Influence of Major Hurricanes “Helene” and “Milton” in 2024 on EVA of the Long Ocean Water Level Record at Key West, USA
Abstract
1. Introduction
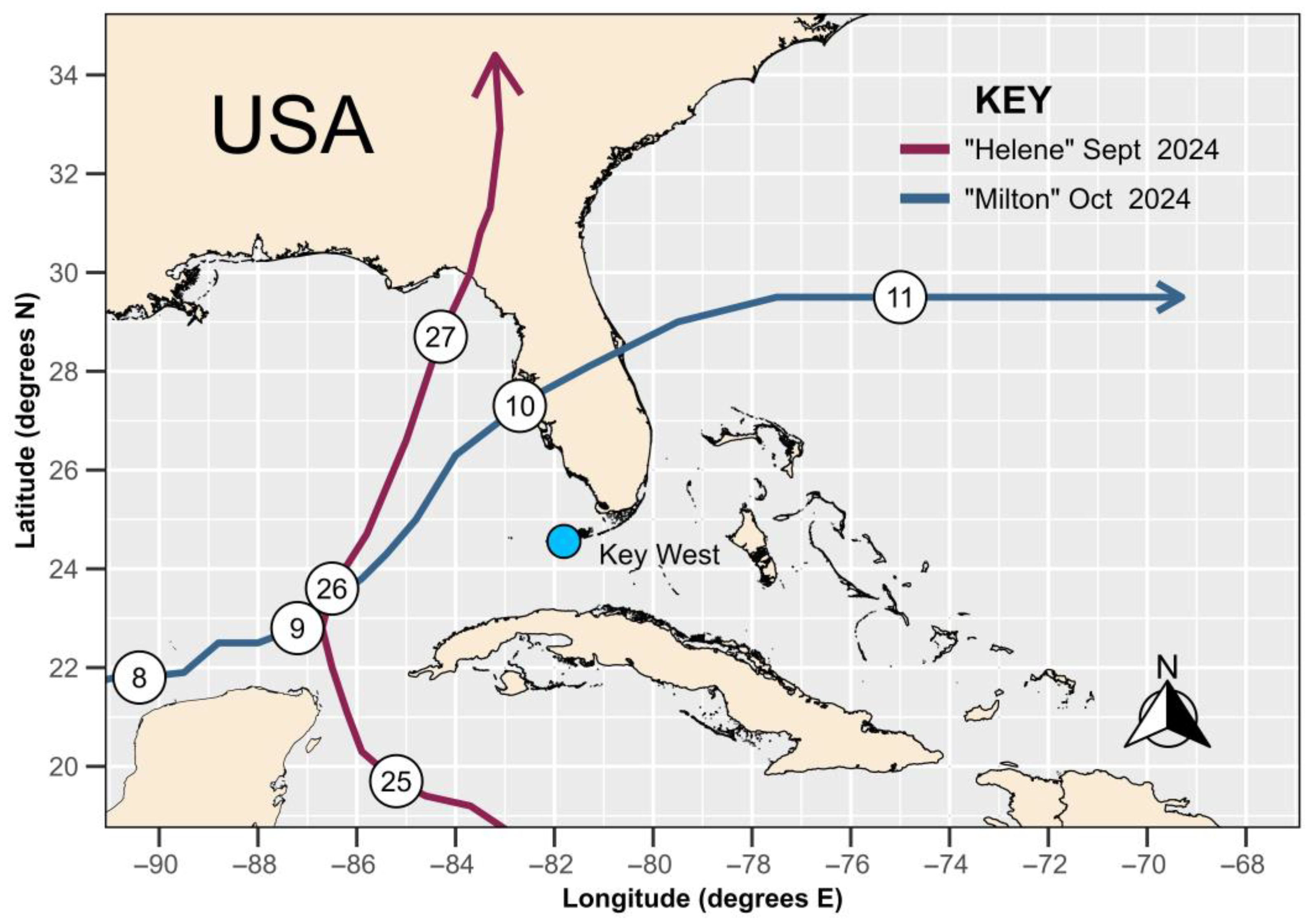
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Methodology
3. Results
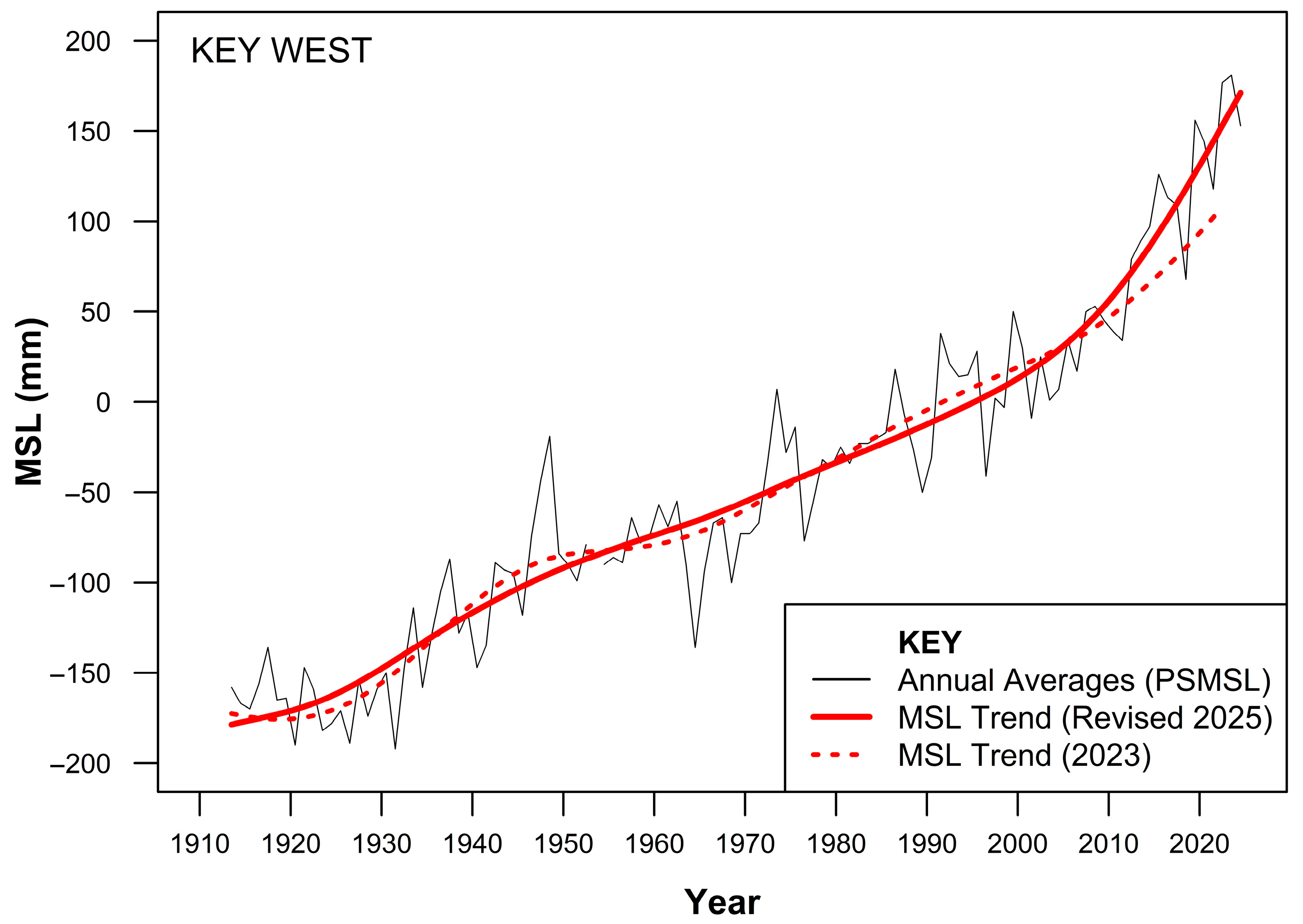
3.1. MSL and Hourly Tide Gauge Record
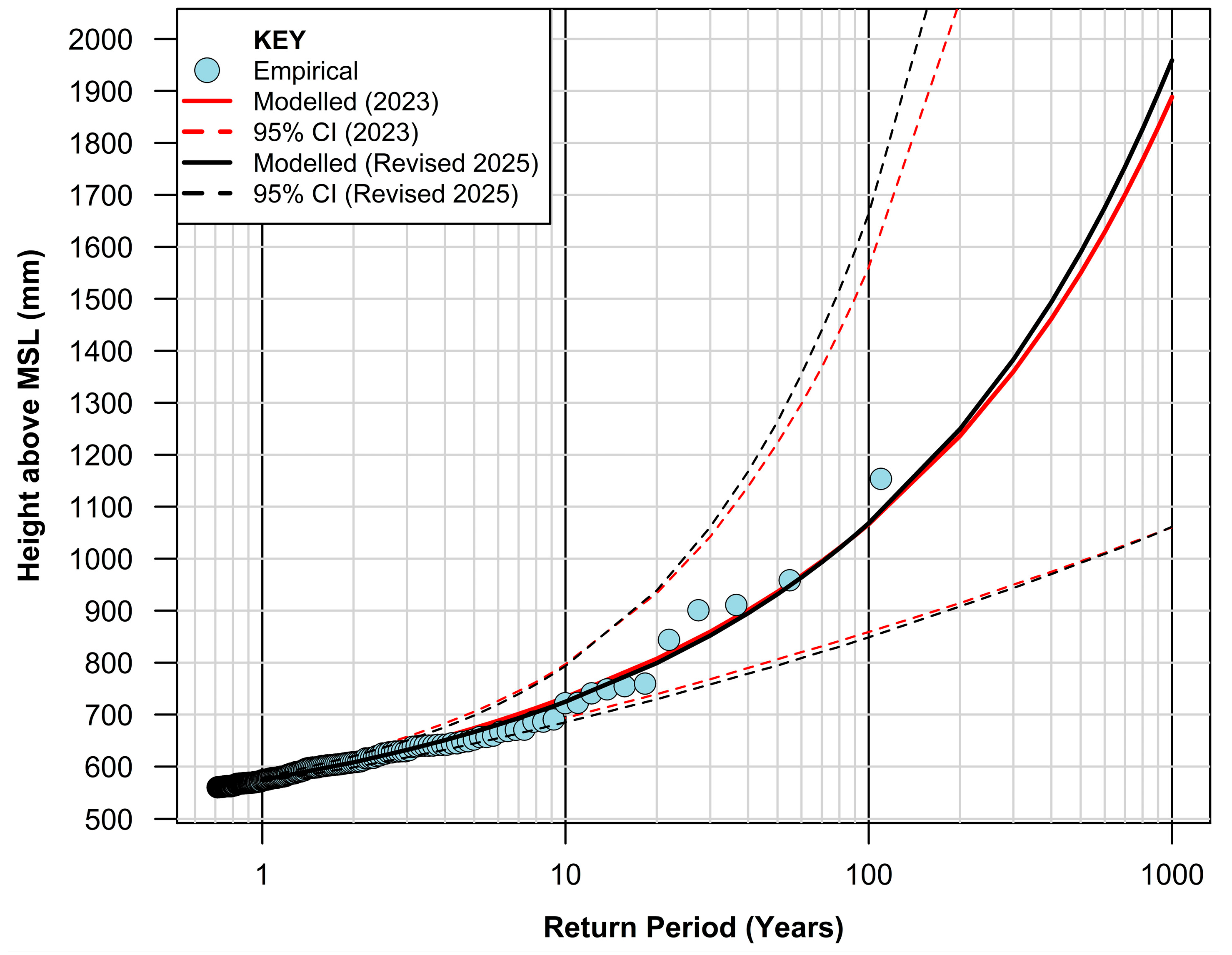
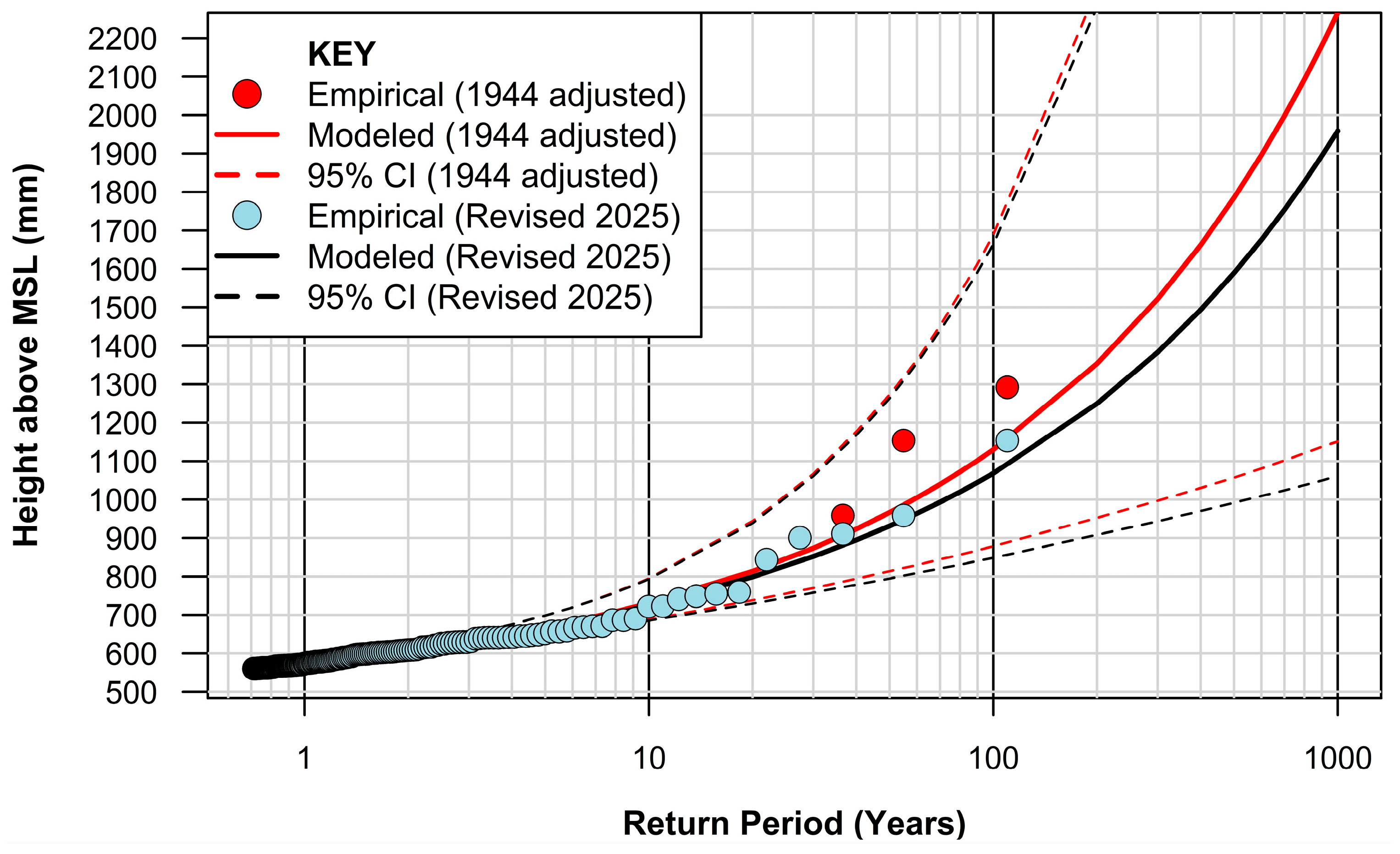
3.2. Extreme Value Analysis
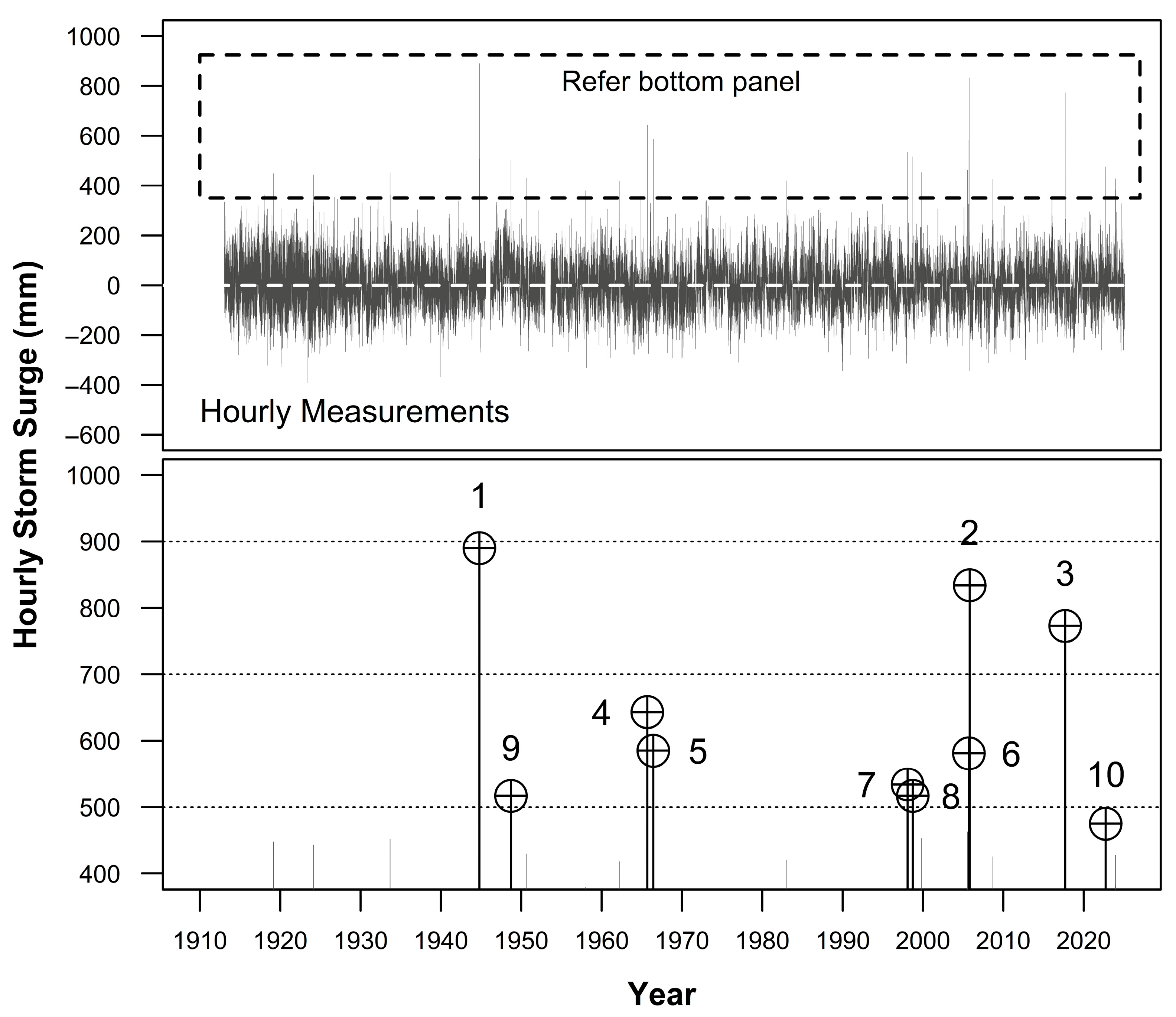
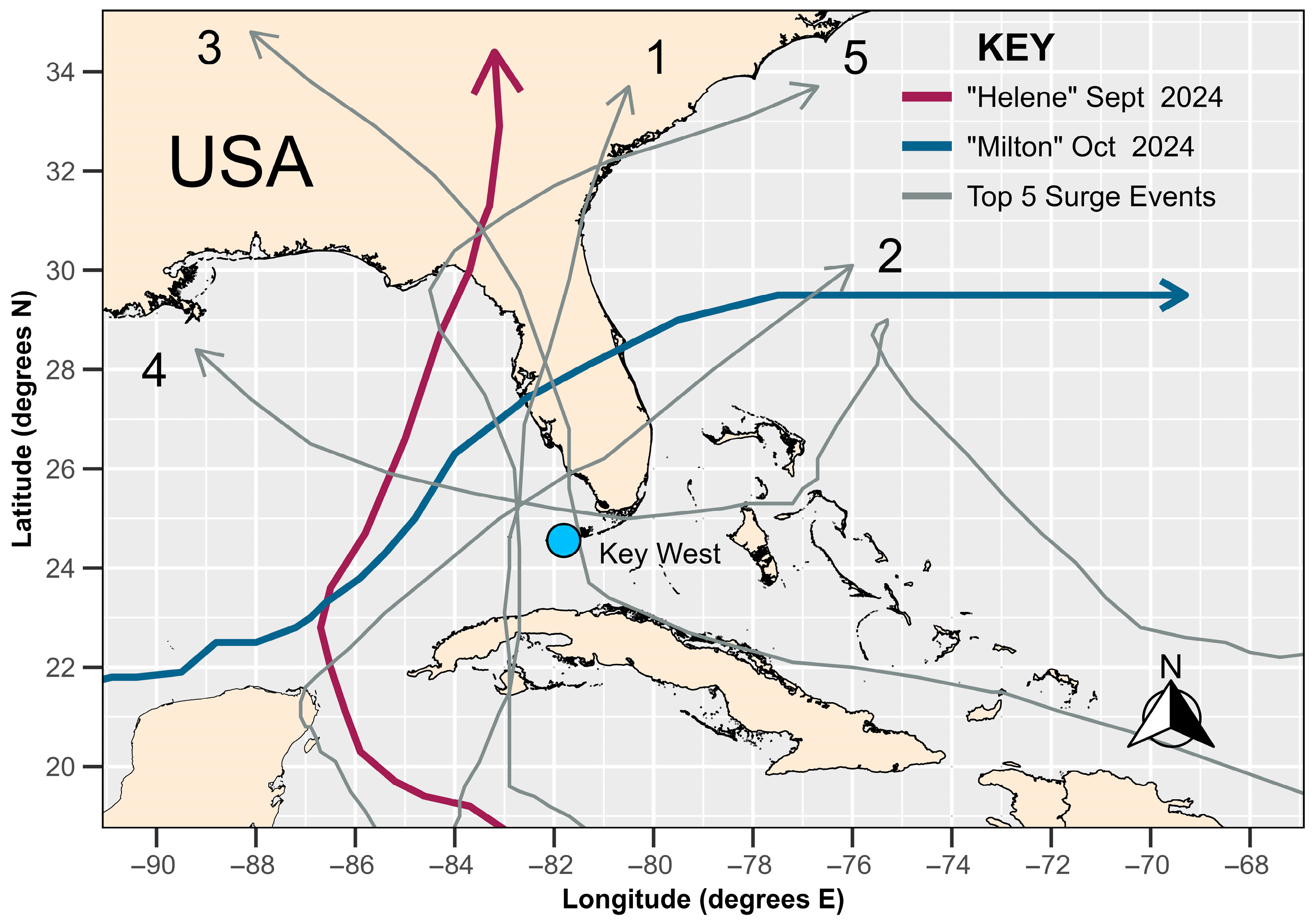
