Development of Salt-Assisted Liquid–Liquid Extraction for Simultaneous Quantification of Andrographolide and 14-Deoxy-11,12-didehydroandrographolide in Plasma Using HPLC-DAD: Method Validation and Pharmacokinetic Assessment Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Plant Materials and AP Extract (APE)
2.3. Chromatographic Condition
2.4. Biological Sample Extraction Procedures
2.5. SALLE
2.6. SALLE-HPLC-DAD Method Validation
2.6.1. Selectivity and Specificity
2.6.2. Linearity and Range
2.6.3. Sensitivity
2.6.4. Matrix Effect and Carry-Over
2.6.5. Precision and Accuracy
2.6.6. Stability
2.7. Method Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study
2.7.1. Animals
2.7.2. Pharmacokinetic Study
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chromatographic Conditions
3.2. Biological Sample Preparations: Influences of Extraction Methods
3.2.1. PPT and LLE
3.2.2. SALLE: Salt Effect
3.3. SALLE-HPLC-DAD: System Suitability and Method Validation
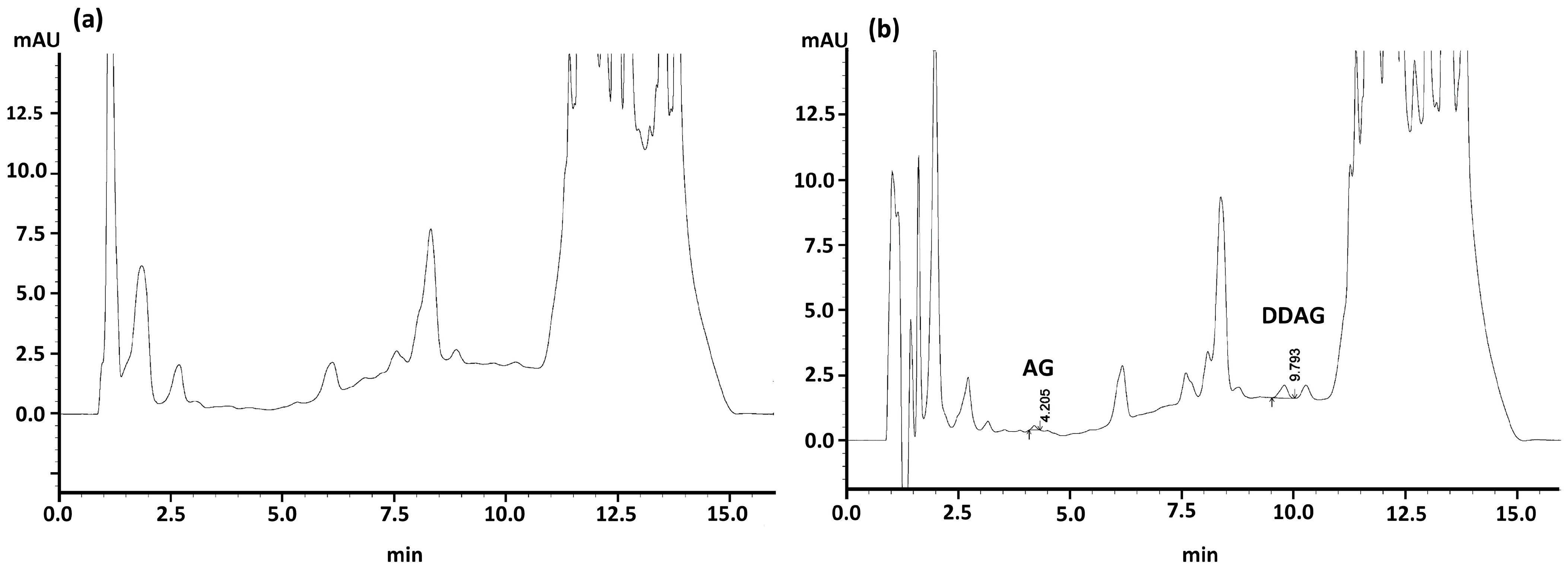
3.3.1. Matrix Effect, Carry-Over, Separation, and Specificity
3.3.2. Range and Linearity of Calibration Curve
3.3.3. Accuracy, Inter- and Intra-Day Precision
3.4. Sensitivity (LLOQ)
3.5. Sample Stability
3.6. Application to Pharmacokinetic Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| AG | Andrographolide |
| AP | Andrographis paniculata |
| APE | AP extract |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| BLQ | Limit of quantitation |
| BW | Body weight |
| Cmax | Maximum plasma concentration |
| DCM | Dichloromethane |
| DDAG | 14-deoxy-11,12-didehydroandrographolide |
| EtOAc | Ethyl acetate |
| HPLC-DAD | High-performance liquid chromatography method coupled with diode array detection |
| LC-MS | Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry |
| LLE | Liquid–liquid extraction |
| LLOQ | Lower limit of quantification |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| MeOH | Methanol |
| MgSO4 | Magnesium sulfate |
| MQC | Medium QC |
| Na2SO4 | Sodium sulfate |
| NaCl | Sodium chloride |
| PPT | Protein precipitation |
| QC | Quality control |
| RSD | Relative standard deviation |
| SALLE | Salt-assisted liquid–liquid extraction |
| SPE | Solid-phase extraction |
| T1/2 | Half-life |
| Tmax | Time to maximum concentration |
| ULOQ | Upper limit of quantification |
References
- Okhuarobo, A.; Falodun, J.E.; Erharuyi, O.; Imieje, V.; Falodun, A.; Langer, P. Harnessing the Medicinal Properties of Andrographis Paniculata for Diseases and beyond: A Review of Its Phytochemistry and Pharmacology. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2014, 4, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thailand: National List of Essential Medicines (NLEM) 2021 (Thai). Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/thailand--national-list-of-essential-medicines-(nlem)-(thai) (accessed on 20 July 2025).
