-
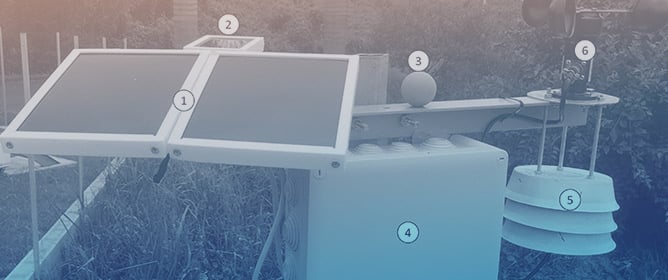 Advancing Urban Microclimate Monitoring: Development of a Low-Tech Environmental Station
Advancing Urban Microclimate Monitoring: Development of a Low-Tech Environmental Station -
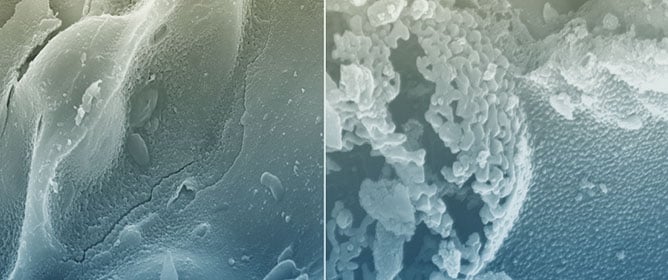 The Influence of Biowaste Type on the Characteristics of Corresponding Biochar Used as Sustainable Sorbent
The Influence of Biowaste Type on the Characteristics of Corresponding Biochar Used as Sustainable Sorbent -
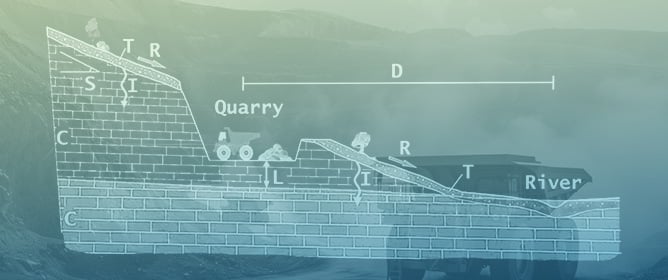 Categorization of the Potential Impact of Italian Quarries on Water Resources through a Multi-Criteria Decision Aiding-Based Model
Categorization of the Potential Impact of Italian Quarries on Water Resources through a Multi-Criteria Decision Aiding-Based Model -
 Cement Mortars Based on Polyamide Waste Modified with Fly Ash from Biomass Combustion—A New Material for Sustainable Construction
Cement Mortars Based on Polyamide Waste Modified with Fly Ash from Biomass Combustion—A New Material for Sustainable Construction -
 Formation, Characteristics, and Influencing Factors of the Plastisphere
Formation, Characteristics, and Influencing Factors of the Plastisphere
Journal Description
Sustainability
Sustainability
is an international, peer-reviewed, open-access journal on environmental, cultural, economic, and social sustainability of human beings, published semimonthly online by MDPI. The Canadian Urban Transit Research & Innovation Consortium (CUTRIC), International Council for Research and Innovation in Building and Construction (CIB) and Urban Land Institute (ULI) are affiliated with Sustainability and their members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE and SSCI (Web of Science), GEOBASE, GeoRef, Inspec, AGRIS, RePEc, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Environmental Studies) / CiteScore - Q1 (Geography, Planning and Development)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 18.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Sustainability.
- Companion journals for Sustainability include: World, Sustainable Chemistry, Conservation, Future Transportation, Architecture, Standards, Merits and Wind.
Impact Factor:
3.9 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.0 (2022)
Latest Articles
Variation in Debris-Flow-Prone Areas with Ecosystem Stability: A Case Study of the Qipan Catchment in the Wenchuan Earthquake Region
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3855; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093855 (registering DOI) - 04 May 2024
Abstract
The spatial distribution of vegetation in a basin has a far-reaching influence on the potential for sediment separation and transport capacity. However, many landslides induced by strong earthquakes have greatly changed the existing pattern, which further increases the probability of debris flow in
[...] Read more.
The spatial distribution of vegetation in a basin has a far-reaching influence on the potential for sediment separation and transport capacity. However, many landslides induced by strong earthquakes have greatly changed the existing pattern, which further increases the probability of debris flow in a basin during heavy rainfall and has a significant impact on the stability of the basin. Thus, this study selected the debris flow basin in the Qipan catchment of the Wenchuan earthquake area as the research object. Multisource and high-precision remote sensing images were used to analyze the land use changes in the basin, and the index of connectivity (IC) was introduced to analyze the evolution of sediment transport capacity. An ecosystem stability assessment method suitable for post-earthquake debris flow basins was proposed. Through quantitative assessment of the ecosystem stability of the basin after the Wenchuan earthquake in 2008 and the two debris flow events after the earthquake, the dynamic relationship between the debris-flow-prone area and the ecosystem stability of the basin was revealed. The results showed that the stability of the ecosystem in the Qipan catchment increased annually, indicating a stable and substable state. The spatial distribution characteristics were lower in the north and south and greater in the middle. By comparing the evaluation results with the actual terrain change trend, the accuracy and feasibility of the evaluation method are verified. The results of this study provide a scientific basis for the formulation of regional disaster prevention strategies and help to accelerate the improvement of regional stability in debris-flow-prone areas.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Protection of Ecosystem and Sustainable Development: Strategies and Practices for Ecological Restoration, Biodiversity Conservation, and Ecosystem Services)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
More than 30 Years of PVC Recycling in Europe—A Critical Inventory
by
Uwe Lahl and Barbara Zeschmar-Lahl
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3854; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093854 (registering DOI) - 04 May 2024
Abstract
PVC has a special status, as chlorine is a component of the polymer molecule. The properties of chlorine are the reason why the polymer molecule needs additivation. PVC is the mass plastic to which the most diverse and quantitatively largest number of additives
[...] Read more.
