Study of Sorption of Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride on Zirconium-Based Metal–Organic Framework Followed by Determination by UV-Vis Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
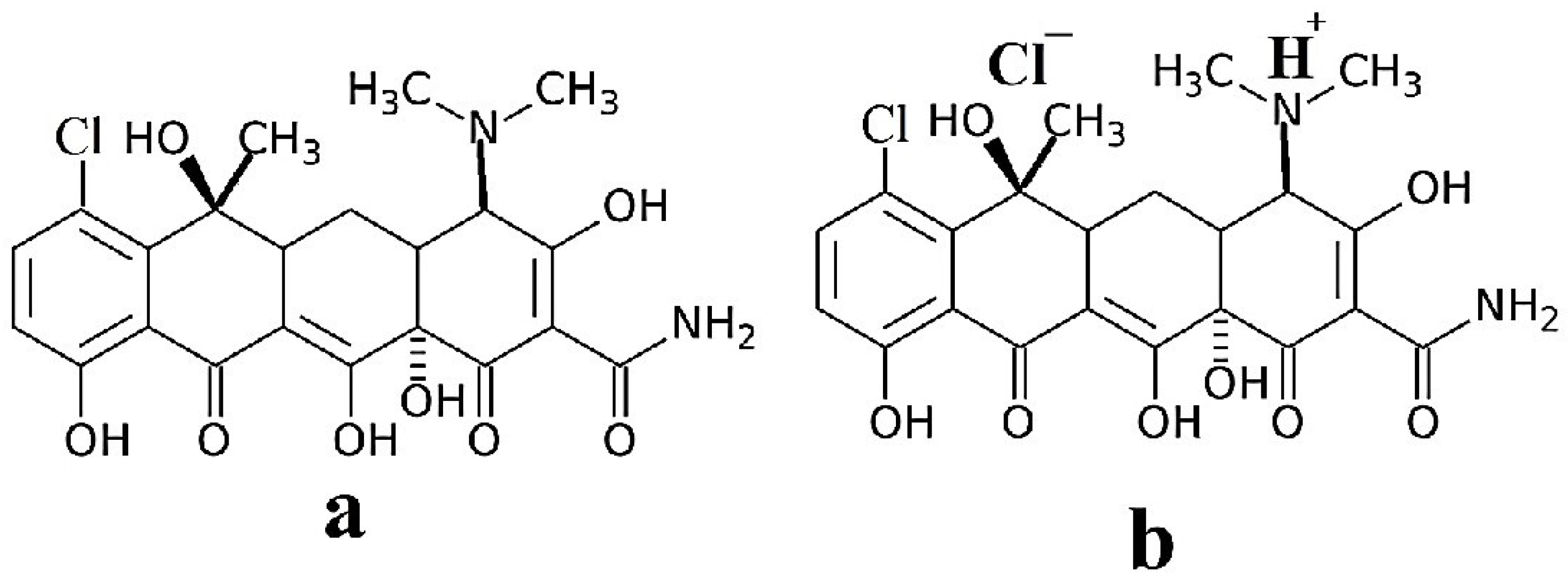
2.1. Reagents and Materials
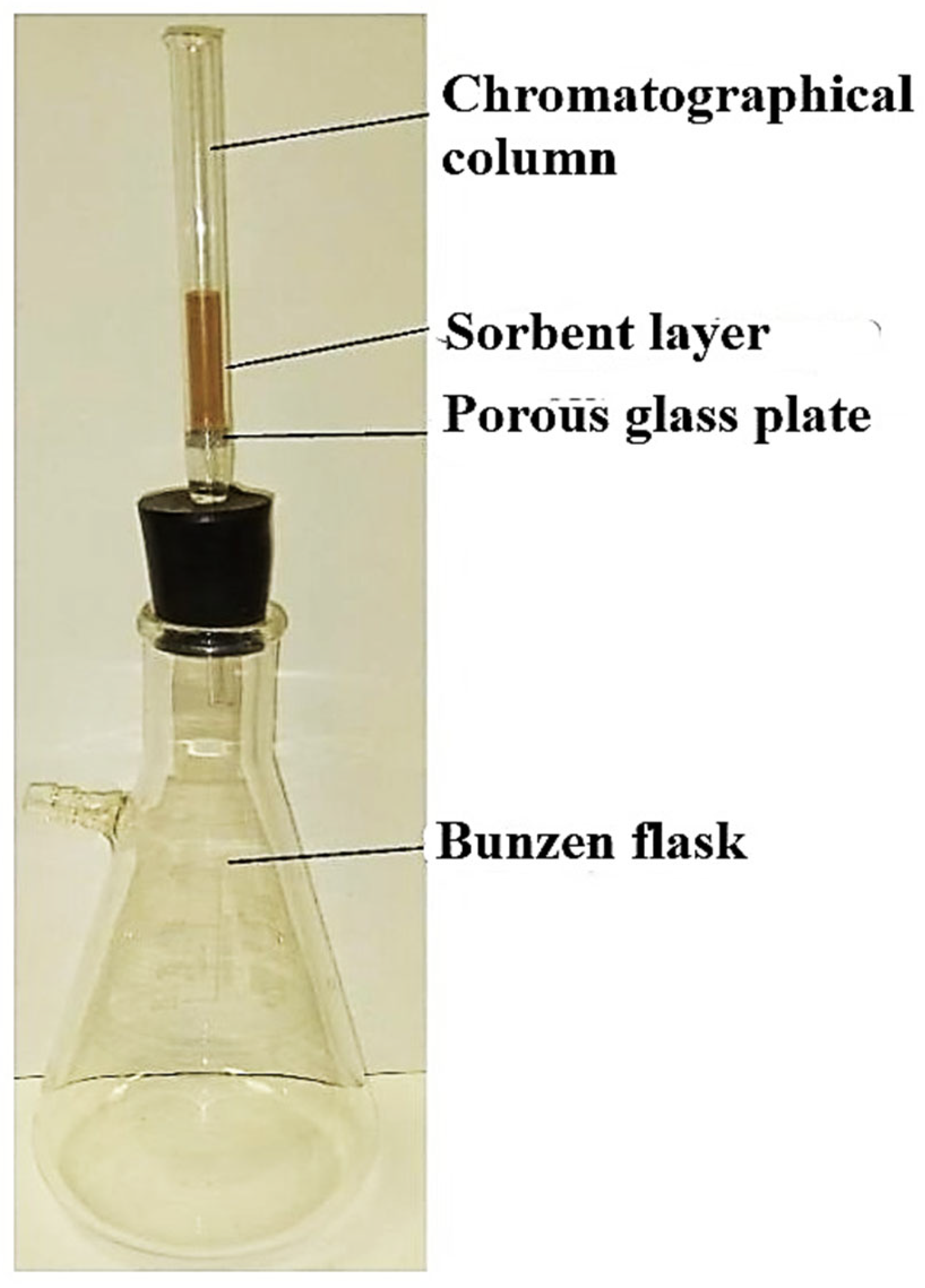
2.2. Apparatus
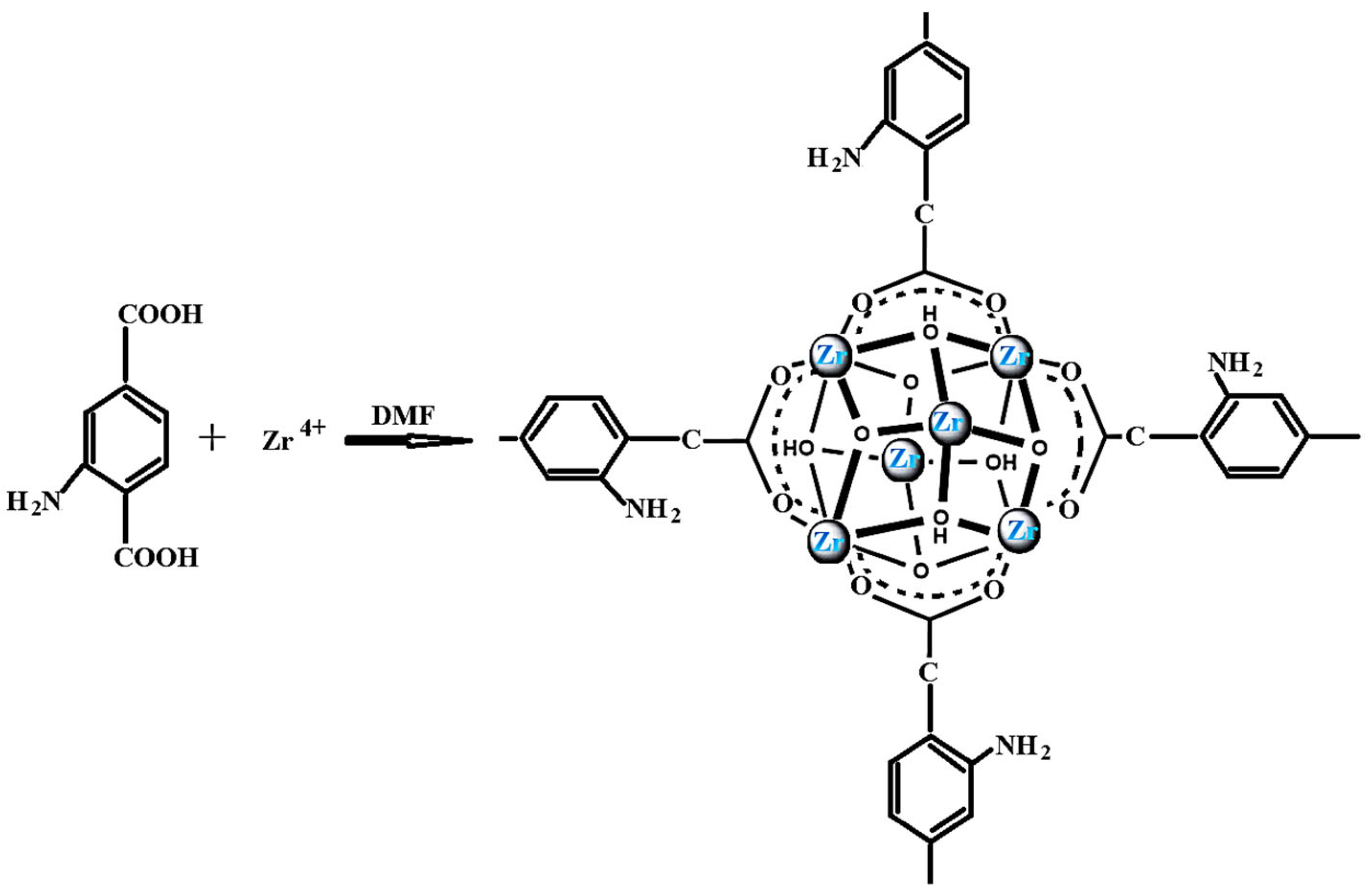
2.3. Synthesis of Sorbent