- Low, M.; Khoo, C.S.; Münch, G.; Govindaraghavan, S.; Sucher, N.J. An in Vitro Study of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Standardised Andrographis Paniculata Extracts and Pure Andrographolide. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheeja, K.; Shihab, P.K.; Kuttan, G. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of the Plant Andrographis Paniculata Nees. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2006, 28, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.L.; Wu, S.J.; Lee, S.C.; Ng, L.T. Antioxidant, Antioedema and Analgesic Activities of Andrographis Paniculata Extracts and Their Active Constituent Andrographolide. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilmi, H.; Pamungkas, I.R.; Tumewu, L.; Hafid, A.F.; Widyawaruyanti, A. Analgesic and Antipyretic Activities of Ethyl Acetate Fraction Tablet of Andrographis Paniculata in Animal Models. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 8848797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, M.; Parai, D.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Mukherjee, S.K. Andrographolide: Antibacterial Activity against Common Bacteria of Human Health Concern and Possible Mechanism of Action. Folia Microbiol. 2017, 62, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Rao, K.; Bhuvaneswari, C.H.; Giri, A.; Mangamoori, L.N. Phytochemical Analysis of Andrographis Paniculata Extract and Its Antimicrobial Activity. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widyawaruyanti, A.; Asrory, M.; Ekasari, W.; Setiawan, D.; Radjaram, A.; Tumewu, L.; Hafid, A.F. In Vivo Antimalarial Activity of Andrographis Paniculata Tablets. Procedia Chem. 2014, 13, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dwivedi, M.K.; Mishra, S.; Sonter, S.; Singh, P.K. Diterpenoids as Potential Anti-Malarial Compounds from Andrographis Paniculata. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2021, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, M.; Sarkar, C.; Saha, S.; Hossain, M.N.; Norouzi, R.; Mubarak, M.S.; Siyadatpanah, A.; Wilairatana, P.; Hossain, R.; Islam, M.T.; et al. Hepatoprotective Activity of Andrographolide Possibly through Antioxidative Defense Mechanism in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2022, 9, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajanna, M.; Bharathi, B.; Shivakumar, B.R.; Deepak, M.; Prashanth, D.; Prabakaran, D.; Vijayabhaskar, T.; Arun, B. Immunomodulatory Effects of Andrographis Paniculata Extract in Healthy Adults—An Open-Label Study. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2021, 12, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.R.; Hule, A. Evaluation of Immunomodulatory Activity of an Extract of Andrographolides from Andographis Paniculata. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiguna, S.P.; Panggabean, J.A.; Atikana, A.; Untari, F.; Izzati, F.; Bayu, A.; Rosyidah, A.; Rahmawati, S.I.; Putra, M.Y. Antiviral Activities of Andrographolide and Its Derivatives: Mechanism of Action and Delivery System. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-X.; Xue, H.-J.; Ye, W.-C.; Fang, B.