- Article
Chemical and Isotopic Characterization of Industrial Gases: An Integrated and Robust Approach Combining Sampling and Analytical Measurements
- Zine Eddine Hamoum,
- Hervé Carrier and
- Isabelle Le Hécho
- + 3 authors
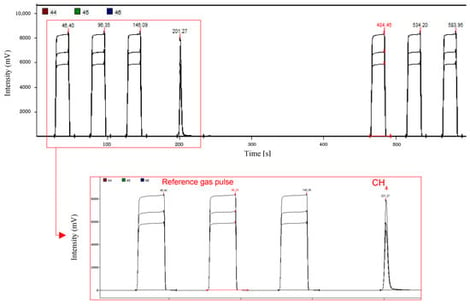
In the context of the energy transition and the increasing deployment of low-carbon gases (hydrogen, biomethane), reliable analytical monitoring is required to support integrity assessment and traceability of gas infrastructures under diverse on-site conditions while limiting analytical costs through standardized sampling and a single analytical system. We developed and validated integrated workflows combining sampling and laboratory analysis for chemical and compound-specific isotope analysis (CSIA) of natural gas and associated gaseous effluents in underground storage. An original quantification approach was implemented, linking sampling pressure to the amount of each compound collected in vials, and coupled with δ13C and δ2H measurements of alkanes (C1–C3), CO2 and H2. Two complementary sampling modes were optimized and compared: conventional high-pressure cylinders and direct collection into vacuum-sealed vials suitable for a broad range of pressures and field conditions. Using reference gas mixtures and operational samples, both approaches showed good reproducibility and isotopic accuracy during laboratory validation and over two years of monitoring. In particular, δ2H determinations for alkanes and H2 remained robust under low-pressure sampling typical of annular spaces (~1–2 bar), despite gas-composition fluctuations. These validated methodologies provide a flexible basis for routine, standardized monitoring of stored and circulating gases, including emerging low-carbon components.
6 February 2026