2.4. Sorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
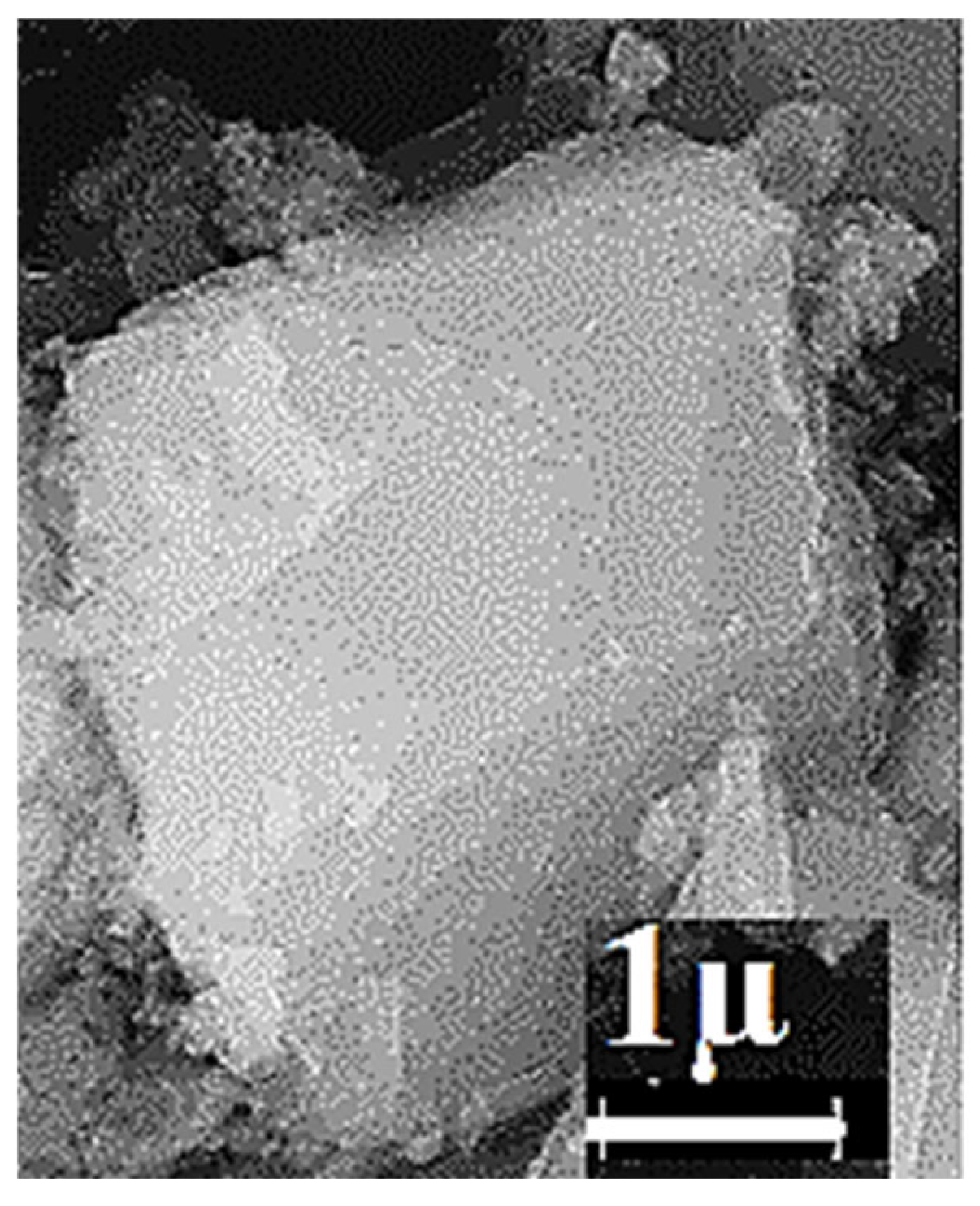
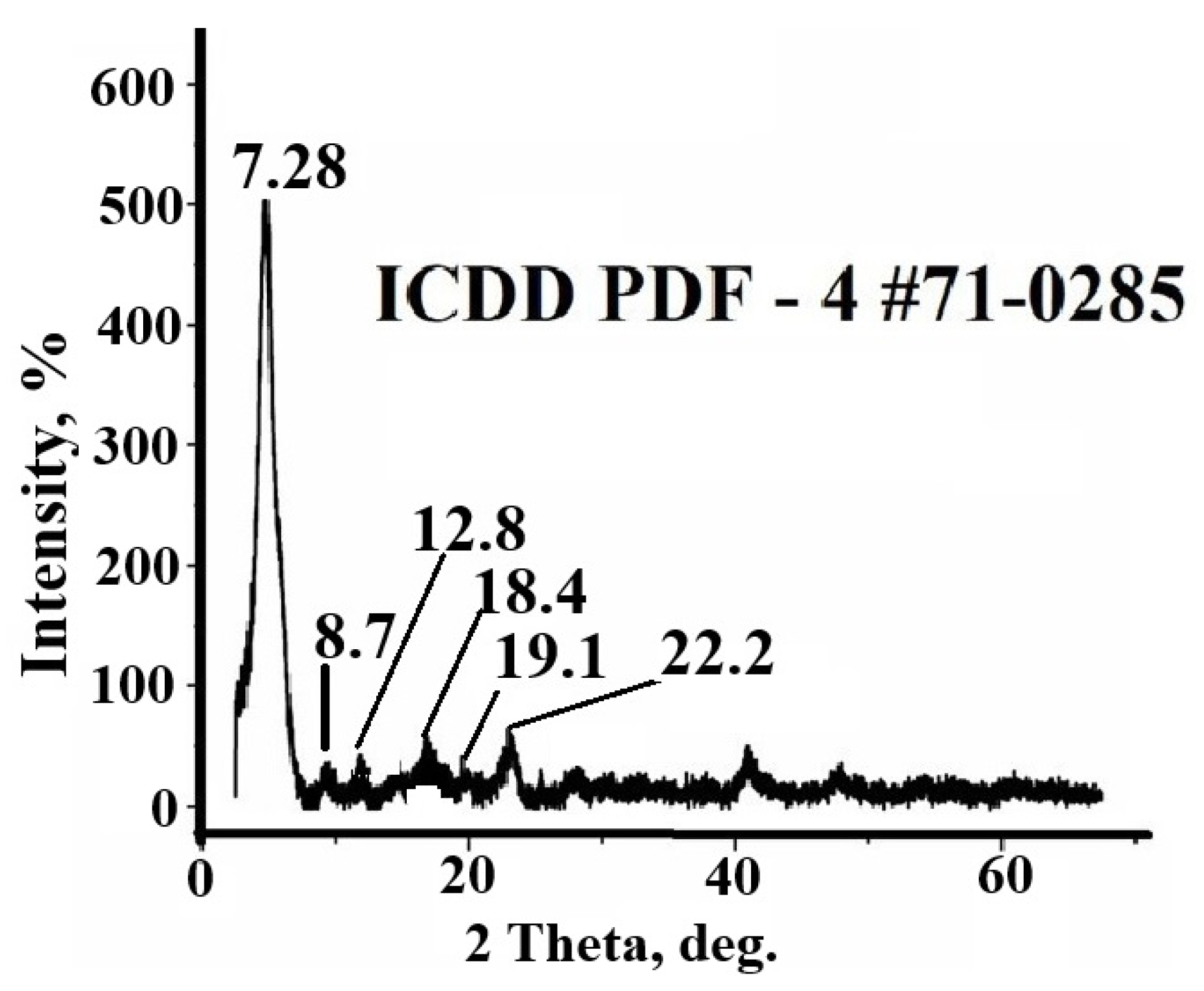
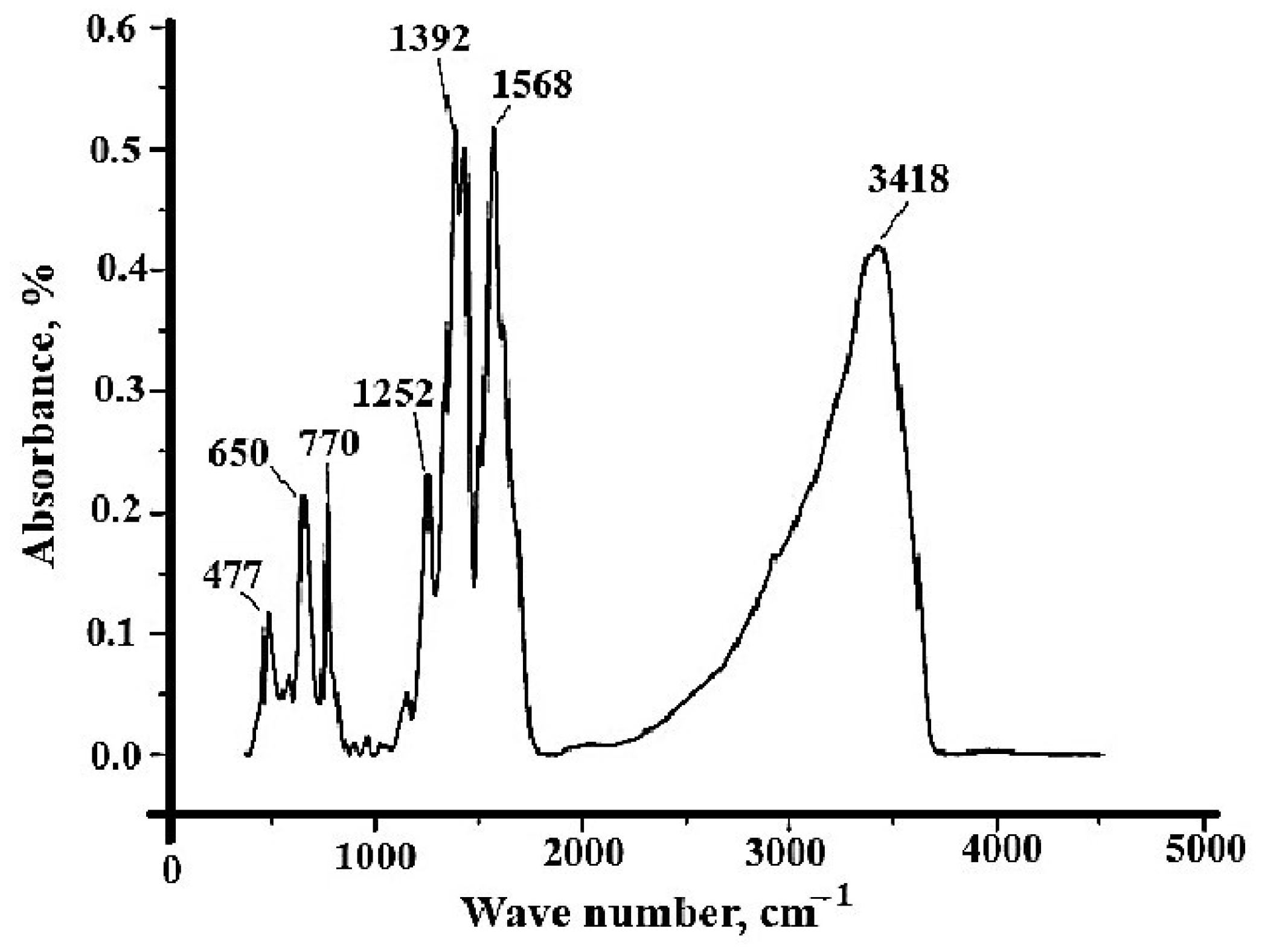
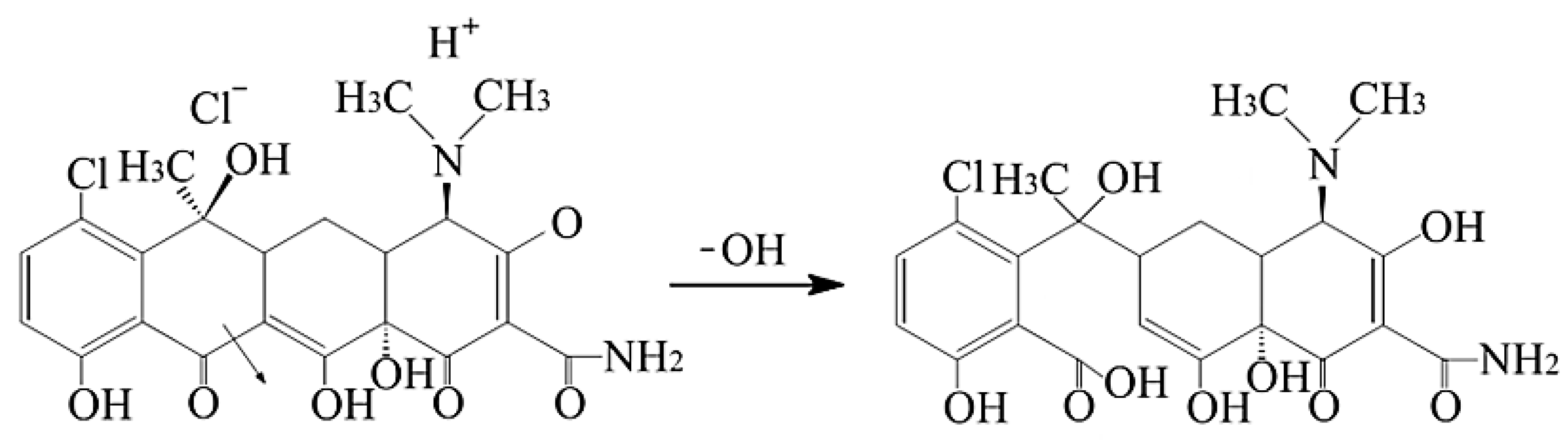
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Sorbent
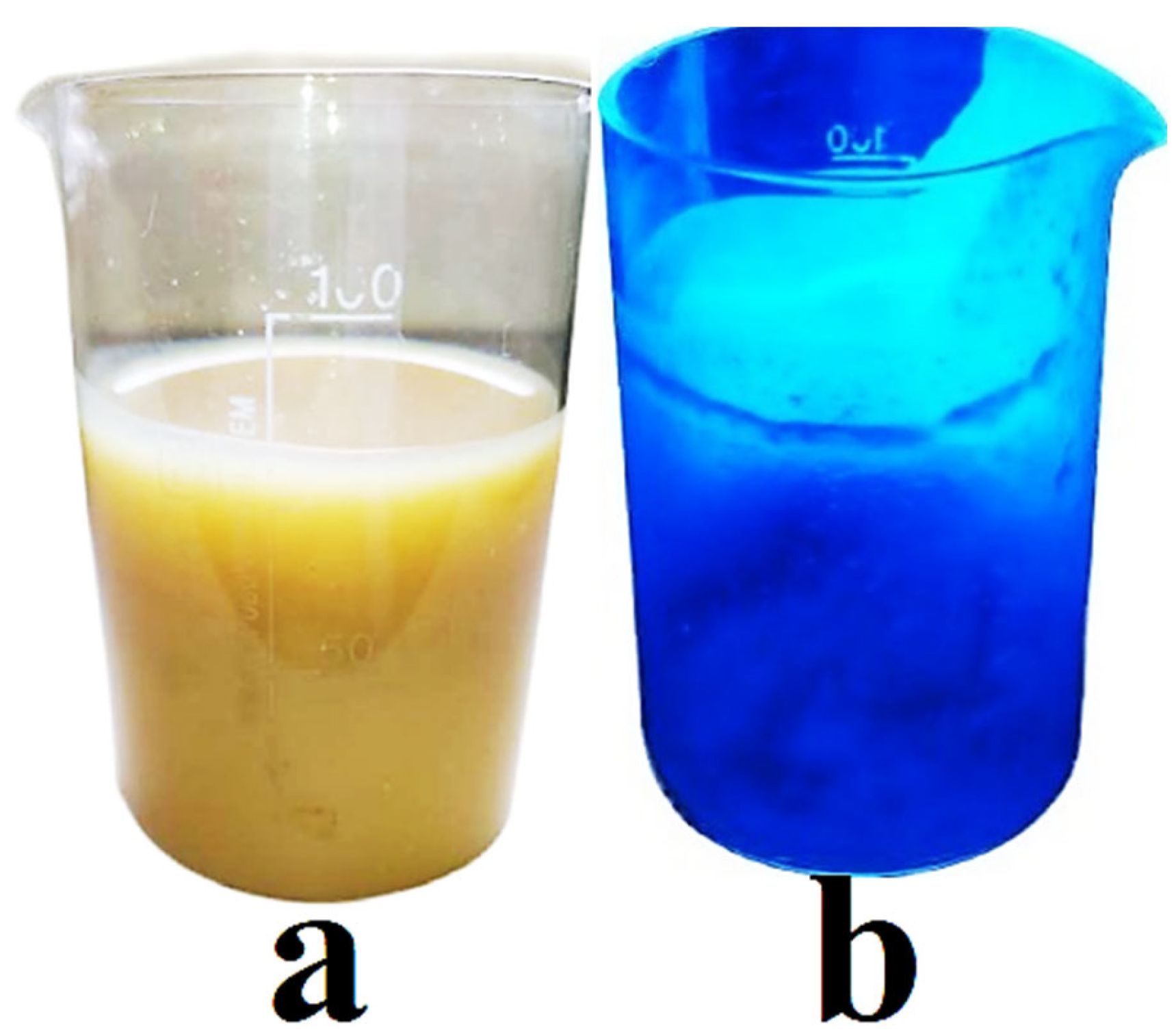
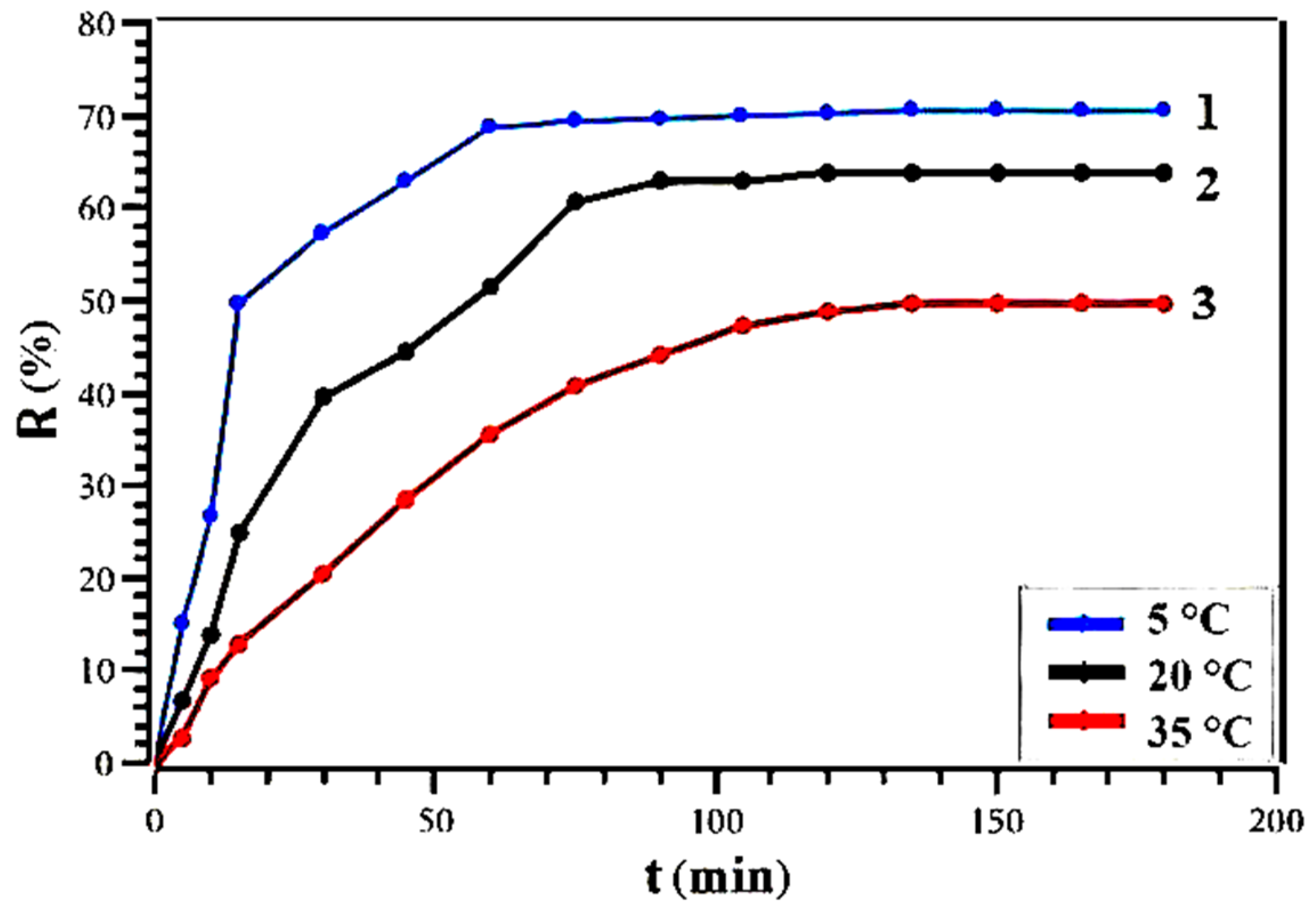
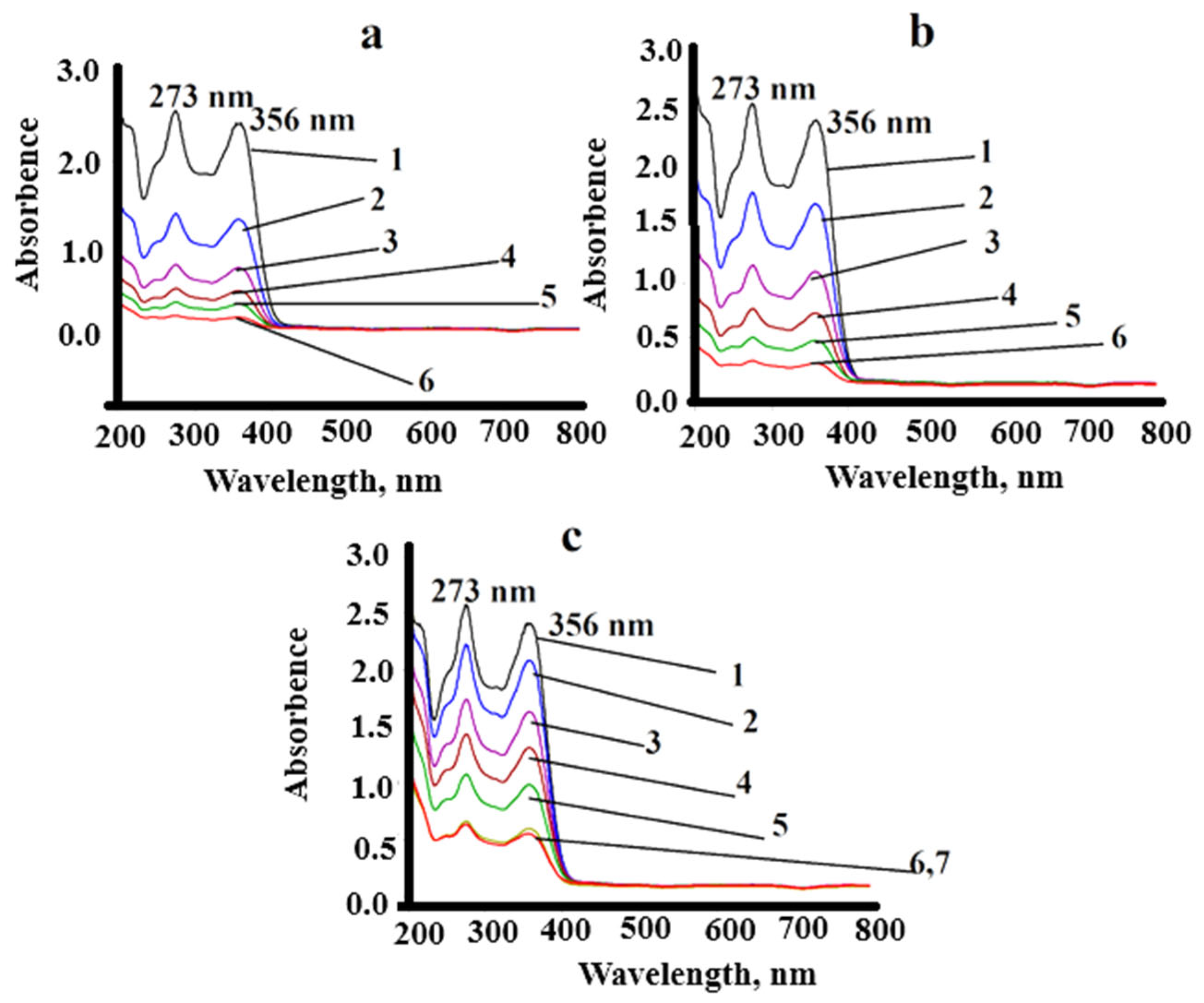
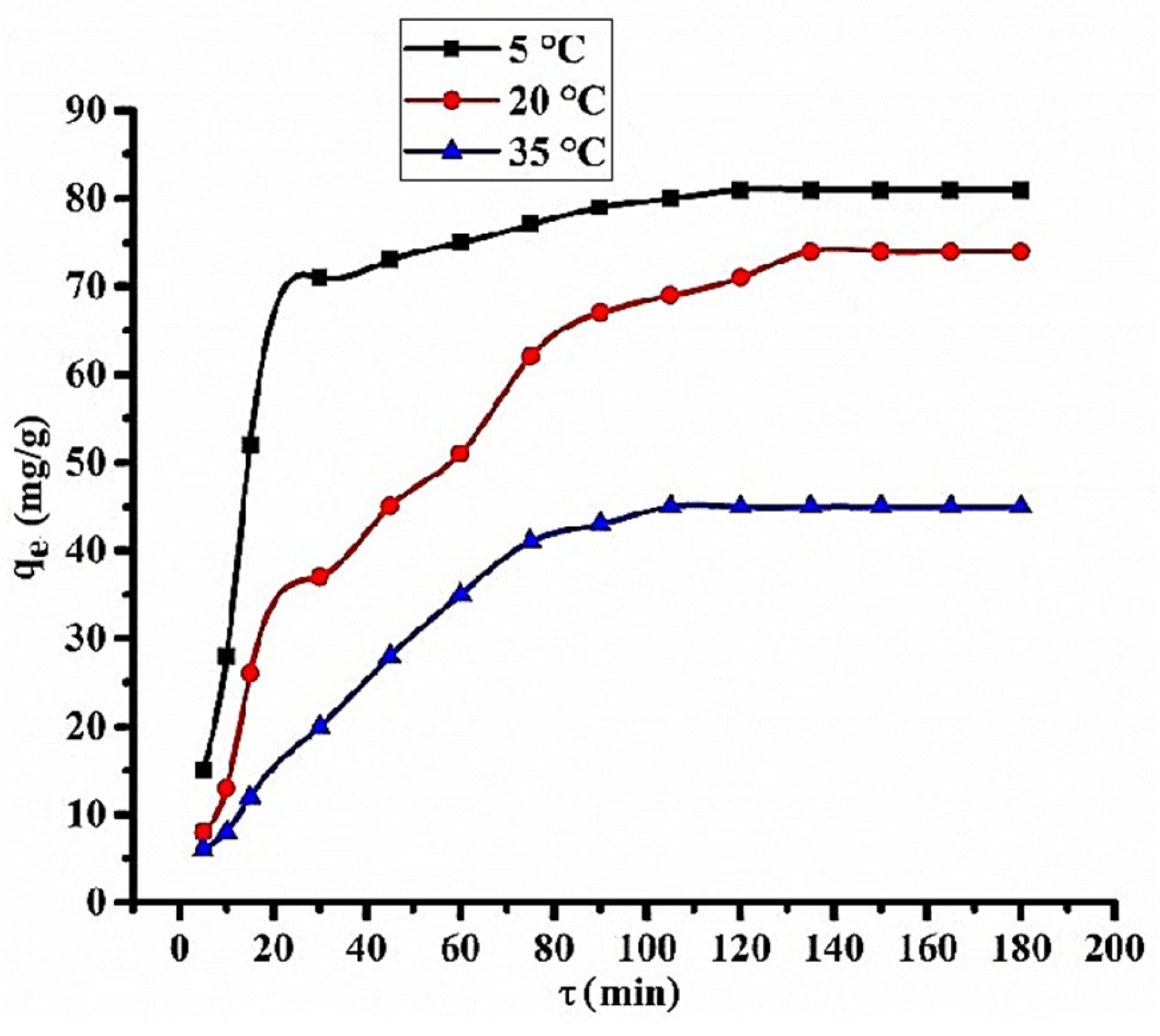
