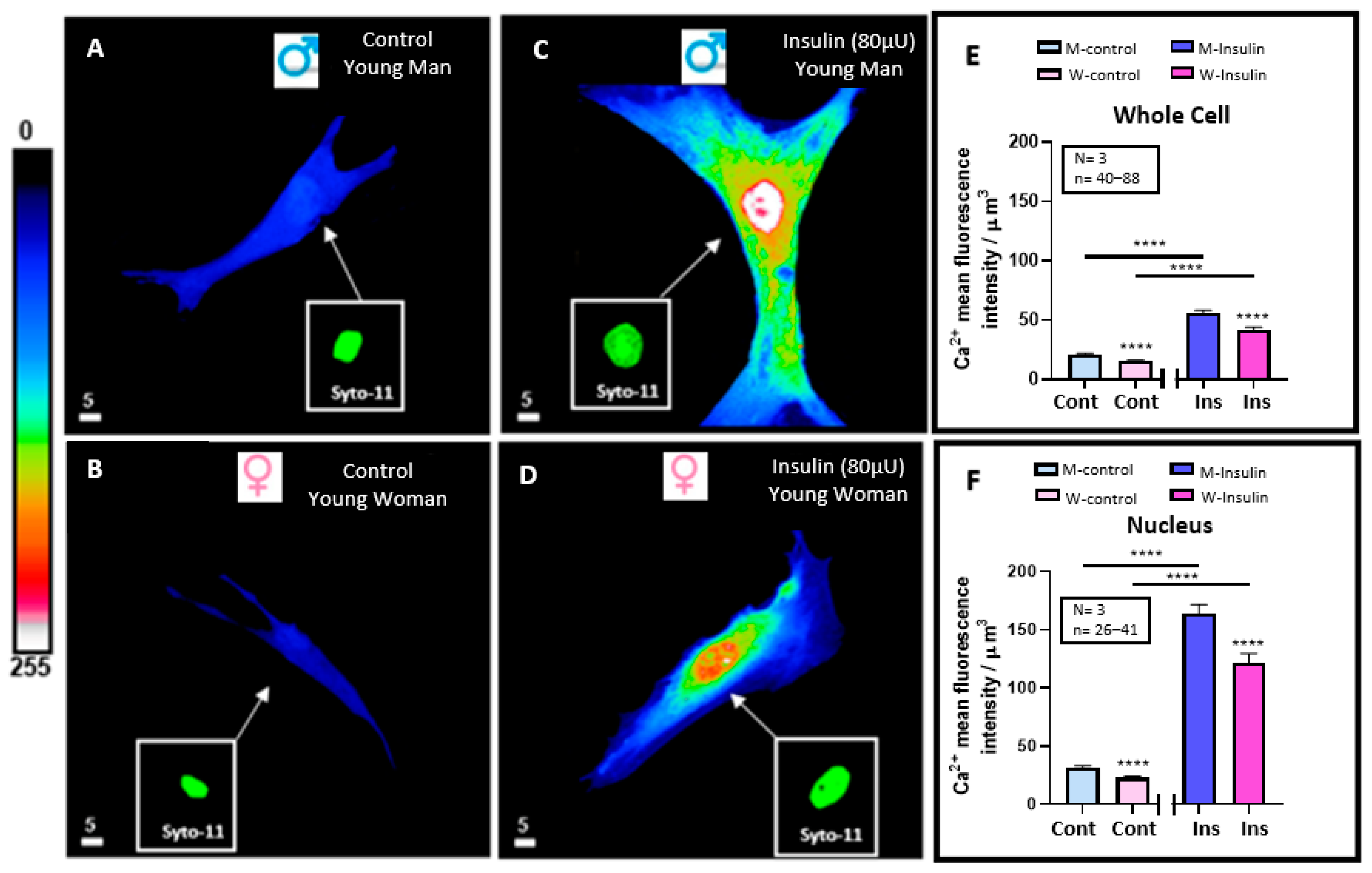
3.2. Effect of 48 h Treatment of Hyperinsulinemia (80 μU/mL) on the Intracellular Ca2+ Levels of VSMCs from Men and Women
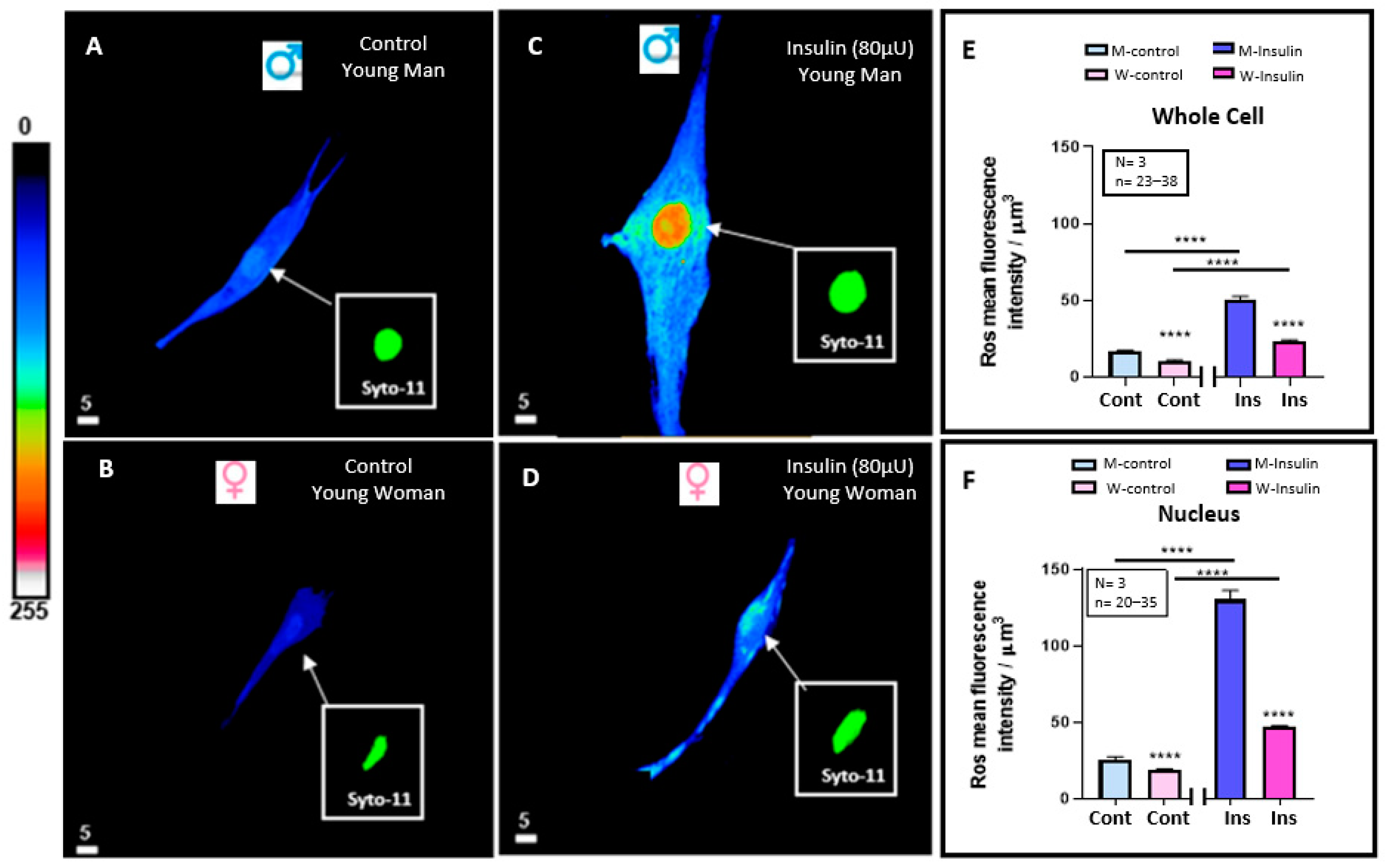
3.3. Effect of 48 h Treatment of Hyperinsulinemia (80 μU/mL) on the Intracellular ROS+ Levels of VSMCs from Men and Women
3.4. Effect of 48 h Treatment of Hyperinsulinemia (80 μU/mL) on the Intracellular Glutathione Levels of VSMCs from Men and Women
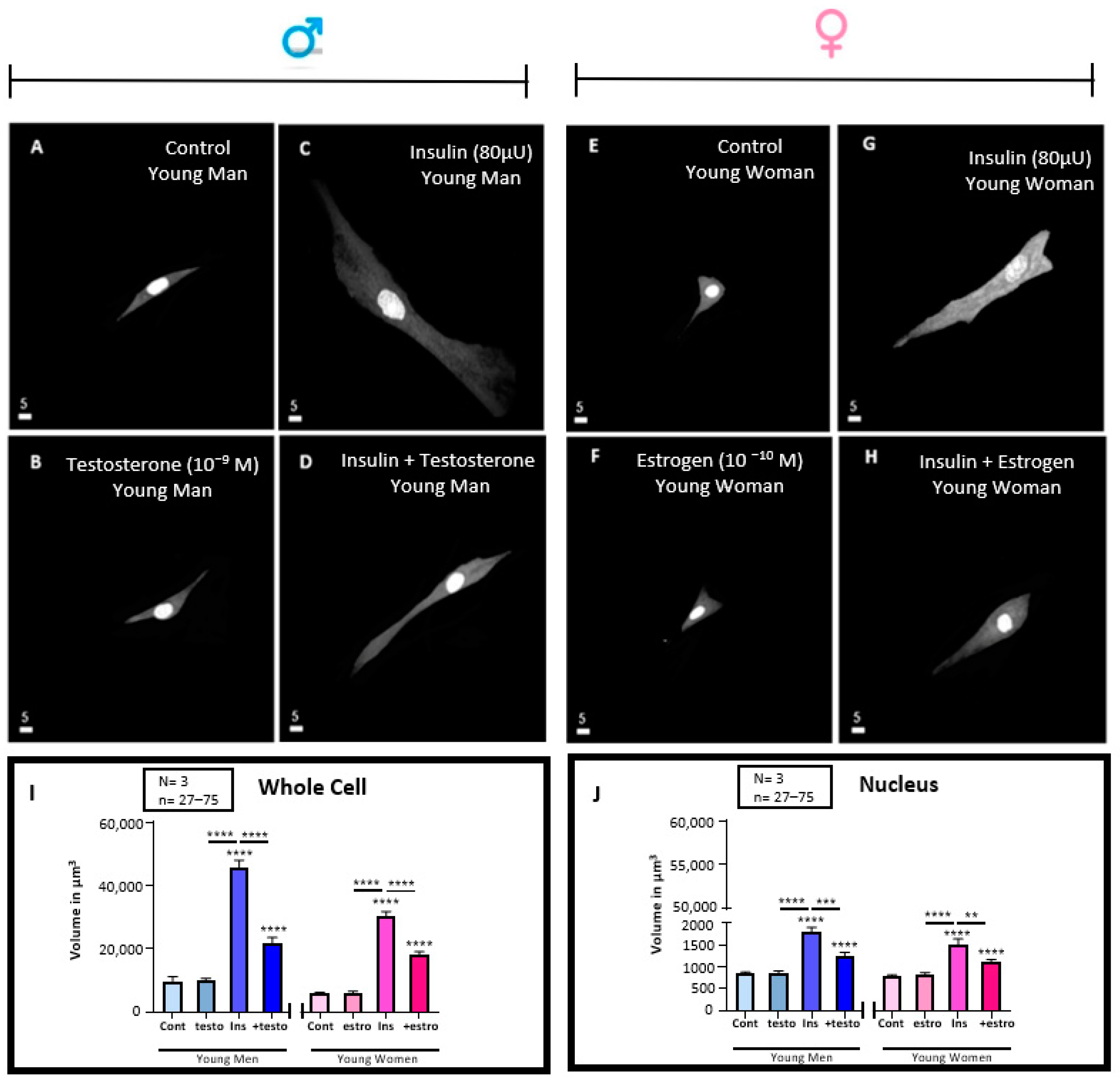
3.5. Effect of 48 h Treatment of Hyperinsulinemia (80 μU/mL) in the Absence and Presence of Testosterone (10−9 M) or Estrogen (10−10) M on the Volume of VSMCs from Men and Women
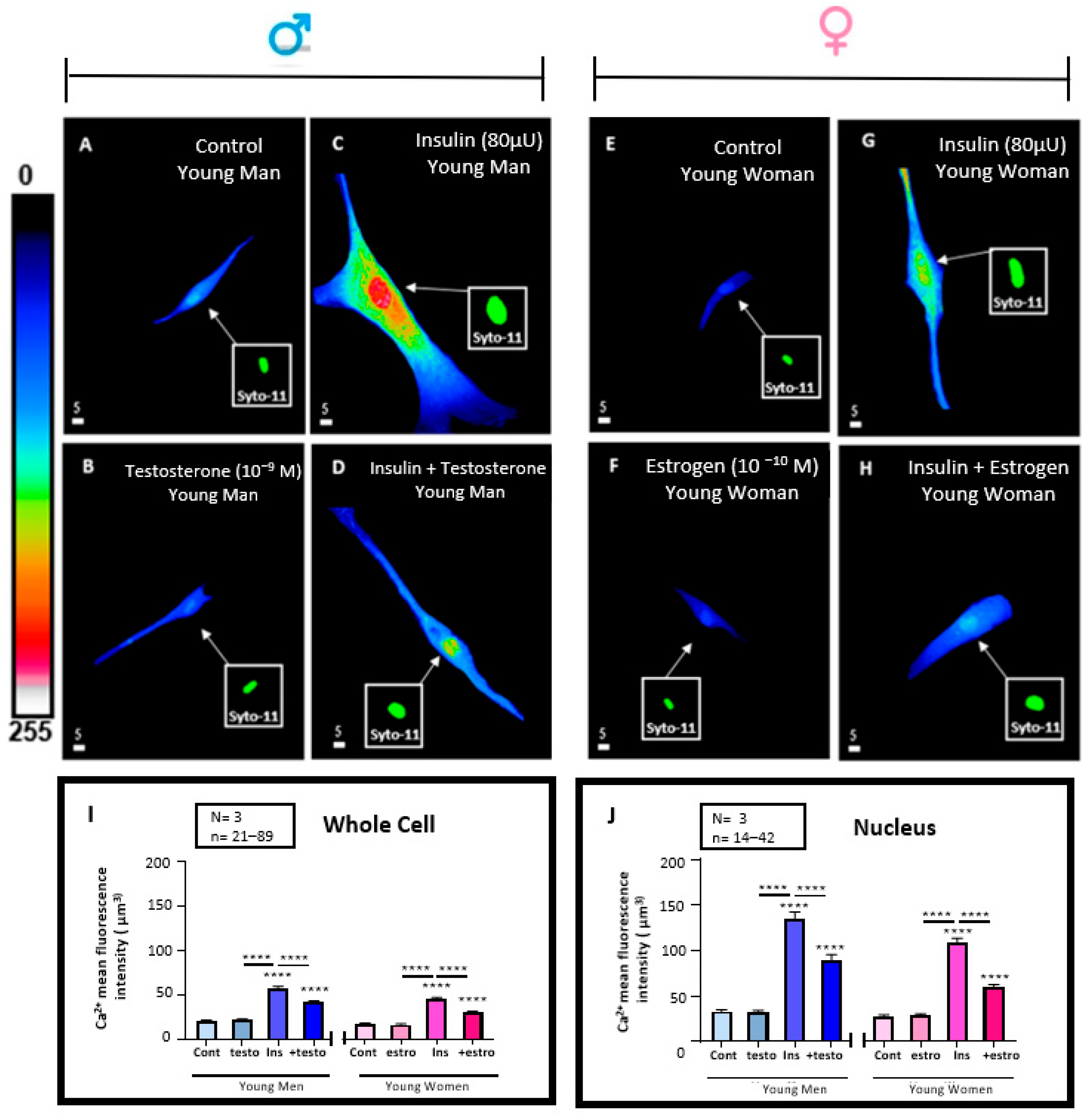
3.6. Effect of 48 h Treatment of Hyperinsulinemia (80 μU/mL) in the Absence and Presence of Testosterone (10−9 M) or Estrogen (10−10) M on the Whole Cells and Their Nuclear Ca2+ Levels of VSMCs from Men and Women
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marfella, R.; Amico, M.D.; Di Filippo, C.; Siniscalchi, M.; Sasso, F.C.; Ferraraccio, F.; Rossi, F.; Paolisso, G. The possible role of the ubiquitin proteasome system in the development of atherosclerosis in diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2007, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, J. Hyperinsulinemia and Its Pivotal Role in Aging, Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes, Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodero, G.; Rigante, D.; Pane, L.C.; Sessa, L.; Quarta, L.; Candelli, M.; Cipolla, C. Cardiometabolic Risk Assessment in a Cohort of Children and Adolescents Diagnosed with Hyperinsulinemia. Diseases 2024, 12, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, J. Overnutrition, Hyperinsulinemia and Ectopic Fat: It Is Time for A Paradigm Shift in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perng, W.; Kelsey, M.M.; Sauder, K.A.; Dabelea, D. How does exposure to overnutrition in utero lead to childhood adiposity? Testing the insulin hypersecretion hypothesis in the EPOCH cohort. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 2237–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Yu, M.G.; Li, Q.; Park, K.; King, G.L. Insulin’s actions on vascular tissues: Physiological effects and pathophysiological contributions to vascular complications of diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2021, 52, 101236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bkaily, G.; Abou Abdallah, N.; Simon, Y.; Jazzar, A.; Jacques, D. Vascular smooth muscle remodeling in health and disease. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 99, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bkaily, G.; Jacques, D. Morphological and Functional Remodeling of Vascular Endothelium in Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bkaily, G.; Jacques, D. Calcium Homeostasis, Transporters, and Blockers in Health and Diseases of the Cardiovascular System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasvariova, M.; Salvaras, L.; Seckarova Michalikova, D.; Tyukos Kaprinay, B.; Knezl, V.; Gasparova, Z.; Stankovicova, T. Assessment of the Cardiovascular Risk of High-Fat-High-Fructose Diet in Hereditary Hypertriacylglycerolemic Rats and Venlafaxine Effect. Physiol. Res. 2024, 73, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazzar, A.; Jacques, D.; Bkaily, G. Insulin-Induced Cardiomyocytes Hypertrophy That Is Prevented by Taurine via beta-alanine-Sensitive Na(+)-Taurine Symporter. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyts, P. The Insulin Receptor and Its Signal Transduction Network. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Corpas, E., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Hofland, J., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Crofts, C.A.P.; Zinn, C.; Wheldon, M.; Schofield, G. Hyperinsulinemia: A unifying theory of chronic disease? Diabesity 2015, 1, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bkaily, G.; Naik, R.; Jaalouk, D.; Jacques, D.; Economos, D.; D’Orleans-Juste, P.; Pothier, P. Endothelin-1 and insulin activate the steady-state voltage dependent R-type Ca2+ channel in aortic smooth muscle cells via a pertussis toxin and cholera toxin sensitive G-protein. Mol. Cell Biochem. 