Journal Description
Metrology
Metrology
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on the science and technology of measurement and metrology, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Engineering (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 32.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 6.4 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Impact Factor:
1.5 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
1.6 (2024)
Latest Articles
AC-Diagnostics of Transport Phenomena in Dilute Suspensions
Metrology 2026, 6(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology6010005 - 12 Jan 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Impedance diagnostics is commonly employed in the study of transport phenomena in conducting media of different sizes. A common reason for choosing the more complex method of exciting the conductive medium at finite frequencies (
Impedance diagnostics is commonly employed in the study of transport phenomena in conducting media of different sizes. A common reason for choosing the more complex method of exciting the conductive medium at finite frequencies (
Open AccessArticle
A Flexible Wheel Alignment Measurement Method via APCS-SwinUnet and Point Cloud Registration
by
Bo Shi, Hongli Liu and Emanuele Zappa
Metrology 2026, 6(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology6010004 - 12 Jan 2026
Abstract
To achieve low-cost and flexible wheel angles measurement, we propose a novel strategy that integrates wheel segmentation network with 3D vision. In this framework, a semantic segmentation network is first employed to extract the wheel rim, followed by angle estimation through ICP-based point
[...] Read more.
To achieve low-cost and flexible wheel angles measurement, we propose a novel strategy that integrates wheel segmentation network with 3D vision. In this framework, a semantic segmentation network is first employed to extract the wheel rim, followed by angle estimation through ICP-based point cloud registration. Since wheel rim extraction is closely tied to angle computation accuracy, we introduce APCS-SwinUnet, a segmentation network built on the SwinUnet architecture and enhanced with ASPP, CBAM, and a hybrid loss function. Compared with traditional image processing methods in wheel alignment, APCS-SwinUnet delivers more accurate and refined segmentation, especially at wheel boundaries. Moreover, it demonstrates strong adaptability across diverse tire types and lighting conditions. Based on the segmented mask, the wheel rim point cloud is extracted, and an iterative closest point algorithm is then employed to register the target point cloud with a reference one. Taking the zero-angle condition as the reference, the rotation and translation matrices are obtained through point cloud registration. These matrices are subsequently converted into toe and camber angles via matrix-to-angle transformation. Experimental results verify that the proposed solution enables accurate angle measurement in a cost-effective, simple, and flexible manner. Furthermore, repeated experiments further validate its robustness and stability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Applied Industrial Metrology: Methods, Uncertainties, and Challenges)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Recent Advances in Digital Fringe Projection Profilometry (2022–2025): Techniques, Applications, and Metrological Challenges—A Review
by
Mishraim Sanchez-Torres, Ismael Hernández-Capuchin, Cristina Ramírez-Fernández, Eddie Clemente, José Luis Javier Sánchez-González and Alan López-Martínez
Metrology 2026, 6(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology6010003 - 12 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Digital fringe projection profilometry (DFPP) is a widely used technique for full-field, non-contact 3D surface measurement, offering precision from the sub-micrometer-to-millimeter scale depending on system geometry and fringe design. This review provides a consolidated synthesis of advances reported between 2022 and 2025, covering
[...] Read more.
Digital fringe projection profilometry (DFPP) is a widely used technique for full-field, non-contact 3D surface measurement, offering precision from the sub-micrometer-to-millimeter scale depending on system geometry and fringe design. This review provides a consolidated synthesis of advances reported between 2022 and 2025, covering projection and imaging architectures, phase formation and unwrapping strategies, calibration approaches, high-speed implementations, and learning-based reconstruction methods. A central contribution of this review is the integration of these developments within a metrological perspective, explicitly relating phase–height transformation, fringe parameters, system geometry, and calibration to dominant uncertainty sources and error propagation. Recent progress highlights trade-offs between sensitivity, robustness, computational complexity, and applicability to non-ideal surfaces, while learning-based and hybrid optical–computational approaches demonstrate substantial improvements in reconstruction reliability under challenging conditions. Remaining challenges include measurements on reflective or transparent surfaces, dynamic scenes, environmental instability, and real-time operation. The review outlines emerging research directions such as physics-informed learning, digital twins, programmable optics, and autonomous calibration, providing guidance for the development of next-generation DFPP systems for precision metrology.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Constraint-Aware Design of Spherical Camera Rigs for Optical Metrology
by
Haider Ali Hasan, Ali Noori Abdulrasool, Hadeel Raad Mahdi and Bashar Alsadik
Metrology 2026, 6(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology6010002 - 7 Jan 2026
Abstract
This paper introduces a constraint-aware optimization framework for designing spherical multi-camera rigs that achieve complete panorama coverage while adhering to physical and field-of-view limitations. The approach assesses coverage using solid-angle geometry and calculates the sampling density in pixels per steradian, providing a measurable,
[...] Read more.
