- Article
Association of Fetal Growth Retardation with Postnatal Osteoprotegerin Concentrations and Aortic Intima–Media Thickness
- Ageliki A. Karatza,
- Eirini Kostopoulou and
- Dionysios Chrysis
- + 6 authors
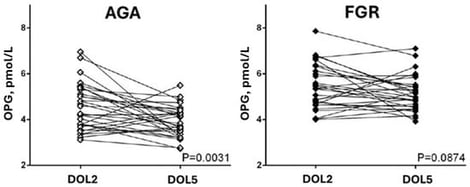
Background: Fetal Growth Retardation (FGR) is considered a risk factor for atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease in adulthood. Osteoprotegerin (OPG), a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, is reported to be elevated in atherosclerosis. Objectives: In this case-control study, we investigated whether FGR affects postnatal OPG serum concentrations and the possible association between OPG levels and aortic intima–media thickness (aIMT), an index of preclinical atherosclerosis. Methods: We studied 30 infants with FGR and 30 appropriate for gestational age (AGA) infants matched for gestational age and sex. Quantitative determination of plasma OPG was performed via enzyme immunoassay on the second (DOL2) and fifth (DOL5) day of life. aIMT was measured in the distal abdominal aorta and adjusted for aortic lumen diameter. Results: Infants with FGR had significantly higher OPG levels on both DOL2 and DOL5 as compared to controls (DOL2: 5.4 ± 1.0 pmol/L vs. 4.6 ± 1.0 pmol/L, p = 0.002 and DOL5: 5.1 ± 0.8 pmol/L vs. 3.9 ± 0.7 pmol/L, p < 0.001). Between DOL2 and DOL5, OPG concentrations did not change significantly in infants with FGR (difference 0.3 ± 0.2 pmol/L, p = 0.087) but decreased slightly in controls (difference 0.7 ± 0.3 pmol/L, p = 0.003). FGR was also associated with increased aIMT (0.11 ± 0.03 vs. 0.06 ± 0.02, p < 0.001). There was a positive correlation between OPG and aIMT on DOL2 (r = 0.494, p < 0.001), which became stronger on DOL5 (r = 0.791, p < 0.001). Conclusions: We report significantly increased concentrations of OPG in infants with FGR and a positive correlation with aIMT. Follow-up studies with repeat OPG and aIMT measurements may be indicated to evaluate whether these findings represent a permanent effect of FGR on the offspring.
8 March 2026