PVC has a special status, as chlorine is a component of the polymer molecule. The properties of chlorine are the reason why the polymer molecule needs additivation. PVC is the mass plastic to which the most diverse and quantitatively largest number of additives are added. This makes PVC difficult to recycle. More than three decades ago, the PVC industry announced its commitment to improve the sustainability of the material through material recycling. We analysed the latest figures from the European PVC industry, ensuring that the statistics included the quantities that enter the market as recyclate. We also analysed the significance of replacing virgin PVC with recyclates. We conclude from this that, after a good three decades, the recycling result is rather meagre. The lion’s share of PVC waste in Europe is still going to waste-to-energy plants, where it tends to be a nuisance. The many announcements to close the chlorine cycle via waste incineration have not got very far either. And the announcements to expand chemical recycling in parallel have not been successful. On the basis of this stocktaking, we have analysed, in a second separately published part, which conclusions can be drawn for regulatory measures, building on a current ECHA investigation report.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainability: Resources and Waste Management)
Open AccessArticle
Use of Recycled Plastic Fibers to Control Shrinkage and Desiccation Cracking in Clayey Soils
by
Carolina Hernández, Gloria Beltrán and Eduardo Botero
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3853; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093853 (registering DOI) - 04 May 2024
Abstract
Two main issues are addressed in this work. The first issue is environmental concerns about managing plastic waste on a large scale by promoting reuse with low energy requirements in the recycling processes. The second issue is the desiccation cracks in fine soils,
[...] Read more.
Two main issues are addressed in this work. The first issue is environmental concerns about managing plastic waste on a large scale by promoting reuse with low energy requirements in the recycling processes. The second issue is the desiccation cracks in fine soils, induced by prolonged droughts, which have motivated the interest in mitigating the adverse effects on the stability of geotechnical works using recycled materials. Therefore, this work addresses a strategy based on the use of recycled polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polypropylene (PP) fibers for the reinforcement of soils prone to cracking. To evaluate the effectiveness of plastic fibers in controlling soil volumetric changes and cracking during drying, several experiments were conducted in an environmental chamber to properly simulate and monitor the desiccation process. Image analysis and suction measurements provided several metrics and parameters, and their usefulness is discussed in detail, both for the unconventional determination of the optimum fiber content by weight with 100% effectiveness in preventing cracking and for correlating fiber content with reductions in shrinkage and cracking patterns, thus contributing to the understanding of the behavior of fiber-reinforced soils. Finally, examples of large-scale applications of recycled plastic fibers in geotechnical works are proposed, and the positive environmental impact is estimated.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Application of Waste Tire in Construction: A Road towards Sustainability and Circular Economy
by
Mohammad R. Hassan and Denis Rodrigue
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3852; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093852 - 03 May 2024
Abstract
The global demand for rubber is on a steady rise, which is driven by the increasing production of automobiles and the growing need for industrial, medical, and household products. This surge in demand has led to a significant increase in rubber waste, posing
[...] Read more.
The global demand for rubber is on a steady rise, which is driven by the increasing production of automobiles and the growing need for industrial, medical, and household products. This surge in demand has led to a significant increase in rubber waste, posing a major global environmental challenge. End-of-life tire (ELT) is a primary source of rubber waste, having significant environmental hazards due to its massive stockpiles. While landfilling is a low-cost and easy-to-implement solution, it is now largely prohibited due to environmental concerns. Recently, ELT rubber waste has received considerable attention for its potential applications in civil engineering and construction. These applications not only enhance sustainability but also foster a circular economy between ELT rubber waste with the civil engineering and construction sectors. This review article presents a general overview of the recent research progress and challenges in the civil engineering applications of ELT rubber waste. It also discusses commercially available recycled rubber-based construction materials, their properties, testing standards, and certification. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, this is the first time such a discussion on commercial products has been presented, especially for civil engineering applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Circular Economy in the Construction Sector)
Open AccessArticle
Deep-Reinforcement-Learning-Based Vehicle-to-Grid Operation Strategies for Managing Solar Power Generation Forecast Errors
by
Moon-Jong Jang and Eunsung Oh
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3851; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093851 - 03 May 2024
Abstract
This study proposes a deep-reinforcement-learning (DRL)-based vehicle-to-grid (V2G) operation strategy that focuses on the dynamic integration of charging station (CS) status to refine solar power generation (SPG) forecasts. To address the variability in solar energy and CS status, this study proposes a novel
[...] Read more.
