Mobile Technology, Gamification and Artificial Intelligence to Improve Sustainability in Education
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Sustainable Education and Approaches".
Viewed by 71761Editors
Interests: ICT in education; didactics; IA, RA, RV, online and ubiquitous learning
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: ICT in education; school organization and supervision; MOOCs; online and ubiquitous learning
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: active methodologies; gamification; methodology; teacher training; personal learning environment; active learning
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
At the World Education Forum 2015, the global community agreed to launch ‘Education 2030: the Incheon Declaration and Framework for Action’, which seeks to ensure access to basic education for all (UNESCO, 2015). That same year, the international community adopted the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), a set of 17 global goals and 169 targets, whose unifying thread is the commitment to ending poverty (United Nations, 2015).
Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG4), which expands on the “Education for All” goals and the education-related Millennium Development Goals, focuses on the education needs of a sustainable society and exhorts the global community to ‘ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all’ (United Nations, 2015).
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) is viewed as a critical element that can improve access to education and address issues related to inclusion, equity, and quality. ICT can also play a transformative role by raising public awareness and reducing the cost of extending new services to a wide audience. For the SDG4 targets to be achieved by the year 2030, it is necessary to leverage existing accessible technologies. Concomitantly, it has been predicted that traditional approaches to using technologies will not be adequate for achieving the universal goals by 2030. Therefore, new, holistic approaches to ICT integration are required (UNESCO, 2015, 2016).
These considerations guide the proposal of this monograph, which aims to collect research studies as well as theoretical contributions, which exemplify and inform good educational practices based on ICT for a sustainable future.
Scientific contributions referring to the following four priority areas for the use of ICT towards achieving SDG4 and Education 2030’s goals will be accepted:
- Mobile technology for transforming and expanding Secondary Education, Technical and Vocational Education, and Training and Higher Education.
- ICT-integrated transformative pedagogies and the use of smart mobile devices to promote collaborative learning and to extend learning spaces beyond traditional classroom contexts.
- ICT for enhancing the competencies of girls, women, and vulnerable groups to ensure that no one is left behind.
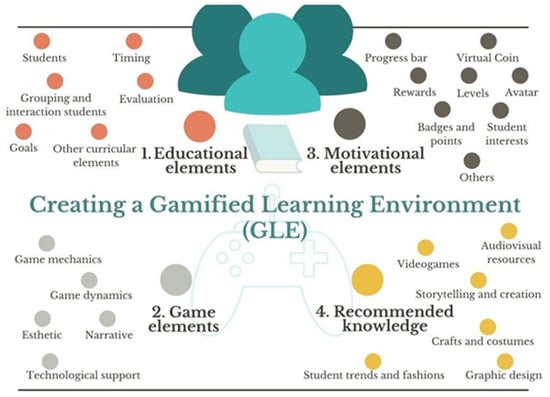
- Digital Transformation and Sustainability: Gamification, Artificial Intelligence, Learning analytics, MOOCs, virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), Social Computing, Big data, OER and open solutions, open social networks, and adaptive learning technologies in online learning.
Prof. Esteban Vázquez-Cano
Dr. Eloy López Meneses
Dr. María Elena Parra-González
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- mobile technology
- digital Transformation
- Sustainability
- transformative pedagogies
- emerging technologies
- ICT for social inclusion