-H.; Liu, Y.-H.; Yuan, S.-H.; Yu, P.; Wang, Y.-Q. Activity of Andrographolide and Its Derivatives against Influenza Virus in Vivo and in Vitro. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.K.; Chen, R.; Lee, R.C.H.; Li, F.; Dai, K.; Zhou, G.-C.; Chu, J.J.H. Discovery of Novel Andrographolide Derivatives as Antiviral Inhibitors against Human Enterovirus A71. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa-ngiamsuntorn, K.; Suksatu, A.; Pewkliang, Y.; Thongsri, P.; Kanjanasirirat, P.; Manopwisedjaroen, S.; Charoensutthivarakul, S.; Wongtrakoongate, P.; Pitiporn, S.; Chaopreecha, J.; et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Activity of Andrographis Paniculata Extract and Its Major Component Andrographolide in Human Lung Epithelial Cells and Cytotoxicity Evaluation in Major Organ Cell Representatives. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hari Kishore, P.; Vijaya Bhaskar Reddy, M.; Kesava Reddy, M.; Gunasekar, D.; Caux, C.; Bodo, B. Flavonoids from Andrographis Lineata. Phytochemistry 2003, 63, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanh, T.T.H.; My, N.T.T.; Cham, P.T.; Quang, T.H.; Cuong, N.X.; Huong, T.T.; Nam, N.H.; Minh, C.V. Diterpenoids and Flavonoids from Andrographis Paniculata. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 68, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.-P.; Kong, L.-R.; Cheng, C.; Lim, J.C.W.; Wong, W.S.F. Protective Role of 14-Deoxy-11,12-Didehydroandrographolide, a Noncytotoxic Analogue of Andrographolide, in Allergic Airway Inflammation. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoopan, N.; Thisoda, P.; Rangkadilok, N.; Sahasitiwat, S.; Pholphana, N.; Ruchirawat, S.; Satayavivad, J. Cardiovascular Effects of 14-Deoxy-11,12-Didehydroandrographolide and Andrographis Paniculata Extracts. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, M.; Misra, T.K.; Roy, D.N. In Vitro Anti-Biofilm Activity of 14-Deoxy-11,12-Didehydroandrographolide from Andrographis Paniculata against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2020, 51, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-J.; Rao, Y.K.; Chen, K.; Lee, Y.-C.; Chung, Y.-S.; Tzeng, Y.-M. Andrographolide and 14-Deoxy-11,12-Didehydroandrographolide from Andrographis Paniculata Attenuate High Glucose-Induced Fibrosis and Apoptosis in Murine Renal Mesangeal Cell Lines. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 132, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Tan, B.K.H. Effects of 14-Deoxyandrographolide and 14-Deoxy-11,12-Didehydroandrographolide on Nitric Oxide Production in Cultured Human Endothelial Cells. Phytother. Res. 1999, 13, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Pharmacopoeia Andrographis Herb. In British Pharmacopoeia 2024; Medicine and Healthcare Product Regulatory Agency (MHRA): London, UK, 2024.
- Fa, T. Thai Herbal Pharmacopoeia; Bureau of Drug and Narcotic, Department of Medical Sciences, Ministry of Public Health: Nonthaburi, Thailand, 2021; pp. 130–139.