This paper introduces a constraint-aware optimization framework for designing spherical multi-camera rigs that achieve complete panorama coverage while adhering to physical and field-of-view limitations. The approach assesses coverage using solid-angle geometry and calculates the sampling density in pixels per steradian, providing a measurable, traceable basis for panoramic optical measurement. By viewing panoramic imaging as a directional measurement challenge, the framework aligns with principles of optical metrology and guarantees uniform, non-contact optical sensing around the sphere. The optimization process includes capsule-based collision constraints, soft coverage losses, and field-of-view intersection modeling to produce physically feasible rig configurations. Experiments show that the optimized rigs provide improved coverage uniformity and less redundancy, with validation through Blender-generated synthetic panoramas confirming the practical performance of the designed optical systems. The proposed approach allows for systematic, measurement-driven design of spherical camera rigs for use in immersive imaging, robotic perception, and structural inspection.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Optical 3D Metrology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessTechnical Note
Three Methods for Combining Probability Distributions and an Alternative to Random-Effects Meta-Analysis
by
Hening Huang
Metrology 2026, 6(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology6010001 - 4 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Many fields or disciplines (e.g., uncertainty analysis in measurement science) require a combination of probability distributions. This technical note examines three methods for combining probability distributions: weighted linear pooling, geometric pooling, and the law of combination of distributions (LCD). Although these methods have
[...] Read more.
Many fields or disciplines (e.g., uncertainty analysis in measurement science) require a combination of probability distributions. This technical note examines three methods for combining probability distributions: weighted linear pooling, geometric pooling, and the law of combination of distributions (LCD). Although these methods have been discussed in the literature, a systematic comparison of them appears insufficient. In particular, there is no discussion in the literature regarding the potential information loss that these methods may cause. This technical note aims to fill this gap. It provides insights into these three methods under the normality assumption. It shows that the weighted linear pooling method preserves all the variability (including heterogeneity) information in the original distributions; neither the geometric pooling method nor the LCD method preserves all the variability information, leading to information loss. We propose an index for measuring the information loss of a method with respect to the weighted linear pooling method. This technical note also shows that the weighted linear pooling method can be used as an alternative to the traditional random-effects meta-analysis. Three examples are presented: the combination of two normal distributions, the combination of three discrete distributions, and the determination of the Newtonian constant of gravitation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Dispersed Particle Concentration on Photoacoustic Flowmetry Using Low-Frequency Transducers
by
Haruka Tsuboi, Taichi Kaizuka and Katsuaki Shirai
Metrology 2025, 5(4), 79; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5040079 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
Photoacoustic (PA) velocimetry offers a promising solution to the limitations of conventional techniques for measuring blood flow velocity. Given its moderate penetration depth and high spatial resolution, PA imaging is considered suitable for measuring low-velocity blood flow in capillaries located at moderate depths.
[...] Read more.
