Topical Advisory Panel applications are now closed. Please contact the Editorial Office with any queries.
Journal Description
Analytica
Analytica
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on analytical chemistry and chemical analysis published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Chemistry, Analytical) / CiteScore - Q2 (Materials Science (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 19 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Impact Factor:
3.6 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.1 (2024)
Latest Articles
Determination of Vanadium in Alkaline Leachates of Vanadium Slags Using High-Resolution Continuum Source Graphite Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (HR-CS GFAAS) Part I: The Influence of Sample Matrix on the Quality of Graphite Atomizer
Analytica 2026, 7(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica7010007 - 8 Jan 2026
Abstract
Interactions between alkaline solutions and the surface of pyrolytically coated graphite tubes (PCGTs) with/without a platform for determination of vanadium using high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry (HR CS GFAAS) are discussed. Changes on the surface of tubes, lifetime of tubes,
[...] Read more.
Interactions between alkaline solutions and the surface of pyrolytically coated graphite tubes (PCGTs) with/without a platform for determination of vanadium using high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry (HR CS GFAAS) are discussed. Changes on the surface of tubes, lifetime of tubes, and formation of memory effect in the determination of vanadium in alkaline solutions (NaOH, Na2CO3, and real alkaline slag leachates) were investigated. Based on the results obtained, it is possible to state that HR CS GFAAS determination of vanadium content in alkaline solutions reveals that PCGTs with a platform are more susceptible than those without a platform to the formation of deposits and degradation of the platform surface, especially after the application of hydroxide environments. More marked and faster formation of deposits leads to shortening of the analytical lifetime of PCGTs with a platform (approx. 70 atomization/analytical cycles (ACs)) compared to PCGTs without a platform (approx. 290 ACs). The mechanical life of both types of tubes is comparable (approx. 500 ACs). Deposits formed on the internal surface of PCGTs can be removed in the presence of a carbonate environment and higher temperatures. Damage to the PCGT surface leads to the formation of scaled shapes and cavities, which can result in decreased absorbance due to losses of vanadium in the cavities (negative measurement error), or in increased absorbance by washing out of vanadium from the cavities (positive measurement error, and formation of memory effect). It was found that more frequent cleaning of PCGTs by performing ACs in an environment of 4 mol L−1 HNO3 can eliminate these unfavourable phenomena. Our results have shown that in the case of samples analysed with different sample environments (acidic vs. alkaline), the surface material of the tube/platform wears out more quickly, and therefore it is necessary to include a cleaning stage after changing the nature of the environment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Spectroscopy)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Iodine and Bromine Analysis in Human Urine and Serum by ICP-MS, Tailored for High-Throughput Routine Analysis in Population-Based Studies
by
Thieli Schaefer Nunes, Lucas Schmidt, Kayla Peterson, Rosalind Wright and Julio Alberto Landero-Figueroa
Analytica 2026, 7(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica7010006 - 6 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone synthesis and is particularly critical during pregnancy, where excess and mainly its deficiencies can impair fetal neurodevelopment and increase maternal complications. Bromine has also gained attention due to its potential to interfere with iodine metabolism and contribute
[...] Read more.
Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone synthesis and is particularly critical during pregnancy, where excess and mainly its deficiencies can impair fetal neurodevelopment and increase maternal complications. Bromine has also gained attention due to its potential to interfere with iodine metabolism and contribute to adverse health effects when present in excess. Monitoring iodine and bromine in biological samples, especially urine and serum, is therefore important for assessing thyroid function and population health. This work presents a simple and robust ICP-MS method for simultaneous determination of bromine and iodine in urine and serum. The procedure uses a 20-fold dilution with 10 mmol L−1 ammonia containing 0.1% (w/w) EDTA-2Na, ensuring solution stability, minimizing sample-to-sample variability, and eliminating the need for matrix-matched calibration. EDTA-2Na effectively prevents precipitation of metal species at high pH, avoiding blockages in the sample introduction system. Method accuracy was confirmed through certified reference materials and spike-recovery experiments, both showing suitable agreement for the two analytes. Precision was consistently strong (RSD < 6%), and low detection limits were achieved (0.78 μg L−1 for Br and 0.24 μg L−1 for I). The use of a high-efficiency nebulizer enabled analysis with only 50 µL of sample, making the method suitable for limited-volume specimens. Overall, this approach provides a sensitive, accurate, and practical solution for large-scale population studies and clinical applications.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Green Hybrid Biopolymeric Beads for Efficient Removal of Copper Ions from Aqueous Solutions: Experimental Studies Assisted by Monte Carlo Simulation
by
Ilias Barrak, Ikrame Ayouch, Zineb Kassab, Youness Abdellaoui, Jaber Raissouni, Said Sair, Mounir El Achaby and Khalid Draoui
Analytica 2026, 7(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica7010005 - 5 Jan 2026
Abstract
The objective of this research is to develop environmentally friendly, risk-free and effective adsorbent composite beads that remove Cu(II) ions from aqueous solutions using cost-effective biopolymers (Carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) and sodium alginate (AL)). The synthesized hydrogel beads (AL@CMC) were dried using two drying modes,
[...] Read more.