- U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention. Powdered Andrographis. Available online: https://doi.usp.org/USPNF/USPNF_M3540_01_01.html (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Suo, X.-B.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.-Q. HPLC Determination of Andrographolide in Rat Whole Blood: Study on the Pharmacokinetics of Andrographolide Incorporated in Liposomes and Tablets. Biomed. Chromatogr. BMC 2007, 21, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songvut, P.; Pholphana, N.; Suriyo, T.; Rangkadilok, N.; Panomvana, D.; Puranajoti, P.; Satayavivad, J. A Validated LC-MS/MS Method for Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Presumptive Phase II Metabolic Pathways Following Oral Administration of Andrographis Paniculata Extract. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačić, J.; Jeličić, M.-L.; Amidžić Klarić, D.; Mornar, A. Green Solid-Phase (Micro)Extraction of Andrographolides’ from Human Plasma Samples Followed by UHPLC-DAD-QqQ-MS/MS Analysis. Separations 2023, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, R.G.; Zeng, S.; Jiang, H.; Fang, W.-J. Current Developments of Bioanalytical Sample Preparation Techniques in Pharmaceuticals. J. Pharm. Anal. 2022, 12, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, L.; He, X.; Fu, Y.; Dong, Z. A Simple UPLC/MS-MS Method for Simultaneous Determination of Lenvatinib and Telmisartan in Rat Plasma, and Its Application to Pharmacokinetic Drug-Drug Interaction Study. Molecules 2022, 27, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, E.; Wagrowski-Diehl, D.M.; Lu, Z.; Mazzeo, J.R. Systematic and Comprehensive Strategy for Reducing Matrix Effects in LC/MS/MS Analyses. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 852, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, C.I.C.; Santos, J.L.M.; Lima, J.L.F.C.; Zagatto, E.A.G. Liquid–Liquid Extraction in Flow Analysis: A Critical Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 652, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Saboe, P.O.; Kruger, J.S.; Tan, E.C.D.; Dempsey, J.W.; Linger, J.G.; Nogué, V.S.; Karp, E.M.; Beckham, G.T. Liquid–Liquid Extraction for in Situ Carboxylic Acid Recovery via Continuous Membrane-Based Emulsion Separations. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 9398–9414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinholds, I.; Pugajeva, I.; Perkons, I.; Bartkevics, V. The Application of Phospholipid Removal Columns and Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography—Tandem Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry for Quantification of Multi-Class Antibiotics in Aquaculture Samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 128, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michopoulos, F.; Edge, A.M.; Hui, Y.-T.; Liddicoat, T.; Theodoridis, G.; Wilson, I.D. Extraction Methods for the Removal of Phospholipids and Other Endogenous Material from a Biological Fluid. Bioanalysis 2011, 3, 2747–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhanova, I.I.; Dikunets, M.A.; Viryus, E.D.; Rodchenkov, G.M. Magnetic Separation as a New Method for the Extraction of Small Molecules from Biological Fluids of Humans. J. Anal. Chem. 2011, 66, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namera, A.; Saito, T. Spin Column Extraction as A New Sample Preparation Method in Bioanalysis. Bioanalysis 2015, 7, 2171–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wietecha-Posłuszny, R.; Garbacik, A.; Woźniakiewicz, M.; Moos, A.; Wieczorek, M.; Kościelniak, P. Application of Microextraction by Packed Sorbent to Isolation of Psychotropic Drugs from Human Serum. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 2249–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jian, W.; Fu, Y. Basic Sample Preparation Techniques in LC-MS Bioanalysis. In Sample Preparation in LC-MS Bioanalysis; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–30. ISBN 978-1-119-27431-5. [Google Scholar]