Photoacoustic (PA) velocimetry offers a promising solution to the limitations of conventional techniques for measuring blood flow velocity. Given its moderate penetration depth and high spatial resolution, PA imaging is considered suitable for measuring low-velocity blood flow in capillaries located at moderate depths. High-resolution measurements based on PA signals from individual blood cells can be achieved using a high-frequency transducer. However, high-frequency signals attenuate rapidly within biological tissue, restricting the measurable depth. Consequently, low-frequency transducers are required for deeper measurements. To date, PA flow velocimetry employing low-frequency transducers remains insufficiently explored. In this study, we investigated the effect of the concentration of particles that mimic blood cells within vessels under low-concentration conditions. The performance of flow velocity measurement was evaluated using an ultrasonic transducer (UST) with a center frequency of 10 MHz. The volume fraction of particles in the solution was systematically varied, and the spatially averaged flow velocity was assessed using two different distinct analysis methods. One method employed a time-shift approach based on cross-correlation analysis. Flow velocity was estimated from PA signal redpairs generated by particles dispersed in the fluid, using consecutive pulsed laser irradiations at fixed time intervals. The other method employed a pulsed Doppler method in the frequency domain, widely applied in ultrasound Doppler measurements. In this method, flow velocity redwas estimated from the Doppler-shifted frequency between the transmitted and received signals of the UST. For the initial analysis, numerical simulations were performed, followed by experiments based on displacement measurements equivalent to velocity measurements. The target was a capillary tube filled with an aqueous solution containing particles at different concentration levels. The time–domain method tended to underestimate flow velocity as particle concentration increased, whereas the pulsed Doppler method yielded estimates consistent with theoretical values, demonstrating its potential for measurements at high concentrations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advancements in Optical Measurement Devices and Technologies)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing GNSS-INS-Based Surveying with Time of Flight Cameras
by
Amna Qayyum, Joël Bachmann and David Eugen Grimm
Metrology 2025, 5(4), 78; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5040078 - 16 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Rapid advancements in surveying technology have necessitated the development of more accurate and efficient tools. Leica Geosystems AG (Heerbrugg, Switzerland), a leading provider of measurement and surveying solutions, has initiated a study to enhance the capabilities of its GNSS INS-based surveying systems. This
[...] Read more.
Rapid advancements in surveying technology have necessitated the development of more accurate and efficient tools. Leica Geosystems AG (Heerbrugg, Switzerland), a leading provider of measurement and surveying solutions, has initiated a study to enhance the capabilities of its GNSS INS-based surveying systems. This research focuses on integrating the Leica GS18 I GNSS receiver and the AP20 AutoPole with a Time of Flight (ToF) camera through sensor fusion. The primary objective is to leverage the unique strengths of each device to improve accuracy, efficiency, and usability in challenging surveying environments. Results indicate that the fused AP20 configuration achieves decimetre-level accuracy (2.7–4.4 cm on signalized points; 5.2–20.0 cm on natural features). In contrast, the GS18 I fused configuration shows significantly higher errors (17.5–26.6 cm on signalized points; 16.1–69.4 cm on natural features), suggesting suboptimal spatio-temporal fusion. These findings confirm that the fused AP20 configuration demonstrates superior accuracy in challenging GNSS conditions compared to the GS18 I setup with deviations within acceptable limits for most practical applications, while highlighting the need for further refinement of the GS18 I configuration.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Accuracy Verification of the Convergent Photogrammetry Method for Levelling Staff Calibration
by
Ondrej Benko and Marek Fraštia
Metrology 2025, 5(4), 77; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5040077 - 14 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The calibration of levelling staff is a key prerequisite for achieving high-precision levelling. Traditionally, this process is carried out using laser interferometric systems, which provide the required accuracy but are demanding in terms of operation, maintenance, and measurement conditions. This paper focuses on
[...] Read more.
The calibration of levelling staff is a key prerequisite for achieving high-precision levelling. Traditionally, this process is carried out using laser interferometric systems, which provide the required accuracy but are demanding in terms of operation, maintenance, and measurement conditions. This paper focuses on verifying the applicability of the convergent photogrammetry method for levelling staff calibration with a target accuracy of 0.010 mm. An experimental prototype of a photogrammetric calibration system (without real scale) was developed and tested using three different lenses, two processing software packages (Photomodeler and Agisoft Metashape), and two different approaches to camera calibration (self-calibration and field calibration). The repeatability of measurements was evaluated based on mutual lengths between selected checkpoints and the accuracy of determining the 3D positions of these points. The results showed that the Nikon AF-S NIKKOR 35 mm f/1.8G ED lens achieved the best repeatability and met the target accuracy requirement, while Photomodeler yielded smaller standard deviations in the determination of control point positions compared to Agisoft Metashape. The findings indicate that convergent photogrammetry, when applied under optimal conditions, has the potential to achieve the accuracy required for high-precision measurements in metrology, and may even offer an alternative to laser interferometric calibration systems in certain applications.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Curves in Archeology: Computing the Volume of a Greek Vase
by
Siddhant Shah, Minfei Liang and Eugene Pinsky
Metrology 2025, 5(4), 76; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5040076 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The concept of dynamic symmetry in art and extensive measurements on Greek vases suggest that a vase and its parts can be inscribed into similar rectangles, with all rectangles having the same ratio of lengths of their side. Such an observation is often
[...] Read more.
