- Review
Degradation and Decomposition of Holopelagic Sargassum: A Review on Process Dynamics
- Román Manuel Vásquez-Elizondo,
- Adrian Fagundo-Mollineda and
- Daniel Robledo
- + 1 author
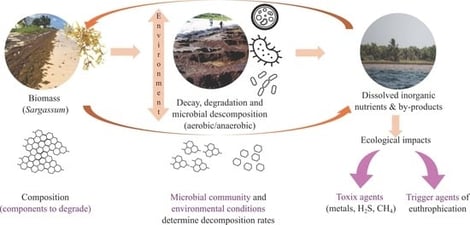
This review synthesizes the literature on the degradation and decomposition of holopelagic Sargassum, with a focus on process dynamics, including microbial contribution, process descriptions, and ecological impacts. Our objective is to consolidate a robust knowledge framework to inform and optimize management strategies in affected areas. Overall, we observed that the current literature relies primarily on isolated field ecological descriptions rather than a coherent, unified research line; mechanistic studies, including bacterial pathways and factors controlling degradation, remain scarce. At the fine scale, microbial community shifts during decomposition are strongly linked to the sequential utilization of distinct organic substrates, thereby favoring the proliferation of microorganisms capable of degrading complex organic molecules and of bacterial groups involved in sulfur respiration, methanogenesis, and nutrient recycling. In the case of sulfur respiration, groups such as Desulfobacterales and Desulfovibrionales may be responsible for the reported H2S emissions, which pose significant public health concerns. At a broad scale, degradation occurs both on beaches during emersion and in the water column during immersion, particularly during massive accumulations. The initial stages are characterized by the release of organic exudates and leachates. Experimental and observational studies confirm a strong early-stage release of H2S until the substrate is largely depleted. Depending on environmental conditions, a significant amount of biomass can be lost; however, this loss is highly variable, with notable consequences for contamination studies. Leachates may also contain low but ecologically significant amounts of arsenic, posing a potential contamination risk. Decomposition contributes to water-quality deterioration and oxygen depletion, with impacts at the individual, population, and ecosystem levels, yet many remain imprecisely attributed. Although evidence of nutrient enrichment in the water column is limited, studies indicate biological nutrient uptake. Achieving a comprehensive understanding of degradation and decomposition, including temporal and spatial dynamics, microbiome interactions, by means of directed research, is critical for effective coastal management, improved mitigation strategies, industrial valorization, and accurate modeling of biogeochemical cycles.
14 January 2026