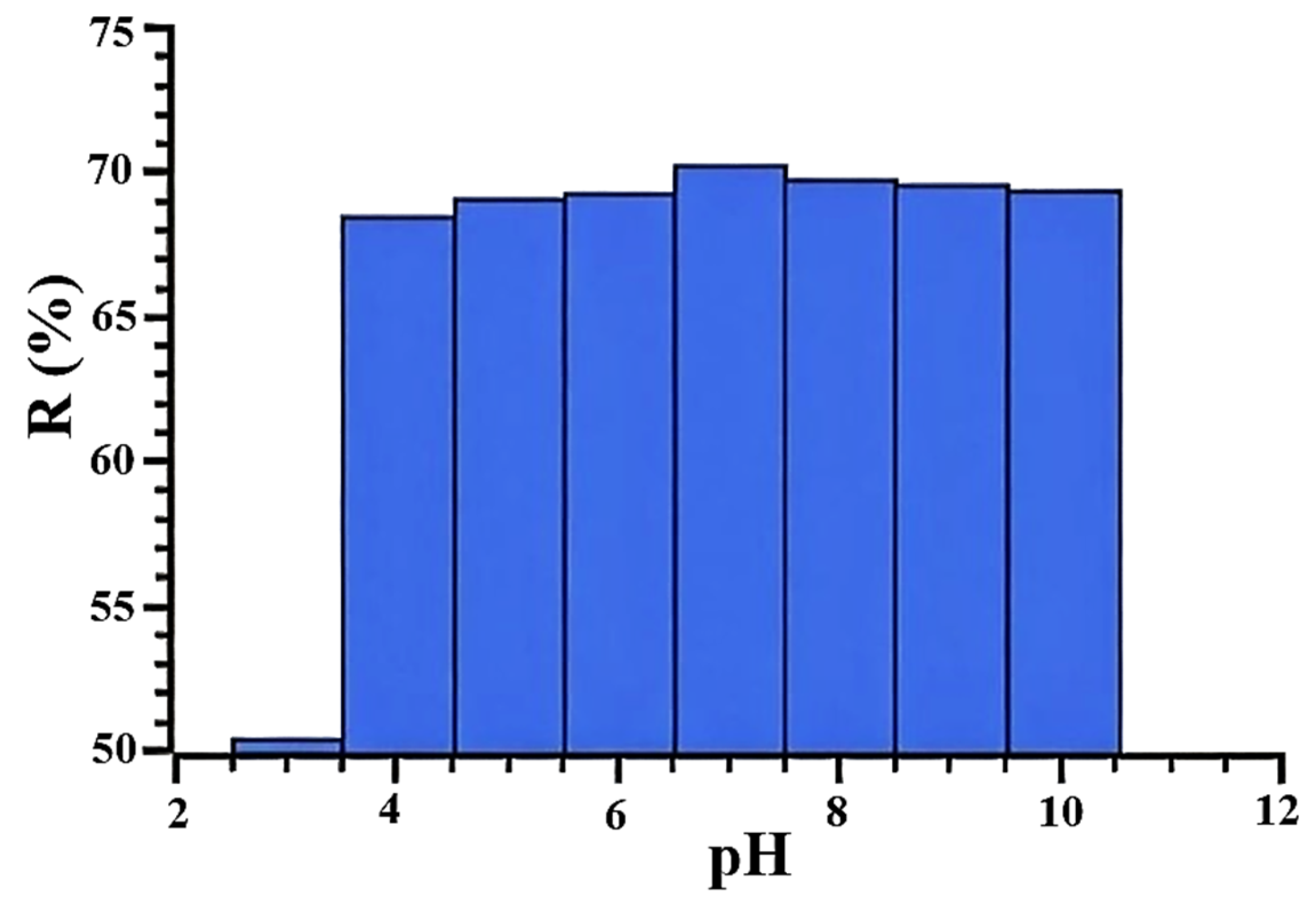
3.2. Solid-Phase Extraction of Chlortetracycline Hydrochloridefrom the Aqueous Solution
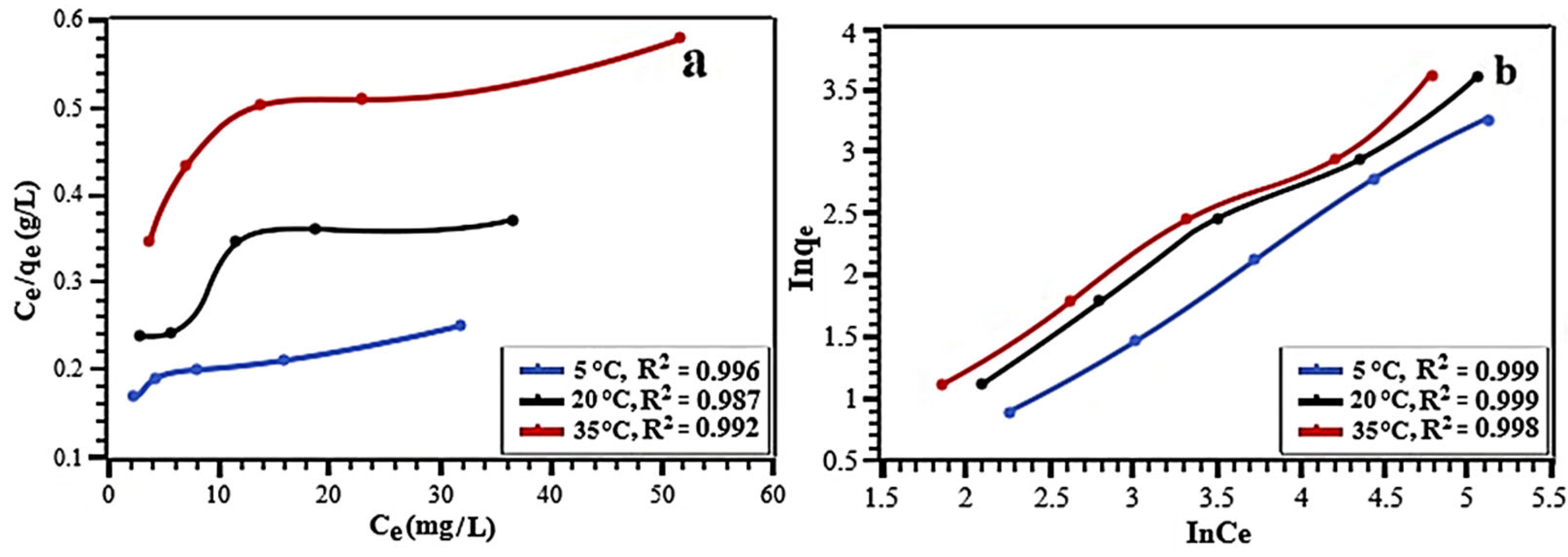
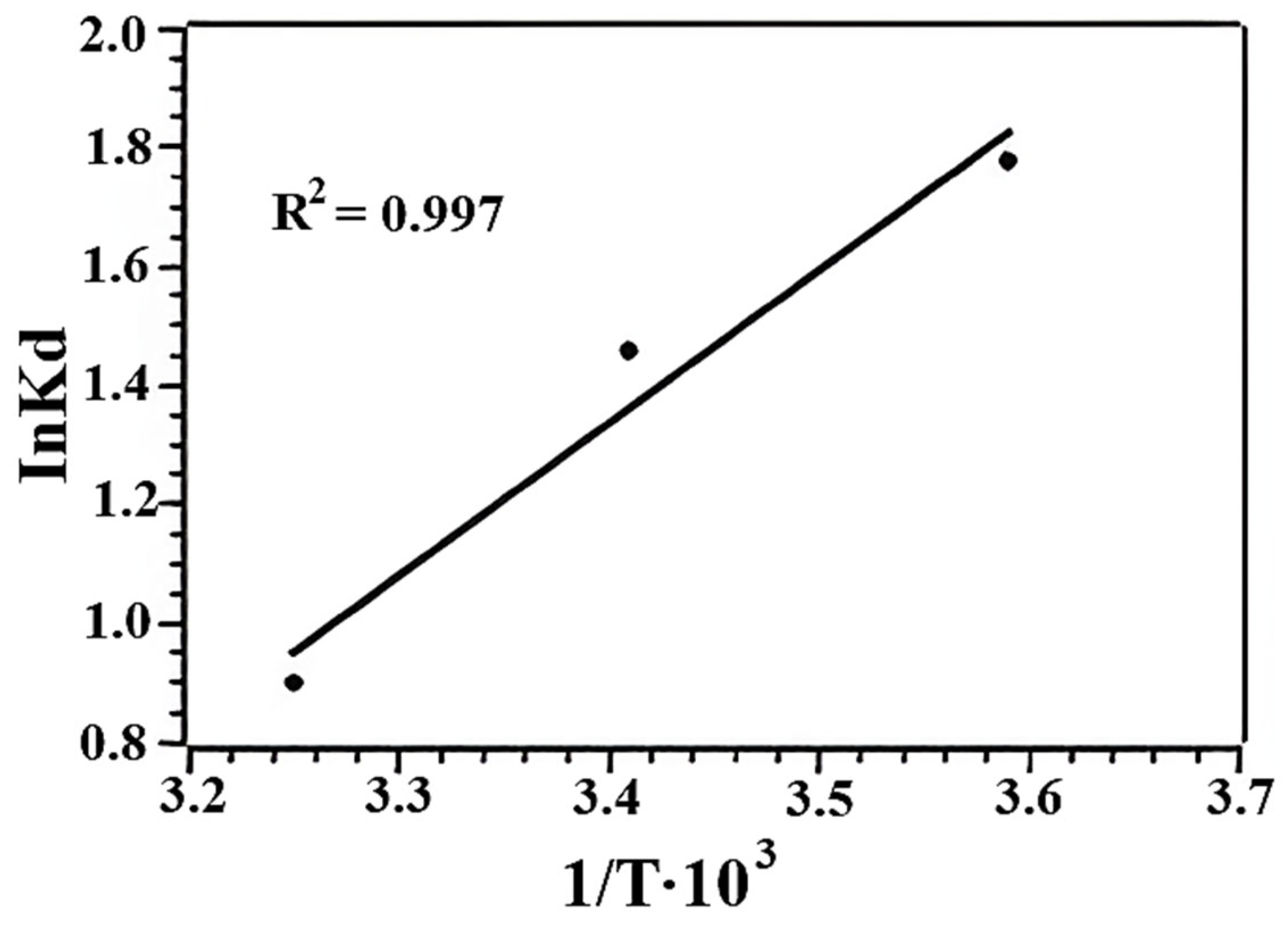
3.3. Study of Solid-Phase Extraction of CTC by Dynamic Method
- 1.
- The use of SPE to concentrate the analyte increases its concentration by 6.95 times, which allows its spectrophotometric determination with acceptable reliability, since the determined values are in the zone of optimal concentrations on the calibration graph.
- 2.
- SPE of the analyte allows one to avoid a long and labor-intensive evaporation procedure to increase the concentration of the analyte, including for GLC and HPLC.
- 3.
- Spectrophotometric analysis does not require expensive equipment, scarce standard samples, and highly qualified personnel.
- 4.
- Studies of the dependence of the degree of extraction of CTC from aqueous solutions allow it to be extracted at an initial concentration of 0.06 mg/L, which is quite sufficient to control the content of the analyte in natural waters and food products, since the standards of the European Union allow the content of CTC from 0.1 to 0.6 mg/kg of the product, depending on its type [39].