This study proposes a deep-reinforcement-learning (DRL)-based vehicle-to-grid (V2G) operation strategy that focuses on the dynamic integration of charging station (CS) status to refine solar power generation (SPG) forecasts. To address the variability in solar energy and CS status, this study proposes a novel approach by formulating the V2G operation as a Markov decision process and leveraging DRL to adaptively manage SPG forecast errors. Utilizing real-world data from the Korea Southern Power Corporation, the effectiveness of this strategy in enhancing SPG forecasts is proven using the PyTorch framework. The results demonstrate a significant reduction in the mean squared error by 40% to 56% compared to scenarios without V2G. Our investigation into the effects of blocking probability thresholds and discount factors revealed insights into the optimal V2G system performance, suggesting a balance between immediate operational needs and long-term strategic objectives. The findings highlight the possibility of using DRL-based strategies to achieve more reliable and efficient renewable energy integration in power grids, marking a significant step forward in smart grid optimization.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Vehicle to Grid—Energy Conversion and Conservation)
Open AccessArticle
Towards High-Efficiency Buildings for Sustainable Energy Transition: Standardized Prefabricated Solutions for Roof Retrofitting
by
Elisa Pennacchia, Carlo Romeo and Claudia Zylka
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3850; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093850 - 03 May 2024
Abstract
Enhancing energy efficiency in buildings plays a pivotal role in realizing the ambitious objective of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, as outlined in the European Green Deal. Roofs represent the technical element most affected by energy phenomena related to heat transfer: in winter,
[...] Read more.
Enhancing energy efficiency in buildings plays a pivotal role in realizing the ambitious objective of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, as outlined in the European Green Deal. Roofs represent the technical element most affected by energy phenomena related to heat transfer: in winter, roofing can lose up to 35% of heat, and the summer heat flux can even be higher. This paper provides a catalogue of optimized and sustainable solutions, with a specific focus on standardization and prefabrication principles, for enhancing the energy efficiency of the most prevalent types of roofs that characterize the national residential building heritage. The methodological approach that guided the research presented in this article was based on the identification and study of the most common roofings in the diverse national residential building heritage, followed by their classification according to their construction era. In the context of essential energy retrofitting of deteriorated residential building stock, 21 optimized standardized solutions have been identified. The outcome of performance evaluations of the proposed solutions allowed the implementation of a matrix that can be a valuable support for designers in selecting the most efficient precalculated and prefabricated solutions for the national residential building heritage based on energy performance and sustainability criteria.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Construction through Utilization of Optimization Tools and Experimental Methods)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Assessment of Residents’ Perception of Possible Benefits and Challenges of Home Vertical Gardens in Kigali, Rwanda
by
Rahman Tafahomi, David Nkurunziza, Gatoni Gwladys Benineza, Reihaneh Nadi and Regis Dusingizumuremyi
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3849; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093849 - 03 May 2024
Abstract
This paper aimed to provide a new insight into the application of home vertical gardens in Kigali, the capital of Rwanda, through a pre-assessment of the inhabitants’ perceptions. There are several studies that indicated the awareness of the way residents think about the
[...] Read more.
This paper aimed to provide a new insight into the application of home vertical gardens in Kigali, the capital of Rwanda, through a pre-assessment of the inhabitants’ perceptions. There are several studies that indicated the awareness of the way residents think about the potential benefits and challenges of home gardens could make a considerable difference in designing and implementing these gardens. The Likert-scaled questionnaire (n = 558) was employed to evaluate how residents perceive vertical gardens, and what issues concern them most. The findings revealed that dwellers are almost familiar with the vertical garden concept and its possible effects on urban environments. The respondents mostly regarded vertical gardens as nice spots to socialize, relax, and interact with nature, and an opportunity for beautification, and recreation by growing ornamental and edible plants. However, they were rather apprehensive about some issues, more importantly, the extra expenses, the complicated operation and maintenance, and the type of structure installed on walls. In conclusion, small-scale and low-cost vertical gardens with lightweight structures and easy-to-use technologies are more likely to encourage householders to embrace home gardens. It is recommended that the vertical garden projects should be integrated into the urban green network strategy, leading to facilitating the processes of decision-making and financing.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sustainable Urban and Rural Development)
►▼
Show Figures
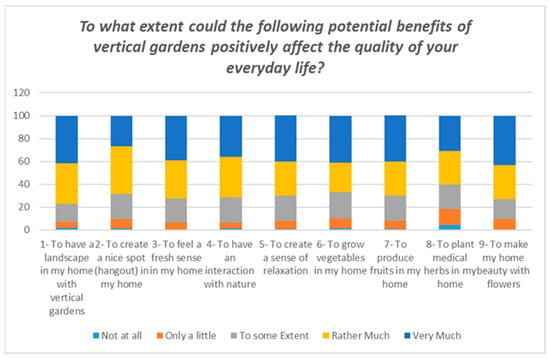
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Effect of Varying Olive Mill Wastewater Concentrations on Soil Free-Living Nematode Communities and Lettuce Growth
by
Panagiotis Kekelis, Cleopatra Pantazi, Snezhana Mourouzidou, Aphrodite Theofilidou, Maria D. Dimou, Vassilis Aschonitis and Nikolaos Monokrousos
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3848; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093848 - 03 May 2024
Abstract
We assessed the impact of increasing olive mill waste (OMW) concentrations (10%, 35%, 70%, and 100% v/v) on soil free-living nematode communities and Lactuca sativa (lettuce) growth, 10 and 45 days after application (DAA). L. sativa plants showed a survival
[...] Read more.