The concept of dynamic symmetry in art and extensive measurements on Greek vases suggest that a vase and its parts can be inscribed into similar rectangles, with all rectangles having the same ratio of lengths of their side. Such an observation is often used in describing self-similarity and fractal geometry. This work proposes a hypothesis that a logarithmic spiral describes the equation of the cross-section of a Greek vase. From extensive measurements, the parameters of such spirals are computed, and explicit formulae are derived for volume based on a few size measurements. The exact formula is quite complex and cannot be easily used, certainly not in antiquity. Therefore, a simple approximation formula is proposed for amphorae, the most important type of vase. This formula expresses the volume of the vase in terms of its diameter and the height of the corresponding solid. The approximation is compared with some exact volume computation results reported for amphorae, and it is shown that the proposed approximation is fairly close to the exact value. The simplicity of the proposed formula suggests an efficient method of calculating volume that was probably known in antiquity.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Towards the Development of an Optical Quantum Frequency Standard Feasible for a Medium-Size NMI
by
Adriana Palos, Ismael Caballero, Daniel de Mercado, Yolanda Álvarez, David Peral and Javier Díaz de Aguilar
Metrology 2025, 5(4), 75; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5040075 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
Centro Español de Metrología (CEM) is developing a quantum frequency standard based on trapped calcium ions, marking its entry into the landscape of the second quantum revolution. Optical frequency standards offer unprecedented precision by referencing atomic transitions that are fundamentally stable and immune
[...] Read more.
Centro Español de Metrología (CEM) is developing a quantum frequency standard based on trapped calcium ions, marking its entry into the landscape of the second quantum revolution. Optical frequency standards offer unprecedented precision by referencing atomic transitions that are fundamentally stable and immune to environmental drift. However, the challenge of developing such a system from scratch is unaffordable for a medium-sized National Metrology Institute (NMI), which seems to limit the ability of an institute such as CEM to contribute to this field of research. To overcome this, CEM has adopted a hybrid strategy, combining commercially available components with custom integration to accelerate deployment. This paper defines and implements an architecture adapted to the constraints of a medium-size NMI, where the main contribution is the systematic design, selection, and interconnection of the subsystems required to realize this standard. The rationale behind the system design is presented, detailing the integration of key elements for ion trapping, laser stabilization, frequency measurement, and system control. Current progress, ongoing developments, and future research directions are outlined, establishing the foundation for spectroscopic measurements and uncertainty evaluation. The project represents a strategic step toward strengthening national capabilities in quantum metrology for a medium-sized NMI.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advancements in Optical Measurement Devices and Technologies)
►▼
Show Figures
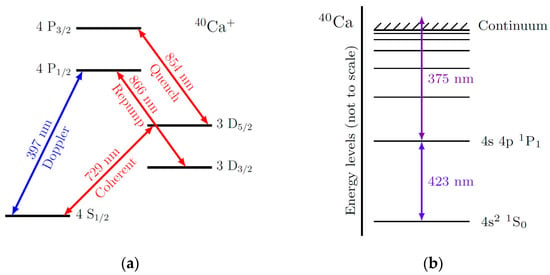
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Critical Role of International Comparisons in Global Metrology System: An Overview
by
Patrice Salzenstein, Thomas Y. Wu and Ekaterina Pavlyuchenko
Metrology 2025, 5(4), 74; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5040074 - 3 Dec 2025
Abstract
International comparisons play a critical role in ensuring precision, accuracy, consistency, and trust in the global metrology system. The Comité International des Poids et Mesures (CIPM) established the Mutual Recognition Arrangement (MRA) in 1999 to facilitate global trade. This paper gives an overview
[...] Read more.
