- Article
Phoneme Automaticity: A Test of the Phonemic Proficiency Hypothesis
- David D. Paige and
- William H. Rupley
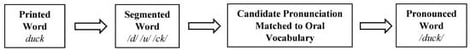
Readers use letter-sound knowledge and blending skills to consciously decode unfamiliar words, gradually building a large inventory of recognizable words. The storage of these words in long-term memory depends on forming connections between phonological sounds and their written forms, which results in a highly accurate and automatic recall of word pronunciations. For words to be read instantly, these phoneme-grapheme connections need to operate automatically, allowing for rapid, effortless recognition. In this study, we examine the connections between rapid access to phonemic sounds, spelling ability, and word reading among first- and second-grade students. Using a quantitative, correlational design, we examined first- and second-grade students’ performance on timed phoneme substitution, spelling, and sight-word reading and tested predictive relations using ordinary least squares regression. The results show that rapid skill in substituting phonemes directly predicts both automatic word reading and spelling. This finding highlights the importance of developing quick phonemic manipulation skills, which are essential for achieving fluent, precise word reading.
10 February 2026