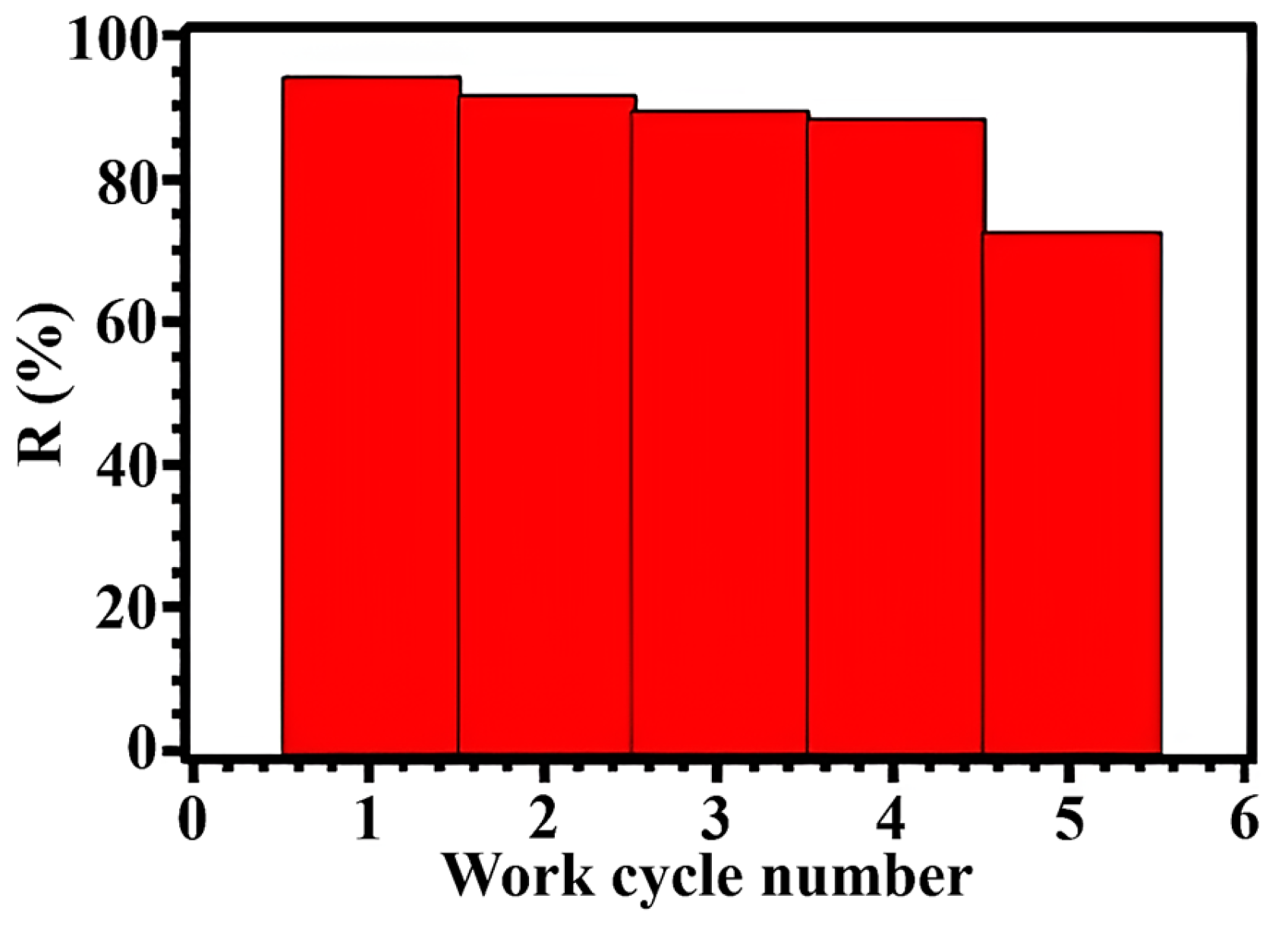
- 5.
- Dynamic SPE demonstrates more acceptable results compared to other methods [40].
3.4. Method for Determination of CTC in Real Objects Using Solid-Phase Extraction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, J.; Kong, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Gu, X.; Gulakhmadov, A. Hotspots of Global Water Resource Changes and Their Causes. Earths Future 2025, 13, e2024EF005461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husein, D.Z.; Hassanien, R.; Al-Hakkani, M.F. Green-synthesized copper nano-adsorbent for the removal of pharmaceutical pollutants from real wastewater samples. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; Ferro-García, M.A.; Prados-Joya, G.; Ocampo-Pérez, R. Pharmaceuticals as emerging contaminants and their removal from water. A review. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1268–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedidi, H.; Reinert, L.; Leveque, J.-M.; Soneda, Y.; Bellakhal, N.; Duclaux, L. The effects of the surface oxidation of activated carbon, the solution pH and the temperature on adsorption of ibuprofen. Carbon 2013, 54, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; de Jonge, N.; Carvalho, P.N.; Nielsen, J.L.; Bester, K. Biodegradation kinetics of organic micropollutants and microbial community dynamics in a moving bed biofilm reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 415, 128963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Becerra, F.Y.; Ortiz, I. Biodegradation of Emerging Organic Micropollutants in Nonconventional Biological Wastewater Treatment: A Critical Review. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, I.; Roberts, M. Tetracycline Antibiotics: Mode of Action, Applications, Molecular Biology, and Epidemiology of Bacterial Resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2001, 65, 232–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cerbo, A.; Pezzuto, F.; Guidetti, G.; Canello, S.; Corsi, L. Tetracyclines: Insights and Updates of their Use in Human and Animal Pathology and their Potential Toxicity. Open Biochem. J. 2019, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.K.; Liu, Y.Y.; Bao, D.; Zhu, G. Effective Removal of Tetracycline Antibiotics from Water using Hybrid Carbon Membranes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ning, D.; Li, W.-J.; Du, X.-M.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Ruan, W.-J. Metal-organic framework based fluorescent sensing of tetracycline type antibiotics applicable to environmental and food analysis. Analyst 2019, 144, 1916–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupeiko, T.G.; Gorbunova, M.O.; Bayan, E.M. Deep purification of aqueous solutions to remove iron(III) with carbonate-containing industrial waste. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2004, 77, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupeiko, T.G.; Bayan, E.M.; Gorbunova, M.O. Use of carbonate-containing industrial waste for treatment of aqueous solutions to remove nickel(II) ions. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2004, 77, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupeiko, T.G.; Gorbunova, M.O.; Bayan, E.M. Deep purification of aqueous solutions to remove chromium(III) with industrial carbonate-containing wastes. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2001, 74, 1698–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utpal, S. Colorimetric Determination of Tetracycline Hydrochloride in Pharmaceutical Preparations. J. AOAC Int. 1987, 70, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkashina, K.D.; Sumina, A.I.; Vakh, K.S.; Bulatov, A.V. Liquid–liquid microextraction of tetracyclines from biological fluids for their subsequent determination by high-performance liquid chromatography with UV detection. J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 75, 1424–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbunova, M.O.; Bayan, E.M. A novel paper-based sensor for determination of halogens and halides by dynamic gas extraction. Talanta 2019, 199, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbunova, M.O.; Bayan, E.M. A rapid field test method for the determination of hydrogen sulfide and sulfides in waters with gas preextraction. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 72, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apyari, V.V.; Furletov, A.A.; Garshev, A.V.; Volkov, P.A.; Gorbunova, M.O.; Shevchenko, A.V. Preparation of reagent indicator papers with silver triangular nanoplates for chemical analysis. Moscow Univ. Chem. Bull. 2017, 72, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbunova, M.O.; Bayan, E.M.; Shevchenko, A.V.; Kulyaginova, M.S. Digital colorimetric determination of chlorides in water using gas extraction and methyl orange. Anal. Control 2017, 21, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Uflyand, I.E.; Zhinzhilo, V.A.; Nikolaevskaya, V.O.; Kharisov, B.I.; Oliva González, C.M.; Kharissova, O.V. Recent Strategies to Improve MOF Performance in Solid Phase Extraction of Organic Dyes. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharisov, B.; Kharissova, O.; Zhinzhilo, V.; Bryantseva, J.; Uflyand, I. Solid-Phase Extraction of Organic Dyes on Mixed-Ligand Zr(IV) Metal–Organic Framework. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharissova, O.V.; Zhinzhilo, V.A.; Bryantseva, J.D.; Uflyand, I.E.; Kharisov, B.I. ZrIV metal–organic framework based on terephthalic acid and 1,10-phenanthroline as an adsorbent for solid phase extraction of tetracycline antibiotics. Mendeleev Commun. 2022, 32, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigma-Aldrich. Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride, Analytical Standard, ≥98.0% (HPLC). Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/RU/en/product/sial/phr1520 (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Konieczka, P. Validation and Regulatory Issues for Sample Preparation. In Comprehensive Sampling and Sample Preparation; Pawliszyn, J., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 2, pp. 699–711. [Google Scholar]
- Timofeev, K.L.; Kulinich, S.A.; Kharlamova, T.S. NH2-Modified UiO-66: Structural Characteristics and Functional Properties. Molecules 2023, 28, 3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, M.J.; Brown, Z.J.; Siu, P.W. A facile synthesis of UiO-66, UiO-67 and their derivatives. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9449–9451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Sarwghadi, M.; Heydarbeigi, A.; Hosseini, S.H.; Nedaie, M. Solid-Phase Extraction of Trace Amounts of Uranium(VI) in Environmental Water Samples Using an Extractant-Impregnated Resin Followed by Detection with UV-Vis Spectrophotometry. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 671564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, M.J.; Moon, S.-Y.; Mondloch, J.E. Exploiting parameter space in MOFs: A 20-fold enhancement of phosphate-ester hydrolysis with UiO-66-NH2. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 2286–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, K.M.; Oveisi, A.R.; Kaykhaii, M.; Rezaei Kahkha, B. Determination of carbamazepine in urine and water samples using amino-functionalized metal-organic framework as sorbent. Chem. Cent. J. 2018, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickolov, Z.; Georgiev, G.; Stoilova, D.; Ivanov, I. Raman and IR study of cobalt acetate dihydrate. J. Mol. Struct. 1995, 354, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harouna-Oumarou, H.A.; Fauduet, H.; Porte, C.; Ho, Y.S. Comparison of kinetic models for the aqueous solid-liquid extraction of tilia sapwood in a continuous stirred tank reactor. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2007, 194, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorodilova, A.I.; Lebedeva, E.L.; Petrova, Y.S.; Neudachina, L.K. Study of Sorption of Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride and Its Subsequent Determination by Capillary Zone Electrophoresis. J. Anal. Chem. 2023, 78, 1659–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, D.; Kamocki, S.; Szwast, M. Evaluation of the Potential of Metal–Organic Compounds ZIF-8 and F300 in a MembraneFiltration–Adsorption Process for the Removal of Antibiotics from Water. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Miao, J.; Wang, X.; Cai, J.; Lin, J. Novel Al-doped UiO-66-NH2 nanoadsorbent with excellent adsorption performance for tetracycline: Adsorption behavior, mechanism, and application potential. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yang, F.; Yang, R.; Sun, L. Preparation of novel ZnO-NP@Zn-MOF-74 composites for simultaneous removal of copper and tetracycline from aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 274, 118949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, Y.