3.3. Storm Surge Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Determination of MSL and Its Influence over Results
4.2. Sensitivity of the Timing of Astronomical Tides with Storm Surge
4.3. Limitations of the Analysis and Results
4.4. Why Did Major Hurricanes “Helene” and “Milton” Have Little Effect on the EVA Results at the Key West Tidal Facility?
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Watson, P.J. Extreme Value Analysis of Ocean Still Water Levels along the USA East Coast—Case Study (Key West, Florida). Coasts 2023, 3, 294–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, A.B.; Cangialosi, J.P.; Chenard, M.; Alaka, L.; Delgado, S. National Hurricane Center Tropical Cyclone Report—Hurricane Helene (AL092024) 24–27 September 2024; National Hurricane Center: Miami, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Beven, J.L.I.; Alaka, L.; Fritz, C. National Hurricane Center Tropical Cyclone Report—Hurricane Milton (AL142024) 5-10 October 2024; National Hurricane Center: Miami, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Coles, S. An Introduction to Statistical Modeling of Extreme Values; Springer London: London, UK, 2001; ISBN 978-1-84996-874-4. [Google Scholar]
- Embrechts, P.; Klüppelberg, C.; Mikosch, T. Modelling Extremal Events; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; ISBN 978-3-642-08242-9. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, P.J. Determining Extreme Still Water Levels for Design and Planning Purposes Incorporating Sea Level Rise: Sydney, Australia. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, R.W.; Harlem, P.W.; Meeder, J.F. Managing the Anthropocene Marine Transgression to the Year 2100 and beyond in the State of Florida U.S.A. Clim. Change 2015, 128, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, W.V.; Hamlington, B.D.; Kopp, R.E.; Weaver, C.P.; Barnard, P.L.; Bekaert, D.; Brooks, W.; Craghan, M.; Dusek, G.; Frederikse, T.; et al. Global and Regional Sea Level Rise Scenarios for the United States: Updated Mean Projections and Extreme Water Level Probabilities Along U.S. Coastlines; NOAA Technical Report NOS 01; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Ocean Service: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2022.