International comparisons play a critical role in ensuring precision, accuracy, consistency, and trust in the global metrology system. The Comité International des Poids et Mesures (CIPM) established the Mutual Recognition Arrangement (MRA) in 1999 to facilitate global trade. This paper gives an overview of the critical role of international comparisons to National Metrology Institutes (NMIs), industrial calibration laboratories, and research laboratories in fostering global measurement equivalence and the CIPM MRA. NMIs rely on Key and Supplementary Comparisons to ensure the mutual recognition of calibration and reference material certificates, vital for global trade and regulatory compliance. Industrial calibration laboratories participate in inter-laboratory or international comparisons to validate their calibration and measurement capability (CMC) and balance their risk management. Research laboratories push the frontiers of measurement science and validate their measurement result via international comparisons. Through some examples of comparisons, the paper illustrates how measurement result discrepancies uncovered in comparisons drive technical improvements, uncertainty component identification, and measurement technique refinement. International comparisons enhance scientific credibility, build public trust, support industrial innovation, and drive evolution in measurement science. As technological demands grow, fostering broader participation in international comparisons by various metrology and research laboratories remains crucial to maintain a robust and reliable global metrology system.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Applied Industrial Metrology: Methods, Uncertainties, and Challenges)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Verification of Microprobe Calibration Based on Actual Diameter Measurement of the Probe Tip Sphere
by
So Ito, Daichi Inukai, Takehiro Tomioka, Yasutomo Sugisawa, Kenta Matsumoto and Kazuhide Kamiya
Metrology 2025, 5(4), 73; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5040073 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In three-dimensional measurement using a microprobing system with a micrometric spherical tip, a deviation in the diameter of the probe tip sphere causes measurement errors. In a typical probing system calibration, the effective diameter of the probe tip sphere is estimated based on
[...] Read more.
In three-dimensional measurement using a microprobing system with a micrometric spherical tip, a deviation in the diameter of the probe tip sphere causes measurement errors. In a typical probing system calibration, the effective diameter of the probe tip sphere is estimated based on the probing coordinates obtained on a calibration artifact with guaranteed dimensional accuracy. On the other hand, the calibration results of the effective diameter of the probe tip include uncertainty sources derived from errors inherent to the calibration artifacts and probing system itself, which cannot be eliminated. In this study, a micro-stylus with a tip sphere having a diameter less than 25 μm was fabricated. The actual diameter of its tip sphere was measured based on the contour form obtained along with the high-precision plane. The effective diameter of the same microprobe tip sphere was also measured by probing inside the precision micro-slit constructed with three gauge blocks. The measurement uncertainties of the actual and effective diameters were calculated and compared to each other. The measurement uncertainty of the actual diameter of the microprobe tip sphere based on the contour form measurement was confirmed to be smaller than that of the effective diameter measurement uncertainty, as it did not include errors inherent in the probing system. Furthermore, because the difference between the actual and effective diameters was smaller than that of the measurement uncertainties, the effectiveness of measuring actual diameter in microprobe calibration has been demonstrated.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
VNA Tools—A Metrology Software Supporting the Digital Traceability Chain
by
Markus Zeier, Michael Wollensack, Johannes Hoffmann, Peter Morrissey, Juerg Ruefenacht and Daniel Stalder
Metrology 2025, 5(4), 72; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5040072 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
This paper presents METAS VNA Tools Version 2.9.0, a metrology software suite designed to support the digital traceability chain in vector network analyzer measurements. Built on the METAS UncLib Version 2.9.0 uncertainty engine, the software enables rigorous modeling of the entire measurement process
[...] Read more.