We assessed the impact of increasing olive mill waste (OMW) concentrations (10%, 35%, 70%, and 100% v/v) on soil free-living nematode communities and Lactuca sativa (lettuce) growth, 10 and 45 days after application (DAA). L. sativa plants showed a survival threshold at OMW10%, with higher concentrations proving fatal. Contrary to expectations, nematode abundance increased with OMW concentration. OMW10% induced a rapid surge in nematode abundance, stabilizing at 45 DAA, resembling control values. OMW35%, OMW70%, and OMW100% plots exhibited persistent, gradual increases, surpassing control values at 45 DAA. All treatments favored fungal feeders, resulting in the overdominance of the genus Aphelenchus both at 10 and 45 DAA. Even though OMW did not exert a toxic effect on nematode populations, this shift in the community structure towards the dominance of a single genus could suggest an imbalance in the soil community, which could have negative implications for soil health and ecosystem functioning. Overall, our study provides insights into the complex interactions between OMW, soil nematode communities, and plant growth, emphasizing the importance of understanding soil ecology for sustainable agricultural management.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Developing a Conceptual Framework for Characterizing and Measuring Social Resilience in Blue-Green Infrastructure (BGI)
by
Angie Campbell, Victoria Chanse and Mirjam Schindler
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3847; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093847 - 03 May 2024
Abstract
Many cities are increasingly adopting blue-green infrastructure (BGI) to bolster their resilience against environmental challenges. Beyond its well-acknowledged environmental benefits, the role of BGI in enhancing social resilience is becoming an equally important area of focus. However, the integration of BGI in fostering
[...] Read more.
Many cities are increasingly adopting blue-green infrastructure (BGI) to bolster their resilience against environmental challenges. Beyond its well-acknowledged environmental benefits, the role of BGI in enhancing social resilience is becoming an equally important area of focus. However, the integration of BGI in fostering social resilience presents complexities, stemming from the evolving and occasionally ambiguous definition of social resilience. Considering the broad application of BGI across various disciplines makes the evaluation of social resilience within a BGI framework complex. Consequently, a structured approach to develop a clear framework tailored to understanding and measuring social resilience in a BGI setting is needed. This study consolidates various existing frameworks of social resilience, especially utilizing the detailed 5S framework proposed by Saja et al. It integrates findings from an extensive review of literature on social resilience to develop a novel conceptual framework—the BGI Social Resilience Framework. This new framework specifically aims to capture the distinct social aspects and advantages associated with BGI. The BGI Social Resilience Framework is organized into a three-tier model, focusing on four critical aspects of social resilience—social values, social capital, social structure, and social equity—and explores how these aspects are interconnected. Characteristics and indicators are customized to accommodate the context of BGI in a way that integrates the physical and human dimensions within a comprehensive approach to measurement that uses a combination of qualitative and quantitative methods. Specifically, this research formulates a theoretical framework for BGI with the aim of investigating BGI strategies and viewpoints that bolster social resilience. The BGI Social Resilience Framework takes into account the varied demographics and the physical characteristics of urban areas to explore ways to create BGI spaces that are more inclusive and that contribute to the enhancement of social resilience.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Urban Green Development and Resilient Cities)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Construction and Characteristics Analysis of the Xi’an Public Transport Network Considering Single-Mode and Multi-Mode Transferring
by
Ruifen Sun, Fengjie Xie, Sirui Huang and Yang Shao
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3846; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093846 - 03 May 2024
Abstract
The connectivity of the urban public transport network and the convenience of transfers between modes of transit are important factors that affect whether passengers choose public transport. Identifying the key nodes that affect network connectivity, direct access, transfers, and clarifying the main factors
[...] Read more.
The connectivity of the urban public transport network and the convenience of transfers between modes of transit are important factors that affect whether passengers choose public transport. Identifying the key nodes that affect network connectivity, direct access, transfers, and clarifying the main factors that restrict the network efficiency play important roles in improving the efficiency of the public transport network and establishing a “green city”. On this premise, this paper constructs two single-layer networks and a composite network that can reflect the transfer relationship between ‘bus–bus’, ‘metro–metro’, and ‘metro–bus’ based on the method of Space-P. The composite network realizes the integration study of homogeneous and heterogeneous stops, lines, and transfer relationships in the public transport network. At the same time, five kinds of centrality indexes are applied to the transport transfer network, and the significance of these indexes in the network is explained. Through the comprehensive analysis of these five types of indexes, the key nodes affecting the network connectivity, direct access and transfer efficiency, can be identified more accurately. Taking the public transport network of Xi’an as an example, the structural characteristics of the networks, including scale-free and small-world characteristics, were empirically analyzed. The main stops that play important roles in networks were identified based on the integrated centrality, degrees, and weight degrees. The research results showed the following: (1) Xi’an’s metro network, bus network, and metro–bus composite network all have scale-free and small-world characteristics. (2) The influence of the key stops of the metro network is concentrated, while the influence of the key stops of the bus network is scattered. (3) The public transport network in the first ring road area of Xi’an has the highest degree of direct access, and the core areas of the south, west, and north of Xi’an also have high direct access. However, the direct access in the area east of Xi’an is slightly lower. (4) Xi’an’s bus transport network covers a large area, showing the characteristics of a dual-core “central + southern” network. (5) The metro–bus composite network demonstrates a closer connection between stops and a more balanced network. (6) Finally, the degree of direct access to stops in the bus transport network and metro transport network shows the characteristics of “the single core is dominant, and the circle diffusion weakens step by step”.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Large-Scale Systems: Sustainable Economy and Transport in the Modern World)
Open AccessArticle
Establishing the Characteristic Compressive Strength Parallel to Fiber of Four Local Philippine Bamboo Species
by
Christine A. T. Panti, Christy S. Cañete, Althea R. Navarra, Kerby D. Rubinas, Lessandro E. O. Garciano and Luis F. López
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3845; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093845 - 03 May 2024
Abstract
Bamboo is considered a sustainable construction material due to its ability to grow quickly and its mechanical properties that are comparable to timber. Contributing to the current effort to establish structural bamboo standards in the National Structural Code of the Philippines (NSCP), this
[...] Read more.