The objective of this research is to develop environmentally friendly, risk-free and effective adsorbent composite beads that remove Cu(II) ions from aqueous solutions using cost-effective biopolymers (Carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) and sodium alginate (AL)). The synthesized hydrogel beads (AL@CMC) were dried using two drying modes, namely air-drying and freeze-drying, and characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR), and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) analysis. The study investigated factors such as pH, adsorbent dosage, reaction time, Cu(II) ions concentration, and temperature to elucidate the adsorption mechanisms involved in removing copper ions. The results indicated that the hydrogel exhibited a maximum adsorption capacity of 99.05 mg·g−1, which is highly competitive compared to previous studies; the AL@CMC beads prepared in this work show a significantly higher adsorption capacity, improved stability due to the interpenetrated biopolymer network, and a clear enhancement from freeze-drying, which greatly increases porosity and active surface area. In addition, the pseudo-second-order nonlinear kinetic model best described the experimental data, implying the chemical nature of the adsorption process. Furthermore, the thermodynamic studies revealed that the adsorption process was endothermic, spontaneous, and homogenous. A Monte Carlo simulation model was utilized to ensure compatibility with the adsorption mechanism, in order to delve deeper into the intricacies of the adsorption process and gain a more comprehensive understanding of its underlying mechanisms and behavior. In conclusion, the prepared hydrogel beads proved to be an effective adsorbent for efficiently removing copper ions, making them a promising solution for addressing Cu(II) ion pollution.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sample Pretreatment and Extraction)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of 3D Printing Parameters on the Electrochemical Response of Additively Manufactured Devices
by
Scarlat Ohanna Dávila da Trindade, Thaís Cristina de Oliveira Cândido, Matheus Martins Guedes and Arnaldo César Pereira
Analytica 2026, 7(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica7010004 - 3 Jan 2026
Abstract
Additive manufacturing, particularly fused deposition modeling (FDM), has emerged as a promising approach for producing electrochemical sensors based on conductive thermoplastic composites. In this study, the effects of various printing parameters (extrusion temperature, layer height and width, printing speed, and the number of
[...] Read more.
Additive manufacturing, particularly fused deposition modeling (FDM), has emerged as a promising approach for producing electrochemical sensors based on conductive thermoplastic composites. In this study, the effects of various printing parameters (extrusion temperature, layer height and width, printing speed, and the number of conductive layers) on the electrochemical performance of PLA/CB electrodes fabricated via FDM were investigated. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analyses showed that properly adjusting these parameters promoted the formation of more efficient conductive pathways and reduced charge transfer resistance during monitoring of the redox behavior of the potassium ferrocyanide/ferricyanide probe. Furthermore, the electrochemical performance of the device was demonstrated through the detection of different model analytes, including dopamine, catechol, hydroquinone, paracetamol, and uric acid. The device was also applied to the determination of dopamine, achieving a detection limit of 0.16 µmol L−1. Overall, the results highlighted that optimizing printing conditions is essential for improving the electrochemical performance of 3D-printed devices, reinforcing the potential of 3D printing as a promising route for the fabrication of electrodes for electroanalytical applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Electroanalysis)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Spectroscopic and Physicochemical Analysis of Bioactive Cobalt(II) β-Diketo Ester Complexes: Insights into DNA and BSA Binding Mechanisms
by
Ignjat Filipović, Snežana Stojanović, Jelena Petronijević, Milena Milutinović, Danijela Nikodijević, Nevena Petrović, Marijana Kosanić and Nenad Joksimović
Analytica 2026, 7(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica7010003 - 29 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The urgent need for effective therapies against cancer and antimicrobial-resistant pathogens motivates the development of novel metal-based complexes. Herein, we report the synthesis and characterization of four novel cobalt(II) complexes with biologically relevant β-diketo ester ligands. The complexes were characterized via UV-Vis, FTIR,
[...] Read more.
The urgent need for effective therapies against cancer and antimicrobial-resistant pathogens motivates the development of novel metal-based complexes. Herein, we report the synthesis and characterization of four novel cobalt(II) complexes with biologically relevant β-diketo ester ligands. The complexes were characterized via UV-Vis, FTIR, mass spectrometry, and elemental analysis. Their biological activities were evaluated through antimicrobial and cytotoxic assays. Complex B1 exhibited the strongest antimicrobial activity, with minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of 0.23 mg/mL against Staphylococcus aureus and Proteus mirabilis, and 0.01 mg/mL against Mucor mucedo, exceeding the performance of ketoconazole. Cytotoxicity studies on SW480 colorectal cancer cells and HaCaT normal keratinocytes identified B3 as the most potent anticancer agent (IC50 = 11.49 µM), selectively targeting tumor cells. Morphological analysis indicated apoptosis as the primary mode of cell death. Mechanistic studies were performed to elucidate interactions with biomolecules. UV-Vis and fluorescence spectroscopy, viscosity measurements, and molecular docking revealed that B3 binds strongly to calf thymus DNA via hydrophobic interactions and groove binding, and exhibits selective binding to bovine serum albumin (site II, subdomain IIIA). These results highlight the potential of cobalt(II) complexes as multifunctional agents with significant antimicrobial and antitumor activities and provide detailed insight into their molecular interactions with DNA and serum proteins.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessSystematic Review
Systematic Review of Different Methods for the Quantification of Vitamin C in Human Plasma Samples by HPLC and UV Detector
by
Miriam Demtschuk and Priska Heinz
Analytica 2026, 7(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica7010002 - 23 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In clinical medicine it is of interest to know vitamin C blood levels. There are numerous variations in published sample preparation methods for quantifying vitamin C using HPLC. For the determination of vitamin C in human probes, the method needs to be simple,
[...] Read more.
