- Article
Hematological Values of Two Species of Amazonian Caimans, Caiman crocodilus and Melanosuchus niger
- Adriano Teixeira de Oliveira,
- Marcio Quara de Carvalho Santos and
- Paulo Henrique Rocha Aride
- + 11 authors
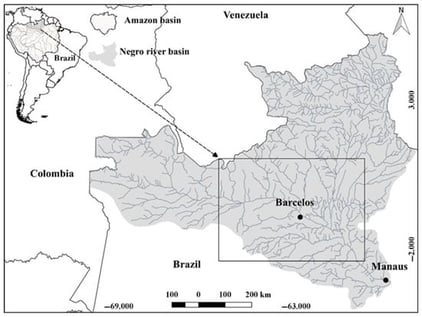
Determining hematological values is essential to provide baseline health and condition data. We evaluated the hematological parameters of free-living individuals of Caiman crocodilus and Melanosuchus niger from the middle Negro River region of Brazil. We captured 18 C. crocodilus and 16 M. niger. Blood was drawn using syringes containing 10% EDTA, and blood parameters were determined as previously described. The analyzed erythrocyte parameters were similar across the species, demonstrating that, despite their different sizes, they share similar strategies for oxygen absorption and transport in the blood. In the morphological analysis of blood cells, erythrocytes, erythroblasts, thrombocytes, lymphocytes, neutrophils, azurophils, heterophils, and basophils were found, and, in the quantification of leukocytes and thrombocytes, it was noted that lymphocytes are the central cells in the blood of the Amazonian caiman. In the plasma metabolite results, no significant differences were observed between glucose and total protein levels. Key physiological parameters were established to assess the health of C. crocodilus and M. niger, enabling the application of this information to sustainable captive production programs and helping to reduce pressure on wild populations.
6 February 2026




![Bathymetric map of Lake Dejguny with marked boat routes during hydroacoustic surveys in November 2005, October 2008, and 2021 (according to Hutorowicz et al., [16]).](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/limnolrev/limnolrev-26-00001/article_deploy/html/images/limnolrev-26-00001-g001-550.jpg)