Bamboo is considered a sustainable construction material due to its ability to grow quickly and its mechanical properties that are comparable to timber. Contributing to the current effort to establish structural bamboo standards in the National Structural Code of the Philippines (NSCP), this study establishes the characteristic compressive strength of four bamboo species: Bambusa vulgaris (36 samples), Dendrocalamus asper (36 samples), Bambusa blumeana (94 samples), and Guadua angustifolia Kunth (30 samples). The samples were subjected to compressive loading following ISO 22157-1 (2017). The characteristic compressive strength values obtained, according to ISO 12122-1 (2014), were 40.35 MPa for B. vulgaris, 40.21 MPa for D. asper, 46.63 MPa for B. blumeana, and 36.99 MPa for G. angustifolia Kunth. Simple linear analysis, one-way ANOVA, and Welch’s t-test were used to analyze the correlation models and establish a comparative analysis of the effects of nodes and geometric and physical properties on the compressive strength of bamboo samples. In comparisons of the characteristic compressive strengths obtained from this study to the strengths of unseasoned structural timber of Philippine woods, all bamboo species showed higher strength values than did other woods, and bamboos thus have great potential as an alternative construction material to timber.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fast-Growing, Bio-Based Construction Materials as Key Drivers to a Net-Zero-Carbon Built Environment)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Introducing the Occupational Health and Safety Potential Midpoint Impact Indicator in Social Life Cycle Assessment
by
Georgios Archimidis Tsalidis
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3844; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093844 - 03 May 2024
Abstract
Occupational health and safety (OSH) is crucial for sustainable development, recognized by corporations, the European Union, and Sustainable Development Goals. This study introduces a characterization model for OSH in the social life cycle assessment (S-LCA) to support the quantification of OHS along product
[...] Read more.
Occupational health and safety (OSH) is crucial for sustainable development, recognized by corporations, the European Union, and Sustainable Development Goals. This study introduces a characterization model for OSH in the social life cycle assessment (S-LCA) to support the quantification of OHS along product supply chains and sustainable decision making. The characterization model aims to provide a practical approach for assessing OHS at the product level with actual working hours or recommends a secondary approach with monetary data, when working hours are unavailable, to calculate the Occupational Health and Safety Potential (OHSP). The developed model was tested in a theoretical case study on shirt production in Europe and globally. The case study shows that the European shirt value chain resulted in higher OHSP values than the global shirt values chain. In addition, the model shows which life cycle stages and organizations highly contributed to the OHSP results. In both approaches, the shirt production stage contributed highly. Differences in results emerged based on the calculation approach, underscoring the model’s versatility, because increasing the complexity of calculating the CFs with monetary values will affect the results based on sectorial monetary output. Additionally, the study mentions benefits to the operationalization of social impact assessment and limitations when the developed characterized model is employed. Last, this study aids in offering a tool for organizations to meet the demands of the new Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive by quantifying and publicizing OHS data.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Development Goals towards Sustainability)
Open AccessArticle
Sustainability Science Communication: Case Study of a True Cost Campaign in Germany
by
Lennart Stein, Amelie Michalke, Tobias Gaugler and Susanne Stoll-Kleemann
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3842; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093842 - 03 May 2024
Abstract
The Anthropocene, marked by human-induced climate change, necessitates urgent action to address climate goals and respect planetary boundaries. While sustainability research provides knowledge, the first challenge lies in communicating the findings in an adequate manner to the public and several stakeholders, such as
[...] Read more.
The Anthropocene, marked by human-induced climate change, necessitates urgent action to address climate goals and respect planetary boundaries. While sustainability research provides knowledge, the first challenge lies in communicating the findings in an adequate manner to the public and several stakeholders, such as economic and political actors. Therefore, this study explores the significance of science communication in sustainability science, focusing on a case study—the True Cost Accounting (TCA) campaign by the University of Greifswald, Technical Institute of Nuremberg, and German retailer PENNY. TCA herein serves as a transparency tool, economic incentive, and discussion basis for sustainable consumption. This study investigates consumer perceptions of ecological prices of foods through a face-to-face survey during the 2023 PENNY campaign, comparing results to an informational campaign carried out in 2021. Findings indicate a high awareness of the true cost campaign in 2023, with 50.8% of participants hearing about it. Consumers’ willingness to pay true costs and potential behavior changes were explored. In comparison to results from the informational campaign of 2021, customers showed a decrease in this WTP when the true prices would actually impact their spending, indicating an attitude–behavior gap. In addition, a willingness to reduce the consumption of animal foods—if TCA was implemented—of 60.5% was determined, which suggests that TCA has the potential for sustainable behavior change. This study highlights factors that influence consumer attitudes and preferences regarding the inclusion of TCAs, such as environmental, social, and animal welfare costs. Customers’ understanding of increased prices—like, in this case, the compensation for environmental and social costs—is an argument in favor of true prices. The results emphasize the need for differentiated scientific communication strategies to bridge knowledge and action gaps in sustainability science.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Transformation to Sustainability and Behavior Change)
►▼
Show Figures
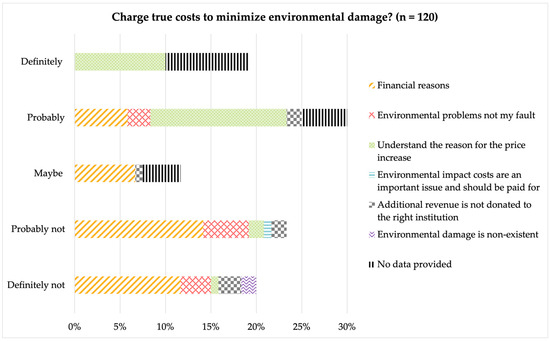
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
University Students’ Perception of the Dehesa and the Associated Traditional Trades
by
Rebeca Guillén-Peñafiel, Ana María Hernández-Carretero and José Manuel Sánchez-Martín
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3843; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093843 - 02 May 2024
Abstract
The dehesas are one of the most emblematic landscapes of the Extremadura region (Spain). Along with its natural values, it preserves a wide repertoire of knowledge and trades rooted in the history and tradition of rural communities. However, the knowledge and practices that
[...] Read more.