In clinical medicine it is of interest to know vitamin C blood levels. There are numerous variations in published sample preparation methods for quantifying vitamin C using HPLC. For the determination of vitamin C in human probes, the method needs to be simple, fast, and accurate. A systematic search in Pubmed was carried out to identify the methods for the quantification of vitamin C with HPLC in combination with a UV detector in human plasma. A total of 83 reports were screened, from which seven methods were selected and examined in detail. Tabular overviews compare the different sample preparation options, HPLC parameters, and validation criteria. Different reagents for protein precipitation and extraction are discussed. By allowing the user to see the criteria of interest at a glance, it can be used as a tool for the rapid development and establishment of a vitamin C determination method using HPLC.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Propylene Glycol as a Promising Eluent in Green Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatographic Separation of Ascorbic Acid and Glutathione in Effervescent Tablets
by
Pasant T. Elbanna, Mohamed A. Hammad, Inas A. Abdallah, Marcello Locatelli and Fotouh R. Mansour
Analytica 2026, 7(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica7010001 - 23 Dec 2025
Abstract
Exploring green organic solvents is a global demand. Most of the currently used solvents pose some concerns regarding environmental sustainability and occupational health risks. In this work, propylene glycol was employed for the first time as a green solvent for mobile phase preparation
[...] Read more.
Exploring green organic solvents is a global demand. Most of the currently used solvents pose some concerns regarding environmental sustainability and occupational health risks. In this work, propylene glycol was employed for the first time as a green solvent for mobile phase preparation in the reversed phase chromatographic separation of a mixture of two antioxidants, glutathione and ascorbic acid. The slight viscosity of propylene glycol was manipulated by using water as a co-fluidizing agent to facilitate pumping. Method optimization was performed using factorial design experimental Expert 13® Software (Minneapolis, MN, USA) to achieve the maximum resolution and the minimum run time. The reported method was properly validated according to the International Conference on Harmonization criteria at the linearity range of 1–500 µg/mL, with acceptable accuracy and precision for both drugs. The method was effectively applied for the quantification of both drugs in their commercial pharmaceutical formulation. The proposed method was assessed for environmental and operator safety by means of global tools like AGREE and MoGAPI and has proved high degrees of greenness. Propylene glycol has several benign properties, such as low volatility, less toxicity, compatibility with UV detectors and very low flammability, that will soon assemble it as a promising alternative for the conventionally used solvents.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Chromatography)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Chemometric Approaches for Identification of Herbal Medicinal Products
by
Olga V. Levitskaya, Tatiana V. Pleteneva, Elena V. Uspenskaya, Daria A. Galkina, Daiaana D. Ogotoeva, Nadezda A. Khodorovich and Anton V. Syroeshkin
Analytica 2025, 6(4), 59; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040059 - 16 Dec 2025
Abstract
Quality control of herbal medicinal products (HMPs) is challenging due to their multicomponent composition. For most HMPs, chemical reference standards (CRSs) required for traditional chromatographic and spectral analyses are unavailable. According to USP and Ph. Eur., an exception is valerian tincture, for which
[...] Read more.
Quality control of herbal medicinal products (HMPs) is challenging due to their multicomponent composition. For most HMPs, chemical reference standards (CRSs) required for traditional chromatographic and spectral analyses are unavailable. According to USP and Ph. Eur., an exception is valerian tincture, for which highly specific CRSs have been developed. The aim of this study was to use principal component analysis (PCA) and the novel two-dimensional diffuse laser scattering (2D-DLS) method to identify HMPs and their aqueous-ethanolic extracts according to their botanical genera without relying on specific marker compounds. Spectral data were compiled into an extensive library covering a wide wavelength range—from 0.02 nm to 15,000 nm. PCA of the spectral data (UV spectrophotometry, fluorimetry, FTIR spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction) enabled clustering of samples by individual botanical genera. The most significant information for sample differentiation was provided by wavenumbers of 1400, 1180, and 931 cm−1 in the IR spectra and wavelengths of 450 nm and 672 nm in the UV and fluorescence spectra, respectively. During model cross-validation, all “blind samples” were correctly classified by botanical genus, achieving a non-error rate (NER) of 100%. Furthermore, the unique 2D-DLS method was used to rapidly identify tinctures without opening the glass bottles.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Analytical Techniques and Methods in Pharmaceutical Science)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Fluorescein-Based Probe for Selective Detection of ClO− and Resultant Mixture as a Fluorescence Sensor for Br− and I−
by
Maksim N. Zavalishin, Gleb A. Nikitin, Vladimir S. Osokin and George A. Gamov
Analytica 2025, 6(4), 58; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040058 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
This paper presents the design and evaluation of a fluorescent probe based on fluorescein hydrazide for the selective detection of hypochlorite (ClO−), bromide (Br−), and iodide (I−) ions in solution. The starting chemosensor, fluorescein hydrazide, is suitable
[...] Read more.
