Investigation of Halloumi Cheese Adulteration Due to the Addition of Milk Powder Using BET and FTIR Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Details
2.2. Pre-Treatment of Samples
2.3. Physicochemical Characteristics
2.4. Characterization Measurements
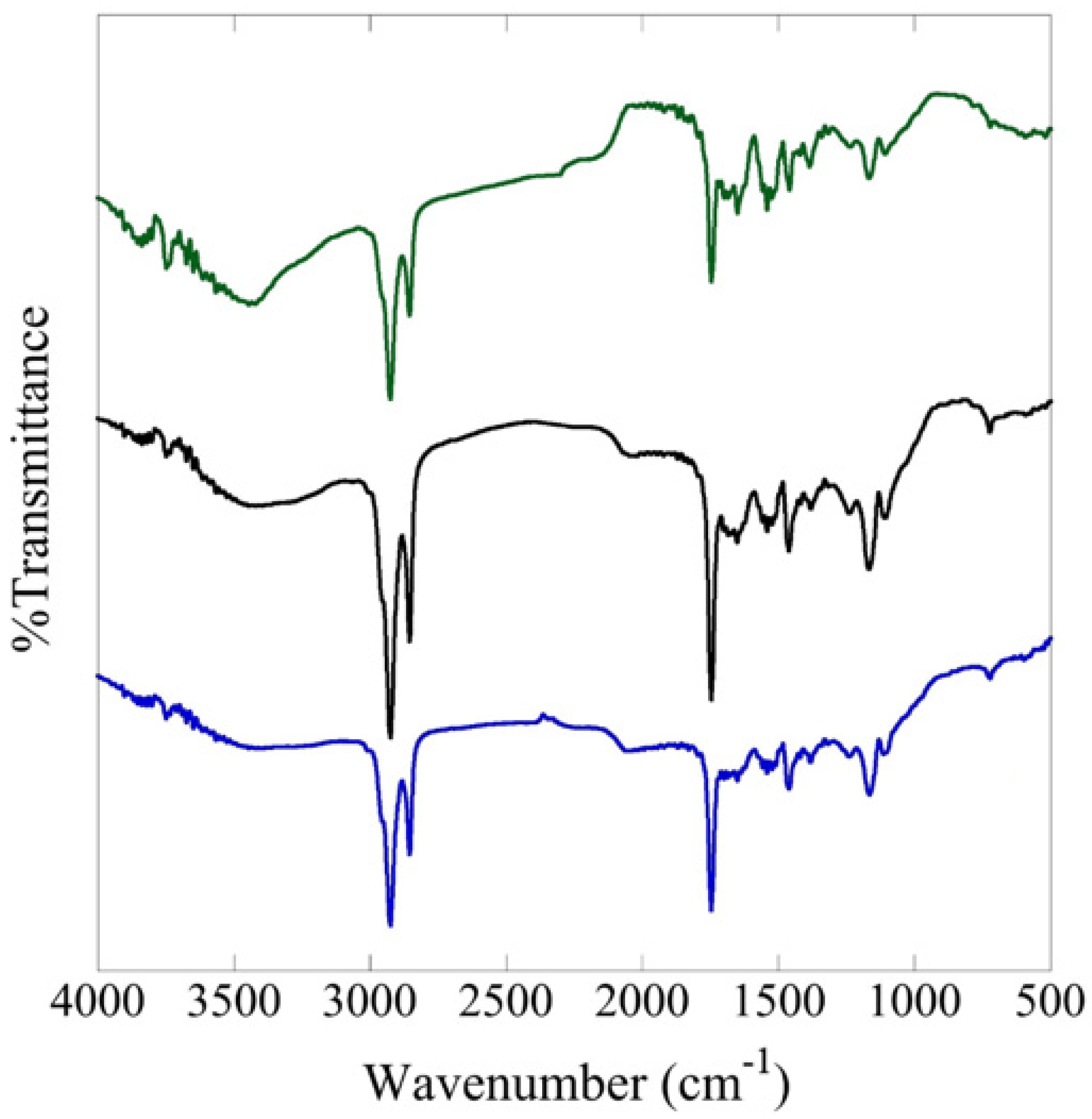
2.4.1. FTIR Data
2.4.2. BET Measurement-Specific Surface Area and Porosity Data
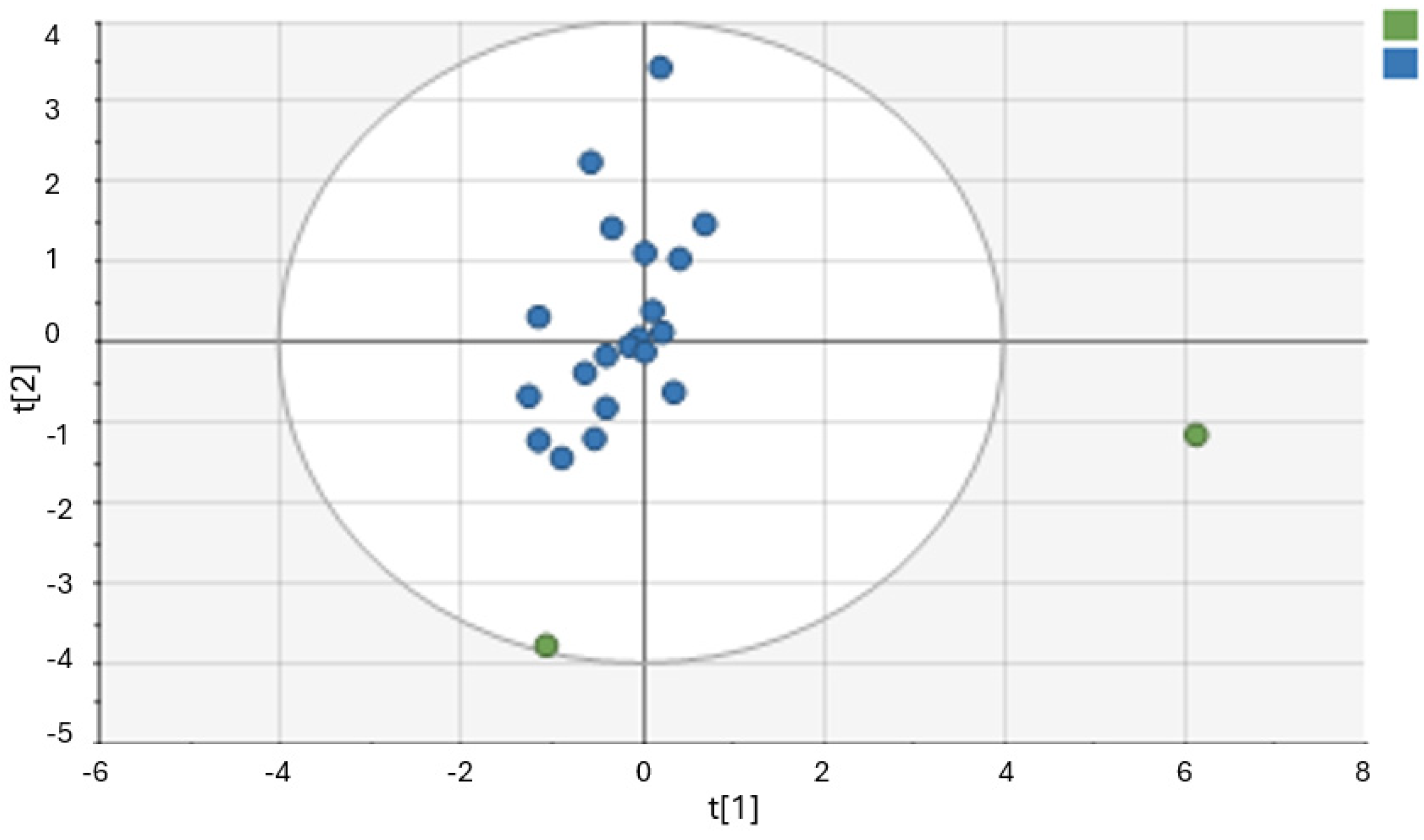
2.5. Chemometrics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Measuremnts
3.2. Characterization of Samples
3.2.1. BET Measurement-Specific Surface Area and Porosity Studies
3.2.2. FTIR Measurements
3.3. Chemometric Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BET | Brunauer–Emmett–Teller analysis |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PDO | Protected Designation of Origin |
| BJH | Barrett–Joyner–Halenda |
| DFT | Density Functional Theory |
| MP | Milk Powder |
References
- Tarapoulouzi, M.; Agriopoulou, S.; Artemi, A. Quality Schemes and Geographical Indicators in the Cheese Agribusiness and the Case of the Cypriot Traditional Cheese Halloumi. In Agribusiness Innovation and Contextual Evolution, Volume I: Strategic, Managerial and Marketing Advancements; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 155–182. [Google Scholar]
- Kedzierska-Matysek, M.; Barlowska, J.; Wolanciuk, A.; Litwinczuk, Z. Physicochemical, mechanical and sensory properties of long-ripened Polish and Italian cheeses and their content of selected minerals. J. Elem. 2018, 23, 985–998. [Google Scholar]
- Strani, L.; Grassi, S.; Alamprese, C.; Casiraghi, E.; Ghiglietti, R.; Locci, F.; Pricca, N.; De Juan, A. Effect of physicochemical factors and use of milk powder on milk rennet-coagulation: Process understanding by near infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food