This paper presents METAS VNA Tools Version 2.9.0, a metrology software suite designed to support the digital traceability chain in vector network analyzer measurements. Built on the METAS UncLib Version 2.9.0 uncertainty engine, the software enables rigorous modeling of the entire measurement process and comprehensive uncertainty evaluation. By encapsulating values, dependencies, and sensitivities in structured uncertainty objects, the software ensures that traceability and correlation information are preserved and propagated throughout complex calibration chains. This approach allows for seamless, modular uncertainty evaluation and supports the generation of digitally signed calibration certificates with embedded calibration data. The methodology enhances transparency, reproducibility, and interoperability, aligning with the goals of digital transformation in metrology. VNA Tools thus provides a robust foundation for implementing traceable, data-driven workflows across all levels of the metrological infrastructure.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Metrological Traceability)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Transit Time Determination Based on Similarity-Symmetry Method in Multipath Ultrasonic Gas Flowmeter
by
Hongliang Zhou, Yanchu Liu and Yunxiao Wu
Metrology 2025, 5(4), 71; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5040071 - 18 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The cross-correlation algorithm, widely used for transit-time determination in ultrasonic gas flowmeters, becomes susceptible to significant errors under high flow rates. Fluid disturbances and noise distort ultrasonic waveforms, causing cycle-skipping errors that result in large, integer-period miscalculations of time-of-flight. To overcome these limitations,
[...] Read more.
The cross-correlation algorithm, widely used for transit-time determination in ultrasonic gas flowmeters, becomes susceptible to significant errors under high flow rates. Fluid disturbances and noise distort ultrasonic waveforms, causing cycle-skipping errors that result in large, integer-period miscalculations of time-of-flight. To overcome these limitations, this study introduces a novel similarity-symmetry method. First, a similarity-based technique is proposed that exploits the stable rising-edge profile of the signal envelope, which remains consistent across flow rates, to accurately pinpoint the arrival time and mitigate cycle-skipping. Second, for multi-path flowmeters, the inherent physical symmetry between upstream and downstream transit times in each channel provides a basis for cross-validation. Any significant asymmetry flags potential cycle-skip events for correction. By integrating these two principles, our hybrid method enhances robustness. Experimental results on a six-path gas flowmeter rig demonstrate that the proposed approach reduces average flow rate errors by 75% compared to the standard cross-correlation method and maintains the maximum relative error below 1% when the flow rate is above 71.78 m3/h. This work provides a reliable solution for high-precision gas flow measurement in demanding conditions, with direct relevance to applications such as natural gas custody transfer and industrial process control where measurement accuracy is critical.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Traceability in Data Spaces: From Individual Measurements to a Digital Product Passport
by
Sascha Eichstädt and Jens Niederhausen
Metrology 2025, 5(4), 70; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5040070 - 18 Nov 2025
Abstract
Data spaces are digital realms of data and information shared between stakeholders and peer groups. They underpin several developments in sectors ranging from the automotive industry, through social sciences, to governmental networks. Digital traceability of information in data spaces is needed to validate
[...] Read more.
Data spaces are digital realms of data and information shared between stakeholders and peer groups. They underpin several developments in sectors ranging from the automotive industry, through social sciences, to governmental networks. Digital traceability of information in data spaces is needed to validate statements about metadata, data quality, and data features. In many cases, this also directly translates to metrological traceability of measurements to the SI. The concept and development of Digital Product Passports bring these traceability aspects together to form a tool for a digital quality infrastructure. This paper outlines the general principles of digital metrological traceability based on digital certificates, a digital international system of units, and Digital Product Passports.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Metrological Traceability)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Highly Efficient, Low-Cost Microwave Resonator for Exciting a Diamond Sample from a Miniaturized Quantum Magnetometer
by
André Bülau, Daniela Walter, Magnus Kofoed, Florian Janek, Volker Kible and Karl-Peter Fritz
Metrology 2025, 5(4), 69; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5040069 - 17 Nov 2025
Abstract
Optically detected magnetic resonance (ODMR) of nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamonds, in addition to optical excitation with green light, requires microwave excitation and thus a microwave structure. While many different microwave structures including microwave resonators have been presented in the past, none of them
[...] Read more.