This paper presents the design and evaluation of a fluorescent probe based on fluorescein hydrazide for the selective detection of hypochlorite (ClO−), bromide (Br−), and iodide (I−) ions in solution. The starting chemosensor, fluorescein hydrazide, is suitable for detecting hypochlorite anions in solution, as observed for the first time. The Br− and I− ions could be discovered after activating the probe with hypochlorite. Upon interaction with ClO− ions, the proposed probe exhibits a significant increase in fluorescence emission, a sharp rise in absorbance, and a distinct color change, which is attributed to the conversion from the spirolactam closed form to the open form of the fluorescein ring. ClO− and Br− ions added together were found to brominate the probe in an acetonitrile–water mixture, resulting in a pronounced bathochromic shift in both absorption and emission spectra. Notably, the combination of ClO− and I− was more effective in cleaving the spirolactam ring than hypochlorite alone. Quantum chemical calculations were used to understand the detection mechanism of Br and I ions in a probe–hypochlorite mixture. The probe demonstrated exceptional selectivity and rapid response towards the target analytes, with detection limits determined to be 2.61 μM for ClO−, 66 nM for Br−, and 13 nM for I−. Furthermore, it successfully monitored fluctuations in ClO−, Br−, and I− concentrations within complex systems, highlighting its potential application in environmental and biological monitoring.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sensors)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Label-Free Electrochemical Genosensor for Klotho Detection Based on Gold Nanoparticle-Modified Electrodes and Mixed Self-Assembled Monolayers
by
Juan Pablo Hervás-Pérez, Laura Martín-Carbajo and Marta Sánchez-Paniagua
Analytica 2025, 6(4), 57; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040057 - 9 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Alterations in the expression of the Klotho gene have been associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD), and its potential as an early diagnostic biomarker is currently under active investigation. In this work, we report the development of a highly sensitive, label-free electrochemical DNA-based
[...] Read more.
Alterations in the expression of the Klotho gene have been associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD), and its potential as an early diagnostic biomarker is currently under active investigation. In this work, we report the development of a highly sensitive, label-free electrochemical DNA-based biosensor for the detection of a 100 mer DNA fragment corresponding to a partial region of Klotho mRNA. The proposed bioplatform integrates mixed self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) and gold nanoparticles for efficient DNA immobilization within a sandwich-type configuration, coupled with impedimetric detection. Different SAM architectures were evaluated by cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, with the binary monolayer composed of 1-hexadecanethiol (HDT) and the capture probe (CP) exhibiting the best analytical performance. The use of gold nanoparticle-modified screen-printed carbon electrodes (AuNPs–SPCEs) resulted in a 1.4-fold increase in the signal-to-noise ratio compared to screen-printed gold electrodes. Additionally, the incorporation of a blocking step using bovine serum albumin (BSA–HDT–CP–AuNPs–SPCE) enhanced the sensitivity by 1.6-fold compared to the unblocked system. The genosensor displayed a linear response in the concentration range of 3 × 10−10 to 7.5 × 10−8 M, achieving a detection limit of 0.09 nM. Relative standard deviations below 7.5% were obtained for different Klotho concentrations, confirming high intra-assay and intermediary precision. Selectivity assays demonstrated negligible signals for non-complementary sequences, while recovery experiments in spiked human serum samples yielded satisfactory values between 96.5% and 103.4%.
Full article
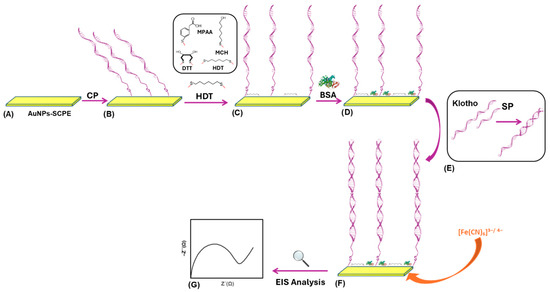
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Effect of Mineral and Organic Acid Addition on the Ethanol Organosolv Treatment of Waste Orange Peels for Producing Hesperidin-Enriched Extracts
by
Hiba Agnaou, Hela Refai, Spyros Grigorakis and Dimitris P. Makris
Analytica 2025, 6(4), 56; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040056 - 9 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Waste orange peels (WOP) are a major orange processing residue, and they may be a rich source of precious bioactive polyphenols. Amongst the various WOP constituents, hesperidin holds a prominent position as the most abundant polyphenolic metabolite, with proven biological properties. The current
[...] Read more.