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration National Hurricane Center. Available online: https://www.nhc.noaa.gov/data/#hurdat (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- PSMSL Permanent Service for Mean Sea Level. Available online: https://www.psmsl.org/data/obtaining/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Holgate, S.J.; Matthews, A.; Woodworth, P.L.; Rickards, L.J.; Tamisiea, M.E.; Bradshaw, E.; Foden, P.R.; Gordon, K.M.; Jevrejeva, S.; Pugh, J. New Data Systems and Products at the Permanent Service for Mean Sea Level. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 29, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Center for Operational Oceano-Graphic Products and Services (CO-OPS). Available online: https://tidesandcurrents.noaa.gov/stationhome.html?id=8724580 (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Beirlant, J.; Goegebeur, Y.; Teugels, J.; Segers, J. Statistics of Extremes; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2004; ISBN 9780470012383. [Google Scholar]
- Pickands, J. Statistical Inference Using Extreme Order Statistics. Ann. Stat. 1975, 3, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkema, A.A.; De Haan, L. Residual Life Time at Great Age. Ann. Probab. 1974, 2, 792–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, M.; Hüsler, J.; Reiss, R.-D. Statistics of Extremes. In Laws of Small Numbers: Extremes and Rare Events; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 455–471. ISBN 978-3-0348-0009-9. [Google Scholar]
- Broomhead, D.S.; King, G.P. Extracting Qualitative Dynamics from Experimental Data. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1986, 20, 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golyandina, N.; Nekrutkin, V.; Zhigljavsky, A.A. Analysis of Time Series Structure: SSA and Related Techniques; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Vautard, R.; Ghil, M. Singular Spectrum Analysis in Nonlinear Dynamics, with Applications to Paleoclimatic Time Series. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1989, 35, 395–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P.J. Improved Techniques to Estimate Mean Sea Level, Velocity and Acceleration from Long Ocean Water Level Time Series to Augment Sea Level (and Climate Change) Research. Ph.D. Thesis, University of New South Wales, Kensington, NSW, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, P.J. Status of Mean Sea Level Rise around the USA (2020). GeoHazards 2021, 2, 80–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Generalized Additive Models. Stat. Sci. 1986, 1, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.J. Generalized Additive Models. In Statistical Models in S; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2017; pp. 249–307. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, S.N.; Goude, Y.; Shaw, S. Generalized Additive Models for Large Data Sets. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C Appl. Stat. 2015, 64, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R Development Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Arns, A.; Wahl, T.; Haigh, I.D.; Jensen, J.; Pattiaratchi, C. Estimating Extreme Water Level Probabilities: A Comparison of the Direct Methods and Recommendations for Best Practise. Coast. Eng. 2013, 81, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilleland, E.; Katz, R.W. ExtRemes 2.0: An Extreme Value Analysis Package in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2016, 72, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarrott, C.; MacDonald, A. A Review of Extreme Value Threshold Estimation and Uncertainty Quantification. Revstat-Stat. J. 2012, 10, 33–60. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, S.; Resnick, S. A Discussion on Mean Excess Plots. Stoch. Process. Their Appl. 2010, 120, 1492–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA NOS What Is Storm Surge? Available online: https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/stormsurge-stormtide.html (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- UK Met Office Storm Surge. Available online: https://weather.metoffice.gov.uk/learn-about/weather/types-of-weather/storms/storm-surge (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Oppenheimer, M.; Glavovic, B.; Hinkel, J.; van de Wal, R.; Magnan, A.K.; Abd-Elgawad, A.; Cai, R.; Cifuentes-Jara, M.; DeConto, R.M.; Ghosh, T.; et al. Sea Level Rise and Implications for Low Lying Islands, Coasts and Communities. In IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate; The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fox-Kemper, B.; Hewitt, H.T.; Xiao, C.; Aðalgeirsdóttir, G.; Drijfhout, S.S.; Edwards, T.L.; Golledge, N.R.; Hemer, M.; Kopp, R.E.; Krinner, G.; et al. Ocean, Cryosphere and Sea Level Change. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1211–1362. [Google Scholar]
- May, C.L.; Osler, M.S.; Stockdon, H.F.; Barnard, P.L.; Callahan, J.A.; Collini, R.C.; Ferreira, C.M.; Finzi Hart, J.; Lentz, E.E.; Mahoney, T.B.; et al. Coastal Effects. In Fifth National Climate Assessment; Crimmins, A.R., Avery, C.W., Easterling, D.R., Kunkel, K.E., Stewart, B.C., Maycock, T.K., Eds.; U.S. Global Change Research Program: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- National Hurricane Center and Central Pacific Hurricane Center NOAA Website. Available online: https://www.nhc.noaa.gov/surge/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- National Weather Service NOAA Severe Weather Outbreak in South Florida: 2 February 1998. Available online: https://www.weather.gov/mfl/groundhogday (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Houston, J.R.; Dean, R.G. Sea-Level Acceleration Based on U.S. Tide Gauges and Extensions of Previous Global-Gauge Analyses. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baart, F.; Van Koningsveld, M.; Stive, M.J.F. Trends in Sea-Level Trend Analysis. J. Coast. Res. 2012, 28, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoghue, J.F.; Parkinson, R.W. Discussion of: Houston, JR and Dean, RG, 2011. Sea-Level Acceleration Based on US Tide Gauges and Extensions of Previous Global-Gauge Analyses. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 409–417. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 994–996. [Google Scholar]
- Houston, J.R.; Dean, R.G. Reply to: Donoghue, JF and Parkinson, RW, 2011. Discussion of: Houston, JR and Dean, RG, 2011. Sea-Level Acceleration Based on US Tide Gauges and Extensions of Previous Global-Gauge Analyses. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 409–417. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 997–998. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmstorf, S.; Vermeer, M. Discussion of: Houston, JR and Dean, RG, 2011. Sea-Level Acceleration Based on US Tide Gauges and Extensions of Previous Global-Gauge Analyses. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 409–417. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 784–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, J.R.; Dean, R.G. Reply to: Rahmstorf, S. and Vermeer, M., 2011. Discussion of: Houston, JR and Dean, RG, 2011. Sea-Level Acceleration Based on US Tide Gauges and Extensions of Previous Global-Gauge Analyses. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 409–417. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 788–790. [Google Scholar]
- Houston, J.R.; Dean, R.G. Effects of Sea-Level Decadal Variability on Acceleration and Trend Difference. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 290, 1062–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, H.; Dangendorf, S.; Petersen, A.C. A Review of Trend Models Applied to Sea Level Data with Reference to the “Acceleration-Deceleration Debate”. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 3873–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubechies, I. Orthonormal Bases of Compactly Supported Wavelets. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 1988, 41, 909–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubechies, I. Ten Lectures on Wavelets; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Grossmann, A.; Morlet, J. Decomposition of Hardy Functions into Square Integrable Wavelets of Constant Shape. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 1984, 15, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, A.; Kronland-Martinet, R.; Morlet, J. Reading and Understanding Continuous Wavelet Transforms. In Proceedings of the Wavelets: Time-Frequency Methods and Phase Space Proceedings of the International Conference, Marseille, France, 14–18 December 1987; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990; pp. 2–20. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, P.J. Development of a Unique Synthetic Data Set to Improve Sea-Level Research and Understanding. J. Coast. Res. 2015, 31, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P.J. Identifying the Best Performing Time Series Analytics for Sea Level Research. In Time Series Analysis and Forecasting: Contributions to Statistics; Rojas, I., Pomares, H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 261–278. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, P.J. TrendSLR: Estimating Trend, Velocity and Acceleration from Sea Level Records; Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN). 2019. Available online: https://r-packages.io/packages/TrendSLR (accessed on 23 September 2025).
- City of Miami, Florida Website. Available online: https://www.miami.gov/My-Government/Climate-Change-in-the-City-of-Miami/King-Tides (accessed on 1 April 2025).
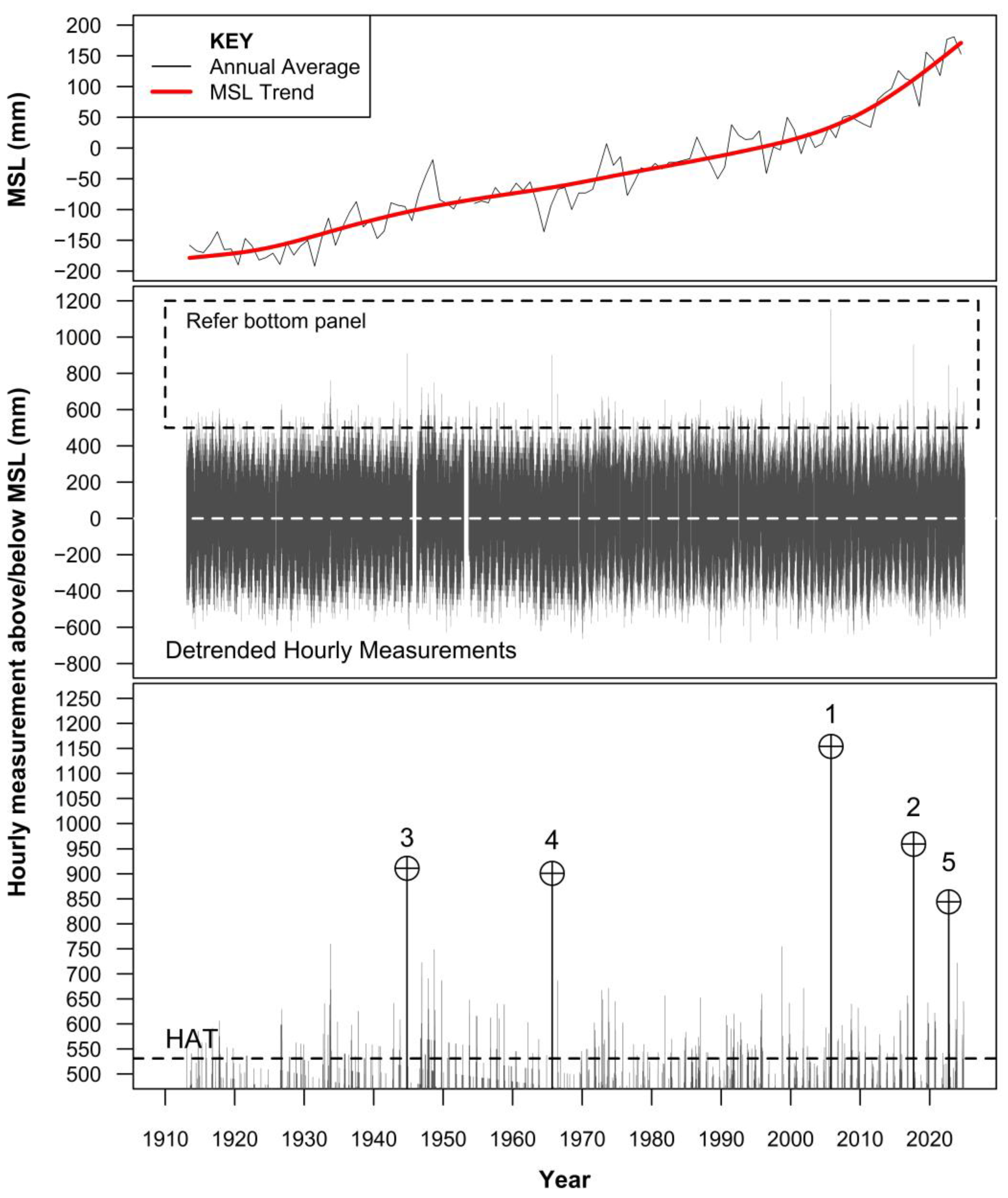
| Rank | Height Above MSL (mm) 1 | Date (Time, h) | Hurricane Event 2 | Coincident Tide (mm) 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1154 | 24 October 2005 (0700) | Wilma | 343 |
| 2 | 959 | 10 September 2017 (1700) | Irma | 256 |
| 3 | 911 | 18 October 1944 (2200) | Unnamed | 21 |
| 4 | 901 | 8 September 1965 (1400) | Betsy | 336 |
| 5 | 844 | 28 September 2022 (0300) | Ian | 396 |
| 6 | 760 | 5 October 1933 (0300) | Unnamed | 436 |
| 7 | 755 | 25 September 1998 (1800) | Georges | 238 |
| 8 | 749 | 21 September 1948 (1700) | Unnamed | 292 |
| 9 | 741 | 21 September 2005 (0200) | Rita | 318 |
| 10 | 723 | 9 December 1946 (0200) | - | 429 |
| Return Period (Years) | Height Above MSL (mm) (2023) | Height Above MSL (mm) (Revised 2025) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 576 | 574 |
| 2 | 613 | 608 |
| 5 | 674 | 667 |
| 10 | 733 | 725 |
| 20 | 807 | 799 |
| 50 | 937 | 932 |
| 100 | 1067 | 1068 |
| 200 | 1236 | 1250 |
| 500 | 1550 | 1590 |
| 1000 | 1888 | 1959 |
| Rank | Storm Surge (mm) 1 | Date (Time, h) | Hurricane Event 2 | Min Proximity to Track Path (km) 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 890 | 18 October 1944 (2200) | Unnamed | 110 |
| 2 | 834 | 24 October 2005 (0800) | Wilma | 117 |
| 3 | 773 | 10 September 2017 (1400) | Irma | 32 |
| 4 | 643 | 8 September 1965 (1500) | Betsy | 68 |
| 5 | 585 | 8 June 1966 (2000) | Alma | 90 |
| 6 | 581 | 21 September 2005 (0000) | Rita | 64 |
| 7 | 534 | 2 February 1998 (2200) | - | - |
| 8 | 517 | 25 September 1998 (1800) | Georges | 6 |
| 9 | 502 | 21 September 1948 (2000) | Unnamed | 22 |
| 10 | 475 | 28 September 2022 (0100) | Ian | 110 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Watson, P.J. Influence of Major Hurricanes “Helene” and “Milton” in 2024 on EVA of the Long Ocean Water Level Record at Key West, USA. Coasts 2025, 5, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts5040041
Watson PJ. Influence of Major Hurricanes “Helene” and “Milton” in 2024 on EVA of the Long Ocean Water Level Record at Key West, USA. Coasts. 2025; 5(4):41. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts5040041
Chicago/Turabian StyleWatson, Phil J. 2025. "Influence of Major Hurricanes “Helene” and “Milton” in 2024 on EVA of the Long Ocean Water Level Record at Key West, USA" Coasts 5, no. 4: 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts5040041
APA StyleWatson, P. J. (2025). Influence of Major Hurricanes “Helene” and “Milton” in 2024 on EVA of the Long Ocean Water Level Record at Key West, USA. Coasts, 5(4), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts5040041