Optically detected magnetic resonance (ODMR) of nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamonds, in addition to optical excitation with green light, requires microwave excitation and thus a microwave structure. While many different microwave structures including microwave resonators have been presented in the past, none of them fulfilled the need to fit inside the miniaturized quantum magnetometer with limited space used in this work. This is why a novel microwave resonator design using commercially available printed circuit board technology is proposed. It is demonstrated that this design is of small form factor, highly power efficient and low-cost, with very good reproducibility, and in addition, it can be fabricated as a flexible printed circuit board to be bent and thus fit into the miniaturized sensor used in this work. The design choices made for the resonator and the way in which it was trimmed and optimized geometrically are presented and ODMR spectra made with a miniaturized quantum sensor in combination with such a resonator, which was fed by a microwave generator set to different microwave powers, are shown. These measurements revealed that a microwave power of −4 dBm is sufficient to excite the ms = ±1 states of the nitrogen-vacancy centers, while exceeding −1 dBm already introduces sidebands in the ODMR spectrum. This underlines the efficiency of the resonator in exciting the nitrogen-vacancies of the diamond in the sensor platform used and can lead to development of low-power quantum sensors in the future.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers Collection: Celebration of the First Impact Factor of Metrology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Estimation of Surface Normals of Aerospace Fasteners from 3D Terrestrial Laser Scanner Point Clouds
by
Kate Pexman, Stuart Robson and Hannah Corcoran
Metrology 2025, 5(4), 68; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5040068 - 9 Nov 2025
Abstract
Measurement systems such as laser trackers and 3D imaging systems are being increasingly adopted across the manufacturing industry. These metrology technologies can allow for live, high-precision measurement in a digital system, enabling the spatial component of the digital manufacturing twin. In aircraft wing
[...] Read more.
Measurement systems such as laser trackers and 3D imaging systems are being increasingly adopted across the manufacturing industry. These metrology technologies can allow for live, high-precision measurement in a digital system, enabling the spatial component of the digital manufacturing twin. In aircraft wing manufacturing, drilling and fastening operations must be guided by precise measurements from a digital design model. With thousands of fasteners on each aircraft wing, even small errors in alignment of surface covers to wing ribs and spars can impact component longevity due to aerodynamic drag. Determining surface conformance of airstream-facing surfaces is currently largely performed though manual gauge checking by human operators. In order to capture the surface details and reverse engineer components to assure tolerance has been achieved, laser scanners could be utilised alongside a precise registration strategy. This work explores the quality of the aerostructure surface in a captured point cloud and the subsequent accuracy of surface normal determination from planar fastener heads. These point clouds were captured with a reference hand-held laser scanner and two terrestrial laser scanners. This study assesses whether terrestrial laser scanners can achieve <0.5° surface normal accuracy for aerospace fastener alignment. Accuracy of the surface normals was achieved with a nominal mean discrepancy of 0.42 degrees with the Leica RTC360 3D Laser Scanner (Leica Geosystems AG, Heerbrugg, Switzerland) and 0.27 degrees with the Surphaser 80HSX Ultra Short Range (Basis Software Inc., Redmond, WA, USA).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Optical 3D Metrology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Distinguishing Constant and Variable Bias in Systematic Error: A New Error Model for Metrology and Clinical Laboratory Quality Control
by
Atilla Barna Vandra and Ágota Drégelyi-Kiss
Metrology 2025, 5(4), 67; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5040067 - 5 Nov 2025
Abstract
This study presents a novel error model that distinguishes between constant and variable components of systematic error (bias) in measurement systems, particularly within clinical laboratory settings. Traditional approaches often conflict with these components, resulting in miscalculations of total error and measurement uncertainty. Through
[...] Read more.
This study presents a novel error model that distinguishes between constant and variable components of systematic error (bias) in measurement systems, particularly within clinical laboratory settings. Traditional approaches often conflict with these components, resulting in miscalculations of total error and measurement uncertainty. Through mathematical deduction and computer simulations, the authors demonstrate that the standard deviation derived from long-term quality control (QC) data includes both random error and the variable bias component, challenging its use as a sole estimator of random error. The proposed model defines the constant component of systematic error (CCSE) as a correctable term, while the variable component (VCSE(t)) behaves as a time-dependent function that cannot be efficiently corrected. The study further reveals that long-term QC data are not normally distributed, contradicting prevailing assumptions in metrology. It advocates for revised definitions in the International Vocabulary of Metrology (VIM3), emphasizing the need to distinguish between bias types determined under different measurement conditions. By applying this refined model, laboratories can enhance decision-making accuracy and more accurately estimate measurement error and uncertainty. The findings have implications beyond clinical laboratories, suggesting a paradigm shift in how systematic error is conceptualized and managed across all domains of metrology.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Measurement Uncertainty)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Integrating Reverse Engineering for Digital Model Reconstruction and Remanufacturing of Mechanical Components: A Systematic Review
by
Binoy Debnath, Zahra Pourfarash, Bhairavsingh Ghorpade and Shivakumar Raman
Metrology 2025, 5(4), 66; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5040066 - 5 Nov 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Reverse engineering (RE) is increasingly recognized as a vital methodology for reconstructing mechanical components, particularly in high-value sectors such as aerospace, transportation, and energy, where technical documentation is often missing or outdated. This study presents a systematic review that investigates the application, challenges,
[...] Read more.