Waste orange peels (WOP) are a major orange processing residue, and they may be a rich source of precious bioactive polyphenols. Amongst the various WOP constituents, hesperidin holds a prominent position as the most abundant polyphenolic metabolite, with proven biological properties. The current work was performed to provide detailed information on the effect of various acid catalysts to assist hesperidin recovery, using an ethanol organosolv treatment. The treatment developed was first examined by comparing inorganic (HCl) and natural organic (oxalic, citric) acids for their influence on process performance, extraction kinetics, and severity. Following this, optimization was accomplished through response surface methodology, and the extracts produced were investigated with respect to their polyphenolic composition and antioxidant characteristics. The HCl-catalyzed treatment, carried out with 70% ethanol/2% HCl, was proven the most efficacious, giving a total polyphenol yield of 30.7 mg gallic acid equivalents per g of dry mass, and it was shown that the treatment yield was related to severity, obeying a power model. Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry analysis of the extract generated under optimized conditions (170 min, 80 °C) revealed that hesperidin was extensively hydrolyzed into hesperetin 7-O-glucoside and aglycone (hesperetin). Such an effect was very limited with the oxalic acid-catalyzed treatment, whereas citric acid did not affect the original polyphenolic composition. Overall, the HCl-catalyzed treatment was of significantly higher performance, providing a total flavanone yield of 21.22 mg per g dry mass. The results of this investigation may be of value in adjusting treatment settings for (i) increased flavonoid recovery from WOP and (ii) producing extracts enriched in hesperidin and/or its hydrolysis derivatives. Such practical recommendations may assist the establishment of WOP valorization processes in an integrated biorefinery prospect.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
LIBS of Low-Alloyed Lead Systems: Chemometric Data Processing and Quantitative Analysis
by
Vitaliy Fomin, Milana Turovets, Nabira Kelesbek, Assanali Ainabayev, Daniyar Sadyrbekov, Dauletkhan Kaykenov, Askhat Borsynbayev, Nurbakyt Azhibay and Saule Aldabergenova
Analytica 2025, 6(4), 55; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040055 - 6 Dec 2025
Abstract
A probabilistic–deterministic design of experiments (PDDoE) approach was employed to optimize laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) parameters for the quantitative determination of minor components in lead-based alloys. The PDDoE optimization identified 18 J laser pump lamp energy, 1 µs delay, and 1 µs exposure
[...] Read more.
A probabilistic–deterministic design of experiments (PDDoE) approach was employed to optimize laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) parameters for the quantitative determination of minor components in lead-based alloys. The PDDoE optimization identified 18 J laser pump lamp energy, 1 µs delay, and 1 µs exposure as optimal conditions, minimizing spectral dispersion (5–8%) and ensuring stable plasma formation. The acquired spectra were subsequently processed in an R-based automated workflow, where Linear, Lasso, and Ridge regression models were used to establish quantitative relationships between normalized line intensities and atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) reference data. The resulting models demonstrated high accuracy (R2 = 0.97 for Sn, 0.985 for Sb, 0.982 for Bi, 0.919 for As, and 0.905 for Ag), with prediction errors (RMSE) below 10% and limits of quantification (LOQ) under 0.05 wt.%. Principal component analysis (PCA) applied to 43 historical (19th–20th century) and technogenic samples (19th–20th century) allowed us to isolate clusters of Pb–Sb alloys corresponding to secondary accumulator materials, alongside a diffuse group of nearly pure Pb specimens containing variable minor impurities. The combined PDDoE–LIBS–R analytical framework provides a reproducible, non-destructive, and chemometrically validated methodology for the quantitative characterization and classification of archeological and industrial lead alloys.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Chemometrics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development of Glass Cup Aqueous Sampling and Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction/Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry for Measuring Ethanol, Acetaldehyde and Acetone Emission from Human Skin Surface
by
Keita Saito, Yuki Takeuchi and Hiroyuki Kataoka
Analytica 2025, 6(4), 54; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040054 - 2 Dec 2025
Abstract
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted from human skin are promising biomarkers for non-invasive health assessment and disease diagnosis. However, efficient collection and sensitive analytical methods for skin VOCs remain challenging. We developed a method for measuring ethanol, acetaldehyde, and acetone from palmar skin
[...] Read more.