The dehesas are one of the most emblematic landscapes of the Extremadura region (Spain). Along with its natural values, it preserves a wide repertoire of knowledge and trades rooted in the history and tradition of rural communities. However, the knowledge and practices that have characterized life in this environment are currently under serious threat. Faced with this problem, this study was based on the premise that, for individuals to commit themselves to the care and transmission of heritage, it is first necessary for them to know, understand and value it. For this reason, the main objective was to determine the knowledge and appreciation of university students with respect to the dehesa and the ancestral practice of grazing. It also aimed to analyze which are the most valued methodologies, activities, and future strategies for understanding and preserving these cultural landscapes and their ancestral practices. To this end, 400 university students were surveyed, and various quantitative and qualitative analyses were carried out. Quantitative techniques include analyses based on weighted averages, contingency tables and the chi-square test, while qualitative techniques are based on word frequency analysis and inductive content analysis. Despite coming from an environment dominated by this landscape and being one of the few regions that still preserve the ancestral practice of pastoralism, the results corroborated the students’ lack of understanding of the dehesa and the variety of uses it offers. In addition, it was evident that they have hardly frequented this landscape and have not participated in on-site educational experiences. It also revealed the importance of experiential and sensory activities in the understanding and appreciation of the rural environment and its traditions. The results can be useful for improving the design of educational tourism products based on intangible heritage. It can also be useful for adapting teaching strategies and activities to the level of knowledge and experiences of students, helping to ensure the success of the educational experience.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Development in Urban and Rural Tourism)
Open AccessArticle
Drivers of Spontaneous Plant Communities in Urban Parks: A Case from Nanjing, China
by
Wenjie Xu, Wenjing Dai, Yanfen Ding, Shanshan Song, Qian Liu and Wei Yang
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3841; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093841 - 02 May 2024
Abstract
Urban plant diversity is one of the key elements for sustainable urban development. Urban plant landscapes not only create a variety of experiences for residents but also have a positive effect on their physiology and psychology. In order to better introduce nature into
[...] Read more.
Urban plant diversity is one of the key elements for sustainable urban development. Urban plant landscapes not only create a variety of experiences for residents but also have a positive effect on their physiology and psychology. In order to better introduce nature into urban green spaces, this study conducted a field survey in Nanjing, China, to analyze the current situation of spontaneous plants in Nanjing’s urban green spaces and propose a plant planning strategy that takes into account both ecology and residents’ well-being. This study surveyed the herbaceous plant resources in 96 sample plots in nine typical urban parks in Nanjing, and recorded 284 plant species in 192 genera and 78 families. The research results show that the differences in plant diversity, richness, and evenness among urban parks in Nanjing are significant; combined with cluster analysis and ranking results, the total area of urban parks, green space construction time, lighting conditions, and management frequency have an impact on plant communities. Further analysis of the species composition of plant communities showed that moderate management frequency in urban parks can increase plant diversity. With the advantages of both high ecological benefits and low management costs, a model of “artificial plants + native spontaneous plants” was finally proposed for the planting of herbaceous plants in sustainable urban green spaces.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence Replacing Humans in Making Human Resource Management Decisions on Fairness: A Case of Resume Screening
by
Fei Cai, Jiashu Zhang and Lei Zhang
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3840; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093840 - 02 May 2024
Abstract
A growing number of organizations have used artificial intelligence (AI) to make decisions to replace human resource (HR) workers; yet, the fairness perceptions of the people affected by the decision are still unclear. Given that an organization’s sustainability is significantly influenced by individuals’
[...] Read more.
