- Article
Synergistic Effect of Fe Doping and Oxygen Vacancies on the Optical Properties and CO2 Reduction Mechanism of Bi4O5Br2
- Gaihui Liu,
- Xie Huang and
- Suqin Xue
- + 5 authors
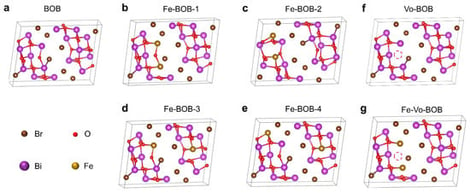
In this study, the synergistic effects of Fe doping and oxygen vacancies on the structural, electronic, and optical properties of Bi4O5Br2, as well as their influence on the photocatalytic CO2 reduction mechanism, were systematically explored through first-principles calculations. The results reveal that Fe-doped, oxygen-defective, and Fe–Vo co-modified Bi4O5Br2 systems exhibit excellent thermodynamic and dynamic stability. Oxygen vacancies introduce defect states near the Fermi level, narrowing the band gap and enhancing charge localization and CO2 adsorption, while Fe doping induces strong spin polarization and introduces Fe 3d impurity levels that effectively couple with O 2p orbitals, promoting charge transfer and visible-light absorption. The coexistence of Fe dopants and oxygen vacancies produces a significant synergistic effect, forming a continuous energy-level bridge that enhances charge separation and broadens the light absorption range. Gibbs free energy analyses further demonstrate that the Fe–Vo–BOB system exhibits the lowest energy barriers and the most favorable thermodynamics for CO2-to-CO conversion. This study provides deep insight into the defect–dopant synergy in Bi4O5Br2 and offers valuable theoretical guidance for engineering highly efficient visible-light-driven photocatalysts in solar energy conversion and environmental remediation.
11 February 2026