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emitted from human skin are promising biomarkers for non-invasive health assessment and disease diagnosis. However, efficient collection and sensitive analytical methods for skin VOCs remain challenging. We developed a method for measuring ethanol, acetaldehyde, and acetone from palmar skin using glass cup aqueous sampling followed by headspace solid-phase microextraction (HS-SPME) coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Compounds were extracted using a carboxen/polydimethylsiloxane fiber by HS-SPME and separated using a DB-1 capillary column within 5 min. The HS-SPME/GC-MS method showed linearity (5–1000 ng/mL, r ≥ 0.990) with detection limits of 0.56, 1.01, and 0.15 ng/mL for ethanol, acetaldehyde, and acetone, respectively. Intra-day and inter-day precision were ≤9.3% and ≤9.7%, with accuracy ranged of 94–110%. Five-minute palm contact with water caused VOC release to increase linearly, and samples remained stable for 24 h at −20 °C. Following ingestion of a 500 mL alcoholic beverage (5% ethanol), ethanol and acetaldehyde emissions peaked at 95 and 24 ng/cm2/min after 1 h, while acetone gradually increased to 1.3 ng/cm2/min after 6 h. This simple, rapid method enables practical assessment of skin VOCs for health monitoring and environmental exposure evaluation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sample Pretreatment and Extraction)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Molecular Structure-Sensitive Detection in MALDI-MS Utilizing Ag, CdTe, and Water-Splitting Photocatalyst
by
Jiawei Xu and Tatsuya Fujino
Analytica 2025, 6(4), 53; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040053 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
We have developed mold matrices that can be employed to distinguish between enantiomers (D- and L-glucose) and structural isomers (n- and iso-stearic acid) in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Utilizing a temperature-responsive polymer, a molecular structure recognition film was created around metal or
[...] Read more.
We have developed mold matrices that can be employed to distinguish between enantiomers (D- and L-glucose) and structural isomers (n- and iso-stearic acid) in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Utilizing a temperature-responsive polymer, a molecular structure recognition film was created around metal or semiconductor particles, such as silver (Ag) or cadmium telluride (CdTe), forming the core. Molecules that fit the template structure were selectively ionized. To elucidate the properties of the mold matrix, the relationship between molecular recognition rate and peak intensity of analyte ion was investigated by varying polymer film thickness around the core. The relationship between molecular recognition rate and hydrophobicity of the template molecule was also examined. It was found that increasing the amount of polymer forming the molecular recognition film improved the molecular recognition rate. However, the peak intensity of the analyte ion decreased. It was also found that using highly hydrophobic molecules as template molecules resulted in high molecular recognition rates. In addition, a water-splitting photocatalyst was synthesized and utilized to fabricate the mold matrix. It was applicable to both positive and negative ion generation while recognizing the molecular structure of the analyte.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sample Pretreatment and Extraction)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Thermal Stability and Degradation of Three Similar-Structured Endogenous Estrogens
by
Amalia Ridichie, Adriana Ledeţi, Cosmina Bengescu, Laura Sbârcea, Răzvan Adrian Bertici, Denisa Laura Ivan, Gabriela Vlase, Titus Vlase, Francisc Peter and Ionuţ Ledeţi
Analytica 2025, 6(4), 52; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040052 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
Estrogens are cholesterol-derived hormones, with four endogenous estrogens being presented in the scientific literature, namely, estradiol, estrone, estriol, and estetrol. In this study, we aim to obtain a complete thermoanalytical profile for the three most important endogenous estrogens: estradiol, estriol, and estrone. To
[...] Read more.
Estrogens are cholesterol-derived hormones, with four endogenous estrogens being presented in the scientific literature, namely, estradiol, estrone, estriol, and estetrol. In this study, we aim to obtain a complete thermoanalytical profile for the three most important endogenous estrogens: estradiol, estriol, and estrone. To achieve this, the TG/DTG were registered in non-isothermal conditions at five different heating rates (β = 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 °C min−1). To describe the mechanisms of the degradation processes, a complex kinetic analysis was performed by applying a preliminary method (ASTM E698), two isoconversional methods (Flynn–Wall–Ozawa and Friedman), and the non-parametric kinetic method. The results indicate that estradiol undergoes a single-step degradation process, while estriol and estrone present a complex degradation process. The determination of the shelf life of pharmaceutical products represents a critical factor in ensuring their safety and efficacy. This parameter can be estimated from the activation energy derived from non-isothermal experiments through the application of the Arrhenius equation and appropriate kinetic models.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Analytical Techniques and Methods in Pharmaceutical Science)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Integration of Hyperspectral Imaging with Machine Learning for Quality Assessment of Nuts: A Systematic Review
by
Ebenezer O. Olaniyi, Christopher Kucha and Fanbin Kong
Analytica 2025, 6(4), 51; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040051 - 20 Nov 2025
Abstract
Nuts such as pecans, almonds, peanuts, pistachios, and walnuts are nutrient-dense foods rich in unsaturated fatty acids and antioxidant compounds. Their regular consumption has been linked to significant health benefits, including reduced risks of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and high cholesterol. With increasing global
[...] Read more.