- Cristale, J.; Becker, R.W.; Tornisielo, V.L.; Dantas, R.F.; Bartelt-Hunt, S.; Onanong, S.; Snow, D.D. Comparison of Salting-out Assisted Liquid-Liquid Extraction to Polymeric Solid Phase Extraction for Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry of Neonicotinoids Insecticides and Metabolites in Wastewater: Occurrence and Aquatic Risk Assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 373, 126136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.S.T.; Ladner, Y.; Amin, N.; Cho, C.; Perrin, C. Salting-out Assisted Liquid-Liquid Extraction (SALLE): Principle, Optimization, and Applications in Blood Sample Analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2025, 257, 116720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.Q.; Weng, N. Salting-out Assisted Liquid-Liquid Extraction for Bioanalysis. Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 1583–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, A.M.; Zultanski, S.L.; Waldman, J.H.; Zhong, Y.-L.; Shevlin, M.; Peng, F. General Principles and Strategies for Salting-Out Informed by the Hofmeister Series. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2017, 21, 1355–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Kim, E.; El-Shourbagy, T.A. Salting-out Assisted Liquid/Liquid Extraction with Acetonitrile: A New High Throughput Sample Preparation Technique for Good Laboratory Practice Bioanalysis Using Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. BMC 2009, 23, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Rodila, R.; Gage, E.; Hautman, M.; Fan, L.; King, L.L.; Wu, H.; El-Shourbagy, T.A. High-Throughput Salting-out Assisted Liquid/Liquid Extraction with Acetonitrile for the Simultaneous Determination of Simvastatin and Simvastatin Acid in Human Plasma with Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 661, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Council for Harmonisation’s (ICH). ICH Harmonised Guideline: Bioanalytical Method Validation and Study Sample Analysis (M10); European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- International Council for Harmonisation’s (ICH). ICH Q2(R2) Validation of Analytical Procedures; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- <621> Chromatography. Available online: https://doi.usp.org/USPNF/USPNF_M99380_06_01.html (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Xie, S. PKSolver: An Add-in Program for Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Data Analysis in Microsoft Excel. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2010, 99, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, H.P.; Thapa, P.; Van Schepdael, A. Simple HPLC-UV Method for the Quantification of Metformin in Human Plasma with One Step Protein Precipitation. Saudi Pharm. J. 2014, 22, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, S.A.; Eissa, M.S.; Ahmed, H.M. Simple Protein Precipitation Extraction Technique Followed by Validated Chromatographic Method for Linezolid Analysis in Real Human Plasma Samples to Study Its Pharmacokinetics. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1043, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, B.; Adkar, S.S.; Prabhudesai, A.V.; Viswanathan, C.V. Selective Extraction of Phospholipids from Egg Yolk. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1979, 56, 585–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevc, G.; Löbbecke, L.; Nagel, N.; Vierl, U. Phospholipid-Alcohol Interactions: Effects of Chain-Length and Headgroup Variations. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 1996, 109, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, L.; Fontes, A.L.; Salsinha, S.; Machado, M.; Correia, I.; Gomes, A.M.; Pintado, M.; Rodríguez-Alcalá, L.M. Suitable Simple and Fast Methods for Selective Isolation of Phospholipids as a Tool for Their Analysis. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 1835–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, G.; Mirzaeei, S.; Kiani, A. Determination of Acyclovir in Human Serum by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Using Liquid–Liquid Extraction and Its Application in Pharmacokinetic Studies. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 816, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shaik, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Nhkata, K.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, C.; Kim, S.-H.; Lü, J. Preparation of Penta-O-Galloyl-β-d-Glucose from Tannic Acid and Plasma Pharmacokinetic Analyses by Liquid–Liquid Extraction and Reverse-Phase HPLC. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 54, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Fast, D.M. Systematic Evaluation of Supported Liquid Extraction in Reducing Matrix Effect and Improving Extraction Efficiency in LC–MS/MS Based Bioanalysis for 10 Model Pharmaceutical Compounds. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 891–892, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Špadina, M.; Dufrêche, J.-F.; Pellet-Rostaing, S.; Marčelja, S.; Zemb, T. Molecular Forces in Liquid-Liquid Extraction. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2021, 37, 10637–10656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, G.M.; Perović, J.M.; Nikolić, R.S.; Cakić, M.D. Salting-out Extraction of Catechol and Hydroquinone from Aqueous Solutions and Urine Samples. Facta Univ. Ser. Phys. Chem. Technol. 2003, 2, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rizzo, S.; Celano, R.; Campone, L.; Rastrelli, L.; Piccinelli, A.L. Salting-out Assisted Liquid-Liquid Extraction for the Rapid and Simple Simultaneous Analysis of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids and Related N-Oxides in Honey and Pollen. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 108, 104457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Zhang, H.; Huang, L.; Nishinari, K. Effects of the Lyotropic Series Salts on the Gelation of Konjac Glucomannan in Aqueous Solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, O.S.; Sodeinde, K.O.; Adediran, A.A.; Nishinari, K.; Olatunji, O.S.; Ayanda, O.S. Effects of Lyotropic Series Salts on the Functional Properties of Bambaragroundnut (Voandzeia Subterranean) Protein Isolate. Food Res. 2022, 6, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Timasheff, S.N. On the Role of Surface Tension in the Stabilization of Globular Proteins. Protein Sci. Publ. Protein Soc. 1996, 5, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei, M.; Kazemzadeh, Y.; Martyushev, D.A.; Dai, Z.; Riazi, M. Effect of Chemicals on the Phase and Viscosity Behavior of Water in Oil Emulsions. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welz, A.; Koba, M.; Kośliński, P.; Siódmiak, J. Comparison of LC-MS and LC-DAD Methods of Detecting Abused Piperazine Designer Drugs. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomlim, L.; Jirayupong, N.; Plubrukarn, A. Heat-Accelerated Degradation of Solid-State Andrographolide. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Fang, L.-H.; Du, G.-H. Andrographolide. In Natural Small Molecule Drugs from Plants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanaya, T.; Chuangrattanawan, C.; Chootip, K.; Pekthong, D.; Plubrukarn, A. Fates of Diterpene Lactones in Storage Andrographis Paniculata Extracts. Phytochem. Anal. PCA 2025, 36, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johari, N.A.; Sapi’i, N.A.; Jiunn Hieng, A.L.; Ab Latif, N.; Amran, S.I.; Hasham, R.; Jemon, K. In Vitro and in Silico Evaluation of Andrographis Paniculata Ethanolic Crude Extracts on Fatty Acid Synthase Expression on Breast Cancer Cells. BioMedicine 2024, 14, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, F.; Xiang, S. Pharmacological Effects and Pharmacokinetic Profiles of Dehydroandrographolide. Mediators Inflamm. 2025, 2025, 4123997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panossian, A.; Hovhannisyan, A.; Mamikonyan, G.; Abrahamian, H.; Hambardzumyan, E.; Gabrielian, E.; Goukasova, G.; Wikman, G.; Wagner, H. Pharmacokinetic and Oral Bioavailability of Andrographolide from Andrographis Paniculata Fixed Combination Kan Jang in Rats and Human. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2000, 7, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, T.G.; Mi, Z. The Structural Basis of Camptothecin Interactions with Human Serum Albumin: Impact on Drug Stability. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.-C.; Liu, Y.-T.; Lin, Y.-J.; Yang, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Yao, H.-T.; Chen, H.-W.; Lii, C.-K. Bioavailability of the Diterpenoid 14-Deoxy-11,12-Didehydroandrographolide in Rats and up-Regulation of Hepatic Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme and Drug Transporter Expression. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2019, 61, 152841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, R.; Chen, Y.; Wu, F. Regio-Selective PEGylation of 14-Deoxy-11,12-Didehydroandrographolide and Their Biological Evaluation. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 5909–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellampillai, B.; Pawar, A.P. Improved Bioavailability of Orally Administered Andrographolide from pH-Sensitive Nanoparticles. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2011, 35, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bera, R.; Ahmed, S.K.M.; Sarkar, L.; Sen, T.; Karmakar, S. Pharmacokinetic Analysis and Tissue Distribution of Andrographolide in Rat by a Validated LC-MS/MS Method. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duval, V.; Karlsson, M.O. Impact of Omission or Replacement of Data below the Limit of Quantification on Parameter Estimates in a Two-Compartment Model. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, M.; Veigure, R.; Couchman, L.; Barker, C.I.S.; Standing, J.F.; Takkis, K.; Evard, H.; Johnston, A.; Herodes, K.; Leito, I.; et al. Utilization of Data below the Analytical Limit of Quantitation in Pharmacokinetic Analysis and Modeling: Promoting Interdisciplinary Debate. Bioanalysis 2018, 10, 1229–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jusko, W.J. Use of Pharmacokinetic Data Below Lower Limit of Quantitation Values. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 2628–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Sheng, H.-H.; Feng, N.-P.; Wei, H.; Wang, Z.-T.; Wang, C.-H. Preparation of Andrographolide-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Their In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluations: Characteristics, Release, Absorption, Transports, Pharmacokinetics, and Antihyperlipidemic Activity. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 4414–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Wang, T.; Tang, L.; Liu, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, Z.; Cai, Z.; Hu, M.; Liu, Z. Poor Oral Bioavailability of a Promising Anticancer Agent Andrographolide Is Due to Extensive Metabolism and Efflux by P-Glycoprotein. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 5007–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipduangta, P.; Chansakaow, S.; Tansakul, P.; Meungjai, R.; Dilokthornsakul, P. Polymer Matrix and Manufacturing Methods in Solid Dispersion System for Enhancing Andrographolide Solubility and Absorption: A Systematic Review. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornpitchanarong, C.; Akkaramongkolporn, P.; Nattapulwat, N.; Opanasopit, P.; Patrojanasophon, P. Development and Optimization of Andrographis Paniculata Extract-Loaded Self-Microemulsifying Drug Delivery System Using Experimental Design Model. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramanick, D.; Rani, K.N.; Singh, V.K.; Basist, P.; Khan, R.; Al-Tamimi, J.H.; Noman, O.M.; Ibrahim, M.N.; Alhalmi, A. Enhancement of Cognitive Function by Andrographolide-Loaded Lactose β-Cyclodextrin Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Optimization, and Behavioural Assessment. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Salt Types and Concentrations | Extraction Efficiency (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| AG | DDAG | |