Control 2021, 119, 107494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaoui, S.; Tarapoulouzi, M.; Agriopoulou, S.; D’Amore, T.; Varzakas, T. Current state of milk, dairy products, meat and meat products, eggs, fish and fishery products authentication and chemometrics. Foods 2023, 12, 4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU Regulation 2021/591. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg_impl/2021/591/oj (accessed on 4 April 2025).
- Grassi, S.; Tarapoulouzi, M.; D’Alessandro, A.; Agriopoulou, S.; Strani, L.; Varzakas, T. How chemometrics can fight milk adulteration. Foods 2022, 12, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebling e Tavares, J.P.; da Silva Medeiros, M.L.; Barbin, D.F. Near-infrared techniques for fraud detection in dairy products: A review. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 1943–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaim, J.; Śliwa, M.; Kuterasiński, Ł.; Samson, K.; Ruggiero-Mikołajczyk, M.; Zimowska, M.; Mordarski, G.; Karcz, R.; Podobiński, J.; Datka, J.; et al. Gas-phase hydrogenation and decarbonylation of furfuryl aldehyde over catalysts containing Cu and Ni. Catal. Today 2024, 441, 114897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sławińska, A.; Tyszka-Czochara, M.; Serda, P.; Oszajca, M.; Ruggiero-Mikołajczyk, M.; Pamin, K.; Karcz, R.; Łasocha, W. Newly-obtained two organic-inorganic hybrid compounds based on potassium peroxidomolybdate and dicarboxypyridinic acid: Structure determination, catalytic properties, and cytotoxic effects of eight peroxidomolybdates in colon and hepatic cancer cells. Materials 2021, 15, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, E.; Chen, X.; López-Cartes, C.; Monzón, A.; Delgado, J.J. Induced-aggregates in photocatalysis: An unexplored approach to reduce the noble metal co-catalyst content. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 676, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffirio, S.; Pylypko, S.; Fiorot, S.; Schiavi, I.; Fiore, S.; Santarelli, M.; Ferrero, D.; Smeacetto, F.; Fiorilli, S. Hydrothermally-assisted recovery of Yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) from end-of-life solid oxide cells. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2022, 33, e00473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.S.; Moravkar, K.K.; Jha, D.K.; Lonkar, V.; Amin, P.D.; Chalikwar, S.S. A concise summary of powder processing methodologies for flow enhancement. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahapatra, P.L.; Das, S.; Keasberry, N.A.; Ibrahim, S.B.; Saha, D. Copper ferrite inverse spinel-based highly sensitive and selective chemiresistive gas sensor for the detection of formalin adulteration in fish. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 960, 170792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M. Nanosensor platforms for detection of milk adulterants. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2023, 5, 100159. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, S.; Jamwal, R. Use of FTIR spectroscopy integrated with multivariate chemometrics as a swift, and non-destructive technique to detect various adulterants in virgin coconut oil: A comprehensive review. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 2, 100203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.; Binti Julmohammad, N.; Koh, W.Y.; Abdullah Sani, M.S.; Rasti, B. Application of ATR-FTIR incorporated with multivariate data analysis for discrimination and quantification of urea as an adulterant in UHT milk. Foods 2023, 12, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifah, M.F.; Irnawati; Ruslin; Nisa, K.; Windarsih, A.; Rohman, A. The application of FTIR spectroscopy and chemometrics for the authentication analysis of horse milk. Int. J. Food Sci. 2022, 2022, 7643959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irnawati, I.; Windarsih, A.; Indrianingsih, A.W.; Apriyana, W.; Ratnawati, Y.A.; Nadia, L.O.M.H.; Rohman, A. Rapid detection of tuna fish oil adulteration using FTIR-ATR spectroscopy and chemometrics for halal authentication. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 13, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Jamwal, R.; Suman, P.; Singh, D.K. Expeditious and accurate detection of palm oil adulteration in virgin coconut oil by utilizing ATR-FTIR spectroscopy along with chemometrics and regression models. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 3, 100377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciursă, P.; Pauliuc, D.; Dranca, F.; Ropciuc, S.; Oroian, M. Detection of honey adulterated with agave, corn, inverted sugar, maple and rice syrups using FTIR analysis. Food Control 2021, 130, 108266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas-Escudero, J.; Galan-Madruga, D.; Cáceres, J.O. Rapid, reliable and easy-to-perform chemometric-less method for rice syrup adulterated honey detection using FTIR-ATR. Talanta 2023, 253, 123961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lestari, D.; Rohman, A.; Syofyan, S.; Yuliana, N.D.; Abu Bakar, N.K.B.; Hamidi, D. Analysis of beef meatballs with rat meat adulteration using Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy in combination with chemometrics. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 1446–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirnawati, W.; Lestari, D.; Rohman, A.; Andayani, R.; Hamidi, D. Analysis of Adulteration Dog Meat in Beef Sausages Using FTIR Spectroscopy Combined with Chemometrics. Res. Sq. 2023, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paulo, E.H.; Rech, A.M.; Weiler, F.H.; Nascimento, M.H.; Filgueiras, P.R.; Ferrão, M.F. Evaluation of adulteration in soy-based beverages by water addition using chemometrics applied to ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Food Control 2024, 166, 110746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle, J.L.P.; Ferreiro-González, M.; Ruiz-Rodríguez, A.; Fernández, D.; Palma, M. Detection of adulterations in fruit juices using machine learning methods over FT-IR spectroscopic data. Agronomy 2022, 12, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarapoulouzi, M.; Kokkinofta, R.; Theocharis, C.R. Chemometric analysis combined with FTIR spectroscopy of milk and Halloumi cheese samples according to species’ origin. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 3262–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarapoulouzi, M.; Kyriacou, S.; Ioannidis, I.; Pashalidis, I.; Theocharis, C. FTIR Spectroscopy for Detecting Milk Powder Adulteration in Cyprus Goat Milk: A Preliminary Step Toward Safeguarding Halloumi Cheese Authenticity. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Food, 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Tarapoulouzi, M.; Theocharis, C.R. Discrimination of Cheddar, Kefalotyri, and Halloumi cheese samples by the chemometric analysis of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. J. Food Process Eng. 2022, 45, e13933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarapoulouzi, M.; Logan, N.; Hardy, M.; Montgomery, H.; Haughey, S.A.; Elliott, C.T.; Theocharis, C.R. A Pre-Trial Study to Identify Species of Origin in Halloumi Cheese Utilising Chemometrics with