Reverse engineering (RE) is increasingly recognized as a vital methodology for reconstructing mechanical components, particularly in high-value sectors such as aerospace, transportation, and energy, where technical documentation is often missing or outdated. This study presents a systematic review that investigates the application, challenges, and future directions of RE in mechanical component reconstruction. Adopting the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) framework, 68 peer-reviewed studies were identified, screened, and synthesized. The review highlights RE applications in restoration, redesign, internal geometry modeling, and simulation-driven performance assessment, leveraging technologies such as 3D scanning, CAD modeling, and finite element analysis. However, persistent challenges remain across five domains: product complexity, tolerance and dimensional variations, scanning limitations, integration barriers, and human-material-process dependencies, which hinder automation, accuracy, and manufacturability. Future research opportunities include the automated conversion of point cloud data into editable boundary representation (B-rep) models and AI-driven approaches for feature recognition, geometry reconstruction, and the generation of simulation-ready models. Additionally, advancements in scanning techniques to capture hidden or internal features more effectively are crucial. Overall, this review provides a comprehensive synthesis of current practices and challenges while proposing pathways to advance RE in industrial applications, fostering greater automation, accuracy, and integration in digital manufacturing workflows.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Next-Generation Interferometry with Gauge-Invariant Linear Optical Scatterers
by
Christopher R. Schwarze, Anthony D. Manni, David S. Simon, Abdoulaye Ndao and Alexander V. Sergienko
Metrology 2025, 5(4), 65; https://doi.org/10.3390/metrology5040065 - 29 Oct 2025
Abstract
Measurement technology employing optical interference phenomena such as a fringe pattern or frequency shift has been evolving for more than a century. Systems are being designed better, and their components are being built better. However, the major components themselves hardly change. Most modern
[...] Read more.
Measurement technology employing optical interference phenomena such as a fringe pattern or frequency shift has been evolving for more than a century. Systems are being designed better, and their components are being built better. However, the major components themselves hardly change. Most modern interferometers rely on the same conventional set of components to separate the electromagnetic field into multiple beams, such as plate optics and beam splitters. This naturally limits the design scope and thus the potential applicability and performance. However, recent investigations suggest that incorporating novel, higher-dimensional linear optical splitters in interferometer design can lead to several improvements. In this work, we review the underlying theory of these novel optical scatterers and some demonstrated configurations with enhanced resolution. The basic principles of optical interference and optical phase sensing are discussed in tandem. Emphasis is placed on both familiar and unfamiliar scatterers, such as the maximally symmetric Grover multiport, whose actions are left unchanged by certain gauge transformations. These higher-dimensional, gauge-invariant multiports embody a new class of building blocks that can tailor optical interference to metrology in unconventional ways.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advancements in Optical Measurement Devices and Technologies)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Metrology
Advances in Seismic Measurement Devices and Technologies
Guest Editor: Livio D'AlviaDeadline: 15 March 2026
Special Issue in
Metrology
Feature Papers Collection: Celebration of the First Impact Factor of Metrology
Guest Editors: Han Haitjema, Markus Bär, Samanta PianoDeadline: 1 May 2026
Special Issue in
Metrology
Measuring by Light: Innovations in Optical Measurement and Sensing for Advanced Metrology
Guest Editors: Steve Vanlanduit, Yuanchen ZengDeadline: 15 June 2026
Special Issue in
Metrology
Applied Industrial Metrology: Methods, Uncertainties, and Challenges
Guest Editor: Patrice SalzensteinDeadline: 25 June 2026