A growing number of organizations have used artificial intelligence (AI) to make decisions to replace human resource (HR) workers; yet, the fairness perceptions of the people affected by the decision are still unclear. Given that an organization’s sustainability is significantly influenced by individuals’ perceptions of fairness, this study takes a resume-screening scenario as an example to explore the impact of AI replacing humans on applicants’ perceptions of fairness. This study adopts the method of the online scenario experiment and uses SPSS to analyze the experimental data: 189 and 214 people, respectively, participated in two online scenarios, with two independent variables of decision makers (AI and humans), two dependent variables of procedural and distributive fairness, and two moderating variables of outcome favorability and the expertise of AI. The results show that the applicants tend to view AI screening resumes as less fair than humans. Furthermore, moderating effects exist between the outcome favorability and the expertise of AI. This study reveals the impact of AI substituting for humans in decision-making on fairness. The proposed model can help organizations use AI to screen resumes more effectively. And future research can explore the collaboration between humans and AI to make human resource management decisions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Psychology of Sustainability and Sustainable Development)
Open AccessArticle
Walking in Tandem with the City: Exploring the Influence of Public Art on Encouraging Urban Pedestrianism within the 15-Minute Community Living Circle in Shanghai
by
Ran Tan, Yu Wu and Suhui Zhang
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3839; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093839 - 02 May 2024
Abstract
As a new urban model, the 15-min city has gradually become a touchstone with which to measure the future sustainability of cities. With a time-limited planning of urban living circles, urban residents can be allowed to access basic daily needs, such as food,
[...] Read more.
As a new urban model, the 15-min city has gradually become a touchstone with which to measure the future sustainability of cities. With a time-limited planning of urban living circles, urban residents can be allowed to access basic daily needs, such as food, health and education, while walking or cycling, thus reducing motor traffic and carbon dioxide emissions and contributing to the improvement of people’s well-being and the environmental climate. Within the temporal and spatial confines of the 15-min living sphere, governmental authorities and community bodies commonly integrate public art installations into public spaces to enrich spatial dynamics, cultivate cultural identities, enhance environmental aesthetics, elevate service quality, and foster communal interactions. This study aims to probe into the impact of public art on encouraging urban pedestrianism within the specific context of the 15-min community living sphere along the Suzhou River in northern Shanghai. Drawing upon Stimulus–Organism–Response (SOR) theory, a theoretical framework is constructed to unravel the mechanisms by which public art influences residents’ propensity for walking, encompassing the attributes of public art, perceived value, and walking intention. Employing Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA), the model is analyzed to scrutinize the proposed hypotheses. Through this research, we establish and substantiate a novel and pertinent theoretical perspective for advancing human-centric and sustainable urban regeneration. The findings underscore that integrating public art within the framework of constructing 15-min community living spheres contributes to catalyzing proactive urban pedestrianism by enhancing its value proposition.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Assessment for the Sustainable Development of Components of the Tourism and Recreational Potential of Rural Areas of the Aktobe Oblast of the Republic of Kazakhstan
by
Kuat Saparov, Miroslava Omirzakova, Aigul Yeginbayeva, Aigul Sergeyeva, Kairat Saginov and Gulnash Askarova
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3838; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093838 - 02 May 2024
Abstract
The assessment of sustainable tourism development in the rural areas of the Aktobe oblast of Kazakhstan involved thoroughly analyzing multiple dimensions. Environmental, socio-economic, and cultural sustainability aspects were considered to comprehensively understand the region’s tourism potential. The study began by evaluating the available
[...] Read more.
The assessment of sustainable tourism development in the rural areas of the Aktobe oblast of Kazakhstan involved thoroughly analyzing multiple dimensions. Environmental, socio-economic, and cultural sustainability aspects were considered to comprehensively understand the region’s tourism potential. The study began by evaluating the available tourism resources in rural Aktobe. This included assessing natural attractions such as landscapes, wildlife, and geological features, as well as cultural heritage sites and infrastructure like accommodation facilities and transportation networks. A crucial aspect of the study was to analyze the environmental impact of tourism activities in rural areas. This involved evaluating the effects on ecosystems and natural resources. The measures for conserving these resources were also identified. Another focus was on the socio-cultural aspects of tourism development. The study aimed to preserve local traditions, cultural heritage, and community identity amidst tourism growth. Strategies for achieving socio-cultural sustainability were devised. Ranking methods were employed to identify key factors influencing rural tourism development. These methods helped prioritize areas for improvement and resource allocation. A balanced approach was adopted to assess the interaction between different dimensions of sustainability. This ensured that environmental, economic, and socio-cultural aspects were considered equally to achieve overall sustainable tourism development. ArcGIS 10 was used for data analysis and visualization. Maps and charts were created to represent spatial and statistical information, aiding in identifying trends and patterns. The study findings were crucial for identifying priority areas for infrastructure development and formulating strategies and programs for rural tourism promotion. The study aimed to ensure that tourism development aligns with the principles of sustainable development, benefiting both the local communities and the environment. The study provided valuable insights into the current status of rural tourism in Aktobe oblast and offered recommendations for sustainable development, contributing to the region’s long-term prosperity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sustainability in Geographic Science)
Open AccessArticle
What Is Necessary for Digital Transformation of Large Manufacturing Companies? A Necessary Condition Analysis
by
Ziye Zhang, Meiying Wu and Jiajie Yin
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3837; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093837 - 02 May 2024
Abstract
Digital transformation is of significant importance to the sustainable development of manufacturing companies and the construction of the digital economy. However, this major change is often hindered by numerous complex antecedents. What are the key factors in the digital transformation of manufacturing companies,
[...] Read more.