Near-Infrared and Hyperspectral Imaging Technologies. Analytica 2024, 5, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanazawa, H.; Ohshika, K.; Matsuzawa, T. Precision evaluation in kr adsorption for small bet surface area measurements of less than 1 m2. Adsorption 2000, 6, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarapoulouzi, M.; Theocharis, C.R. Discrimination of Cheddar and Kefalotyri cheese samples: Analysis by chemometrics of proton-NMR and FTIR spectra. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foschi, M.; Biancolillo, A.; Reale, S.; Poles, F.; D’Archivio, A.A. Classification of “Ricotta” whey cheese from different milk and Designation of Origin-protected samples through infrared spectroscopy and chemometric analysis. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 138, 107019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
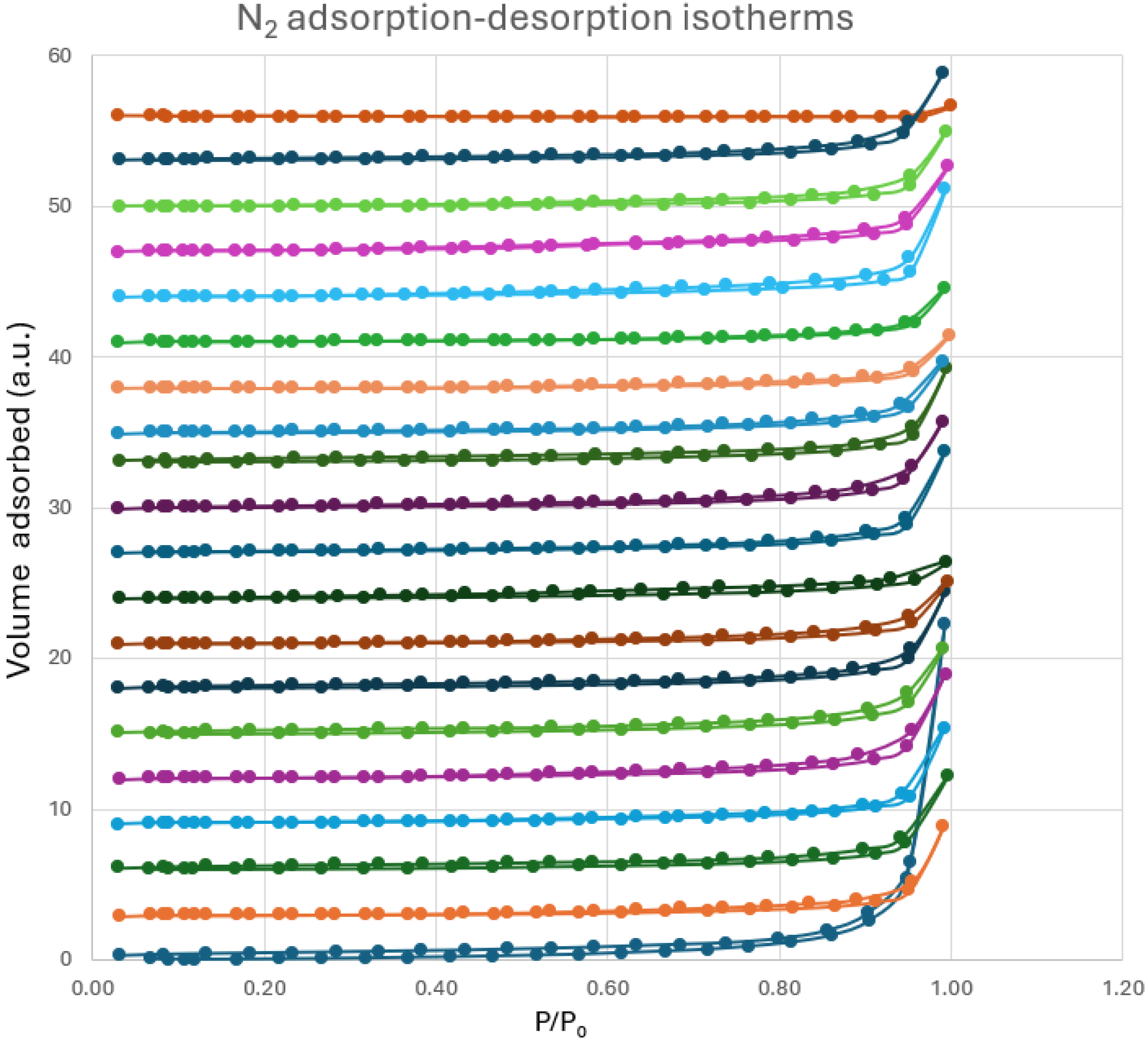

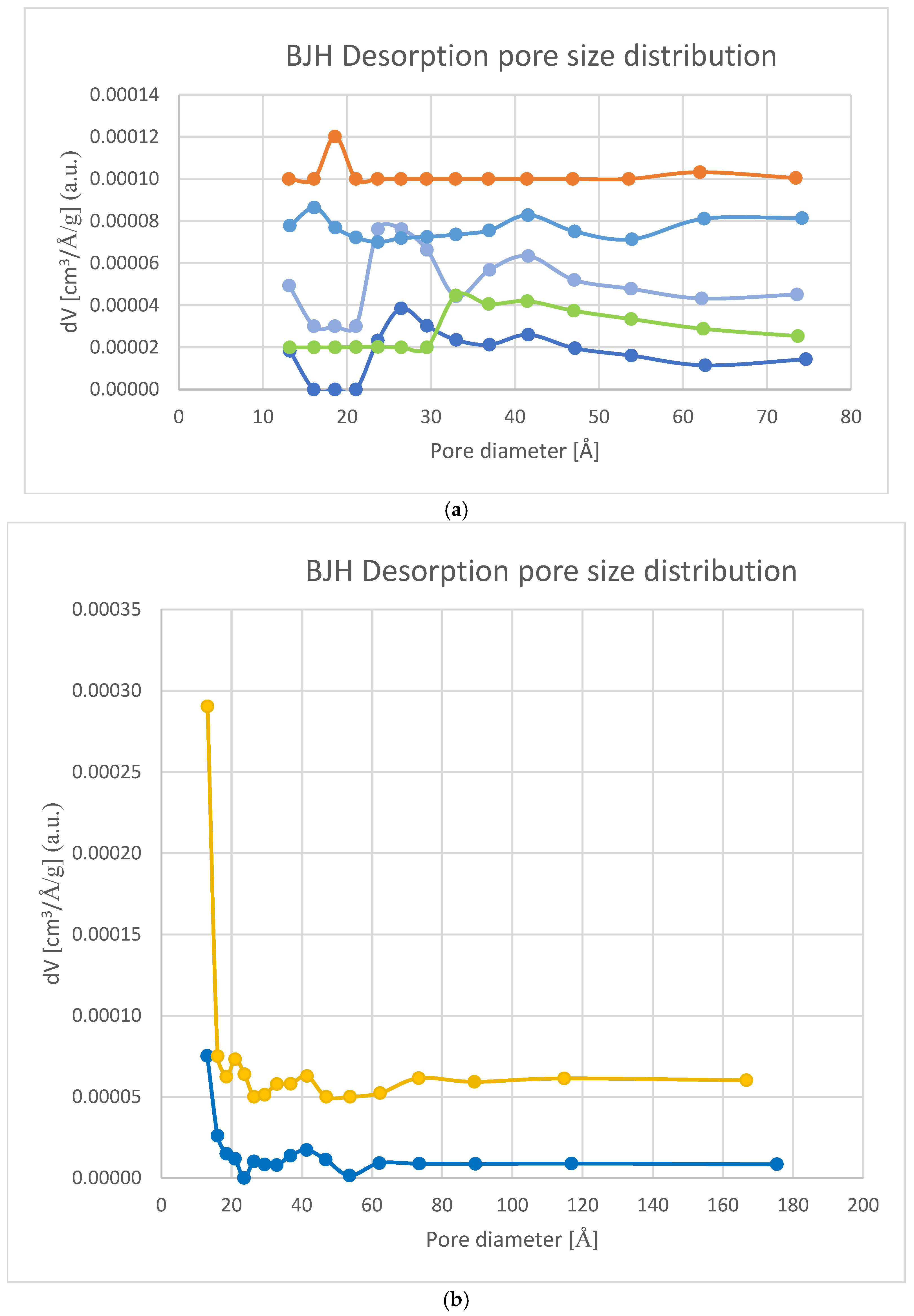
| Sample | Specific Surface Area BET [m2/g] | Pore Size Distribution (Pore Diameter) [Å] | Pore Volume [cm3/g] |
|---|---|---|---|
0% MP | 0.2 | (13), 26, 33, 42, (115) | 0.0043 |
0% MP | 0.5 | 13, (19), (42), 53 | 0.0111 |
0% MP | 0.7 | (13), 37, 54, 181 | 0.0350 |
0% MP | 0.4 | 13, 33, 42 | 0.0099 |
0% MP | 0.3 | 13, (21), 42, 73, (116) | 0.0101 |
0% MP | 0.5 | 13, 37 | 0.0106 |
0% MP | 0.5 | 13, 41 | 0.0116 |
0% MP | 0.7 | 16, (24), 47 | 0.0092 |
0% MP | 0.5 | 13, (21), 41, (89) | 0.0106 |
0% MP | 0.3 | 13, (27), 41, (73) | 0.0070 |
0% MP | 0.5 | 13, (24), 36, (62) | 0.0095 |
0% MP | 0.6 | 16, 21, 33, (41), (114) | 0.0100 |
0% MP | 0.6 | 13, (21), 54 | 0.0080 |
0% MP | 0.2 | (13), 37, 63, (311) | 0.0059 |
0% MP | 0.2 | 13, (41), (61) | 0.0061 |
0% MP | 0.4 | 13, 26, 42, 74, (312) | 0.0118 |
0% MP | 0.4 | 13, 23, 25, 41, (73) | 0.0096 |