Nuts such as pecans, almonds, peanuts, pistachios, and walnuts are nutrient-dense foods rich in unsaturated fatty acids and antioxidant compounds. Their regular consumption has been linked to significant health benefits, including reduced risks of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and high cholesterol. With increasing global demand, ensuring the quality of nuts before they reach consumers is critical. Conventional quality assessment methods dominate the industry but are often subjective, destructive, time-intensive, environmentally burdensome, and laborious. Therefore, there is an urgent need for rapid, non-destructive, and objective alternatives capable of meeting modern quality standards. In this systematic review, we summarize traditional approaches for evaluating nut quality parameters and introduce hyperspectral imaging as a novel technique with promising applications. We examine its use in detecting nut adulteration, assessing chemical composition, identifying defects, and evaluating other quality traits. Limitations of hyperspectral imaging in industrial settings are also discussed, along with potential solutions and future directions. Given the relatively limited research area, approximately 44 relevant studies were critically reviewed. This work provides valuable insights for researchers and industry stakeholders developing innovative technologies for nut quality assessment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Spectroscopy)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development of Salt-Assisted Liquid–Liquid Extraction for Simultaneous Quantification of Andrographolide and 14-Deoxy-11,12-didehydroandrographolide in Plasma Using HPLC-DAD: Method Validation and Pharmacokinetic Assessment Application
by
Peera Tabboon, Ekapol Limpongsa, Rapee Jarungsirawat, Supawan Wechprakhon, Jidapa Niyommoh, Amika Wantong and Napaphak Jaipakdee
Analytica 2025, 6(4), 50; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040050 - 17 Nov 2025
Abstract
A high-performance liquid chromatography method coupled with diode array detection (HPLC-DAD) was developed for simultaneous quantification of andrographolide (AG) and 14-deoxy-11,12-didehydroandrographolide (DDAG) in rat plasma. A salt-assisted liquid–liquid extraction (SALLE) procedure was optimized, with MgSO4 yielding the highest extraction efficiency (>90% for
[...] Read more.
A high-performance liquid chromatography method coupled with diode array detection (HPLC-DAD) was developed for simultaneous quantification of andrographolide (AG) and 14-deoxy-11,12-didehydroandrographolide (DDAG) in rat plasma. A salt-assisted liquid–liquid extraction (SALLE) procedure was optimized, with MgSO4 yielding the highest extraction efficiency (>90% for both AG and DDAG), outperforming conventional solvent extraction, and being comparable to solid-phase extraction. The method exhibited acceptable linearity (125–2000 ng/mL, R2 > 0.99), with low limits of detection and quantification of 60 and 70 ng/mL for AG and 201 and 234 ng/mL for DDAG, respectively, while adhering to the ICH M10 criteria for accuracy, precision, and stability under various storage conditions. Stability testing of the prepared samples demonstrated that >99% AG and 95% DDAG were retained when stored at low temperatures, specifically below 4 °C. The developed method was successfully applied in a pharmacokinetic study following oral administration of Andrographis paniculata extract (containing AG 7.5 mg/kg) to healthy Wistar rats. The SALLE-HPLC-DAD method developed herein enables selective AG quantification without significant matrix interference. In conclusion, this study introduces an alternative sample preparation and analytical method that is fast, cost-effective, and reliable, making it suitable for pharmacokinetic studies of the principal biomarker of Andrographis paniculata.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Chromatography)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Robust LC–MS/MS Methodology for Low-Level PFAS in Sludge Matrices
by
Luoana Florentina Pascu, Valentina Andreea Petre, Vasile Ion Iancu, Ioana Antonia Cimpean and Florentina Laura Chiriac
Analytica 2025, 6(4), 49; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040049 - 17 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are persistent environmental contaminants that tend to accumulate in solid matrices such as sewage sludge, raising concerns regarding their fate and potential ecological risks. This study aimed to develop and validate a robust analytical method for the accurate
[...] Read more.
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are persistent environmental contaminants that tend to accumulate in solid matrices such as sewage sludge, raising concerns regarding their fate and potential ecological risks. This study aimed to develop and validate a robust analytical method for the accurate determination of PFAS in dehydrated sludge. A liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) method was optimized for 28 PFAS, including perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids (PFCAs) and sulfonic acids (PFSAs). Solid–liquid extraction with basic methanol was followed by cleanup using a cartridge packed with ferrite and sodium sulfate to remove moisture and particulate interferences. Chromatographic separation was performed with an Avantor® ACE® PFAS Delay column coupled to an Agilent triple quadrupole MS operating in negative electrospray ionization mode. The method achieved excellent sensitivity (MDL < 0.02 µg/g dry weight for most compounds), satisfactory precision (RSD < 15%), and recoveries between 80–118%. Optimization of mobile phase additives, gradient conditions, and MS parameters enhanced chromatographic resolution and signal-to-noise ratio. The validated method demonstrates high reliability for PFAS determination in complex solid matrices and can be applied as a valuable tool for environmental monitoring and risk assessment of sludge management practices.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Moderate Heating Temperatures on Physical, Mechanical and Spectral Properties of Flaxseeds and Pressed Oils
by
Abraham Kabutey, Su Su Soe, Mahmud Musayev and Sonia Habtamu Kibret
Analytica 2025, 6(4), 48; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040048 - 17 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The study evaluated the effect of moderate heating temperatures on physical, mechanical, and spectral properties of bulk flaxseeds and pressed oils. The samples of bulk flaxseeds were measured at 60 mm pressing height and subjected to pretreatment temperatures between 40 °C and 60
[...] Read more.