| Control (no salt addition) | 50.66 ± 4.44 | 56.03 ± 4.32 |
| NaCl, 1 M | 81.75 ± 4.81 * | 69.31 ± 1.64 * |
| NaCl, 2 M | 86.52 ± 5.59 * | 93.41 ± 6.33 * |
| Na2SO4,1 M | 0.00 ± 0.00 * | 7.24 ± 2.41 * |
| Na2SO4, 2 M | N/A | N/A |
| MgSO4, 1 M | 82.64 ± 2.68 * | 81.70 ± 1.28 * |
| MgSO4, 2 M | 93.75 ± 0.56 * | 95.39 ± 2.95 * |
| Parameters | AG | DDAG |
|---|---|---|
| Capacity factor | 3.05 ± 0.01 | 8.33 ± 0.02 |
| Resolution | 16.46 ± 0.41 | 25.49 ± 0.11 |
| Tailing factor | 1.17 ± 0.06 | 1.23 ± 0.01 |
| Column efficiency | 6702 ± 147 | 29,631 ± 252 |
| Analytical Method | Actives | Linearity Range (ng/mL) | R2 | LOD (ng/mL) | LOQ (ng/mL) | EE (%) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SALLE-HPLC-DAD * | AG | 125–2000 | 0.9973 ± 0.0029 | 60.3 ± 13.6 | 70.3 ± 28.9 | 93–94 | - |
| DDAG | 125–2000 | 0.9974 ± 0.0023 | 201.1 ± 45.5 | 234.3 ± 96.3 | 92–98 | ||
| LLE-HPLC-DAD | AG | 53−530,000 | 0.996 | 15 | 53 | 65–72 | [28] |
| DDAG | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| PPT-HPLC-MS/MS | AG | 0.98–1000 | >0.99 | - | 0.98 | 78–81 | [29] |
| DDAG | 0.98–1000 | >0.99 | - | 0.98 | 81–89 | ||
| SPE-HPLC-MS/MS | AG | 4000–12,000 | 0.9989 | 40 | 150 | 97–99 | [30] |
| DDAG | 4000–12,000 | 0.9987 | 20 | 60 | 92–95 |
| Concentration (ng/mL) | AG | DDAG | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision (RSD, %) | Accuracy * (% Recovery) | Precision (RSD, %) | Accuracy * (% Recovery) | |||
| Inter-Day | Intra-Day | Inter-Day | Intra-Day | |||
| 125 | 9.5 | 5.1 | 91.8 ± 4.7 | 9.9 | 2.0 | 103.1 ± 10.7 |
| 1000 | 5.6 | 2.0 | 99.2 ± 2.0 | 8.6 | 9.6 | 99.3 ± 8.6 |
| 2000 | 8.6 | 2.6 | 91.4 ± 2.4 | 5.2 | 4.7 | 102.3 ± 5.0 |
| Storage Time and Condition | Percentage Remaining (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| AG | DDAG | |
| Control (0 h) | 102.83 ± 6.70 | 95.48 ± 3.40 |
| 4 h Bench-top | 67.44 ± 6.72 | 88.20 ± 9.50 |
| 24 h autosampler | 99.94 ± 6.70 | 96.70 ± 4.73 |
| Freeze–thaw (3 cycles) | 90.64 ± 5.81 | 83.99 ± 2.01 |
| 14 days at −20 °C | 106.74 ± 6.83 | 94.57 ± 6.58 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Tmax (h) | 1.0 ± 0.0 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 219.0 ± 46.5 |
| AUC (ng·h/mL) | 309.5 ± 4.8 |
| T1/2 (h) | 0.8 ± 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tabboon, P.; Limpongsa, E.; Jarungsirawat, R.; Wechprakhon, S.; Niyommoh, J.; Wantong, A.; Jaipakdee, N. Development of Salt-Assisted Liquid–Liquid Extraction for Simultaneous Quantification of Andrographolide and 14-Deoxy-11,12-didehydroandrographolide in Plasma Using HPLC-DAD: Method Validation and Pharmacokinetic Assessment Application. Analytica 2025, 6, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040050
Tabboon P, Limpongsa E, Jarungsirawat R, Wechprakhon S, Niyommoh J, Wantong A, Jaipakdee N. Development of Salt-Assisted Liquid–Liquid Extraction for Simultaneous Quantification of Andrographolide and 14-Deoxy-11,12-didehydroandrographolide in Plasma Using HPLC-DAD: Method Validation and Pharmacokinetic Assessment Application. Analytica. 2025; 6(4):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040050
Chicago/Turabian StyleTabboon, Peera, Ekapol Limpongsa, Rapee Jarungsirawat, Supawan Wechprakhon, Jidapa Niyommoh, Amika Wantong, and Napaphak Jaipakdee. 2025. "Development of Salt-Assisted Liquid–Liquid Extraction for Simultaneous Quantification of Andrographolide and 14-Deoxy-11,12-didehydroandrographolide in Plasma Using HPLC-DAD: Method Validation and Pharmacokinetic Assessment Application" Analytica 6, no. 4: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040050
APA StyleTabboon, P., Limpongsa, E., Jarungsirawat, R., Wechprakhon, S., Niyommoh, J., Wantong, A., & Jaipakdee, N. (2025). Development of Salt-Assisted Liquid–Liquid Extraction for Simultaneous Quantification of Andrographolide and 14-Deoxy-11,12-didehydroandrographolide in Plasma Using HPLC-DAD: Method Validation and Pharmacokinetic Assessment Application. Analytica, 6(4), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040050