-H.; Du, Q.; Pi, X. Effective removal of tetracycline from water using copper alginate@graphene oxide with in-situ grown MOF-525 composite: Synthesis, characterization and adsorption mechanisms. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanmaz, N.; Demircivi, P. Adsorption of tetracycline using one-pot synthesis zirconium metal-organic framework (UiO-66) decorated hydroxyapatite. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 397, 124171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robati, D.; Rajabi, M.; Moradi, O.; Najafi, F.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. Kinetics and thermodynamics of malachite green dye adsorption from aqueous solutions on graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 214, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Sun, A.; Xu, R.; Chen, R. Enhancing solid-phase extraction of tetracyclines with a hybrid biochar sorbent: A comparative study of chlorella and bamboo biochars. J. Chromatogr. A 2024, 1730, 465092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, J.M. Commission regulation (EU) №37/2010 of 22 December 2009 on pharmacologically active substances and their classification regarding maximum residue limits in food stuffs of animal origin. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, 1, 1–72. [Google Scholar]


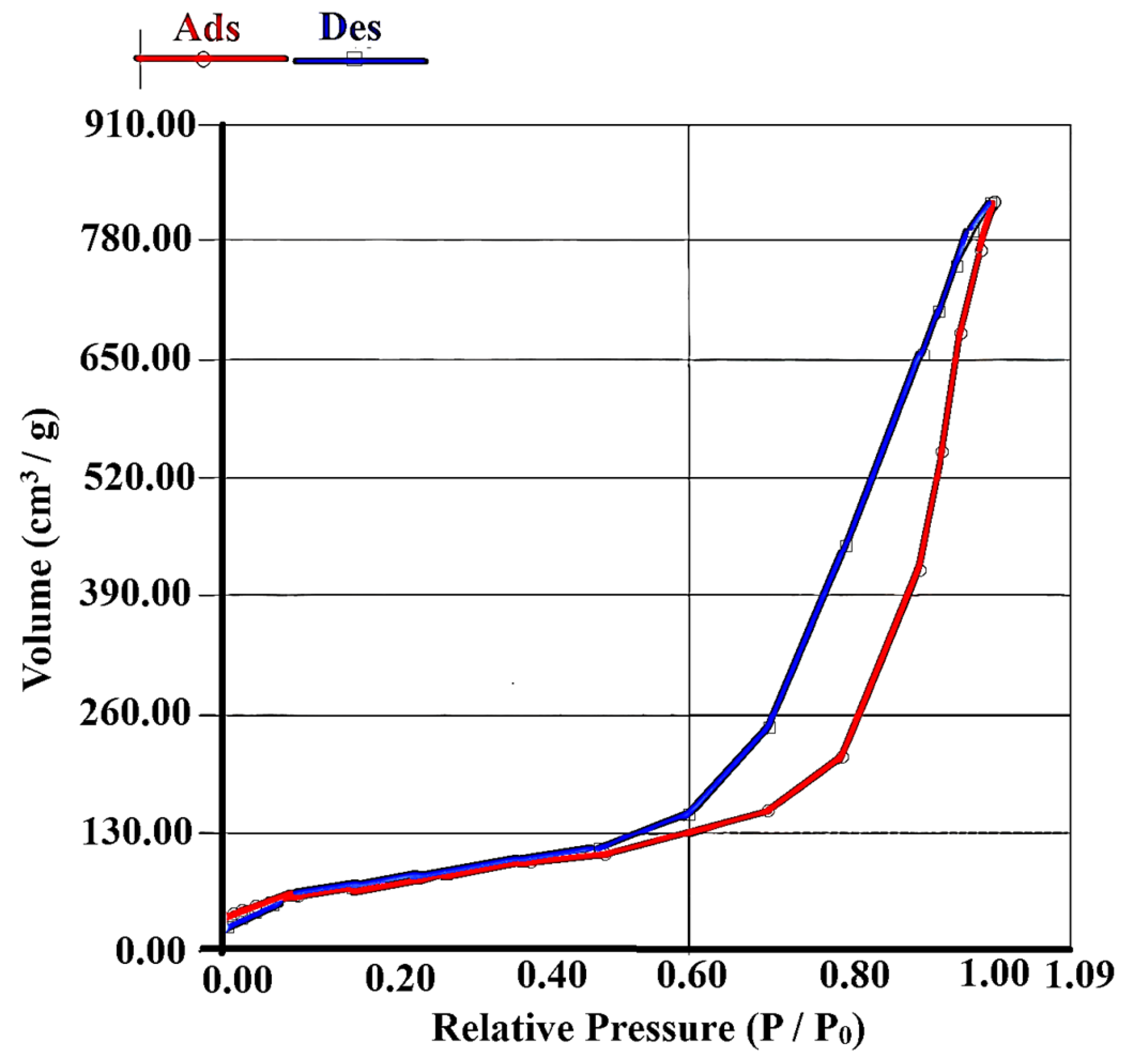
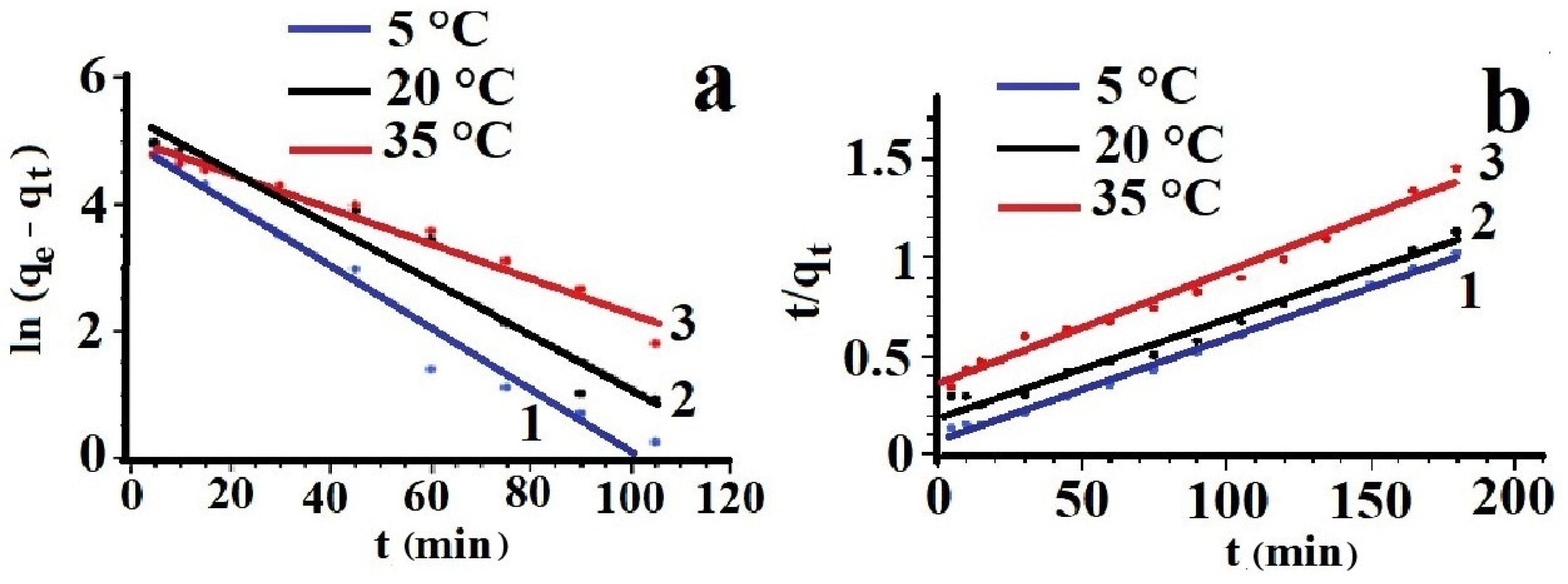

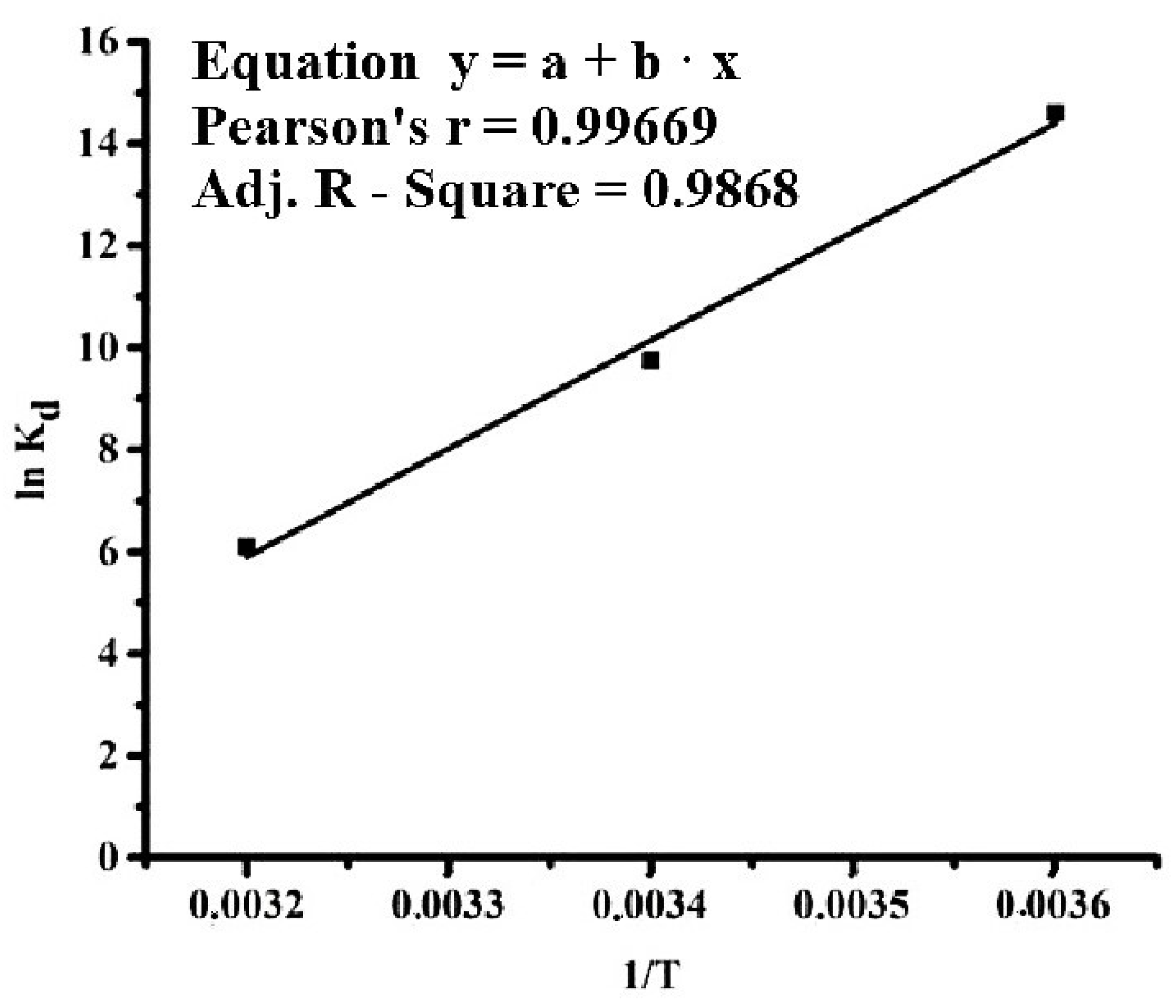
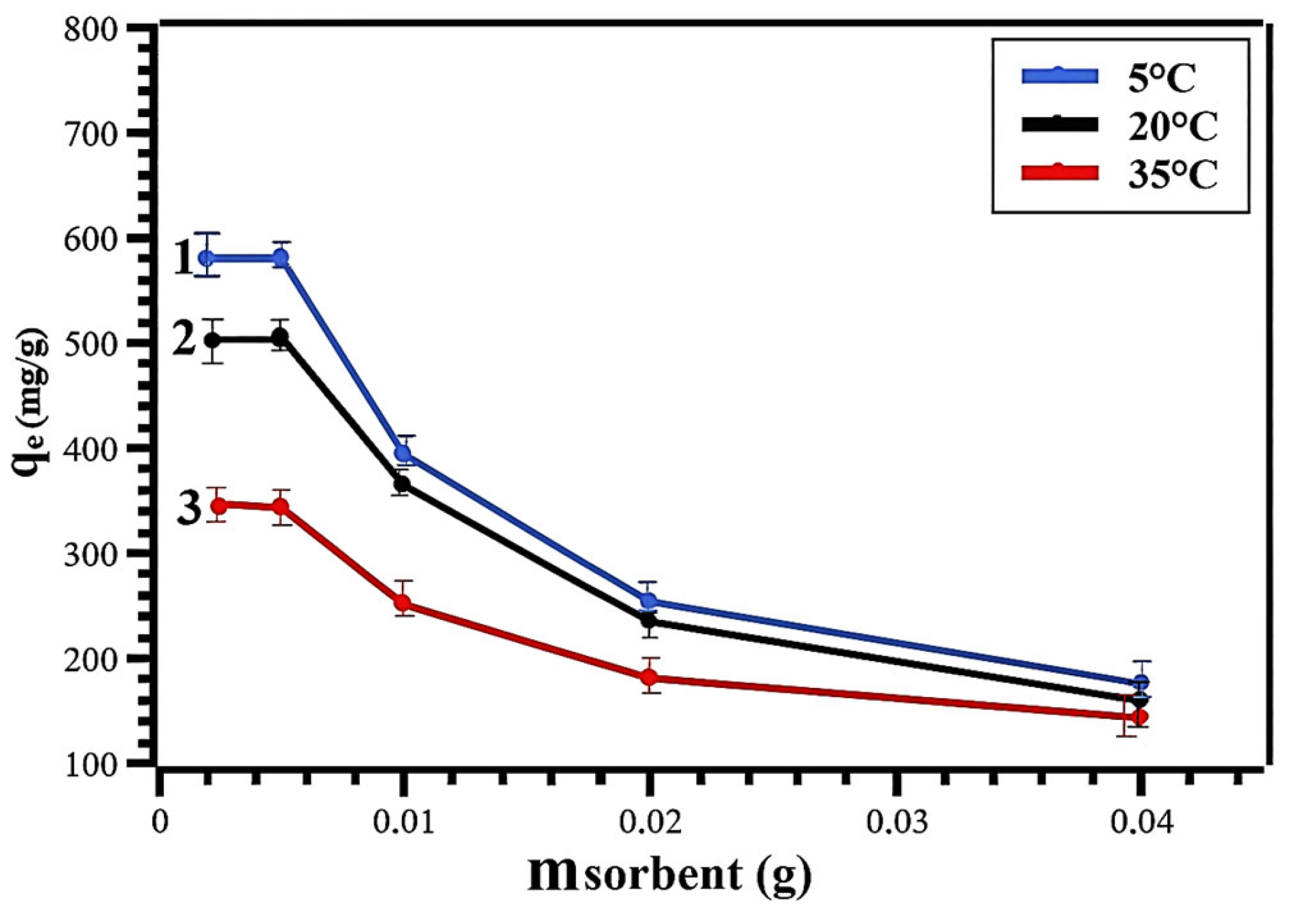
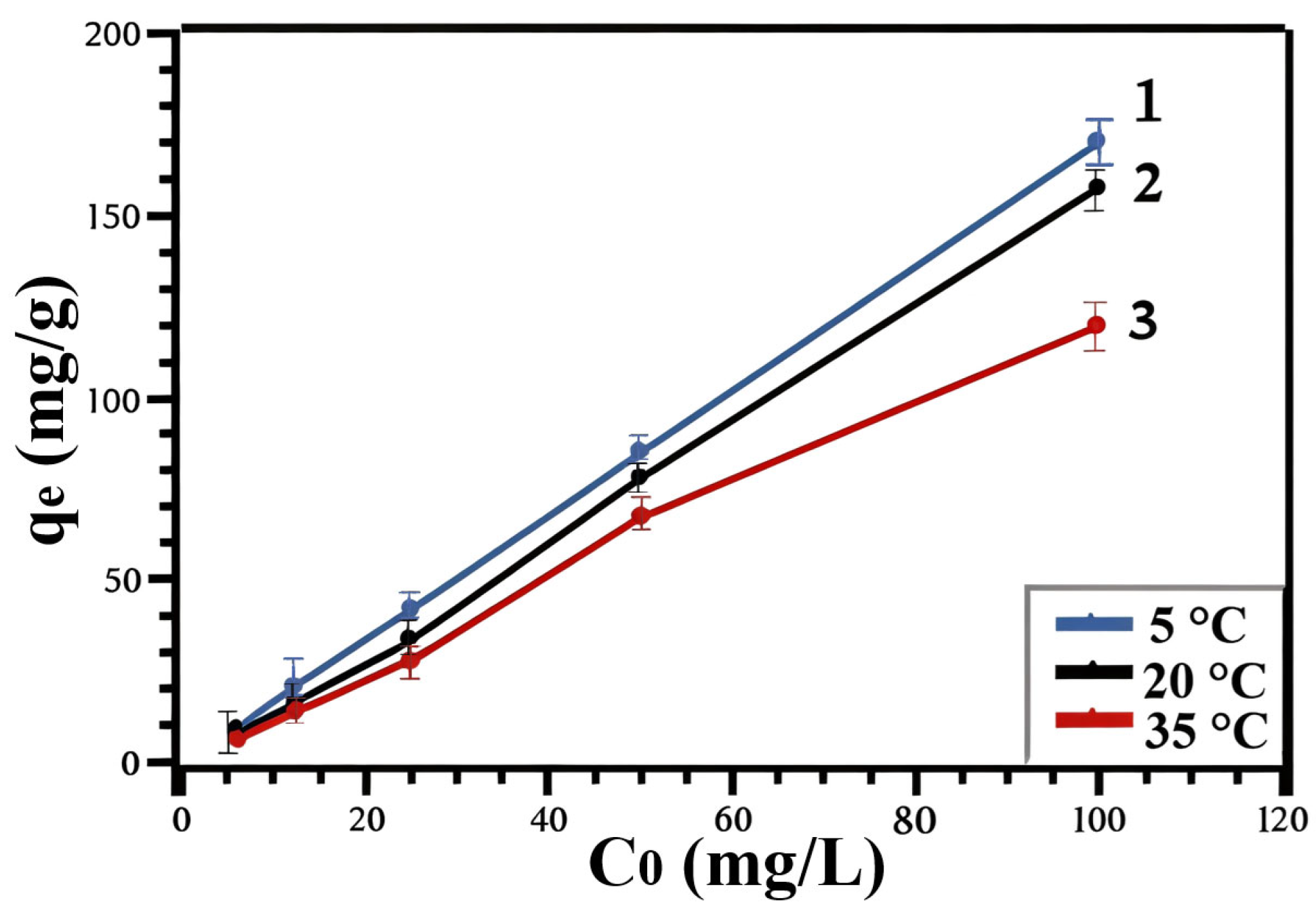

| SBET (m2/g) | Vpore (cm3/g) | Vmicropore (cm3/g) | Average Pore Size (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 820 | 0.95 | 0.23 | 7.97 |
| t, °C | 5 | 20 | 35 |
| ln k | 0.085 | 0.25 | 0.4 |
| t, °C | ΔG0 (kJ mol−1) | ΔH0 (kJ mol−1) | ΔS0 (J mol−1K−1) | Ea (kJ mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | −6.19 | −4.41 | 39.88 | 6.48 |
| 20 | −5.45 | |||
| 35 | −4.60 |
| t (°C) | 5 | 20 | 35 |
| qmax (mg/g) | 578 | 502 | 337 |
| Model | Parameter | T, K | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 278 | 293 | 308 | ||
| Langmuir | qmax | 252.1 | 165.8 | 122.1 |
| KL | 0.023 | 0.024 | 0.021 | |
| R2 | 0.996 | 0.987 | 0.992 | |
| Freundlich | 1/n | 0.54 | 0.58 | 0.69 |
| KF | 2.21 | 2.18 | 1.87 | |
| R2 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.998 | |
| MOF Sorbent | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Applicable pH Range | Regeneration Cycles | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZIF-8 | 442.2 | 5–7 | 4 | [32] |
| Al-doped UiO-66-NH2 | 520 | 4–10 | 3 | [33] |
| ZnO-NP@Zn-MOF-74 | 118.9 | 7 | 4 | [34] |
| Alg-Cu@GO@MOF-525 | 533 | 6–7 | Not reported | [35] |
| UiO-66@HAp | 52.9 | Not reported | Not reported | [36] |
| Zr-NH2-BDC | 578 | 4–10 | 5 | This work |
| T (K) | Kc | ΔG0 (kJ/mol) | ΔH0 (kJ/mol) | ΔS0 (J/mol K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 278 | 5.9 | −4.12 | −0.046 | 5.76 |
| 293 | 4.4 | −3.63 | ||
| 308 | 2.4 | −2.31 |
| CTC Introduced (mg) | CTC Found (mg) | Rdes (%) | Sr | EF | Kd | K | LOD (mg/L) | LOQ (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.15 | 0.14008±0.0014 (±1.02%) | 97.3±0.2 | 0.02 | 6.95 | 30.0 | 97.5 | 0.06 | 0.06–90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bryantseva, J.D.; Gorbunova, M.O.; Zhinzhilo, V.A.; Uflyand, I.E. Study of Sorption of Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride on Zirconium-Based Metal–Organic Framework Followed by Determination by UV-Vis Detection. Analytica 2025, 6, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6030028
Bryantseva JD, Gorbunova MO, Zhinzhilo VA, Uflyand IE. Study of Sorption of Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride on Zirconium-Based Metal–Organic Framework Followed by Determination by UV-Vis Detection. Analytica. 2025; 6(3):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6030028
Chicago/Turabian StyleBryantseva, Julia D., Marina O. Gorbunova, Vladimir A. Zhinzhilo, and Igor E. Uflyand. 2025. "Study of Sorption of Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride on Zirconium-Based Metal–Organic Framework Followed by Determination by UV-Vis Detection" Analytica 6, no. 3: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6030028
APA StyleBryantseva, J. D., Gorbunova, M. O., Zhinzhilo, V. A., & Uflyand, I. E. (2025). Study of Sorption of Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride on Zirconium-Based Metal–Organic Framework Followed by Determination by UV-Vis Detection. Analytica, 6(3), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6030028