The study evaluated the effect of moderate heating temperatures on physical, mechanical, and spectral properties of bulk flaxseeds and pressed oils. The samples of bulk flaxseeds were measured at 60 mm pressing height and subjected to pretreatment temperatures between 40 °C and 60 °C at 5 °C intervals at a constant heating time of 30 min. The uniaxial compression process, comprising a pressing chamber of a diameter of 60 mm with a plunger, was used for extracting the oil under a load of 300 kN and a speed of 5 mm/min. Prior to the oil extraction, the moisture content of the flaxseeds samples was determined to be 8.15 ± 0.07% d.b., and that of oil content was 40.32 ± 0.02%. Based on the results obtained, porosity, density, oil yield, and oil expression efficiency significantly correlated positively (p-value < 0.05) with the increase in heating temperatures. However, kinematic and dynamic viscosities, compressive stress, deformation energy, and hardness did not significantly correlate (p-value > 0.05) with heating temperature. The study revealed that heating temperatures increased oil yield from 11.54% to 24.18% and oil expression efficiency from 28.62% to 59.96% with the corresponding deformation energy of 0.698 ± 0.011 kJ at 60 °C. The findings suggest that mild thermal pretreatment of flaxseeds improves oil recovery with minimal energy requirement under the linear compression process.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Review of Vibrational Spectroscopy Studies of Coatings Based on Hexavalent or Trivalent Chromium Baths
by
Julio C. Avalos, Eugenia Aldeco-Pérez, Julieta Torres-González, Raul Garcia-Garcia and German Orozco
Analytica 2025, 6(4), 47; https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040047 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
Major vibrational spectroscopy studies have focused on the preparation of chromium coatings via chemical processes (conversion coatings), and few studies have focused on electrochemical processes (electrodeposition). Initially, the chemical precursors were hexavalent chromium salts, but these compounds are now replaced by less toxic
[...] Read more.
Major vibrational spectroscopy studies have focused on the preparation of chromium coatings via chemical processes (conversion coatings), and few studies have focused on electrochemical processes (electrodeposition). Initially, the chemical precursors were hexavalent chromium salts, but these compounds are now replaced by less toxic trivalent ions. There is a profound understanding of the process when vibrational spectroscopy is used in combination with other techniques. This is the case for chromium(VI) conversion coatings, and the results of several techniques, such as synchrotron infrared microspectroscopy, have made it possible to understand the structure of the two-layer coating and the chemical composition of each layer. Vibrational spectroscopy confirmed the mechanism for coating formation, in which ferricyanide was a redox mediator. In addition, vibrational spectroscopy was effective in determining the mechanism of corrosion resistance of the coatings. Conversely, there are very few studies on the electrodeposition of trivalent chromium ions, and the mechanics of electrodeposition are unknown. To simplify the use of spectroscopy, spectra of potassium dichromate and chromium(III) sulfate are presented as references for coating studies, and a compilation of
(This article belongs to the Collection Analytical and Applied Chemistry: The Challenges and Opportunities for Growth in the 21st Century)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Analytica, Foods, Molecules, Processes, Separations, Chemosensors
Application of Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry and Related Techniques, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Chao Kang, Ronald BeckettDeadline: 30 April 2026
Topic in
Analytica, Metals, Molecules, Processes, Separations
Advances in Solvent Extraction
Topic Editors: Guoquan Zhang, Weizao LiuDeadline: 31 May 2026
Topic in
Analytica, Molecules, Separations, Chemistry, Chemosensors
Advances in Counter-Current Chromatography
Topic Editors: Shihua Wu, Xinyi Huang, Zhi YangDeadline: 30 October 2026
Topic in
Analytica, Chemistry, Molecules, Pharmaceuticals, Separations, Sustainability
Beyond Green Analytical Chemistry: Designing Sustainable Analytical Laboratories of the Future
Topic Editors: Sami El Deeb, Maria Kristina ParrDeadline: 31 December 2026

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Analytica
Environmental Pollutants in Biological Fluids
Guest Editor: Rosangela EllianiDeadline: 28 February 2026
Special Issue in
Analytica
Advances in Chemical Analysis Procedures (Part III): Future Trends in Reducing the Environmental Impact
Guest Editors: Marcello Locatelli, Halil Ibrahim Ulusoy, Imran Ali, Abuzar Kabir, Fotouh RashedDeadline: 28 February 2026
Special Issue in
Analytica
Bio-Based and Eco-Friendly Materials in Analytical Applications
Guest Editors: Adrián Fuente-Ballesteros, Marcello LocatelliDeadline: 31 March 2026
Special Issue in
Analytica
Green Analytical Techniques and Their Applications
Guest Editors: Fotouh Rashed, Marcello Locatelli, Alaa BedairDeadline: 31 August 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Analytica
Analytical and Applied Chemistry: The Challenges and Opportunities for Growth in the 21st Century
Collection Editors: Victoria Samanidou, Marcello Locatelli, Roberto Mandrioli, Thomas W. Bocklitz