0% MP | 0.3 | 33, 41, (89), (158) | 0.0081 |
0% MP | 0.4 | 16, 41, (63), (74), (90) | 0.0093 |
1% MP | 0.02 | (13), 21, 42 | 0.0087 |
5% MP | 0.23 | (13), 27, 41 | 0.0081 |
Min Max | 0.02 0.7 | 13 311 | 0.0043 0.0350 |
| Subregion (cm−1) | Relative Intensity of Absorption | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0% MP, Blue | 1% MP, Black | 5% MP, Green | |
| 3000–2800 | medium | strong | medium |
| 1750–1650 | medium | strong | medium |
| 1650–1500 | weak | medium | strong |
| 1500–1450 | weak | medium | weak |
| 1450–1300 | medium | weak | weak |
| 1300–1000 | weak | medium | weak |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarapoulouzi, M.; Ruggiero-Mikołajczyk, M.; Pashalidis, I.; Theocharis, C.R. Investigation of Halloumi Cheese Adulteration Due to the Addition of Milk Powder Using BET and FTIR Measurements. Analytica 2025, 6, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6030034
Tarapoulouzi M, Ruggiero-Mikołajczyk M, Pashalidis I, Theocharis CR. Investigation of Halloumi Cheese Adulteration Due to the Addition of Milk Powder Using BET and FTIR Measurements. Analytica. 2025; 6(3):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6030034
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarapoulouzi, Maria, Małgorzata Ruggiero-Mikołajczyk, Ioannis Pashalidis, and Charis R. Theocharis. 2025. "Investigation of Halloumi Cheese Adulteration Due to the Addition of Milk Powder Using BET and FTIR Measurements" Analytica 6, no. 3: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6030034
APA StyleTarapoulouzi, M., Ruggiero-Mikołajczyk, M., Pashalidis, I., & Theocharis, C. R. (2025). Investigation of Halloumi Cheese Adulteration Due to the Addition of Milk Powder Using BET and FTIR Measurements. Analytica, 6(3), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6030034