1998, 183, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, X.; Xiao, Y.; Tu, T.; Liu, C.; Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. The triglyceride-glucose index and its obesity-related derivatives as predictors of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hypertensive patients: Insights from NHANES data with machine learning analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2025, 24, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormazabal, V.; Nair, S.; Elfeky, O.; Aguayo, C.; Salomon, C.; Zuñiga, F.A. Association between insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regensteiner, J.G.; Golden, S.; Huebschmann, A.G.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Chang, A.Y.; Chyun, D.; Fox, C.S.; Kim, C.; Mehta, N.; Reckelhoff, J.F.; et al. Sex Differences in the Cardiovascular Consequences of Diabetes Mellitus: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015, 132, 2424–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regensteiner, J.G.; Reusch, J.E.B. Sex Differences in Cardiovascular Consequences of Hypertension, Obesity, and Diabetes: JACC Focus Seminar 4/7. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 1492–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautzky-Willer, A.; Leutner, M.; Harreiter, J. Sex differences in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 986–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.A.; do Carmo, J.M.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Mouton, A.J.; Hall, J.E. Role of Hyperinsulinemia and Insulin Resistance in Hypertension: Metabolic Syndrome Revisited. Can. J. Cardiol. 2020, 36, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, R. Postmenopausal Women With a “Normal” BMI Might Be Overweight or Even Obese. JAMA 2018, 319, 1185–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, G.H.; Jocken, J.W.E.; Blaak, E.E. Sexual dimorphism in cardiometabolic health: The role of adipose tissue, muscle and liver. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, D.K.; Samanta, L.; Kesari, K.K.; Mukherjee, S. Editorial: Hormonal imbalance-associated oxidative stress and protective benefits of nutritional antioxidants. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1368580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Nouri, M.; Kohanmoo, A.; Homayounfar, R.; Akhlaghi, M. The influence of gender and waist circumference in the association of body fat with cardiometabolic diseases. BMC Nutr. 2025, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.H.; Kim, C.K.; Al-Khaled, T.; Chervinko, M.A.; Wishna, A.; Mirza, R.G.; Vajaranant, T.S. Comparative Insights into the Role of Sex Hormones in Glaucoma Among Women and Men. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2025, 105, 101336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bkaily, G.; Pothier, P.; D’Orléans-Juste, P.; Simaan, M.; Jacques, D.; Jaalouk, D.; Belzile, F.; Hassan, G.; Boutin, C.; Haddad, G.; et al. The use of confocal microscopy in the investigation of cell structure and function in the heart, vascular endothelium and smooth muscle cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 1997, 172, 171–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, Y.; Jacques, D.; Bkaily, G. High salt-induced morphological and glycocalyx remodeling of human vascular smooth muscle cells is reversible but induces a high sodium salt-like sensitive memory. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2023, 101, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, S.; Bellavite, P.; Affuso, F. Chronically Increased Levels of Circulating Insulin Secondary to Insulin Resistance: A Silent Killer. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Hossain, K.S.; Das, S.; Kundu, S.; Adegoke, E.O.; Rahman, M.A.; Hannan, M.A.; Uddin, M.J.; Pang, M.G. Role of Insulin in Health and Disease: An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corkey, B.E. Diabetes: Have we got it all wrong? Insulin hypersecretion and food additives: Cause of obesity and diabetes? Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 2432–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Liu, H.Y.; Hong, T.; Liu, Z. Excess exposure to insulin may be the primary cause of insulin resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 298, E372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniyappa, R.; Quon, M.J. Insulin action and insulin resistance in vascular endothelium. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2007, 10, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.P.; Bisogni, V.; Rossitto, G.; Maiolino, G.; Cesari, M.; Zhu, R.; Seccia, T.M. Practice Recommendations for Diagnosis and Treatment of the Most Common Forms of Secondary Hypertension. High. Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2020, 27, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, Z.; Alipour, P.; Raparelli, V.; Norris, C.M.; Pilote, L. The role of sex and gender in hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2023, 37, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhawari, H.H.; Al-Shelleh, S.; Alhawari, H.H.; Al-Saudi, A.; Aljbour Al-Majali, D.; Al-Faris, L.; AlRyalat, S.A. Blood Pressure and Its Association with Gender, Body Mass Index, Smoking, and Family History among University Students. Int. J. Hypertens. 2018, 2018, 4186496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connelly, P.J.; Currie, G.; Delles, C. Sex Differences in the Prevalence, Outcomes and Management of Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2022, 24, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ahn, Y.J.; Asmis, R. Sexual dimorphism in glutathione metabolism and glutathione-dependent responses. Redox Biol. 2020, 31, 101410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, T.; Tsutsui, H.; Ohashi, N.; Hayashidani, S.; Suematsu, N.; Tsuchihashi, M.; Tamai, H.; Takeshita, A. Greater oxidative stress in healthy young men compared with premenopausal women. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutanto, H.; Lyon, A.; Lumens, J.; Schotten, U.; Dobrev, D.; Heijman, J. Cardiomyocyte calcium handling in health and disease: Insights from in vitro and in silico studies. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2020, 157, 54–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebschmann, A.G.; Huxley, R.R.; Kohrt, W.M.; Zeitler, P.; Regensteiner, J.G.; Reusch, J.E.B. Sex differences in the burden of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk across the life course. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jazzar, A.; Jacques, D.; Abou-Aichi, A.; Bkaily, G. In Vitro Chronic Hyperinsulinemia Induces Remodelling of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells from Young Men and Women in a Sex Hormone Independent Manner. Pathophysiology 2025, 32, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32010012
Jazzar A, Jacques D, Abou-Aichi A, Bkaily G. In Vitro Chronic Hyperinsulinemia Induces Remodelling of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells from Young Men and Women in a Sex Hormone Independent Manner. Pathophysiology. 2025; 32(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleJazzar, Ashley, Danielle Jacques, Amira Abou-Aichi, and Ghassan Bkaily. 2025. "In Vitro Chronic Hyperinsulinemia Induces Remodelling of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells from Young Men and Women in a Sex Hormone Independent Manner" Pathophysiology 32, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32010012
APA StyleJazzar, A., Jacques, D., Abou-Aichi, A., & Bkaily, G. (2025). In Vitro Chronic Hyperinsulinemia Induces Remodelling of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells from Young Men and Women in a Sex Hormone Independent Manner. Pathophysiology, 32(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology32010012