Digital transformation is of significant importance to the sustainable development of manufacturing companies and the construction of the digital economy. However, this major change is often hindered by numerous complex antecedents. What are the key factors in the digital transformation of manufacturing companies, and what is their relative importance? Accordingly, this paper identifies the key factors for digital transformation in large manufacturing companies from the “Ability–Motivation–Opportunity” (AMO) perspective. This study uses a necessary condition analysis (NCA) to conduct a necessity causality study on data collected from 67 listed Chinese manufacturing companies between 2016 and 2020. The results show that the digital transformation of large manufacturing companies is influenced by four necessary conditions: managerial myopia, industry concentration (very large effect), dynamic capabilities, and industrial digitalization (large effect). Managerial myopia and industry concentration have a negative necessary impact on digital transformation. The types of conditions and the level of bottlenecks required at different stages of digital transformation vary significantly. This study reveals the necessary causal relationships between organizational abilities, motivation, external opportunities, and digital transformation, providing empirical evidence to promote the digital transformation practices of manufacturing companies.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Phosphate Removal Efficiency and Life Cycle Assessment of Different Anode Materials in Electrocoagulation Treatment of Wastewater
by
Guangpu Li, Bin Zheng, Wenqing Zhang, Qiaona Liu, Mingzheng Li and Haibing Zhang
Sustainability 2024, 16(9), 3836; https://doi.org/10.3390/su16093836 - 02 May 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The excessive discharge of phosphorus-containing wastewater contributes to eutrophication, posing a serious threat to aquatic ecosystems. Therefore, methods such as electrocoagulation should be utilized to remove phosphorus from wastewater prior to discharging it into a water body. In this study, we aimed to
[...] Read more.
The excessive discharge of phosphorus-containing wastewater contributes to eutrophication, posing a serious threat to aquatic ecosystems. Therefore, methods such as electrocoagulation should be utilized to remove phosphorus from wastewater prior to discharging it into a water body. In this study, we aimed to determine the effectiveness of electrocoagulation in treating simulated phosphorus-containing wastewater under different parameters, including anode material (aluminum, iron, and magnesium), electrode distance (ED) (1, 2.5, and 4.5 cm), pH (3, 6, and 9), and current density (CD) (3, 6, and 9 mA/cm2). Additionally, three models of phosphate removal, the pseudo-first-order (PFO), pseudo-second-order (PSO), and Behnajady–Modirshahla–Ghanbery (BMG) models, were used to simulate the relationship between phosphate concentration and time in the electrocoagulation process using the three metals for phosphate removal. The experimental results showed that the aluminum system had the highest removal efficiency (90%) when energized for 20 min under a CD of 3 mA/cm2, followed by those of the iron (80%) and magnesium (35%) systems. Furthermore, a life cycle assessment (LCA) showed that the aluminum electrode system had a smaller environmental impact than the iron and magnesium electrode systems. Therefore, the aluminum electrode system is suitable for phosphorus removal from wastewater.
Full article
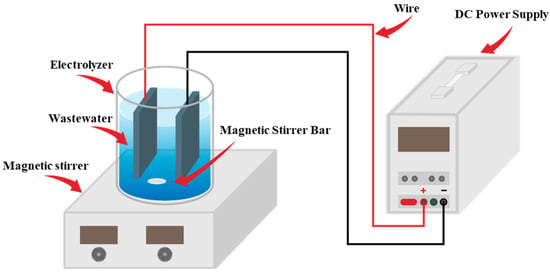
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Sustainability Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Buildings, Infrastructures, Materials, Smart Cities, Sustainability
Smart Material and Smart Construction Technologies for Urban Development
Topic Editors: Sathees Nava, Kate NguyenDeadline: 14 May 2024
Topic in
Energies, Materials, Processes, Solar, Sustainability
Solar Thermal Energy and Photovoltaic Systems, 2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Pedro Dinis Gaspar, Pedro Dinho da Silva, Luís C. PiresDeadline: 31 May 2024
Topic in
Education Sciences, Entropy, JAL, Societies, Sustainability
Sustainability in Aging and Depopulation Societies
Topic Editors: Shiro Horiuchi, Gregor Wolbring, Takeshi MatsudaDeadline: 15 June 2024
Topic in
Laws, Societies, Sustainability
Cannabis Legalization in the United States: Public Policy, Social Welfare, and Public Health Implications
Topic Editors: Robert Mark Silverman, Kelly PattersonDeadline: 30 June 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Sustainability
New Technologies and Pathways to Sustainable Conservation of Cultural Heritage
Guest Editors: Laura Medeghini, Michela Botticelli, Alessandro CiccolaDeadline: 10 May 2024
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Market Potential for Carsharing Services
Guest Editor: Lucia RotarisDeadline: 25 May 2024
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Sustainability and Indoor Environmental Quality
Guest Editors: Mateja Dovjak, Janja Vaupotic, Fumito Maruyama, So FujiyoshiDeadline: 31 May 2024
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Human Behavior, Urban Health and Sustainability
Guest Editors: Hao Wu, Lingbo Liu, Yang YuDeadline: 15 June 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Tourism Research and Regional Sciences
Collection Editors: Lóránt Dénes Dávid, Laszlo VASA, Setiawan Priatmoko
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Mobile Technology, Gamification and Artificial Intelligence to Improve Sustainability in Education
Collection Editors: Eloy López Meneses, Esteban Vázquez-Cano, María Elena Parra-González
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Urban Planning and Built Environment
Collection Editors: Yupeng Wang, Liyang Fan, Shi-Jie Cao, Xilian Luo
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Sustainable Soil Management in a Changing Climate
Collection Editors: Georgios Koubouris, José Alfonso Gómez, Luuk Fleskens, Giuseppe Montanaro








